Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Richelle and Gressyl
Richelle and Gressyl
Uploaded by
gressylmaepainagan17Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Richelle and Gressyl
Richelle and Gressyl
Uploaded by
gressylmaepainagan17Copyright:
Available Formats
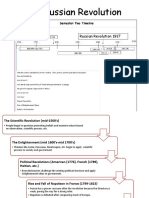
War and Revolution in Russia COLD WAR
1. World War I and Nicholas II's Downfall (1917): *UNITED STATES AND USSR (Union of the Soviet
Socialist Republics)
- Russia allied with Germany and Austria initially. -
Nicholas II's ineffective leadership led to discontent.
-After World War II, the world entered a new era
- In 1917, popular unrest forced Nicholas II to marked by the emergence of two powerful
abdicate. countries, the United States and the USSR (Union
of Soviet Socialist Republics), as the main
2. Russian Revolution and Civil War (1917-1921):
superpowers. This period is often referred to as
- Bolsheviks, led by Lenin, seized power in the Cold War.
Petrograd (October 1917).
*The Soviet Union was virtually exhausted
- Civil war between Reds (communists) and Whites
(monarchists). - Bolsheviks dissolved the Constituent
by 1945;
Assembly, established harsh control. - Lenin's tough deal
with Germany and the creation of the Cheka (secret police). -agricultural production had declined by two-
thirds, industrial production was skewed toward
3. Building Communism (1921-1953): military needs, and housing was in such short
supply that 25 million people were homeless or
- Lenin's death led to power struggles; Stalin
emerged as leader. living in makeshift shelters.
- Stalin's dictatorship transformed the Communist *After World war II
Party.
-the Soviet Union emerged as the second-most
- Emphasis on socialist realism in art, challenging powerful nation globally, despite demobilizing
traditional norms. the majority of its 11-million-man army.
4. Industrialization and Collectivization (1920s-1930s): *Soviet forces occupied northern Iran until May 1946, and
stayed in Austria until Nikita Khrushchev withdrew them
- NEP initially, but Stalin's Five-Year Plan focused in 1955.
on rapid industrialization.
*The conquest of Berlin
- Collectivization led to struggles with peasants,
causing a massive famine. -Following the conquest of Berlin and the division
- Purges and totalitarianism under Stalin in the
of Germany into four occupation zones by the
1930s, eliminating opposition. Allies, Soviet-occupied East Berlin and East
Germany were taken over by the German
5. Totalitarian System and Foreign Affairs: Communist Party, renamed the SED (Socialist
Unity Party of Germany). Stalin was keen to keep
- Stalin's regime marked the first totalitarian Germany divided and weak. When, in 1948, the
system, controlling all aspects of life. United States introduced a currency reform in the
western sectors without consulting the USSR,
- The Soviet Union's dream of global socialist Stalin ordered Berlin, located over 100 miles
revolution didn't materialize. inside the eastern sector, blockaded.
- Stalin initially misjudged Hitler, signed a pact in
1939, but later faced a brutal attack in 1941.
- The Great Fatherland War (WWII) led to
territorial expansion and increased patriotism.
These key points highlight the tumultuous period of war,
revolution, and the establishment of the Soviet Union in the
early to mid-20th century.
You might also like
- Accounting For The Iphone at AppleDocument2 pagesAccounting For The Iphone at AppleLuiz Beatrice100% (3)
- 500 Days of SummerDocument3 pages500 Days of SummerWilliam BehNo ratings yet
- RussiaDocument4 pagesRussianachoNo ratings yet
- The Russian Revolution 41 ESO InglésDocument8 pagesThe Russian Revolution 41 ESO InglésAndrés Tallón CastroNo ratings yet
- The Russian RevolutionDocument13 pagesThe Russian RevolutionFlorosia StarshineNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document4 pagesLecture 5MishaalNo ratings yet
- The Russian RevolutionDocument16 pagesThe Russian RevolutionVega Suffo JiménezNo ratings yet
- HISTORY NOTES Part 1Document13 pagesHISTORY NOTES Part 1Laura MontagutNo ratings yet
- 30.1 Revolutions in RussiaDocument33 pages30.1 Revolutions in Russianafeel navinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 25 - Ussr Lenin To Stalin PDFDocument11 pagesLecture 25 - Ussr Lenin To Stalin PDFSergi Pérez-Rejón GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Russian RevolutionDocument26 pagesRussian RevolutionNisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Soviet Union Study NotesDocument20 pagesSoviet Union Study NotesbreepaigeNo ratings yet
- Domestic Situation at The End of WW1Document6 pagesDomestic Situation at The End of WW1TamaraNo ratings yet
- Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin: PravdaDocument1 pageJoseph Vissarionovich Stalin: PravdaLaura RyanNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide p1.-3.Document3 pagesRevision Guide p1.-3.Josh Hardman100% (1)
- Chapter 30 OutlineDocument8 pagesChapter 30 OutlineJustin HeNo ratings yet
- ATA II, Course XIII (SOVIET UNION and First)Document45 pagesATA II, Course XIII (SOVIET UNION and First)y SNo ratings yet
- 24 1Document22 pages24 1D KangNo ratings yet
- Communism Economy B: SocialismDocument3 pagesCommunism Economy B: SocialismShahbaz MerajNo ratings yet
- Russian RevolutionDocument28 pagesRussian Revolutionapi-52920438No ratings yet
- Totalitarian States Rereport by JulietaDocument15 pagesTotalitarian States Rereport by Julietacoldprincess871No ratings yet
- The Soviet UnionDocument3 pagesThe Soviet UnionDANNA MARCELA MENDEZ QUIROZNo ratings yet
- The Russian RevolutionDocument23 pagesThe Russian RevolutionAisha RahatNo ratings yet
- Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin: PravdaDocument1 pageJoseph Vissarionovich Stalin: PravdaboeiniNo ratings yet
- Historia Temas 7 y 8Document12 pagesHistoria Temas 7 y 8leyre prietøNo ratings yet
- 1 Interwar Period 1Document34 pages1 Interwar Period 1Raymond NuvalNo ratings yet
- Revolutions of 1917-1923 - WikipediaDocument36 pagesRevolutions of 1917-1923 - WikipediaPravin MasalgeNo ratings yet
- Dictatorships USSR and ItalyDocument3 pagesDictatorships USSR and Italynyimae09No ratings yet
- History NotesDocument8 pagesHistory NotesBlackDreamcatcherNo ratings yet
- Speilvogel CH 28 prt3Document7 pagesSpeilvogel CH 28 prt3irregularflowers100% (2)
- World CH 14 Sect 1 NotesDocument9 pagesWorld CH 14 Sect 1 NotesMadison HawkinsNo ratings yet
- Instructional ToolDocument22 pagesInstructional Toolapi-317616426No ratings yet
- History Cheat Sheet Chapter 1-2Document2 pagesHistory Cheat Sheet Chapter 1-2Almudena AmoNo ratings yet
- Russia and The Soviet Union Notes Complete Syllabus Modern History 65c0bf22b5ca3Document22 pagesRussia and The Soviet Union Notes Complete Syllabus Modern History 65c0bf22b5ca3f26db065cfddccNo ratings yet
- Chap 21Document6 pagesChap 21MatthewNo ratings yet
- Russia Under StalinDocument17 pagesRussia Under Stalinapi-3832366100% (1)
- History Chapt. 19Document16 pagesHistory Chapt. 19alharmabdulbari699No ratings yet
- "Joseph Stalin - Premier of Union of Soviet Socialist Republics"Document4 pages"Joseph Stalin - Premier of Union of Soviet Socialist Republics"Va SylNo ratings yet
- UssrDocument25 pagesUssrxxdeadlypancakezxxNo ratings yet
- Units 7 and 8 HistoryDocument8 pagesUnits 7 and 8 HistoryMaría GarcíaNo ratings yet
- ww2 HistoryDocument14 pagesww2 HistorymarthimarinoNo ratings yet
- Documento Sin TítuloDocument7 pagesDocumento Sin Títuloh5zgpznwpbNo ratings yet
- Rise of CommunismDocument2 pagesRise of CommunismShafadul IslamNo ratings yet
- The Rise of Militarism and DictatorsDocument7 pagesThe Rise of Militarism and DictatorsMuhammad Umar SalmanNo ratings yet
- COLD WAR CLASS-11 Chandrabhan SirDocument17 pagesCOLD WAR CLASS-11 Chandrabhan SirTanay BansalNo ratings yet
- Russian RevolutionDocument18 pagesRussian RevolutionAndrea Navarro100% (1)
- OriginsDocument3 pagesOriginspeppapigNo ratings yet
- The Rise of The Soviet Union As A SuperpowerDocument8 pagesThe Rise of The Soviet Union As A Superpowersaroso0708No ratings yet
- Revolutions in RussiaDocument2 pagesRevolutions in RussiaJackie ParkNo ratings yet
- Russian RevoluionDocument13 pagesRussian RevoluionUrvashi SinghNo ratings yet
- Timeline ChinaDocument3 pagesTimeline ChinaDragonNerf Mc & MoreNo ratings yet
- The Beginnings of The Cold WarDocument3 pagesThe Beginnings of The Cold WarOSCAR SUY-PEREZNo ratings yet
- Guerra Fría 4º ESODocument9 pagesGuerra Fría 4º ESOAndrés Tallón CastroNo ratings yet
- SS Day7 WWI-WWIIDocument31 pagesSS Day7 WWI-WWIIWhite knight 209 gamingNo ratings yet
- History - The Cold WarDocument16 pagesHistory - The Cold WarJuliaNo ratings yet
- Baked Radish: As You Proceed Into New Rounds of Inquiry..Document3 pagesBaked Radish: As You Proceed Into New Rounds of Inquiry..Lars vanheuverzwynNo ratings yet
- Why Was There A Communist Revolution in Russia in 1917?Document40 pagesWhy Was There A Communist Revolution in Russia in 1917?izruda_bgNo ratings yet
- Histor WorksheetDocument8 pagesHistor Worksheetdr7dh8c2sdNo ratings yet
- Contemporary HistoryDocument30 pagesContemporary History5my8mkr8fzNo ratings yet
- Bio World Leader Joseph Stalin 19230 TrueDocument8 pagesBio World Leader Joseph Stalin 19230 Trueapi-311995468No ratings yet
- Isa 220Document16 pagesIsa 220baabasaamNo ratings yet
- Test - Present - Perfect - Review 9th 1Document3 pagesTest - Present - Perfect - Review 9th 1greidy nicolay cucaita moralesNo ratings yet
- Ôn b1 - Viết thưDocument3 pagesÔn b1 - Viết thưHằng LêNo ratings yet
- My Best EnemyDocument5 pagesMy Best EnemyJack RubyNo ratings yet
- COT Watch MaterialDocument6 pagesCOT Watch MaterialRay PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis & Security Valuation (Fifth Edition)Document46 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis & Security Valuation (Fifth Edition)arunjangra566No ratings yet
- Culture As Colloquy: Flann O'Brien's Post Modern Dialogue With Irish TraditionDocument24 pagesCulture As Colloquy: Flann O'Brien's Post Modern Dialogue With Irish Traditionbooksgirl12No ratings yet
- What Makes Man Truly HumanDocument8 pagesWhat Makes Man Truly HumanMarylene Mullasgo100% (1)
- Pre Quali 2019Document9 pagesPre Quali 2019Haidie DiazNo ratings yet
- Indian Ocean Trade Webquest Full Lesson Plan-1Document6 pagesIndian Ocean Trade Webquest Full Lesson Plan-1api-263050741No ratings yet
- Linking Managers' Emotional Intelligence, Cognitive Ability and Firm Performance: Insights From Vietnamese Firms 1. Research's ProblemDocument10 pagesLinking Managers' Emotional Intelligence, Cognitive Ability and Firm Performance: Insights From Vietnamese Firms 1. Research's ProblemĐức TùngNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT8 IDocument12 pagesEXPERIMENT8 IAbhay KotnalaNo ratings yet
- Survey Questionnaire Dear Respondents, Greetings!Document3 pagesSurvey Questionnaire Dear Respondents, Greetings!Rachelle NobsNo ratings yet
- Victimology at The Transition From The 20th To The 21st Century PDFDocument19 pagesVictimology at The Transition From The 20th To The 21st Century PDFatjoerossNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument21 pagesQuestion Bankjai_selvaNo ratings yet
- Court Order Dismissing Police Officer Case Against Deray McKesson, Black Lives MatterDocument24 pagesCourt Order Dismissing Police Officer Case Against Deray McKesson, Black Lives MatterLegal InsurrectionNo ratings yet
- Peranso - Light Curve and Period Analysis SoftwareDocument7 pagesPeranso - Light Curve and Period Analysis SoftwareUlisses RoqueNo ratings yet
- Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure in COPDDocument11 pagesAcute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure in COPDbanu kuhanNo ratings yet
- ArticleZaghdoudi Nov2020Document21 pagesArticleZaghdoudi Nov2020farhiNo ratings yet
- Stress QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesStress Questionnairehammads88100% (1)
- Eco Project-Ms Esl EflDocument6 pagesEco Project-Ms Esl Eflapi-524845185No ratings yet
- Cats PDFDocument44 pagesCats PDFAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Solar RadiationtransDocument51 pagesSolar RadiationtransmrizqynugrahaNo ratings yet
- Curse of Poverty Prayers2Document4 pagesCurse of Poverty Prayers2sar originariusNo ratings yet
- Aclu RM 001110Document67 pagesAclu RM 001110tuguimadaNo ratings yet
- O Come All Ye Faithful Planetshakers Christmas Vol 2 FDocument3 pagesO Come All Ye Faithful Planetshakers Christmas Vol 2 FBA GomNo ratings yet
- (E743.Book) Free PDF The Substance of Politics by Angadipuram AppadoraiDocument5 pages(E743.Book) Free PDF The Substance of Politics by Angadipuram Appadoraichakali raghu100% (1)
- DIR-FLoortime Interested Providers 020311Document2 pagesDIR-FLoortime Interested Providers 020311circlestretchNo ratings yet