Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer in Problem Solving2
Reviewer in Problem Solving2
Uploaded by
Reygenlyn CasilCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Research Methods in The Behavioral ScienceDocument3 pagesResearch Methods in The Behavioral ScienceJB100% (1)
- Stages of Math InvestigationDocument26 pagesStages of Math InvestigationMario M. Ramon97% (32)
- Mental Math Number Talk Strategies PDFDocument26 pagesMental Math Number Talk Strategies PDFwargoNo ratings yet
- Geometry Problems For Math Competitions Jerry Gu Z Lib OrgDocument317 pagesGeometry Problems For Math Competitions Jerry Gu Z Lib OrgAbhaya RanjanNo ratings yet
- (Molecular Biology Biochemistry and Biophysics 31) S. I. Chan, D. F. Bocian, N. O. Petersen (Auth.), Dr. Ernst Grell (Eds.) - Membrane Spectroscopy-Springer Berlin Heidelberg (1981)Document508 pages(Molecular Biology Biochemistry and Biophysics 31) S. I. Chan, D. F. Bocian, N. O. Petersen (Auth.), Dr. Ernst Grell (Eds.) - Membrane Spectroscopy-Springer Berlin Heidelberg (1981)Gabriela MarzariNo ratings yet
- Interventions MathDocument3 pagesInterventions Mathapi-637797233No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 & 2 - NotesDocument9 pagesChapter 1 & 2 - NotesShanalene ManaloNo ratings yet
- 7 Science ModuleDocument15 pages7 Science ModuleSteven PradoNo ratings yet
- D. Preliminary ActivitiesDocument16 pagesD. Preliminary ActivitiesAi Lyn100% (1)
- 2 Metode IlmiahDocument23 pages2 Metode Ilmiahsri watiniNo ratings yet
- The Scientific MethodDocument1 pageThe Scientific MethodChristian GomezNo ratings yet
- AGRICDocument3 pagesAGRIClayla landNo ratings yet
- UCAT DM Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesUCAT DM Cheat Sheetmatthewgao78No ratings yet
- BRM NotesDocument8 pagesBRM NotesKaatiya KaatiyaNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Hybrid Module S7 Q1 M1 Week 1.editedDocument14 pagesEnhanced Hybrid Module S7 Q1 M1 Week 1.editedHannah Joy LontayaoNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Short ResponsesDocument2 pagesRubric For Short ResponsesRichard RilloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PR1Document3 pagesReviewer in PR1Karylle PingolNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 1 WEEK 1.1: Not For SaleDocument5 pagesScience Quarter 1 WEEK 1.1: Not For SaleLeilani BacayNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Psychology Unit 3 BDocument8 pagesCognitive Psychology Unit 3 BazkaNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument5 pagesResearch Reviewerenriquezchloe167No ratings yet
- G12 S2W2 Inquiries Investigations and Immersions DLLDocument3 pagesG12 S2W2 Inquiries Investigations and Immersions DLLAnna Agravante-SulitNo ratings yet
- Research9 q3 Mod1 ResearchDesign v3Document38 pagesResearch9 q3 Mod1 ResearchDesign v3ROSSELLE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Problem-Solving: Get SharpDocument31 pagesProblem-Solving: Get SharpSudhagarNo ratings yet
- Research Process: Chapter Three Information Systems 3 YearDocument75 pagesResearch Process: Chapter Three Information Systems 3 YearEbisa ChemedaNo ratings yet
- A Plan For Problem Solving: Main IDEADocument1 pageA Plan For Problem Solving: Main IDEAsosan khanjaniNo ratings yet
- Aim: at The End of Semester Every Student Should Have A Draft of Thesis ProposalDocument38 pagesAim: at The End of Semester Every Student Should Have A Draft of Thesis ProposalaldonesiaNo ratings yet
- III ReviewerDocument15 pagesIII ReviewerChristian CalauadNo ratings yet
- Las Science 7 Q1 W1Document4 pagesLas Science 7 Q1 W1Eileen NagaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document29 pagesModule 3Abel E. SadjiNo ratings yet
- Test Construction PDFDocument4 pagesTest Construction PDFCaesar Franz RuizNo ratings yet
- PR1 Quarter 3 Topics - 111601Document8 pagesPR1 Quarter 3 Topics - 111601janela1230No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Research Powerpoint PresentationDocument22 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Research Powerpoint PresentationSTHEMBILE MthethwaNo ratings yet
- Ted 7 Teaching Mathematics Report 2Document16 pagesTed 7 Teaching Mathematics Report 2Ricardo SantillanNo ratings yet
- Fact-Sheet-Principle in Teaching MathDocument1 pageFact-Sheet-Principle in Teaching MathJhon Phillip BalacuitNo ratings yet
- Iii PPT W1.2Document23 pagesIii PPT W1.2kimellareyNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Module Q1 - Final PrintDocument60 pagesScience 7 Module Q1 - Final PrintRene Castillo JrNo ratings yet
- Subject: Practical Research II: Page 1 of 22Document22 pagesSubject: Practical Research II: Page 1 of 22Alexis CastilloNo ratings yet
- III ReviewerDocument3 pagesIII ReviewerdigakristinejoyNo ratings yet
- MEC101 C3 - Eng. Soln.Document24 pagesMEC101 C3 - Eng. Soln.kamalNo ratings yet
- Science Process SkillsDocument17 pagesScience Process SkillsBerna TenioNo ratings yet
- Week 3. Math in The Modern WorldDocument7 pagesWeek 3. Math in The Modern WorldHoney Gene M. YumolNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PR2 Part 1Document3 pagesReviewer PR2 Part 1Maureen Dayo100% (1)
- Learning Module: MatterDocument205 pagesLearning Module: MatterJanine Munoz0% (2)
- Four-Step in Problem Solving ProcessDocument1 pageFour-Step in Problem Solving ProcessMA. ADELE FE MANULATNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 ModuleDocument17 pagesPractical Research 2 ModuleCJ WATTPAD100% (1)
- Exam Strategies How To Tackle Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesExam Strategies How To Tackle Exam QuestionsAnonymous IGrPMnSBjNo ratings yet
- Schools Division of ZambalesDocument13 pagesSchools Division of ZambalesAbegail FortalezaNo ratings yet
- Fs 5 Episode 7Document12 pagesFs 5 Episode 7Mark Anthony Nieva Rafallo100% (9)
- How To Write Better Essays NotesDocument5 pagesHow To Write Better Essays NotesKristina Katrina Anne BorjaNo ratings yet
- The Research ProcessDocument4 pagesThe Research ProcessCake ManNo ratings yet
- PS DLP 4Document3 pagesPS DLP 4Rhomelyn AbellarNo ratings yet
- Recap of Major ConceptsDocument5 pagesRecap of Major ConceptsdamianNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Investigation: Wendy Mae G. Lapuz, LPTDocument13 pagesMathematical Investigation: Wendy Mae G. Lapuz, LPTWendy Mae Lapuz100% (1)
- Week 1 PR1 LectureDocument3 pagesWeek 1 PR1 LectureKenneth GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Weeks 8, 9 & 10, Term 3 Maths Topic: DataDocument5 pagesWeeks 8, 9 & 10, Term 3 Maths Topic: Dataapi-525572712No ratings yet
- Scientific Method Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesScientific Method Lesson PlanPaul Tamuria100% (2)
- Research-II-Quarter 1 SLEM 1 MODULEDocument15 pagesResearch-II-Quarter 1 SLEM 1 MODULELian Gwyneth Tomas100% (1)
- RSRCH Ch01 RsrchBscs1Document13 pagesRSRCH Ch01 RsrchBscs1alfyomar79No ratings yet
- PR1Q3 ReviewerDocument7 pagesPR1Q3 ReviewerIt’s yanaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Psychology NotesDocument10 pagesCognitive Psychology NotesnausheenalinizamiNo ratings yet
- 1.scientific InvestigationDocument49 pages1.scientific InvestigationNina Angela CateNo ratings yet
- Study Guide First QuarterDocument3 pagesStudy Guide First QuarterValNo ratings yet
- Study Guide to Accompany Computers Data and ProcessingFrom EverandStudy Guide to Accompany Computers Data and ProcessingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Resine Ip 2015-04 - Version3Document2 pagesResine Ip 2015-04 - Version3Enrique AntonioNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles Function: Types of Driver's Cab Driver's Cab Concept International Long-Distance TransportDocument16 pagesBasic Principles Function: Types of Driver's Cab Driver's Cab Concept International Long-Distance TransportAdrian A UPD100% (1)
- (609abe21 5e49 4cef A311 8d29d537f135) MACD Tolomatic HowAchieveOptimalPerformanceDocument2 pages(609abe21 5e49 4cef A311 8d29d537f135) MACD Tolomatic HowAchieveOptimalPerformanceKhor Tze MingNo ratings yet
- 44 001gb-Er 8-Er 11-AusterasDocument22 pages44 001gb-Er 8-Er 11-AusterasWi DuddaaNo ratings yet
- Lighting in Interior DesignDocument17 pagesLighting in Interior DesignEric MagnayeNo ratings yet
- Rational ExponentsDocument1 pageRational ExponentsSherelyn Salanda AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Next Word Prediction With NLP and Deep LearningDocument13 pagesNext Word Prediction With NLP and Deep LearningAlebachew MekuriawNo ratings yet
- AC310 Series Inverter Technical Manual (Detailed Version) 20230706Document380 pagesAC310 Series Inverter Technical Manual (Detailed Version) 20230706Leo MedvederNo ratings yet
- SAMSUNGVR22EOCHASSISLW22N23NLCDTVSMDocument64 pagesSAMSUNGVR22EOCHASSISLW22N23NLCDTVSMvideosonNo ratings yet
- Sp@Nner FBTC ScriptDocument8 pagesSp@Nner FBTC ScriptSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- How AI Can Pump New Life Into Oilfields: Fueling Oil and Gas Industry PerformanceDocument12 pagesHow AI Can Pump New Life Into Oilfields: Fueling Oil and Gas Industry PerformancesaeedNo ratings yet
- Conjoint Analysis Case Study PDFDocument8 pagesConjoint Analysis Case Study PDFSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- cx30 OmDocument33 pagescx30 OmBala RajuNo ratings yet
- OTM Glossary For LOL - 20190723Document17 pagesOTM Glossary For LOL - 20190723Rahul Harsh RajéNo ratings yet
- Week 38 PPCDocument1 pageWeek 38 PPCSantu PaulNo ratings yet
- 16th+Mar+-+IUPAC+Nomenclature+ +Top+50+NEET+Questions+ +last+20+yearsDocument107 pages16th+Mar+-+IUPAC+Nomenclature+ +Top+50+NEET+Questions+ +last+20+yearsGame SNo ratings yet
- Slides MLRDocument17 pagesSlides MLRmrityunjayNo ratings yet
- French Numerical AdjectivesDocument1 pageFrench Numerical Adjectivesdiah_mulcil06No ratings yet
- Srs Mitesh Srs Details of Upscgovin PDFDocument13 pagesSrs Mitesh Srs Details of Upscgovin PDFShanmukha GopuNo ratings yet
- 99-Incoming ACH - EDI 820 File Format Untranslated - Segment Breakdown (FIS)Document5 pages99-Incoming ACH - EDI 820 File Format Untranslated - Segment Breakdown (FIS)Venkatapavan SinagamNo ratings yet
- RAFT Foundation FDocument30 pagesRAFT Foundation FBhargav BbvsNo ratings yet
- Locator Control in Oracle InventoryDocument11 pagesLocator Control in Oracle InventoryMuhammad AyubNo ratings yet
- Btech Ece 8 Sem Digital Image Processing 2011Document7 pagesBtech Ece 8 Sem Digital Image Processing 2011Abhijit DasNo ratings yet
- Bleak Documentation Release Henrik Blidh Jul 07, 2021Document54 pagesBleak Documentation Release Henrik Blidh Jul 07, 2021Iván Jiménez LabsNo ratings yet
- Physics IA PDFDocument27 pagesPhysics IA PDFFelipe Perez Brena PugaNo ratings yet
- CONNECT C Versão 5.X AcertosDocument81 pagesCONNECT C Versão 5.X AcertosWilsonWilsonNo ratings yet
Reviewer in Problem Solving2
Reviewer in Problem Solving2
Uploaded by
Reygenlyn CasilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reviewer in Problem Solving2
Reviewer in Problem Solving2
Uploaded by
Reygenlyn CasilCopyright:
Available Formats
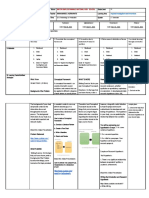
Reviewer in problem solving 3.
Unit method
4. Backwards method
Lesson 1: ROUTINE AND NON-ROUTINE
5. Break problem into steps
PROBLEMS
6. Convert words to symbols
What is problem solving? 7. Build a list or table
8. Disregarding useless information
- Problem solving is the application 9. Look for patterns
of mathematical skills. 10. Look for standard examples
Routine and Non-Routine problem Lesson 3: Investigations
solving.
Investigation
Routine
- Open-ended problem in which
- From the curriculum point of view, students can choose to go in
routine problem solving involves different directions.
Using at least one arithmetic’s - Investigations are an excellent way
operation and/or ratio to solve to establish cooperative learning
problems that are practical in nature. strategies in the classroom. Most
- working out how much medicine to investigation require you to:
give a child and measuring it 1. Explore the investigation
correctly 2. Gather and record data
- using or interpreting statistics at 3. Look for patterns
work to predict demand for goods so 4. Make conjectures(guesses)
that an order can be placed with a 5. Test the conjecture and then
wholesaler refine it and test it again
- do not require Hots 6. Explain or prove results
Non-Routine 7. Make generalizations
8. Extend the problem
- It composes of a complex problem 9. Communicate findings
that requires some degree of
creativity 3-digit number investigation
- It requires Hots or higher order
thinking skills.
- Solve in multiples ways Exploration
The fundamentals of problem solving - Read the Investigations, discuss
what the investigation is for you and
Process asking you to do.
- Understand the problem - Making conjecture
- Solve the problem - Go to More data to test
- Check the answer - Revise conjectures
1. Understand the problem - Verify conjecture
- Students need to start by reading (or - Organize data
listening) - Device conjectures generalization
- Several reading or repetition - Verify conjectures
- Thinking about the problem - Extend the problem
2. Solving the problem
- Use hands on materials Mathematical investigations
- Draw a diagram-help students to - Refers to the sustained exploration
visualize and organize the info. of mathematical situation.
- Guess and check - Problem solving is part.
- Organize the information Systematic exploration of the
- Look for the patterns given situation
- Break the problem into parts Formulating problems and
- Make it simpler conjectures
3. Checking the problem
Attempting to provide
Lesson 2: Strategies for solving problem
Strategies
1. Read carefully and then do basic
operation (if applicable)
2. Guess and check strategy
You might also like
- Research Methods in The Behavioral ScienceDocument3 pagesResearch Methods in The Behavioral ScienceJB100% (1)
- Stages of Math InvestigationDocument26 pagesStages of Math InvestigationMario M. Ramon97% (32)
- Mental Math Number Talk Strategies PDFDocument26 pagesMental Math Number Talk Strategies PDFwargoNo ratings yet
- Geometry Problems For Math Competitions Jerry Gu Z Lib OrgDocument317 pagesGeometry Problems For Math Competitions Jerry Gu Z Lib OrgAbhaya RanjanNo ratings yet
- (Molecular Biology Biochemistry and Biophysics 31) S. I. Chan, D. F. Bocian, N. O. Petersen (Auth.), Dr. Ernst Grell (Eds.) - Membrane Spectroscopy-Springer Berlin Heidelberg (1981)Document508 pages(Molecular Biology Biochemistry and Biophysics 31) S. I. Chan, D. F. Bocian, N. O. Petersen (Auth.), Dr. Ernst Grell (Eds.) - Membrane Spectroscopy-Springer Berlin Heidelberg (1981)Gabriela MarzariNo ratings yet
- Interventions MathDocument3 pagesInterventions Mathapi-637797233No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 & 2 - NotesDocument9 pagesChapter 1 & 2 - NotesShanalene ManaloNo ratings yet
- 7 Science ModuleDocument15 pages7 Science ModuleSteven PradoNo ratings yet
- D. Preliminary ActivitiesDocument16 pagesD. Preliminary ActivitiesAi Lyn100% (1)
- 2 Metode IlmiahDocument23 pages2 Metode Ilmiahsri watiniNo ratings yet
- The Scientific MethodDocument1 pageThe Scientific MethodChristian GomezNo ratings yet
- AGRICDocument3 pagesAGRIClayla landNo ratings yet
- UCAT DM Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesUCAT DM Cheat Sheetmatthewgao78No ratings yet
- BRM NotesDocument8 pagesBRM NotesKaatiya KaatiyaNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Hybrid Module S7 Q1 M1 Week 1.editedDocument14 pagesEnhanced Hybrid Module S7 Q1 M1 Week 1.editedHannah Joy LontayaoNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Short ResponsesDocument2 pagesRubric For Short ResponsesRichard RilloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PR1Document3 pagesReviewer in PR1Karylle PingolNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 1 WEEK 1.1: Not For SaleDocument5 pagesScience Quarter 1 WEEK 1.1: Not For SaleLeilani BacayNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Psychology Unit 3 BDocument8 pagesCognitive Psychology Unit 3 BazkaNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument5 pagesResearch Reviewerenriquezchloe167No ratings yet
- G12 S2W2 Inquiries Investigations and Immersions DLLDocument3 pagesG12 S2W2 Inquiries Investigations and Immersions DLLAnna Agravante-SulitNo ratings yet
- Research9 q3 Mod1 ResearchDesign v3Document38 pagesResearch9 q3 Mod1 ResearchDesign v3ROSSELLE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Problem-Solving: Get SharpDocument31 pagesProblem-Solving: Get SharpSudhagarNo ratings yet
- Research Process: Chapter Three Information Systems 3 YearDocument75 pagesResearch Process: Chapter Three Information Systems 3 YearEbisa ChemedaNo ratings yet
- A Plan For Problem Solving: Main IDEADocument1 pageA Plan For Problem Solving: Main IDEAsosan khanjaniNo ratings yet
- Aim: at The End of Semester Every Student Should Have A Draft of Thesis ProposalDocument38 pagesAim: at The End of Semester Every Student Should Have A Draft of Thesis ProposalaldonesiaNo ratings yet
- III ReviewerDocument15 pagesIII ReviewerChristian CalauadNo ratings yet
- Las Science 7 Q1 W1Document4 pagesLas Science 7 Q1 W1Eileen NagaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document29 pagesModule 3Abel E. SadjiNo ratings yet
- Test Construction PDFDocument4 pagesTest Construction PDFCaesar Franz RuizNo ratings yet
- PR1 Quarter 3 Topics - 111601Document8 pagesPR1 Quarter 3 Topics - 111601janela1230No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Research Powerpoint PresentationDocument22 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Research Powerpoint PresentationSTHEMBILE MthethwaNo ratings yet
- Ted 7 Teaching Mathematics Report 2Document16 pagesTed 7 Teaching Mathematics Report 2Ricardo SantillanNo ratings yet
- Fact-Sheet-Principle in Teaching MathDocument1 pageFact-Sheet-Principle in Teaching MathJhon Phillip BalacuitNo ratings yet
- Iii PPT W1.2Document23 pagesIii PPT W1.2kimellareyNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Module Q1 - Final PrintDocument60 pagesScience 7 Module Q1 - Final PrintRene Castillo JrNo ratings yet
- Subject: Practical Research II: Page 1 of 22Document22 pagesSubject: Practical Research II: Page 1 of 22Alexis CastilloNo ratings yet
- III ReviewerDocument3 pagesIII ReviewerdigakristinejoyNo ratings yet
- MEC101 C3 - Eng. Soln.Document24 pagesMEC101 C3 - Eng. Soln.kamalNo ratings yet
- Science Process SkillsDocument17 pagesScience Process SkillsBerna TenioNo ratings yet
- Week 3. Math in The Modern WorldDocument7 pagesWeek 3. Math in The Modern WorldHoney Gene M. YumolNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PR2 Part 1Document3 pagesReviewer PR2 Part 1Maureen Dayo100% (1)
- Learning Module: MatterDocument205 pagesLearning Module: MatterJanine Munoz0% (2)
- Four-Step in Problem Solving ProcessDocument1 pageFour-Step in Problem Solving ProcessMA. ADELE FE MANULATNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 ModuleDocument17 pagesPractical Research 2 ModuleCJ WATTPAD100% (1)
- Exam Strategies How To Tackle Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesExam Strategies How To Tackle Exam QuestionsAnonymous IGrPMnSBjNo ratings yet
- Schools Division of ZambalesDocument13 pagesSchools Division of ZambalesAbegail FortalezaNo ratings yet
- Fs 5 Episode 7Document12 pagesFs 5 Episode 7Mark Anthony Nieva Rafallo100% (9)
- How To Write Better Essays NotesDocument5 pagesHow To Write Better Essays NotesKristina Katrina Anne BorjaNo ratings yet
- The Research ProcessDocument4 pagesThe Research ProcessCake ManNo ratings yet
- PS DLP 4Document3 pagesPS DLP 4Rhomelyn AbellarNo ratings yet
- Recap of Major ConceptsDocument5 pagesRecap of Major ConceptsdamianNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Investigation: Wendy Mae G. Lapuz, LPTDocument13 pagesMathematical Investigation: Wendy Mae G. Lapuz, LPTWendy Mae Lapuz100% (1)
- Week 1 PR1 LectureDocument3 pagesWeek 1 PR1 LectureKenneth GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Weeks 8, 9 & 10, Term 3 Maths Topic: DataDocument5 pagesWeeks 8, 9 & 10, Term 3 Maths Topic: Dataapi-525572712No ratings yet
- Scientific Method Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesScientific Method Lesson PlanPaul Tamuria100% (2)
- Research-II-Quarter 1 SLEM 1 MODULEDocument15 pagesResearch-II-Quarter 1 SLEM 1 MODULELian Gwyneth Tomas100% (1)
- RSRCH Ch01 RsrchBscs1Document13 pagesRSRCH Ch01 RsrchBscs1alfyomar79No ratings yet
- PR1Q3 ReviewerDocument7 pagesPR1Q3 ReviewerIt’s yanaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Psychology NotesDocument10 pagesCognitive Psychology NotesnausheenalinizamiNo ratings yet
- 1.scientific InvestigationDocument49 pages1.scientific InvestigationNina Angela CateNo ratings yet
- Study Guide First QuarterDocument3 pagesStudy Guide First QuarterValNo ratings yet
- Study Guide to Accompany Computers Data and ProcessingFrom EverandStudy Guide to Accompany Computers Data and ProcessingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Resine Ip 2015-04 - Version3Document2 pagesResine Ip 2015-04 - Version3Enrique AntonioNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles Function: Types of Driver's Cab Driver's Cab Concept International Long-Distance TransportDocument16 pagesBasic Principles Function: Types of Driver's Cab Driver's Cab Concept International Long-Distance TransportAdrian A UPD100% (1)
- (609abe21 5e49 4cef A311 8d29d537f135) MACD Tolomatic HowAchieveOptimalPerformanceDocument2 pages(609abe21 5e49 4cef A311 8d29d537f135) MACD Tolomatic HowAchieveOptimalPerformanceKhor Tze MingNo ratings yet
- 44 001gb-Er 8-Er 11-AusterasDocument22 pages44 001gb-Er 8-Er 11-AusterasWi DuddaaNo ratings yet
- Lighting in Interior DesignDocument17 pagesLighting in Interior DesignEric MagnayeNo ratings yet
- Rational ExponentsDocument1 pageRational ExponentsSherelyn Salanda AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Next Word Prediction With NLP and Deep LearningDocument13 pagesNext Word Prediction With NLP and Deep LearningAlebachew MekuriawNo ratings yet
- AC310 Series Inverter Technical Manual (Detailed Version) 20230706Document380 pagesAC310 Series Inverter Technical Manual (Detailed Version) 20230706Leo MedvederNo ratings yet
- SAMSUNGVR22EOCHASSISLW22N23NLCDTVSMDocument64 pagesSAMSUNGVR22EOCHASSISLW22N23NLCDTVSMvideosonNo ratings yet
- Sp@Nner FBTC ScriptDocument8 pagesSp@Nner FBTC ScriptSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- How AI Can Pump New Life Into Oilfields: Fueling Oil and Gas Industry PerformanceDocument12 pagesHow AI Can Pump New Life Into Oilfields: Fueling Oil and Gas Industry PerformancesaeedNo ratings yet
- Conjoint Analysis Case Study PDFDocument8 pagesConjoint Analysis Case Study PDFSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- cx30 OmDocument33 pagescx30 OmBala RajuNo ratings yet
- OTM Glossary For LOL - 20190723Document17 pagesOTM Glossary For LOL - 20190723Rahul Harsh RajéNo ratings yet
- Week 38 PPCDocument1 pageWeek 38 PPCSantu PaulNo ratings yet
- 16th+Mar+-+IUPAC+Nomenclature+ +Top+50+NEET+Questions+ +last+20+yearsDocument107 pages16th+Mar+-+IUPAC+Nomenclature+ +Top+50+NEET+Questions+ +last+20+yearsGame SNo ratings yet
- Slides MLRDocument17 pagesSlides MLRmrityunjayNo ratings yet
- French Numerical AdjectivesDocument1 pageFrench Numerical Adjectivesdiah_mulcil06No ratings yet
- Srs Mitesh Srs Details of Upscgovin PDFDocument13 pagesSrs Mitesh Srs Details of Upscgovin PDFShanmukha GopuNo ratings yet
- 99-Incoming ACH - EDI 820 File Format Untranslated - Segment Breakdown (FIS)Document5 pages99-Incoming ACH - EDI 820 File Format Untranslated - Segment Breakdown (FIS)Venkatapavan SinagamNo ratings yet
- RAFT Foundation FDocument30 pagesRAFT Foundation FBhargav BbvsNo ratings yet
- Locator Control in Oracle InventoryDocument11 pagesLocator Control in Oracle InventoryMuhammad AyubNo ratings yet
- Btech Ece 8 Sem Digital Image Processing 2011Document7 pagesBtech Ece 8 Sem Digital Image Processing 2011Abhijit DasNo ratings yet
- Bleak Documentation Release Henrik Blidh Jul 07, 2021Document54 pagesBleak Documentation Release Henrik Blidh Jul 07, 2021Iván Jiménez LabsNo ratings yet
- Physics IA PDFDocument27 pagesPhysics IA PDFFelipe Perez Brena PugaNo ratings yet
- CONNECT C Versão 5.X AcertosDocument81 pagesCONNECT C Versão 5.X AcertosWilsonWilsonNo ratings yet