Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsBotany: Stems Reviewer
Botany: Stems Reviewer
Uploaded by
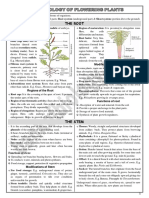
a yellow flowerStems are plant organs composed of nodes and internodes that serve several functions. They provide support, transport water and nutrients, produce new tissues, and in some cases store food or perform photosynthesis. Stems can be herbaceous or woody, aboveground or underground, and have various textures, directions of growth, and structures. The internal structures of stems include vascular tissues, ground tissues like cortex and pith, and meristematic tissues. Woody stems undergo secondary growth through lateral meristems that produce bark, sapwood, and heartwood.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Botany Plant MorphologyDocument42 pagesBotany Plant MorphologyNigel Nicholls100% (7)
- PlantsDocument38 pagesPlantsmohamadarafah3No ratings yet
- Bio1 Sa1 RevDocument15 pagesBio1 Sa1 RevแดฟนีNo ratings yet
- The Stem and LeavesDocument2 pagesThe Stem and LeavesMaria Vanessa SagarioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - Shoots, Stems and LeavesDocument15 pagesLecture 8 - Shoots, Stems and LeaveszaiNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document6 pagesCH 5Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument34 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plantss11146366No ratings yet
- Campbell Biology: Chapter 35: Plant Structure, Growth, and Developement NotesDocument11 pagesCampbell Biology: Chapter 35: Plant Structure, Growth, and Developement NotesspeedyveilNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument8 pagesMorphologymrdevil1.2007No ratings yet
- Botlec The Stems 4Document10 pagesBotlec The Stems 4Jeff MarianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter I (The Plant Body)Document45 pagesChapter I (The Plant Body)Pyae SoneNo ratings yet
- FRW Complete MergedDocument430 pagesFRW Complete Mergedsikandar zaman 768No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document44 pagesChapter 6Leorey Evaristo AjeroNo ratings yet
- Botany StemDocument36 pagesBotany Stemartadiel28No ratings yet
- Chapter II. Plant MorphologyDocument47 pagesChapter II. Plant MorphologylovryantadenaamilingacadsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 BotanyDocument31 pagesChapter 6 BotanyGiovanne BuendiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Plant TissueDocument10 pagesLesson 4 - Plant TissueLenard Kent VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Leaves: Form & FunctionDocument19 pagesLeaves: Form & FunctionShiba TatsuyaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Unit 31Document31 pagesModule 1 Unit 31Jane MontecalvoNo ratings yet
- Theories of The Origin of Solar SystemDocument18 pagesTheories of The Origin of Solar SystemGWYNETH REIN CARI�ONo ratings yet
- 5 Morphology in Flowering Plants-Notes - SampleDocument2 pages5 Morphology in Flowering Plants-Notes - SampleManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Transport Water and SolutesDocument4 pagesTransport Water and SolutesAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Morfologi BatangDocument44 pages3.2 Morfologi Batanglutfiatun nimahNo ratings yet
- 5-Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument15 pages5-Morphology of Flowering PlantsVasant Kumar VarmaNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy and Physiology 2023Document120 pagesPlant Anatomy and Physiology 2023dolattay25No ratings yet
- Structures and Functions in PlantsDocument32 pagesStructures and Functions in PlantsAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- LeavesDocument19 pagesLeavesRhusella Adrianne de GraciaNo ratings yet
- Structure of PlantsDocument17 pagesStructure of PlantsJillian Lao100% (5)
- Mauseth Chapter 05 PDFDocument2 pagesMauseth Chapter 05 PDFCharlotte AmanteNo ratings yet
- Plant Form and FunctionDocument32 pagesPlant Form and FunctionPaula SanicoNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions in Plants: Roots, Stems, and LeavesDocument32 pagesStructures and Functions in Plants: Roots, Stems, and LeavesDanielle AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- MorfhologyDocument60 pagesMorfhologyMohd. FarhanNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Ruel-VelosoDocument70 pagesPlant Anatomy Ruel-VelosoKhy Renz BajajNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantDocument41 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantAbhinandan PatilNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument23 pagesMorphologysittimunisaasaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - StemDocument30 pagesLesson 6 - StemReuth Thessalonica Dela VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Roots Basic BotanyDocument25 pagesRoots Basic BotanyManjunath Ajanal100% (1)
- Angiosperm AllDocument104 pagesAngiosperm AllLava KarnaNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument44 pagesPlantsSanjeev ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Diwey Perez Ikitan Jomer Jireh Pinalapal Jane Prudenciano Ruffa Prudenciano Marvin Carl Chico Tintin Pastor TagapuenDocument29 pagesDiwey Perez Ikitan Jomer Jireh Pinalapal Jane Prudenciano Ruffa Prudenciano Marvin Carl Chico Tintin Pastor TagapuenKristina PonceNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPDocument10 pagesExperiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPMirahmad FadzlyNo ratings yet
- How Roots DevelopDocument9 pagesHow Roots DevelopPhoebe BorjaNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Leaves and StemsDocument77 pagesWeek 8 - Leaves and StemsPrincess De LeonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsYashiNo ratings yet
- STEMDocument12 pagesSTEMScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- The Plant StemDocument7 pagesThe Plant Stemkarl riveraNo ratings yet
- Botany - Root System, Structure and Medicinal ImportanceDocument14 pagesBotany - Root System, Structure and Medicinal ImportanceAira Germaine TanganNo ratings yet
- Stem LeavesDocument20 pagesStem LeavesMerrylFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Plant Morphology 2020Document10 pagesPlant Morphology 2020Dipangkar SarkarNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument87 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsRenu83% (6)
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsJigyansa DashNo ratings yet
- Comonicacion EmpasarialDocument4 pagesComonicacion EmpasarialPari Pe RuNo ratings yet
- Tissue-Group of Cells With A Common Function, Structure or Both. Organ - Consists of Several Types of Tissues That Have A Particular FunctionDocument4 pagesTissue-Group of Cells With A Common Function, Structure or Both. Organ - Consists of Several Types of Tissues That Have A Particular FunctionMohammad Raffi GampongNo ratings yet
- Morphology in Flowering PlantsDocument207 pagesMorphology in Flowering PlantsAlifiya DholkawalaNo ratings yet
- CH - 5 Xi BioDocument13 pagesCH - 5 Xi BioShine RoselineNo ratings yet
- LeavesDocument25 pagesLeaveschelseapujeda4No ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- 2급 생활스포츠지도사 연수교재Document428 pages2급 생활스포츠지도사 연수교재박수빈No ratings yet
- Early Development ZygoteDocument1 pageEarly Development Zygotechong_sun_7No ratings yet
- Ch-5: The Fundamental Unit of Life Class-Ix ScienceDocument12 pagesCh-5: The Fundamental Unit of Life Class-Ix Scienceapi-400692183100% (1)
- Cytotaxonomic BackgroundDocument13 pagesCytotaxonomic BackgroundAqsa AzeemNo ratings yet
- Biol 121 NotesDocument5 pagesBiol 121 NotesGurleenKheevaNo ratings yet
- Silent Valley Survey Report 2021 - FinalDocument28 pagesSilent Valley Survey Report 2021 - FinalAnuraj KaimalNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9: Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production: Animal HusbandryDocument6 pagesChapter - 9: Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production: Animal Husbandrypanup98No ratings yet
- FourthBi 2010Document522 pagesFourthBi 2010hamideh_cheraghchiNo ratings yet
- Bakteri PeriodontalDocument31 pagesBakteri PeriodontalShahnaz DwiNo ratings yet
- A Molecular Signal Integration Network Underpinning Arabidopsis Seed GerminationDocument15 pagesA Molecular Signal Integration Network Underpinning Arabidopsis Seed GerminationSyahraeni EndahNo ratings yet
- 2023 QPDocument27 pages2023 QPNiketa TennakoonNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument6 pagesBiology NoteshelloNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Physiology SAT REVEIWDocument35 pagesPlant Anatomy Physiology SAT REVEIWFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- CV Sharif Hala Feb - 2017Document6 pagesCV Sharif Hala Feb - 2017Sharif HalaNo ratings yet
- Molecular MarkerDocument26 pagesMolecular MarkershivamNo ratings yet
- History of MicrobioDocument6 pagesHistory of MicrobioMaria Angela Del GallegoNo ratings yet
- Punnett Square Practice - Worksheet 2Document4 pagesPunnett Square Practice - Worksheet 2api-502781581No ratings yet
- 5e Unit PlanDocument6 pages5e Unit Planapi-308976504100% (1)
- Phylum EchinodermataDocument32 pagesPhylum Echinodermataapi-255334265100% (1)
- Respons Sepuluh Kultivar Mentimun (Cucumis Sativus L.) Terhadap Infeksi Tobacco Mosaic VirusDocument9 pagesRespons Sepuluh Kultivar Mentimun (Cucumis Sativus L.) Terhadap Infeksi Tobacco Mosaic VirusAgatha PriscillaNo ratings yet
- WDCM Reference Strain Catalogue Version 19Document30 pagesWDCM Reference Strain Catalogue Version 19Supervisor MBNo ratings yet
- Investigations Into Compost Tea For The Control of Plant Pathogenic FungiDocument12 pagesInvestigations Into Compost Tea For The Control of Plant Pathogenic FungiPennsylvania Association for Sustainable Agriculture100% (1)
- E Zine Chickencolours 1 PDFDocument32 pagesE Zine Chickencolours 1 PDFCharbel nehmeNo ratings yet
- Ace3 Wks Unit4Document4 pagesAce3 Wks Unit4natacha100% (1)
- Wildlife Conservation Efforts in India: Project By: Rishon Nandi XADocument21 pagesWildlife Conservation Efforts in India: Project By: Rishon Nandi XASHAMITA NANDINo ratings yet
- Studies On Hanguana For Sunda II - Five New Forest Species From Peninsular Malaysia and Recircumscription of Hanguana Malayana - (Willdenowia 40 (2), 205-219) - Nurfazilah Et Al., 2010Document15 pagesStudies On Hanguana For Sunda II - Five New Forest Species From Peninsular Malaysia and Recircumscription of Hanguana Malayana - (Willdenowia 40 (2), 205-219) - Nurfazilah Et Al., 2010Peter BoyceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Griffiths An Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11th Edition 2015Document47 pagesChapter 17 - Griffiths An Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11th Edition 2015Xime RdzNo ratings yet
- Kecernaan Nutrien Dan Performa Domba Lokal Yang Diberi Ransum Kombinasi Berbagai Sumber Protein Berbasis Tongkol JagungDocument5 pagesKecernaan Nutrien Dan Performa Domba Lokal Yang Diberi Ransum Kombinasi Berbagai Sumber Protein Berbasis Tongkol JagungBetty MegaNo ratings yet
- Soal Pat Bahasa Inggris KLS 8 2020 - 1Document3 pagesSoal Pat Bahasa Inggris KLS 8 2020 - 1saefulrohmanNo ratings yet
- Pruning Tomato Plants: How and When To Do ItDocument8 pagesPruning Tomato Plants: How and When To Do ItM Mohsin ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
Botany: Stems Reviewer
Botany: Stems Reviewer
Uploaded by
a yellow flower0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesStems are plant organs composed of nodes and internodes that serve several functions. They provide support, transport water and nutrients, produce new tissues, and in some cases store food or perform photosynthesis. Stems can be herbaceous or woody, aboveground or underground, and have various textures, directions of growth, and structures. The internal structures of stems include vascular tissues, ground tissues like cortex and pith, and meristematic tissues. Woody stems undergo secondary growth through lateral meristems that produce bark, sapwood, and heartwood.
Original Description:
Original Title
Botany : Stems Reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentStems are plant organs composed of nodes and internodes that serve several functions. They provide support, transport water and nutrients, produce new tissues, and in some cases store food or perform photosynthesis. Stems can be herbaceous or woody, aboveground or underground, and have various textures, directions of growth, and structures. The internal structures of stems include vascular tissues, ground tissues like cortex and pith, and meristematic tissues. Woody stems undergo secondary growth through lateral meristems that produce bark, sapwood, and heartwood.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesBotany: Stems Reviewer
Botany: Stems Reviewer
Uploaded by
a yellow flowerStems are plant organs composed of nodes and internodes that serve several functions. They provide support, transport water and nutrients, produce new tissues, and in some cases store food or perform photosynthesis. Stems can be herbaceous or woody, aboveground or underground, and have various textures, directions of growth, and structures. The internal structures of stems include vascular tissues, ground tissues like cortex and pith, and meristematic tissues. Woody stems undergo secondary growth through lateral meristems that produce bark, sapwood, and heartwood.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
. BOTANY REVIEWER .
● Decumbent – reclining on the ground
STEMS — — — — — — — — — — — — — -
Stems – an organ,, collection of integrated tissues
arranged as nodes and internodes ● Prostrate /
Procumbent – lying
● Nodes – leaves, buds & flowers attach
flat on the ground
● Internodes – b/w nodes
FUNCTIONS OF THE STEMS
● Support leaves and reproductive structures
● Creeping – rooting at the nodes when
● Provide internal transport (xylem - water ;
phloem - food)
closely pressed to the ground,, w/ runners /
● Produce new living tissues stolons
● Some are modified to store food
● If green: can photosynthesize (manufactures
carbohydrates)
TYPES OF STEMS ● Scandent / Climbing – stems
● Herbaceous ascend by means support
○ Monocot*,, lacks secondary growth
○ Grow to small diameter Based on Location
○ Soft & flexible Aboveground
○ Buds w/o protective scales ● Tendrils – long coiling structures,, for
○ Covered with epidermis attachment & support of climbing plant
○ Lives for only 1 season
*includes some dicots e.g. pechay ● Stolons / Runners – horizontally oriented
stem,, grows along the solid surface,, for
● Woody vegetative reproduction (ex. Strawberry,
○ Dicot,, has secondary growth bermuda grass)
○ Increasing diameter of the stem
○ Covered with periderm/bark ● Thorns – modified stems,, protects from
○ Lives after a year grazers (ex. Bougainvillea, roses)
Based on Visibility ● Cladodes / Cladophylls – flat,, leaf-like,,
● Acaulescent – No obvious stem above the modified for photosynthesis (ex. Asparagus,
ground,, Only leaves are seen (ex: grasses) cactus)
● Caulescent – w/ obvious stems above ● Culms – hollow / solid stem,, w/ distinct
ground (ex: roses) nodes & internodes,, sometimes forms roots
at the nodes (ex. sugarcane, bamboo)
Based on Texture
● Herbaceous – Soft and fleshy,, lives for only ● Succulent – store large amounts of water,,
a short period of time common in desert plants (ex. cactus)
● Woody – Permanent woody tissues,, hard Underground
and covered w/ bark ● Bulb – large & round-ish bud,, w/ small
basal stem at its lower part (stores nutrients)
● Suffrutescent – Only base is woody,, mix of (ex. onions, tulips)
the two above
● Corm – stubby, short, fleshy vertically
Based on Direction of Growth oriented stems,, stores nutrients (ex. gabi
gladiolus)
● Erect – perpendicular to the
ground
● Rhizomes – grow horizontally near the soil
surface,, roots & buds develop @ nodes to
grow into new plants (ex. ginger)
● Ascending – obliquely
● Tubers – swollen regions that store food,, w/ ● Vascular Bundles – scattered throughout
buds called eyes (ex. potatoes) the stem,, each is enclosed in bundle
sheath (sclerenchyma cells) for support
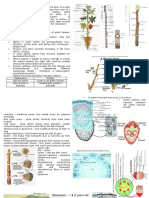
EXTERNAL STRUCTURES OF STEMS
● Bud – undeveloped shoot,, w/ embryonic ● Ground Tissue – where vascular tissues
meristems are,, same functions as cortex & pith (dicot)
○ Terminal Bud – @ the tip of the stem
○ Axillary Bud – “lateral buds”,, @ the *no lateral meristems,, primary growth only,, don’t
axilis produce secondary tissues wood & bark
*Forms stems w/ leaves / flowers when they
grow STEMS OF WOODY PLANTS
Secondary Growth – activity of 2 lateral meristems
● Cork Cambium – cells of outer lateral
● Bud Scale – modified leaves,, outer meristems
protective layer (lateral & terminal bud),, ○ cork cells
covers dormant terminal bud ○ cork parenchyma (phelloderm)
Periderm (outer bark) = cork cambium + cork cells +
● Bud Scale Scars – develop when bud scale phelloderm
falls off ● Vascular Cambium – gives rise to
secondary:
● Leaf Scar – shows where leaf was attached ○ Xylem (wood) – water & minerals
to the stem ○ Phloem (inner bark) – carbohydrates
(sucrose)
● Bundle Scar – tiny bumps / small dots in
leaf scar,, broken ends of vascular bundles ● Cork Cambium (Phellogen) – cylinder of
passing fr. stem to leaves dividing cells
● Lenticels – sites of loosely arranged cells ● Cork Cells (Phellem) – dead @ maturity,,
that allow gas exchange,, aid in identifying waterproof,, protect woody stem
the plant
● Cork Parenchyma (Phelloderm) – stores
● Nodes & Internodes – (check 1st page) water & food
INTERNAL STRUCTURES OF STEMS ● Rays – chains of parenchyma cells,,
On Dicots pathways for lateral transport of water,
● Epidermis – outer covering,, provides materials & carbohydrates
protection,, w/ cuticle
Thickening of stem due to secondary growth
● Cortex – complex tissue (parenchyma, ● Epidermis & stomata die
collenchyma, sclerenchyma),, part of ground ● Stomata replaced by lenticels
tissue system
● Bark – old, inactive secondary phloem
● Vascular Tissues – support & conduction,, ● Sapwood – secondary xylem,, softer,, water
extend throughout the stem & continuous w/ can pass through
the roots and leaves ● Heartwood – hard,, older @ the center,, not
conducting water
● Vascular Bundles
○ Xylem – inner side
■ Tracheids,, vessel elements
○ Phloem – towards the outside
■ Fibers,, phloem fiber cap
○ Vascular Cambium – b/w xylem &
phloem
● Pith – center,, for storage
On Monocots
● Epidermis – outer covering,, provides
protection,, w/ cuticle
You might also like
- Botany Plant MorphologyDocument42 pagesBotany Plant MorphologyNigel Nicholls100% (7)
- PlantsDocument38 pagesPlantsmohamadarafah3No ratings yet
- Bio1 Sa1 RevDocument15 pagesBio1 Sa1 RevแดฟนีNo ratings yet
- The Stem and LeavesDocument2 pagesThe Stem and LeavesMaria Vanessa SagarioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - Shoots, Stems and LeavesDocument15 pagesLecture 8 - Shoots, Stems and LeaveszaiNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document6 pagesCH 5Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument34 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plantss11146366No ratings yet
- Campbell Biology: Chapter 35: Plant Structure, Growth, and Developement NotesDocument11 pagesCampbell Biology: Chapter 35: Plant Structure, Growth, and Developement NotesspeedyveilNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument8 pagesMorphologymrdevil1.2007No ratings yet
- Botlec The Stems 4Document10 pagesBotlec The Stems 4Jeff MarianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter I (The Plant Body)Document45 pagesChapter I (The Plant Body)Pyae SoneNo ratings yet
- FRW Complete MergedDocument430 pagesFRW Complete Mergedsikandar zaman 768No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document44 pagesChapter 6Leorey Evaristo AjeroNo ratings yet
- Botany StemDocument36 pagesBotany Stemartadiel28No ratings yet
- Chapter II. Plant MorphologyDocument47 pagesChapter II. Plant MorphologylovryantadenaamilingacadsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 BotanyDocument31 pagesChapter 6 BotanyGiovanne BuendiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Plant TissueDocument10 pagesLesson 4 - Plant TissueLenard Kent VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Leaves: Form & FunctionDocument19 pagesLeaves: Form & FunctionShiba TatsuyaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Unit 31Document31 pagesModule 1 Unit 31Jane MontecalvoNo ratings yet
- Theories of The Origin of Solar SystemDocument18 pagesTheories of The Origin of Solar SystemGWYNETH REIN CARI�ONo ratings yet
- 5 Morphology in Flowering Plants-Notes - SampleDocument2 pages5 Morphology in Flowering Plants-Notes - SampleManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Transport Water and SolutesDocument4 pagesTransport Water and SolutesAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Morfologi BatangDocument44 pages3.2 Morfologi Batanglutfiatun nimahNo ratings yet
- 5-Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument15 pages5-Morphology of Flowering PlantsVasant Kumar VarmaNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy and Physiology 2023Document120 pagesPlant Anatomy and Physiology 2023dolattay25No ratings yet
- Structures and Functions in PlantsDocument32 pagesStructures and Functions in PlantsAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- LeavesDocument19 pagesLeavesRhusella Adrianne de GraciaNo ratings yet
- Structure of PlantsDocument17 pagesStructure of PlantsJillian Lao100% (5)
- Mauseth Chapter 05 PDFDocument2 pagesMauseth Chapter 05 PDFCharlotte AmanteNo ratings yet
- Plant Form and FunctionDocument32 pagesPlant Form and FunctionPaula SanicoNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions in Plants: Roots, Stems, and LeavesDocument32 pagesStructures and Functions in Plants: Roots, Stems, and LeavesDanielle AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- MorfhologyDocument60 pagesMorfhologyMohd. FarhanNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Ruel-VelosoDocument70 pagesPlant Anatomy Ruel-VelosoKhy Renz BajajNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantDocument41 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantAbhinandan PatilNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument23 pagesMorphologysittimunisaasaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - StemDocument30 pagesLesson 6 - StemReuth Thessalonica Dela VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Roots Basic BotanyDocument25 pagesRoots Basic BotanyManjunath Ajanal100% (1)
- Angiosperm AllDocument104 pagesAngiosperm AllLava KarnaNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument44 pagesPlantsSanjeev ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Diwey Perez Ikitan Jomer Jireh Pinalapal Jane Prudenciano Ruffa Prudenciano Marvin Carl Chico Tintin Pastor TagapuenDocument29 pagesDiwey Perez Ikitan Jomer Jireh Pinalapal Jane Prudenciano Ruffa Prudenciano Marvin Carl Chico Tintin Pastor TagapuenKristina PonceNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPDocument10 pagesExperiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPMirahmad FadzlyNo ratings yet
- How Roots DevelopDocument9 pagesHow Roots DevelopPhoebe BorjaNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Leaves and StemsDocument77 pagesWeek 8 - Leaves and StemsPrincess De LeonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsYashiNo ratings yet
- STEMDocument12 pagesSTEMScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- The Plant StemDocument7 pagesThe Plant Stemkarl riveraNo ratings yet
- Botany - Root System, Structure and Medicinal ImportanceDocument14 pagesBotany - Root System, Structure and Medicinal ImportanceAira Germaine TanganNo ratings yet
- Stem LeavesDocument20 pagesStem LeavesMerrylFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Plant Morphology 2020Document10 pagesPlant Morphology 2020Dipangkar SarkarNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument87 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsRenu83% (6)
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsJigyansa DashNo ratings yet
- Comonicacion EmpasarialDocument4 pagesComonicacion EmpasarialPari Pe RuNo ratings yet
- Tissue-Group of Cells With A Common Function, Structure or Both. Organ - Consists of Several Types of Tissues That Have A Particular FunctionDocument4 pagesTissue-Group of Cells With A Common Function, Structure or Both. Organ - Consists of Several Types of Tissues That Have A Particular FunctionMohammad Raffi GampongNo ratings yet
- Morphology in Flowering PlantsDocument207 pagesMorphology in Flowering PlantsAlifiya DholkawalaNo ratings yet
- CH - 5 Xi BioDocument13 pagesCH - 5 Xi BioShine RoselineNo ratings yet
- LeavesDocument25 pagesLeaveschelseapujeda4No ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- 2급 생활스포츠지도사 연수교재Document428 pages2급 생활스포츠지도사 연수교재박수빈No ratings yet
- Early Development ZygoteDocument1 pageEarly Development Zygotechong_sun_7No ratings yet
- Ch-5: The Fundamental Unit of Life Class-Ix ScienceDocument12 pagesCh-5: The Fundamental Unit of Life Class-Ix Scienceapi-400692183100% (1)
- Cytotaxonomic BackgroundDocument13 pagesCytotaxonomic BackgroundAqsa AzeemNo ratings yet
- Biol 121 NotesDocument5 pagesBiol 121 NotesGurleenKheevaNo ratings yet
- Silent Valley Survey Report 2021 - FinalDocument28 pagesSilent Valley Survey Report 2021 - FinalAnuraj KaimalNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9: Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production: Animal HusbandryDocument6 pagesChapter - 9: Strategies For Enhancement in Food Production: Animal Husbandrypanup98No ratings yet
- FourthBi 2010Document522 pagesFourthBi 2010hamideh_cheraghchiNo ratings yet
- Bakteri PeriodontalDocument31 pagesBakteri PeriodontalShahnaz DwiNo ratings yet
- A Molecular Signal Integration Network Underpinning Arabidopsis Seed GerminationDocument15 pagesA Molecular Signal Integration Network Underpinning Arabidopsis Seed GerminationSyahraeni EndahNo ratings yet
- 2023 QPDocument27 pages2023 QPNiketa TennakoonNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument6 pagesBiology NoteshelloNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Physiology SAT REVEIWDocument35 pagesPlant Anatomy Physiology SAT REVEIWFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- CV Sharif Hala Feb - 2017Document6 pagesCV Sharif Hala Feb - 2017Sharif HalaNo ratings yet
- Molecular MarkerDocument26 pagesMolecular MarkershivamNo ratings yet
- History of MicrobioDocument6 pagesHistory of MicrobioMaria Angela Del GallegoNo ratings yet
- Punnett Square Practice - Worksheet 2Document4 pagesPunnett Square Practice - Worksheet 2api-502781581No ratings yet
- 5e Unit PlanDocument6 pages5e Unit Planapi-308976504100% (1)
- Phylum EchinodermataDocument32 pagesPhylum Echinodermataapi-255334265100% (1)
- Respons Sepuluh Kultivar Mentimun (Cucumis Sativus L.) Terhadap Infeksi Tobacco Mosaic VirusDocument9 pagesRespons Sepuluh Kultivar Mentimun (Cucumis Sativus L.) Terhadap Infeksi Tobacco Mosaic VirusAgatha PriscillaNo ratings yet
- WDCM Reference Strain Catalogue Version 19Document30 pagesWDCM Reference Strain Catalogue Version 19Supervisor MBNo ratings yet
- Investigations Into Compost Tea For The Control of Plant Pathogenic FungiDocument12 pagesInvestigations Into Compost Tea For The Control of Plant Pathogenic FungiPennsylvania Association for Sustainable Agriculture100% (1)
- E Zine Chickencolours 1 PDFDocument32 pagesE Zine Chickencolours 1 PDFCharbel nehmeNo ratings yet
- Ace3 Wks Unit4Document4 pagesAce3 Wks Unit4natacha100% (1)
- Wildlife Conservation Efforts in India: Project By: Rishon Nandi XADocument21 pagesWildlife Conservation Efforts in India: Project By: Rishon Nandi XASHAMITA NANDINo ratings yet
- Studies On Hanguana For Sunda II - Five New Forest Species From Peninsular Malaysia and Recircumscription of Hanguana Malayana - (Willdenowia 40 (2), 205-219) - Nurfazilah Et Al., 2010Document15 pagesStudies On Hanguana For Sunda II - Five New Forest Species From Peninsular Malaysia and Recircumscription of Hanguana Malayana - (Willdenowia 40 (2), 205-219) - Nurfazilah Et Al., 2010Peter BoyceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Griffiths An Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11th Edition 2015Document47 pagesChapter 17 - Griffiths An Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11th Edition 2015Xime RdzNo ratings yet
- Kecernaan Nutrien Dan Performa Domba Lokal Yang Diberi Ransum Kombinasi Berbagai Sumber Protein Berbasis Tongkol JagungDocument5 pagesKecernaan Nutrien Dan Performa Domba Lokal Yang Diberi Ransum Kombinasi Berbagai Sumber Protein Berbasis Tongkol JagungBetty MegaNo ratings yet
- Soal Pat Bahasa Inggris KLS 8 2020 - 1Document3 pagesSoal Pat Bahasa Inggris KLS 8 2020 - 1saefulrohmanNo ratings yet
- Pruning Tomato Plants: How and When To Do ItDocument8 pagesPruning Tomato Plants: How and When To Do ItM Mohsin ChowdhuryNo ratings yet