Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views06-EnergySwitch - Accel - Waveguide-LINAC Components
06-EnergySwitch - Accel - Waveguide-LINAC Components
Uploaded by
Mohamed Abdullah1. There are two types of waveguides used in linear accelerators (linacs): RF power transmission waveguides and accelerating waveguides.
2. RF power transmission waveguides transmit RF power from the power source to the accelerating waveguide, where electrons are accelerated.
3. Accelerating waveguides accelerate electrons to high energy levels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Trilogy of Wireless Power: Basic principles, WPT Systems and ApplicationsFrom EverandTrilogy of Wireless Power: Basic principles, WPT Systems and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- 10 5923 J Ijea 20120206 05Document6 pages10 5923 J Ijea 20120206 05Hashir SaeedNo ratings yet
- Propagation of Radio WavesDocument48 pagesPropagation of Radio WavesLoryliza M DeiparineNo ratings yet
- Microwave TubesDocument36 pagesMicrowave TubesHINDUSTAN KNOW 1No ratings yet
- MIcrowave SourceDocument38 pagesMIcrowave SourceBryan Owen Salcedo SantosNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii - Tuned Amplifiers: Sri Vidya College of Engg & Tech Department of Ece EC 6401 - Electronic Circuits IIDocument3 pagesUnit - Iii - Tuned Amplifiers: Sri Vidya College of Engg & Tech Department of Ece EC 6401 - Electronic Circuits IIRoja MayuriNo ratings yet
- High Frequency CurrentsDocument14 pagesHigh Frequency CurrentsDaniel ZagotoNo ratings yet
- S10 - Q2 - Week 2Document7 pagesS10 - Q2 - Week 2Evefel Ruth SanchezNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biicefof IcrwvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biicefof IcrwvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biicefet of IcrwvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biicefet of IcrwvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biologicefect of IcrwvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biologicefect of IcrwvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Bioicefect of IcrwvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Bioicefect of IcrwvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biologicefect of IcrowvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biologicefect of IcrowvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biologiceffect of MicrowvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biologiceffect of MicrowvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Microwave Active Components TYDocument10 pagesMicrowave Active Components TYIshwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: J Bicefof IcrwvsDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: J Bicefof IcrwvsRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Microwave TubesDocument16 pagesChapter5 Microwave TubesHussna AlhinaiNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: KL Re Jave Biologiceffect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: KL Re Jave Biologiceffect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biolgicefect of IcrwvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biolgicefect of IcrwvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klys Re Jave Biologiceffect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klys Re Jave Biologiceffect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Kly Re Jave Biologiceffect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Kly Re Jave Biologiceffect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: R Jav Biologiceffe/ct of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: R Jav Biologiceffe/ct of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Jav Biologiceffe/ct of MicrowvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Jav Biologiceffe/ct of MicrowvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Communication System Module 1Document13 pages1 Communication System Module 1Anandhu cNo ratings yet
- U WaveDocument54 pagesU WaveRatheesh RsNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klys Refl Jave Tue Biologiceffect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klys Refl Jave Tue Biologiceffect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Ph0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystooscillator Reflx K Traveling Wave Tube Biological Effect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPh0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystooscillator Reflx K Traveling Wave Tube Biological Effect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klyst Refl Jave Tue Biologiceffect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klyst Refl Jave Tue Biologiceffect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Ph0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystrooscillator Reflex KL Traveling Wave Tube Biological Effect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPh0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystrooscillator Reflex KL Traveling Wave Tube Biological Effect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem Microwave Engineering Lab VivaDocument18 pages6th Sem Microwave Engineering Lab VivaAnand Prakash Singh80% (5)
- Ph0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystoci Refle Jave Tue Biologiceffect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPh0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystoci Refle Jave Tue Biologiceffect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecturjhkhe 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecturjhkhe 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Ph0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystocil Refle Traveling Wave Tube Biological Effect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPh0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystocil Refle Traveling Wave Tube Biological Effect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering Lab Viva 1Document10 pagesMicrowave Engineering Lab Viva 1Armando CajahuaringaNo ratings yet
- KlystronDocument34 pagesKlystronkhaledNo ratings yet
- SR. Physics Important QsDocument8 pagesSR. Physics Important QsKeerthanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument91 pagesChapter Threektekk5105No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 8mbDocument35 pagesCHAPTER 3 8mbkrishna_cad28No ratings yet
- Important Question and Answers On Reflex KlystronDocument2 pagesImportant Question and Answers On Reflex KlystronAtanuGoraiNo ratings yet
- Com 2 - Lab: Pulse Amplitude Modulation: Wesleyan University-Philippines Mabini Extension, Cabanatuan CityDocument5 pagesCom 2 - Lab: Pulse Amplitude Modulation: Wesleyan University-Philippines Mabini Extension, Cabanatuan CityRoss Sonny CruzNo ratings yet
- LinacsDocument8 pagesLinacsRoger RassoolNo ratings yet
- University of Mosul College of Engineering Electrical DepartmentDocument12 pagesUniversity of Mosul College of Engineering Electrical Departmentganeen hahgdhaNo ratings yet
- Oscillators Module 02 PDFDocument22 pagesOscillators Module 02 PDFAswin Rajan Bindu100% (1)
- Radio Relay Dielectric Heating Klystron Electron Flow Two-Cavity Klystron Amplifier GridDocument5 pagesRadio Relay Dielectric Heating Klystron Electron Flow Two-Cavity Klystron Amplifier GridPawan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Travelling Wave TubeDocument24 pagesTravelling Wave TubeEden DonatoNo ratings yet
- Electrically Small, Superdirective, and Superconducting AntennasFrom EverandElectrically Small, Superdirective, and Superconducting AntennasNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Transmission: Lecture Notes of Electric Power Transmission CourseFrom EverandElectric Power Transmission: Lecture Notes of Electric Power Transmission CourseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
06-EnergySwitch - Accel - Waveguide-LINAC Components
06-EnergySwitch - Accel - Waveguide-LINAC Components
Uploaded by
Mohamed Abdullah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views7 pages1. There are two types of waveguides used in linear accelerators (linacs): RF power transmission waveguides and accelerating waveguides.
2. RF power transmission waveguides transmit RF power from the power source to the accelerating waveguide, where electrons are accelerated.
3. Accelerating waveguides accelerate electrons to high energy levels.
Original Description:
Original Title
06-EnergySwitch_Accel_Waveguide-LINAC components
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. There are two types of waveguides used in linear accelerators (linacs): RF power transmission waveguides and accelerating waveguides.
2. RF power transmission waveguides transmit RF power from the power source to the accelerating waveguide, where electrons are accelerated.
3. Accelerating waveguides accelerate electrons to high energy levels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views7 pages06-EnergySwitch - Accel - Waveguide-LINAC Components
06-EnergySwitch - Accel - Waveguide-LINAC Components
Uploaded by
Mohamed Abdullah1. There are two types of waveguides used in linear accelerators (linacs): RF power transmission waveguides and accelerating waveguides.
2. RF power transmission waveguides transmit RF power from the power source to the accelerating waveguide, where electrons are accelerated.
3. Accelerating waveguides accelerate electrons to high energy levels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
What are the two types of waveguides are used
in linacs, and what do they do?
1. RF power transmission waveguides
2. Accelerating waveguides
1. The power transmission waveguides
transmit the RF power from the power
source to the accelerating waveguide in
which the electrons are accelerated
2. Accelerates electrons to high energy
1. What is the gas/pressure inside
the accelerating waveguide?
2. What is the gas/pressure inside
the connecting waveguide?
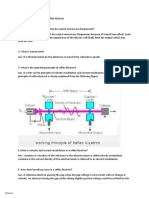
1. What is this structure?
2. What is it for?
3. How does it work?
1. Standing wave accelerating waveguide for 6X linac.
2. Accelerates electrons to high energy (6 MV for this waveguide).
3. The structure is designed to “resonate” at specific frequency. For most
linacs, the frequency is in the S band, 3 GHz. The acceleration the
electron receives in each cavity increases with the microwave power fed
into the waveguide.
Follow Up:
1. What is the dimension of each
cavity?
2. Can you design a smaller
waveguide?
1. Each cavity is ½ wavelength
For S band, f = 3 GHz -> This gives λ = c/f = 10 cm. -> cavity = 5cm.
2. You could use higher frequency (9 GHz in the X band). Cavity is
1/3 shorter in the X band; eg CyberKnife cavity = 3.33 cm.
• How does a Linac vary the energy of electron beams? (4 possible answers)
1. Vary the RF power into the accelerator.
2. Vary the injection beam current or “beam loading”. (TW)
3. Detune the RF source frequency and/or part of accelerating cavities. (TW)
4. Separate the accelerating cavities into two portions. For a low energy mode
the second section has a lower net average RF electric field. (SW)
Truebeam:
Redesigned - Continuously variable energy switch
You might also like
- Trilogy of Wireless Power: Basic principles, WPT Systems and ApplicationsFrom EverandTrilogy of Wireless Power: Basic principles, WPT Systems and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- 10 5923 J Ijea 20120206 05Document6 pages10 5923 J Ijea 20120206 05Hashir SaeedNo ratings yet
- Propagation of Radio WavesDocument48 pagesPropagation of Radio WavesLoryliza M DeiparineNo ratings yet
- Microwave TubesDocument36 pagesMicrowave TubesHINDUSTAN KNOW 1No ratings yet
- MIcrowave SourceDocument38 pagesMIcrowave SourceBryan Owen Salcedo SantosNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii - Tuned Amplifiers: Sri Vidya College of Engg & Tech Department of Ece EC 6401 - Electronic Circuits IIDocument3 pagesUnit - Iii - Tuned Amplifiers: Sri Vidya College of Engg & Tech Department of Ece EC 6401 - Electronic Circuits IIRoja MayuriNo ratings yet
- High Frequency CurrentsDocument14 pagesHigh Frequency CurrentsDaniel ZagotoNo ratings yet
- S10 - Q2 - Week 2Document7 pagesS10 - Q2 - Week 2Evefel Ruth SanchezNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biicefof IcrwvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biicefof IcrwvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biicefet of IcrwvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biicefet of IcrwvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biologicefect of IcrwvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biologicefect of IcrwvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Bioicefect of IcrwvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Bioicefect of IcrwvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biologicefect of IcrowvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biologicefect of IcrowvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biologiceffect of MicrowvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biologiceffect of MicrowvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Microwave Active Components TYDocument10 pagesMicrowave Active Components TYIshwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: J Bicefof IcrwvsDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: J Bicefof IcrwvsRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Microwave TubesDocument16 pagesChapter5 Microwave TubesHussna AlhinaiNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: KL Re Jave Biologiceffect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: KL Re Jave Biologiceffect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biolgicefect of IcrwvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Ja Biolgicefect of IcrwvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klys Re Jave Biologiceffect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klys Re Jave Biologiceffect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Kly Re Jave Biologiceffect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Kly Re Jave Biologiceffect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: R Jav Biologiceffe/ct of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: R Jav Biologiceffe/ct of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Jav Biologiceffe/ct of MicrowvesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Jav Biologiceffe/ct of MicrowvesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Communication System Module 1Document13 pages1 Communication System Module 1Anandhu cNo ratings yet
- U WaveDocument54 pagesU WaveRatheesh RsNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klys Refl Jave Tue Biologiceffect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klys Refl Jave Tue Biologiceffect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Ph0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystooscillator Reflx K Traveling Wave Tube Biological Effect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPh0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystooscillator Reflx K Traveling Wave Tube Biological Effect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klyst Refl Jave Tue Biologiceffect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klyst Refl Jave Tue Biologiceffect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Ph0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystrooscillator Reflex KL Traveling Wave Tube Biological Effect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPh0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystrooscillator Reflex KL Traveling Wave Tube Biological Effect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem Microwave Engineering Lab VivaDocument18 pages6th Sem Microwave Engineering Lab VivaAnand Prakash Singh80% (5)
- Ph0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystoci Refle Jave Tue Biologiceffect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPh0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystoci Refle Jave Tue Biologiceffect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- PH0101 Unit 2 Lecturjhkhe 6Document35 pagesPH0101 Unit 2 Lecturjhkhe 6Rukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Ph0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystocil Refle Traveling Wave Tube Biological Effect of MicrowavesDocument35 pagesPh0101 Unit 2 Lecture 6: Klystocil Refle Traveling Wave Tube Biological Effect of MicrowavesRukshad Asif Jaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering Lab Viva 1Document10 pagesMicrowave Engineering Lab Viva 1Armando CajahuaringaNo ratings yet
- KlystronDocument34 pagesKlystronkhaledNo ratings yet
- SR. Physics Important QsDocument8 pagesSR. Physics Important QsKeerthanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument91 pagesChapter Threektekk5105No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 8mbDocument35 pagesCHAPTER 3 8mbkrishna_cad28No ratings yet
- Important Question and Answers On Reflex KlystronDocument2 pagesImportant Question and Answers On Reflex KlystronAtanuGoraiNo ratings yet
- Com 2 - Lab: Pulse Amplitude Modulation: Wesleyan University-Philippines Mabini Extension, Cabanatuan CityDocument5 pagesCom 2 - Lab: Pulse Amplitude Modulation: Wesleyan University-Philippines Mabini Extension, Cabanatuan CityRoss Sonny CruzNo ratings yet
- LinacsDocument8 pagesLinacsRoger RassoolNo ratings yet
- University of Mosul College of Engineering Electrical DepartmentDocument12 pagesUniversity of Mosul College of Engineering Electrical Departmentganeen hahgdhaNo ratings yet
- Oscillators Module 02 PDFDocument22 pagesOscillators Module 02 PDFAswin Rajan Bindu100% (1)
- Radio Relay Dielectric Heating Klystron Electron Flow Two-Cavity Klystron Amplifier GridDocument5 pagesRadio Relay Dielectric Heating Klystron Electron Flow Two-Cavity Klystron Amplifier GridPawan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Travelling Wave TubeDocument24 pagesTravelling Wave TubeEden DonatoNo ratings yet
- Electrically Small, Superdirective, and Superconducting AntennasFrom EverandElectrically Small, Superdirective, and Superconducting AntennasNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Transmission: Lecture Notes of Electric Power Transmission CourseFrom EverandElectric Power Transmission: Lecture Notes of Electric Power Transmission CourseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)