Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GCFY - Chapter - 5 - Ionic Compounds
GCFY - Chapter - 5 - Ionic Compounds
Uploaded by
Naim RahmanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GCFY - Chapter - 5 - Ionic Compounds
GCFY - Chapter - 5 - Ionic Compounds
Uploaded by
Naim RahmanCopyright:
Available Formats
5, Ionic compounds
1. Ionic; positively; negatively; giant; high; dissolve; electricity; solid
2. copper oxide, zinc chloride, lead bromide and potassium fluoride – they are
compounds of a metal and a non-metal
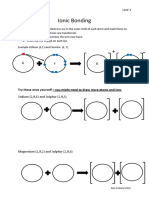
3. a) Diagram showing the outer electron from Li atom (2,1) being transferred to F
+ -
atom (2,7) to form Li ion (2) and F ion (2,8)
b) Diagram showing the outer electron from K atom (2,8,8,1) being transferred
+ -
to Cl atom (2,8,7) to form K ion (2,8,8) and Cl ion (2.8,8)
4.
- - 2-
Fluoride, F Iodide, I Sulfate, SO4
+ LiF LiI
Lithium, Li Li2SO4
2+
Calcium, Ca CaF2 CaI2 CaSO4
+
Iron(III), Fe3 FeF3 FeI3 Fe2(SO4)3
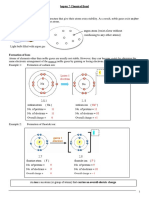
5. a) Diagram showing the outer 2 electrons from Mg atom (2,8,2) being
2+
transferred to two F atoms (2,7), 1 electron to each F atom, to form Mg ion (2,8) and
-
two F ions (2,8)
b) Diagram showing the outer 2 electrons from Mg atom (2,8,2) both being
2+ 2-
transferred to O atom (2,6) to form Mg ion (2,8,) and O ion (2,8)
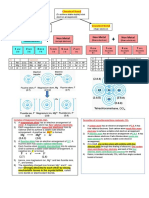
6. a) Group number equals the size of the positive charge on the ions.
b) 8 - Group number = size of charge on negative ion
c) Carbon has 4 electrons in its outer shell so would need to either lose 4
electrons or gain 4 electrons to gain the electronic structure of a noble gas – either
involves too much energy to ever happen.
+
d) Hydrogen can either lose one electron, leaving an H ion which has no
-
electrons at all – leaving just a proton, or it can gain an electron to from the H ion which
has the same electron structure as the noble gas helium.
e) Because the atoms of Group 1 elements, such as lithium, all lose one
electron to form ions with a 1+ charge (and hydrogen can also form a 1+ ion). However,
hydrogen can also form 1- ions, just like the atoms of the elements in Group 7, such as
fluorine, when their atoms gain one electron.
Oxford University Press GCSE Chemistry for You, Fifth Edition © Ryan Books Ltd, 2016 page 1 of 1
You might also like
- Shortridge HDM-250 OIM1 - 081759Document2 pagesShortridge HDM-250 OIM1 - 081759Roberto RiveraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8: Reduction of 4-T-Butylcyclohexanone With Sodium BorohydrideDocument7 pagesExperiment 8: Reduction of 4-T-Butylcyclohexanone With Sodium BorohydrideNorazma ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- Overview On Polypropylene Production and Specification: Kush Kumar RanaDocument98 pagesOverview On Polypropylene Production and Specification: Kush Kumar Ranaranjithkumarbojja100% (6)
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions For Chapter 5, Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions For Chapter 5, Ionic CompoundsAliNo ratings yet
- 5.2.1.2 Ions QuestionsDocument2 pages5.2.1.2 Ions QuestionsVietnamese Expert VS ZTNTSTNo ratings yet
- Structure and Bonding - Lesson 3 - Ionic BondingDocument19 pagesStructure and Bonding - Lesson 3 - Ionic Bondingcharlie markouNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding X ICSE CHEMISTRYDocument34 pagesChemical Bonding X ICSE CHEMISTRYjoycepeter100% (1)
- Ionic Bonding Bump Up Your GradeDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding Bump Up Your GradeMaryam Shakir0% (1)
- Level 2 Notes 2024 - 04chemical BondingDocument25 pagesLevel 2 Notes 2024 - 04chemical BondingMatthew TanNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Ionic Bonding WORKSHEETDocument6 pagesCH 7 Ionic Bonding WORKSHEETkashif mohammedNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Microscopic World 1 S3AC Answers 220811 175227Document10 pagesUnit 7 Microscopic World 1 S3AC Answers 220811 1752274A10 HUI OI YU KATRINANo ratings yet
- Study Guide Review: +1 Because They Lose 1 Electron To Become StableDocument2 pagesStudy Guide Review: +1 Because They Lose 1 Electron To Become Stableanon_906625159No ratings yet
- Chemistry For S2Document7 pagesChemistry For S2ngirisinicholasNo ratings yet
- SuggestedAnswers 07 E PDFDocument9 pagesSuggestedAnswers 07 E PDFCelemusicNo ratings yet
- Answers - Chapter 5Document4 pagesAnswers - Chapter 5Zoe SiewNo ratings yet
- 6A Electrochemistry - AnswerDocument6 pages6A Electrochemistry - AnswerWong Wai Lun100% (1)
- Lesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 1Document13 pagesLesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 1Dishna KarunasekaraNo ratings yet
- Edgcse TTPP cc5-7 SB AnswersDocument6 pagesEdgcse TTPP cc5-7 SB Answersegcarty10090% (1)
- WS - Transition Elements and Oxidation States GFDocument2 pagesWS - Transition Elements and Oxidation States GFHoulin HuangNo ratings yet
- Binary Ionic CompoundsDocument26 pagesBinary Ionic CompoundsMaxine de la Torre100% (1)
- 05 - Group 2 & Redox CORNELLDocument8 pages05 - Group 2 & Redox CORNELLGeorge SolomouNo ratings yet
- XX X X: 2.21 Ionic BondingDocument6 pagesXX X X: 2.21 Ionic BondingSunnyNo ratings yet
- 7-8 NSS Chemical BondingDocument16 pages7-8 NSS Chemical Bonding黃淑敏No ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2: ST ND RD THDocument24 pagesChemistry Unit 2: ST ND RD THjontstufNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Physical Science - Revision QuestionsDocument6 pagesChapter 5 - Physical Science - Revision QuestionsMoghanNo ratings yet
- F4C5 Key Concept: Metal Non Metal Non Metal Non MetalDocument2 pagesF4C5 Key Concept: Metal Non Metal Non Metal Non MetalDOROTHY LING YU CHANG MoeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes On The Periodic Table: Syllabus 5070 O' LevelDocument8 pagesChemistry Notes On The Periodic Table: Syllabus 5070 O' LevelNancy Mohamed0% (1)
- Chemistry Notes On The Periodic Table: Syllabus 5070 O' LevelDocument8 pagesChemistry Notes On The Periodic Table: Syllabus 5070 O' LevelNancy Mohamed100% (1)
- Chemistry of Period II 1Document6 pagesChemistry of Period II 1zakNo ratings yet
- Ions - Ionic BondingDocument35 pagesIons - Ionic BondingAmjadNo ratings yet
- TR - Dominic s2Document112 pagesTR - Dominic s2hervemanzi498No ratings yet
- SuggestedAnswers 07 EDocument8 pagesSuggestedAnswers 07 ERaiNo ratings yet
- 6 The Structure of Matter, BondingDocument86 pages6 The Structure of Matter, BondingRihan MohammedNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table ChemistryDocument8 pagesThe Periodic Table Chemistryadv.erumfatimaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry 93Document58 pagesNuclear Chemistry 93Veda Leigh SyNo ratings yet
- Group 2 ElementsDocument9 pagesGroup 2 Elementskevineben006No ratings yet
- Chapter5chemicalbonds 150401092830 Conversion Gate01Document31 pagesChapter5chemicalbonds 150401092830 Conversion Gate01mei chyiNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Chemial Reaction and EquationsDocument23 pagesCH 1 Chemial Reaction and Equationsvanshagarwal411No ratings yet
- CUP IBChemistry c03 It BondingDocument59 pagesCUP IBChemistry c03 It BondingAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Group Members: Raveena, Gha Yuan, Cheryl, Zhen Zhoa and Huey YanDocument5 pagesGroup Members: Raveena, Gha Yuan, Cheryl, Zhen Zhoa and Huey YanRaveenaNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument72 pagesIonic BondingibanathinkomboniNo ratings yet
- 5 Oxidation and Reduction: Redox (Topic 3) : Page 91 QuestionsDocument6 pages5 Oxidation and Reduction: Redox (Topic 3) : Page 91 QuestionsAbhirup RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Chemical BondsDocument46 pagesChapter 5 Chemical BondsprebasubahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Period IIDocument6 pagesChemistry of Period IIPAUL KOLERENo ratings yet
- PS G10 Chemistry Exemplar (June)Document6 pagesPS G10 Chemistry Exemplar (June)Dean WillemseNo ratings yet
- Revision Chapter 1, 2020 - WatermarkDocument14 pagesRevision Chapter 1, 2020 - Watermarkrabab elkomyNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 BondingDocument29 pagesTopic 4 BondingXandi NalepaNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bond NotesDocument4 pagesIonic Bond Notesapi-197752333100% (1)
- D - F-Block Elements ArchieveDocument9 pagesD - F-Block Elements Archieveʕ•ᴥ•ʔ ANSHUMAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Quiz (Formation of Ions)Document3 pagesQuiz (Formation of Ions)袁愉棋No ratings yet
- D and F Block ElementsDocument7 pagesD and F Block ElementsJeevika ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Ionic Bonds 2016Document7 pages4.1 Ionic Bonds 20164t5ckhp7hvNo ratings yet
- Electronic Configuration and ValencyDocument3 pagesElectronic Configuration and ValencyAngelyn RemediosNo ratings yet
- Detailed Solution Csir Net Dec 2015 FinalDocument26 pagesDetailed Solution Csir Net Dec 2015 FinalAamer100% (9)
- SA2 P2 Term1 DP1 Oct 2023Document6 pagesSA2 P2 Term1 DP1 Oct 2023Rayan Adnan AlOmariNo ratings yet
- Ions and Radicals TextDocument2 pagesIons and Radicals Textameerfati76No ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry - DPP 03 (Of Lec 08) - Lakshya JEE 2024Document2 pagesCoordination Chemistry - DPP 03 (Of Lec 08) - Lakshya JEE 2024dilemic230No ratings yet
- Subject: Chemistry: Gcse Higher Tier Topic Test SeriesDocument7 pagesSubject: Chemistry: Gcse Higher Tier Topic Test SeriesKakoli PaulNo ratings yet
- Valency: Anirban DasguptaDocument15 pagesValency: Anirban DasguptaAnirban Dasgupta100% (2)
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-Pyq-Ans-4. D and F Block ElementsDocument8 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chem-Pyq-Ans-4. D and F Block ElementskrishnaswamyharikaNo ratings yet
- Iron Metabolism: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical ConsequencesFrom EverandIron Metabolism: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical ConsequencesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electrodes for Li-ion Batteries: Materials, Mechanisms and PerformanceFrom EverandElectrodes for Li-ion Batteries: Materials, Mechanisms and PerformanceNo ratings yet
- Science 1x CompoundsDocument2 pagesScience 1x CompoundsAlexander XhuveliNo ratings yet
- NSM 3-5 ManualDocument23 pagesNSM 3-5 Manualatamed32No ratings yet
- 2020 06 15 Foreva Composite TFC1100 Eurocode en V2Document2 pages2020 06 15 Foreva Composite TFC1100 Eurocode en V2pabloNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet of AceclofenacDocument6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet of Aceclofenacopd pharmacyNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Chemistry SafetyDocument3 pagesLab 1 - Chemistry SafetyToni MasilNo ratings yet
- Crystallography: Forms and Planes: Mineralogy Carleton CollegeDocument37 pagesCrystallography: Forms and Planes: Mineralogy Carleton CollegeAde Ku KesahNo ratings yet
- ZHANG Xiaomu, ZHANG Zhiyong, PENG Yun, TIAN Zhiling HE Changhong, XIAO Hongjun, MA ChengyongDocument5 pagesZHANG Xiaomu, ZHANG Zhiyong, PENG Yun, TIAN Zhiling HE Changhong, XIAO Hongjun, MA ChengyongdietersimaNo ratings yet
- Zhang 2019Document18 pagesZhang 2019Aysu UlusalNo ratings yet
- Continuous Saponification and Neutralization Systems: Timothy KellyDocument26 pagesContinuous Saponification and Neutralization Systems: Timothy KellyKunwar Apoorva SinghNo ratings yet
- Evaporation Rate Esters, Derivatives and Other SolventsDocument2 pagesEvaporation Rate Esters, Derivatives and Other SolventsAminulIslamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of Water Lec 3 FinalDocument42 pagesChemical Properties of Water Lec 3 FinalMaha Afzal100% (1)
- Monsanto Experiment 6 ProteinsDocument7 pagesMonsanto Experiment 6 ProteinsRhey Christian MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Joining of Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymer CFRP Composites and Aluminium AlloyDocument72 pagesJoining of Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymer CFRP Composites and Aluminium AlloySorina gNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25: Lipid Metabolism: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesChapter 25: Lipid Metabolism: Multiple ChoiceMaxinefgc Baculo100% (1)
- J Foodchem 2017 09 080Document10 pagesJ Foodchem 2017 09 080Theo MartinezNo ratings yet
- Vervoort, J. (2020)Document13 pagesVervoort, J. (2020)WilliamsRafaelMataRimacNo ratings yet
- CHEM F110 - Lab Manual - Nov 5-2020Document45 pagesCHEM F110 - Lab Manual - Nov 5-2020STUTI MATHUR100% (2)
- Duro Mastic AC - ClearDocument2 pagesDuro Mastic AC - ClearVaittianathan MahavapillaiNo ratings yet
- Avesta 601 Nitric Passivator MSDSDocument8 pagesAvesta 601 Nitric Passivator MSDSfarzan khanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0731708517326328 mainEPOglycationDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0731708517326328 mainEPOglycation01Syafira Khairunissa MNo ratings yet
- Wa0004Document82 pagesWa0004Omar AlnaggarNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-9 Q1 W6-W7 Mod5 ADM-1-photosythesisDocument42 pagesSCIENCE-9 Q1 W6-W7 Mod5 ADM-1-photosythesisJB Dar100% (1)
- Performance of Concrete Reinforced With Jute Fibers Natural Fibers A ReviewDocument17 pagesPerformance of Concrete Reinforced With Jute Fibers Natural Fibers A ReviewMary Joy ManayagaNo ratings yet
- BME Lab ManualDocument97 pagesBME Lab Manualnekifew626No ratings yet
- Brosur Decontamination Kits CBRN ProtectionDocument2 pagesBrosur Decontamination Kits CBRN ProtectionFrilia Elfani PutriNo ratings yet
- Cameron WKM M Pow-R-Seal Gate Valve - PDS0139Document1 pageCameron WKM M Pow-R-Seal Gate Valve - PDS0139Karl Tbsg100% (1)
- Edcp - 1Document19 pagesEdcp - 1Raja AdnanNo ratings yet