Professional Documents
Culture Documents
APPLYING TEST Valid
APPLYING TEST Valid
Uploaded by
Ayesha AhmedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
APPLYING TEST Valid
APPLYING TEST Valid
Uploaded by
Ayesha AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
STEP 1:
NULL HYPOTHESIS:
Average School Life Expectancy(Years) are 10 Years
ALTERNATIVE HYPOTHESIS:
Average School Expectancy(Years) are not 10 Years
STEP 2:
SIGNIFICANCE LEVEL:
Alpha= 0.05
STEP 3:
TEST STATISTICS:
χ−μ ∘
T= s =10.50-10/3.301/√ 20=¿ ¿ 0.5/0.738=0.677
√n
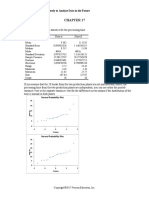
One-Sample Statistics
N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean
School Life Expectancy (Years)
20 10.50 3.301 .738
One-Sample Test
Test Value = 0
95% Confidence Interval of the
Difference
t df Sig. (2-tailed) Mean Difference Lower Upper
School Life Expectancy
14.226 19 .000 10.500 8.96 12.04
(Years)
STEP 4:
CRITICAL REGION:
Ttab= T0.05 =1.729
STEP 5:
REJECTION RULE:
Reject Ho if Tcal > Ttab
STEP 6:
Tcal=0.677 and Ttab=1.729
Conclusion: The Table value is greater than calculated value so null hypothesis is rejected. The test is
significant. Here Alternative hypothesis is accepted which means the average school expectancy
(years) are not 10.
P value and statistical significance:
The two-tailed P value equals 0.0112
By conventional criteria, this difference is considered to be statistically significant.
Confidence interval:
The hypothetical mean is 12.000000
The actual mean is 23.000000
The difference between these two values is 11.000000
The 95% confidence interval of this difference:
From 2.802210 to 19.197790
Intermediate values used in calculations:
t = 2.8085
df = 19
standard error of difference = 3.917
You might also like
- Cambridge Flyers 4 Reading WritingDocument13 pagesCambridge Flyers 4 Reading WritingDavid Morris100% (4)
- DAFMDocument13 pagesDAFMMedha SinghNo ratings yet
- Gary Larson Sample Midterm Sta 101 - DASI - Summer 2, 2015: Dominant Hand Reaction DistancesDocument14 pagesGary Larson Sample Midterm Sta 101 - DASI - Summer 2, 2015: Dominant Hand Reaction DistancesHernando FierroNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing: One Sample CasesDocument35 pagesHypothesis Testing: One Sample Casesdivya aryaNo ratings yet
- Rumusan HipotesisDocument3 pagesRumusan HipotesisNurul AfifahNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: Mean Variance Observations DF T Stat P (T T) One-Tail T Critical One-TailDocument13 pagesProblem 1: Mean Variance Observations DF T Stat P (T T) One-Tail T Critical One-TailMamiyaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet N0. 5.1 B Test On One Sample MeanDocument14 pagesWorksheet N0. 5.1 B Test On One Sample MeanMarleen Aguinaldo BalimbinNo ratings yet
- One Sample and Paired T-TestDocument6 pagesOne Sample and Paired T-TestKevser UnalNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Z-Test Z-Test: State The HypothesesDocument9 pagesHypothesis Testing Z-Test Z-Test: State The HypothesesJhaydiel JacutanNo ratings yet
- 1. a) One-Sample Test for the Mean (σ Unknown)Document5 pages1. a) One-Sample Test for the Mean (σ Unknown)Zhibek TokushovaNo ratings yet
- Test of HypothesisDocument7 pagesTest of Hypothesissuhasnu deyNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument44 pagesHypothesis Testinganpyaa100% (1)
- Chapter 7 (2/3e), 8 (1e) : Hypothesis Testing: One Sample CasesDocument48 pagesChapter 7 (2/3e), 8 (1e) : Hypothesis Testing: One Sample CasesKen SisonNo ratings yet
- One Sample T Test Statistical Problem Set 2Document15 pagesOne Sample T Test Statistical Problem Set 2Ashianna Kim FernandezNo ratings yet
- IA 2A MGT555 Consumer Transportation SurveyDocument7 pagesIA 2A MGT555 Consumer Transportation Surveyummi syafiqahNo ratings yet
- Atiqah Izdihar Binti Mokhtar 2019834546 Assignment 4Document5 pagesAtiqah Izdihar Binti Mokhtar 2019834546 Assignment 4Loveka MokhNo ratings yet
- Mehak Iqbal Task # 1 T-Test # 6 (TV Watched Pre Week) : One-Sample StatisticsDocument8 pagesMehak Iqbal Task # 1 T-Test # 6 (TV Watched Pre Week) : One-Sample StatisticsMehak IqbalNo ratings yet
- Week 2.test of Difference Between MeansDocument25 pagesWeek 2.test of Difference Between Meanscris lomboyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - T-Test IDocument33 pagesLecture 12 - T-Test Iamedeuce lyatuuNo ratings yet
- 6 Hypothesis TestingDocument20 pages6 Hypothesis Testingcenteno.am1993No ratings yet
- Normality Test Ordinal and Nominal DataDocument4 pagesNormality Test Ordinal and Nominal DataNursufyana Ulfa Che MustaffaNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersionDocument59 pagesMeasures of DispersiontiffanyNo ratings yet
- One-Sample Statistics: T-TestDocument2 pagesOne-Sample Statistics: T-Testpp3986No ratings yet
- DAHILOG - Statistics Activity 1Document4 pagesDAHILOG - Statistics Activity 1Ybur Clieve Olsen B. DahilogNo ratings yet
- CUHK STAT5102 Ch2Document25 pagesCUHK STAT5102 Ch2Tsoi Yun PuiNo ratings yet
- T TestsDocument6 pagesT TestsIsaac OmwengaNo ratings yet
- Compare Means One Sample Cases: T-Test (Z-Test)Document42 pagesCompare Means One Sample Cases: T-Test (Z-Test)Frischa NataliaNo ratings yet
- Week 11 LectureDocument17 pagesWeek 11 LectureOlana SufiyanNo ratings yet
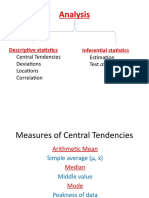
- Analysis: Descriptive Statistics Inferential StatisticsDocument56 pagesAnalysis: Descriptive Statistics Inferential StatisticsNeelakandanNo ratings yet
- 3 ProblemsDocument56 pages3 ProblemsNeelakandanNo ratings yet
- Nurul Airin Dzilwani Bte Mahadi M20152001451 Answers To SPSS PPE6044 TEST 1Document3 pagesNurul Airin Dzilwani Bte Mahadi M20152001451 Answers To SPSS PPE6044 TEST 1Mummy Iecha100% (1)
- Lab 5 - Hypothesis Testing Using One Sample T-Test: Table 1Document7 pagesLab 5 - Hypothesis Testing Using One Sample T-Test: Table 1haptyNo ratings yet
- M17 Levi3979 08 Ism C17Document52 pagesM17 Levi3979 08 Ism C17Li Kin LongNo ratings yet
- E105 DataDocument4 pagesE105 DataJian KarloNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 LasDocument20 pagesQuarter 4 LasDECEDERIO CANDOLENo ratings yet
- Lecture 01-Model Selection and EvaluationDocument29 pagesLecture 01-Model Selection and Evaluationmah dltNo ratings yet
- L4 Hypothesis Tests 2021 FDocument27 pagesL4 Hypothesis Tests 2021 Fama kumarNo ratings yet
- ML Model EvaluationDocument17 pagesML Model EvaluationSTYXNo ratings yet
- Session 1.2 SPSS NotesDocument14 pagesSession 1.2 SPSS NotesArwin Siy LaysonNo ratings yet
- BRM II NotesDocument10 pagesBRM II NotesVIDITI JAJODIANo ratings yet
- Business Analytics Assignment: Submitted ToDocument18 pagesBusiness Analytics Assignment: Submitted Tosoumya MNo ratings yet
- Tugas StatistikaDocument11 pagesTugas Statistika나 나타리No ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics: PAPER #10Document4 pagesAdvanced Statistics: PAPER #10Gian Georgette SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Applied Financial Econometrics - Exercises An Solutions - Week 1Document3 pagesApplied Financial Econometrics - Exercises An Solutions - Week 1irene.billuNo ratings yet
- ST 5Document21 pagesST 5HIMANSHU ATALNo ratings yet
- Stats 250 W15 Exam 2 SolutionsDocument8 pagesStats 250 W15 Exam 2 SolutionsHamza AliNo ratings yet
- 10 - T DistDocument44 pages10 - T DistPriyanka RavaniNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis - Testing General MathDocument20 pagesHypothesis - Testing General MathHa KDOGNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Testing Hypothesis For Means 1Document9 pagesRunning Head: Testing Hypothesis For Means 1Juliet vutemeNo ratings yet
- Project 4 Stats - Jacob MuscianeseDocument3 pagesProject 4 Stats - Jacob Muscianeseapi-706175800No ratings yet
- Statistics ReviewerDocument5 pagesStatistics ReviewerMav CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Statistical Tests: Confidence Intervals Student Test ANOVA Test Fisher Test For Variances Nonparametric TestsDocument21 pagesLecture 6 - Statistical Tests: Confidence Intervals Student Test ANOVA Test Fisher Test For Variances Nonparametric TestsKennethBermudezNo ratings yet
- Z Test For The Mean Data : P-ValueDocument7 pagesZ Test For The Mean Data : P-Valueroohan AdeelNo ratings yet
- Test of Differences Between Two MeansDocument15 pagesTest of Differences Between Two MeansDon Mariano Marcos Elementary SchoolNo ratings yet
- Test of HypothesisDocument8 pagesTest of HypothesisS M NAHID HASANNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides Sec 5 PowerDocument41 pagesLecture Slides Sec 5 Poweragus nugrahaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Introduction With ExamplesDocument43 pages4.1 Introduction With ExamplesdrvramsNo ratings yet
- Arm Project FinalDocument23 pagesArm Project Finalzala ujjwalNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: T Distribution CalculatorDocument7 pagesProblem 1: T Distribution CalculatorJoe ChalhoubNo ratings yet
- Scoring Sat Practice Test 2 DigitalDocument6 pagesScoring Sat Practice Test 2 DigitaldcNo ratings yet
- HR Analytics at GoKart Data File - FinalDocument26 pagesHR Analytics at GoKart Data File - FinalSwikriti KhannaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Language AssessmentDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Language AssessmentWisdiyan Hadi Hastomo100% (1)
- Sertifikat Kalibrasi ElcometerDocument2 pagesSertifikat Kalibrasi ElcometerTata Winata100% (1)
- Software Testing and Audit Ncs-071Document1 pageSoftware Testing and Audit Ncs-071rajeevsahani0% (1)
- MCQ Testing of Hypothesis PDFDocument10 pagesMCQ Testing of Hypothesis PDFKenzie AlmajedaNo ratings yet
- Excercise 4 Correlation Is AlyaDocument6 pagesExcercise 4 Correlation Is AlyaXvia98No ratings yet
- T Test ( Unknown) : Hypothesis Testing Refers To The Formal Procedures Used by Statisticians To Accept or RejectDocument10 pagesT Test ( Unknown) : Hypothesis Testing Refers To The Formal Procedures Used by Statisticians To Accept or RejectPayal DhameliyaNo ratings yet
- Official Transcript: Petoskey High SchoolDocument1 pageOfficial Transcript: Petoskey High SchoolVivian HartmanNo ratings yet
- Twi India PCN Fee 2017 PDFDocument6 pagesTwi India PCN Fee 2017 PDFkirubha_karan2000No ratings yet
- Statistical Inference: (Analytic Statistics) Lec 10Document42 pagesStatistical Inference: (Analytic Statistics) Lec 10Nivar selevanayNo ratings yet
- 7.4. Improvement in The Quality of Students Admitted To The ProgramDocument1 page7.4. Improvement in The Quality of Students Admitted To The ProgramDipshikaDskNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Lecture Slides 1 - Statistical Tests - ANOVADocument24 pagesModule 7 - Lecture Slides 1 - Statistical Tests - ANOVAJessica Jaye RaniesesNo ratings yet
- Sequential Sampling: Sample MeasurementDocument14 pagesSequential Sampling: Sample MeasurementAnonymous FZNn6rB100% (1)
- Unit 6 8602Document22 pagesUnit 6 8602ilyas100% (1)
- Test Hypothesis Finite Sample 2020 10 20 12 04 48 PDFDocument54 pagesTest Hypothesis Finite Sample 2020 10 20 12 04 48 PDFMassimo Ziad AmmarNo ratings yet
- Medical Entrance Coaching Centres in BhopalDocument6 pagesMedical Entrance Coaching Centres in BhopalSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Bảng Giá Tài Liệu Tháng 9/2021 I. Sách CAE,CPE photo từ sách gốcDocument8 pagesBảng Giá Tài Liệu Tháng 9/2021 I. Sách CAE,CPE photo từ sách gốcDistress0% (1)
- The Kruskal-Wallis H Test: By: Dr. Ankit Gaur (B.Pharm, M.SC, Pharm.D, RPH)Document10 pagesThe Kruskal-Wallis H Test: By: Dr. Ankit Gaur (B.Pharm, M.SC, Pharm.D, RPH)Nic OleNo ratings yet
- 10.MSA Analysis For ConturographDocument2 pages10.MSA Analysis For ConturographAdnin DelićNo ratings yet
- Stats Final ExamDocument7 pagesStats Final ExamPaul BandolaNo ratings yet
- Assessment MethodDocument14 pagesAssessment MethodSantoshca1984No ratings yet
- SNO Neet Roll No Appl No Name RankDocument348 pagesSNO Neet Roll No Appl No Name RankjerishNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification (Automated) v1Document1 pageTable of Specification (Automated) v1Ar WinNo ratings yet
- SelectionList R9 WebDocument1,112 pagesSelectionList R9 WebNix AntNo ratings yet
- Paper One: Reading and Writing: Exaver Answer Sheet Level IiiDocument1 pagePaper One: Reading and Writing: Exaver Answer Sheet Level IiiNacho VeraNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Experimental Designs and Significance Testing PDFDocument28 pagesModule 5 Experimental Designs and Significance Testing PDFmilrosebatilo2012No ratings yet
- SAT Math Advanced Rendition TestDocument1 pageSAT Math Advanced Rendition TestomarabdprodNo ratings yet
- Evaluation WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesEvaluation WPS OfficeMery IsabellaNo ratings yet