Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7
Chapter 7
Uploaded by
Ridho Bela NegaraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7
Chapter 7
Uploaded by
Ridho Bela NegaraCopyright:
Available Formats
60 MPa PRO
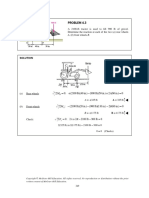
OBLEM 7.2
2
For th
he given statee of stress, dettermine the noormal and sheearing stressess exerted on
the oblique face off the shaded triangular
t elem
ment shown. UseU a methodd of analysis
608
based
d on the equilibbrium of that element,
e as waas done in the derivations off Sec. 7.1A.
90 MPa
M
SO
OLUTION
F 0: A 90
9 A sin 30 coss 30 90 A cos 30 sin 30 60 A cos 30 ccos 30 0
c 30 60 coos 2 30
180sin 30 cos
32.9
3 M Pa
F 0: A 900 A sin 30 sin 30
3 90 A cos 30 cos 30 60 A cos 30 sinn 30 0
90(cos 2 30 sin 2 30) 60 cos 30 sin 30
71.0
7 M Pa
PROOPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyriight © 2015 McG Graw-Hill Educattion. This is proprrietary material soolely for authorizedd instructor use.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
Not authorized for salle or distribution in
i any manner. Thhis document may not be copied, scaanned, duplicated,, forwarded, distributed, or posted
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
on on a website,
a website, in whole
in whole ore part.
or part.
1028
1026
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1026 1/8/2015 10:04:31 AM
PROBLEM 7.6
For the given state of stress, determine (a) the principal planes, (b) the principal
stresses.
SOLUTION
σ x = 28 MPa σ y = 140 MPa τ xy = −42 MPa
2τ xy (2)(−42)
(a) tan 2θ p = = = 0.750
σx − σy 28 − 140
2θ p = 36.87° θ p = 18.43°, 108.43°
2
σx + σy σx − σy 2
(b) σ max, min = ± +τ xy
2 2
2
28 + 140 28 − 140 2
= ± + (−42)
2 2
= 84 ± 70
σ max = 154 MPa
σ min = 14 MPa
PROPRIETARY
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL.
MATERIAL. © 2013 The
Copyright McGraw-Hill
© 2015 Companies,
McGraw-Hill Inc. This
Education. All rights reserved. No
is proprietary part of
material this Manual
solely may be instructor
for authorized displayed,use.
Notreproduced,
authorized orfordistributed
sale or distribution in or
in any form anybymanner. This without
any means, documentthemay
priornotwritten
be copied, scanned,
permission duplicated,
of the publisher,forwarded, distributed,
or used beyond or posted
the limited
on distribution
a website, intowhole or part.
teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. A student using this manual is using it
without permission.
1030
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1030 1/8/2015 10:04:33 AM
PROBLEM 7.12
For the given state of stress, determine (a) the orientation of the planes of
maximum in-plane shearing stress, (b) the corresponding normal stress.
SOLUTION
σ x = 63 MPa σ y = −42 MPa τ xy = 28 MPa
σx −σ y 63 + 42
(a) tan 2θ s = − =− = −1.875
2τ xy (2)(28)
2θ s = −61.93° θ s = −30.96°, 59.04°
2
σx −σ y
(b) τ max = + τ xy
2
2
2
63 + 42 2
= + (28) = 59.5 MPa
2
σx +σy 63 − 42
(c) σ ′ = σ ave = = = 10.5 MPa
2 2
PROPRIETARY
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL.
MATERIAL. © 2013 The
Copyright McGraw-Hill
© 2015 Companies,
McGraw-Hill Inc. This
Education. All rights reserved. No
is proprietary part of
material this Manual
solely may be instructor
for authorized displayed,use.
Notreproduced,
authorized orfordistributed
sale or distribution in or
in any form anybymanner. This without
any means, documentthemay
priornotwritten
be copied, scanned,
permission duplicated,
of the publisher,forwarded, distributed,
or used beyond or posted
the limited
on distribution
a website, intowhole or part.
teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. A student using this manual is using it
without permission.
1036
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1036 1/8/2015 10:04:35 AM
PROBLEM 7.2
22
a Two o members of uniform crosss section 50 80 mm are glued
g togetherr along plane
a 25
a-a that forms ann angle of 255 with the horizontal.
h Knnowing that thhe allowable
a 600 kPa,
stressses for the gluued joint are 800 kPa and k determinne the largest
50 mm
m centtric load P thatt can be applieed.
SO
OLUTION
Forr plane a-a, 65.
P
x 0,
0 xy 0, y
A
P 2
x cos 2 y sin 2 2 xy sin cos 0 sin 655 0
A
A (50 103 )(80 103 )(800 103 )
P 3.90 103 N
s 2 65
sin sin 2 65
6
P
( 2 sin 2 ) sin 65 cos 65 0
( x y )sin cos xy (cos
A
A (50 10 )((80 10 )(600 103 )
3 3
P 6.277 103 N
sin
s 65 cos 65 sinn 65 cos 65
Alllowable value of P is the sm
maller one. P 3.90 kN
PROOPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyriight © 2015 McG Graw-Hill Educattion. This is proprrietary material soolely for authorizedd instructor use.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
Not authorized for salle or distribution in
i any manner. Thhis document may not be copied, scaanned, duplicated,, forwarded, distributed, or posted
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
on on a website,
a website, in whole
in whole ore part.
or part.
1048
1046
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1046 1/8/2015 10:04:42 AM
PROBLEM 7.25
A mechanic uses a crowfoot wrench to loosen a bolt at E. Knowing that
the mechanic applies a vertical 100 N force at A, determine the principal
stresses and the maximum shearing stress at point H located as shown
on top of the 18 mm diameter shaft.
SOLUTION
Equivalent force-couple system at center of shaft in section at point H.
V = 100 N M = (100)(150) = 15000 N ⋅ mm
T = (100)(250) = 25000 N ⋅ mm
1
Shaft cross section: d = 18 mm, c = d = 9 mm
2
π 1
J = c 4 = 10306 mm 4 I = J = 5153 mm 4
2 2
Tc (25000)(9)
Torsion: τ = = = 21.8 N/mm 2 = 21.8 MPa
J 10306
Mc (15000)(9)
Bending: σ = = = 26.2 N/mm 2 = 26.2 MPa
I 5153
Transverse shear: At point H stress due to transverse shear is zero.
Resultant stresses: σ x = 26.2 MPa, σ y = 0, τ xy = 21.8 MPa
1
σ ave = (σ x + σ y ) = 13.1 MPa
2
2
σx − σy
+ τ xy = 13.1 + 21.8 = 25.4 MPa
2 2 2
R=
2
σ a = σ ave + R = 38.5 MPa
σ b = σ ave − R = −12.3 MPa
τ max = R = 25.4 MPa
PROPRIETARY
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL.
MATERIAL. © 2013 The
Copyright McGraw-Hill
© 2015 Companies,
McGraw-Hill Inc. This
Education. All rights reserved. No
is proprietary part of
material this Manual
solely may be instructor
for authorized displayed,use.
Notreproduced,
authorized orfordistributed
sale or distribution in or
in any form anybymanner. This without
any means, documentthemay
priornotwritten
be copied, scanned,
permission duplicated,
of the publisher,forwarded, distributed,
or used beyond or posted
the limited
on distribution
a website, intowhole or part.
teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. A student using this manual is using it
without permission.
1050
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1050 1/8/2015 10:04:45 AM
y P
PROBLEM 7
7.26
6 mm
m A 51 mm Thhe steel pipe AB
A has a 1022-mm outer diameter and a 6-mm wall
A thhickness. Knowing that arm m CD is rigiddly attached to
t the pipe,
T
200 mm D
deetermine the principal
p stressses and the maximum
m shearing stress
att point K.
10 kN
N
C
1 mm
150
H K
z x
SOLUTION
d o 102
1
ro 51 mm ri ro t 45 mm
2 2
J
2
ro4 ri4 4.18555 106 mm 4
4.18555 10 6 m 4
1
I J 2.0927 10 6 m 4
2
o tube in the plane
Forcce-couple systtem at center of p containiing points H and
a K:
Fx 10 kN
10 1003 N
M y (10 103 )(200 103 )
2000 N m
M z (10 103 )(150 103 )
15000 N m
Torsion: oint K, place local
At po l x-axis in negative globbal z-directionn.
T M y 2000 N m
c ro 511 103 m
Tc ((2000)(51 1003 )
xy
J 4.1855 106
24.37 106 Pa
24.37 MPa
PROOPRIETARY MAT TERIAL. Copyrigght © 2015 McGrraw-Hill Educatioon. This is proprietary material soleely for authorizedd instructor use.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
Not authorized
a for salee or distribution inn any manner. Thiis document may not
n be copied, scannned, duplicated, forwarded, distribbuted, or posted
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
on a w
website, in whole or
on a website, in whole or part. part.
1053
1051
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1051 1/8/2015 10:04:45 AM
PROBLEM 7.26 (Continued)
Transverse shear: Stress due to transverse shear V Fx is zero at point K.
Bending:
|M z |c (1500)(51 103 )
| y | 6
36.56 106 Pa 36.56 MPa
I 2.0927 10
Point K lies on compression side of neutral axis.
y 36.56 MPa
Total stresses at point K:
x 0, y 36.56 MPa, xy 24.37 MPa
1
ave ( x y ) 18.28 MPa
2
2
x y 2
R xy 30.46 MPa
2
max ave R 18.28 30.46 max 12.18 MPa
min ave R 18.28 30.46 min 48.7 MPa
max R max 30.5 MPa
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
on on a website,
a website, in whole
in whole or part.
or part.
1054
1052
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1052 1/8/2015 10:04:46 AM
90 MP
Pa PROBLEM
M 7.36
330 MPa
Solve Prob. 7.14, using Mohr’s
M circle.
60 MPa
PROBLEM M 7.13 througgh 7.16 For thhe given statee of stress, deetermine the
normal and shearing
s stresses after the element
e shownn has been rotaated through
(a) 25 clockkwise, (b) 10 counterclockkwise.
SO
OLUTION
x 60 MP
Pa,
y 90 MPa,,
xy 30 MPa
x y
ave 15 MPa
2
Plootted points for Mohr’s circlle:
X : (60 MPa, 30 MPa)
Y : (90 MPa, 300 MPa)
C : (15 MPa, 0)
FX 30
tan 2 p 0.4
0
FC 75
2 p 21.80 P 10.90
2 2
X 752 300 2 80.78 MP
R FC FX Pa
(a) 25 . 2 50
5
2 2 P 50 21.80 288.20
x ave R cos x 56.2
5 MPa
xy R
sin xy 38.2
3 MPa
y ave R cos y 86.2
8 MPa
PROOPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyriight © 2015 McG Graw-Hill Educattion. This is proprrietary material soolely for authorizedd instructor use.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
Not authorized for salle or distribution in
i any manner. Thhis document may not be copied, scaanned, duplicated,, forwarded, distributed, or posted
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
on on a website,
a website, in whole
in whole ore part.
or part.
1064
1062
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1062 1/8/2015 10:04:51 AM
PROB
BLEM 7.36 (Continued)
( d)
(b) 10 . 2 200
2 p 2 21.880 20 41.80
x ave R cos x 455.2 MPa
xy R sin xy 533.8 MPa
y ave R cos y 755.2 MPa
PROOPRIETARY MAT TERIAL. Copyrigght © 2015 McGrraw-Hill Educatioon. This is proprietary material soleely for authorizedd instructor use.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
Not authorized
a for salee or distribution inn any manner. Thiis document may not
n be copied, scannned, duplicated, forwarded, distribbuted, or posted
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
on a w
website, in whole or
on a website, in whole or part. part.
1065
1063
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1063 1/8/2015 10:04:52 AM
PROBLEM 7.44
a Solve Prob. 7.22, using Mohr’s circle.
a 25
PROBLEM 7.22 Two members of uniform cross section 50 80 mm are glued
50 mm together along plane a-a that forms an angle of 25 with the horizontal. Knowing
that the allowable stresses for the glued joint are 800 kPa and 600 kPa,
determine the largest centric load P that can be applied.
P
SOLUTION
x 0
xy 0
y P/A
A (50 103 )(80 103 )
4 103 m 2
P
(1 cos50)
2A
2 A
P
1 cos 50
(2)(4 103 )(800 103 )
P
1 cos 50
P 3.90 103 N
P 2 A (2)(4 103 )(600 103 )
sin 50 P 6.27 103 N
2A sin 50 sin 50
Choosing the smaller value, P 3.90 kN
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
on aonwebsite,
a website, in whole
in whole or part.
or part.
1073
1071
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1071 1/8/2015 10:04:57 AM
100 MPa PROBLEM 7.55
50 MPa
Determine the principal planes and the principal
50 MPa
stresses for the state of plane stress resulting
+ 75 MPa from the superposition of the two states of
308
stress shown.
SOLUTION
Consider the state of stress on the left. We shall express it in terms of horizontal and vertical components.
x 50 cos 30
43.30
y 43.30
xy 50sin 30
25.0
Principal axes and principal stress:
1
ave (118.3 56.7) 87.5
2
x y 1
(118.3 56.7) 30.8
2 2
R (30.8)2 (75)2 81.08
75
tan 2 p 2 p 67.67 p 33.8 , and 123.8
30.8
max ave R 87.5 81.08 max 168.6 MPa
min ave R 87.5 81.08 min 6.42 MPa
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
on aonwebsite,
a website, in whole
in whole or part.
or part.
1087
1084
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1084 1/8/2015 10:05:07 AM
y PROBLEM 7.68
σy
For the state of stress shown, determine the maximum shearing stress
when (a) y 40 MPa, (b) y 120 MPa. (Hint: Consider both in-plane
and out-of-plane shearing stresses.)
80 MPa
140 MPa
z
x
SOLUTION
(a) x 140 MPa, y 40 MPa, xy 80 MPa
1
ave ( x y ) 90 MPa
2
2
x y 2 2 2
R xy 50 80 94.34 MPa
2
a ave R 184.34 MPa (max)
b ave R 4.34 MPa (min)
c 0
1
max (in-plane) ( a b ) R 94.34 MPa
2
1 1
max ( max min ) ( a b ) 94.3 MPa max 94.3 MPa
2 2
(b) x 140 MPa, y 120 MPa, xy 80 MPa
1
ave ( x y ) 130 MPa
2
2
x y 2 2 2
R xy 10 80 80.62 MPa
2
a ave R 210.62 MPa (max)
b ave R 49.38 MPa
c 0 (min)
max a 210.62 MPa min c 0
max (in-plane) R 86.62 MPa
1
max ( max min ) 105.3 MPa max 105.3 MPa
2
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
on on a website,
a website, in whole
in whole or part.
or part.
1102
1097
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1097 1/8/2015 10:05:16 AM
y PROBLEM 7.71
For the state of stress shown, determine the maximum shearing stress
100 MPa
when (a) z 0, (b) z 60 MPa, (c) z 60 MPa.
84 MPa
170 MPa
z
x
z
SOLUTION
1
ave (170 100) 135
2
1 1
( x y ) (170 100) 35
2 2
R (35)2 (84)2 91
A 135 91 226 MPa
B 135 91 44 MPa
(a) z 0. Point Z corresponding to the z axis is located at O, outside the circle drawn through A and B.
The largest of the 3 Mohr’s circles is the circle through O and A. We have
1 1 1
max (OA) A (226) max 113.0 MPa
2 2 2
(b) z 60 MPa. Point Z is located between B and A. The largest of the 3 circles is the one drawn
through A and B.
max R 91.0 MPa
(c) z 60 MPa. Point Z is located outside the circle drawn through A and B. The largest of the 8
Mohr’s circles is the circle through Z and A. We have
1 1
max ( ZA) (60 226) max 143.0 MPa
2 2
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
on aonwebsite,
a website, in whole
in whole or part.
or part.
1105
1100
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1100 1/8/2015 10:05:18 AM
PROBLEM 7.75
For the state of stress shown, determine the value of τ xy for which the
maximum shearing stress is (a) 63 MPa, (b) 84 MPa.
SOLUTION
σ x = 105 MPa σ y = 42 MPa
1
σ ave = (σ x + σ y ) = 73.5 MPa
2
σx −σy
U= = 31.5 MPa
2
τ (MPa)
(a) For τ max = 63 MPa
Center of Mohr’s circle lies at point C.
Lines marked (a) show the limits on τ max .
Limit on σ max is σ max = 2τ max = 126 MPa.
For the Mohr’s circle σ a = σ max
corresponds to point Aa.
R = σ a − σ ave
= 126 − 73.5
= 52.5 MPa
R = U 2 + τ xy
2
τ xy = ± R 2 − U 2
= ± 52.52 − 31.52
= ± 42 MPa
(b) For τ max = 84 MPa
Center of Mohr’s circle lies at point C.
R = 84 MPa
τ xy = ± R 2 − U 2 = ± 78.7 MPa
Checking σ a = 73.5 + 84 = 157.5 MPa
σ b = 73.5 − 84 = −10.5 MPa
σc = 0
1
τ max = (σ max − σ min ) = 84 MPa O.K.
2
PROPRIETARY
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL.
MATERIAL. © 2013 The
Copyright McGraw-Hill
© 2015 Companies,
McGraw-Hill Inc. This
Education. All rights reserved. No
is proprietary part of
material this Manual
solely may be instructor
for authorized displayed,use.
Notreproduced,
authorized orfordistributed
sale or distribution in or
in any form anybymanner. This without
any means, documentthemay
priornotwritten
be copied, scanned,
permission duplicated,
of the publisher,forwarded, distributed,
or used beyond or posted
the limited
on distribution
a website, intowhole or part.
teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. A student using this manual is using it
without permission.
1104
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1104 1/8/2015 10:05:20 AM
y PROBLEM 7.79
σy For the state of stress shown, determine two values of y for which the
maximum shearing stress is 80 MPa.
90 MPa
x
z 60 MPa
SOLUTION
x 90 MPa, z 0, xz 60 MPa
Mohr’s circle of stresses in zx plane:
1
ave ( x z ) 45 MPa
2
2
x y 2
R zx 452 602 75 MPa
2
a ave R 120 MPa, b ave R 30 MPa
Assume max a 120 MPa.
y min max 2 max
120 (2)(80) y 40.0 MPa
Assume min b 30 MPa.
y max min 2 max
30 (2)(80) y 130.0 MPa
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted
on on a website,
a website, in whole
in whole or part.
or part.
1116
1110
BeerMOM_ISM_C07.indd 1110 1/8/2015 10:05:24 AM
You might also like
- Electric Machines Principles Applications and Control Schematics 2nd Edition Dino Zorbas Solutions Manual DownloadDocument15 pagesElectric Machines Principles Applications and Control Schematics 2nd Edition Dino Zorbas Solutions Manual DownloadJoseph Singleton100% (22)
- Centrifugal Pump Design Tuzson 2000Document431 pagesCentrifugal Pump Design Tuzson 2000HectorNo ratings yet
- UCLA Astronomy 3 Practice ExamDocument7 pagesUCLA Astronomy 3 Practice ExamSharon XuNo ratings yet
- 14 2042015Assignment14SolutionDocument5 pages14 2042015Assignment14SolutionInfo Esocket100% (1)
- d7dd76b5-952b-44a2-aedd-abb43ca0e38bDocument38 pagesd7dd76b5-952b-44a2-aedd-abb43ca0e38bMANUEL ALEJANDRO LOZANO BELLIDONo ratings yet
- Tutorial Week 3 SolutionsDocument7 pagesTutorial Week 3 SolutionsQuazar001No ratings yet
- Chapter7 PDFDocument34 pagesChapter7 PDFWillian DiazNo ratings yet
- Physics (DPP - 4) : Hint & SolutionsDocument4 pagesPhysics (DPP - 4) : Hint & SolutionsArshita VermaNo ratings yet
- BSE3421 TrigSheetDocument1 pageBSE3421 TrigSheetuclanfire2010No ratings yet
- Allen DLP 19.7.20 Jee Advanced Unit Test 2 SolDocument7 pagesAllen DLP 19.7.20 Jee Advanced Unit Test 2 SolSrikant SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Cive206 A3Document5 pagesCive206 A3msaedovicNo ratings yet
- Print: Sin Sin Sin (+) /2 60 40 Sin /2 60 Sin 50 Sin 30 0.766 0.54Document4 pagesPrint: Sin Sin Sin (+) /2 60 40 Sin /2 60 Sin 50 Sin 30 0.766 0.5411.vega.tos2No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-01-26 at 9.23.09 AMDocument32 pagesScreenshot 2024-01-26 at 9.23.09 AMsparkle.comic-0kNo ratings yet
- Analysis of StructuresDocument22 pagesAnalysis of StructuresRolandNo ratings yet
- 6 of 6 - Assignment - PracticeDocument3 pages6 of 6 - Assignment - Practicetian jinNo ratings yet
- PV Lab ReportDocument6 pagesPV Lab ReportBen HeoNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Problems Solution: Max MinDocument12 pagesFatigue Problems Solution: Max MinVenkatNo ratings yet
- David Miles - Three Trigonometric Results From A Regular PolygonDocument4 pagesDavid Miles - Three Trigonometric Results From A Regular PolygonEduardo CostaNo ratings yet
- Fe Strength of Materials 0930Document31 pagesFe Strength of Materials 0930fem mece3381No ratings yet
- Problem 11.8: F (T) A T (MS)Document2 pagesProblem 11.8: F (T) A T (MS)김경동No ratings yet
- Hydraulics Solution Sheet 11 - Pumps and TurbinesDocument3 pagesHydraulics Solution Sheet 11 - Pumps and TurbinesSalmanNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump MathDocument6 pagesCentrifugal Pump Mathshamiul himelNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board Class X Mathematics Board Paper - 2015 Solution: Given Quadratic Equation IsDocument22 pagesCBSE Board Class X Mathematics Board Paper - 2015 Solution: Given Quadratic Equation IsNivitha100% (1)
- AITS-2021-OPEN TEST-JEEA-PAPER-2-SolDocument15 pagesAITS-2021-OPEN TEST-JEEA-PAPER-2-SolAyush SrivastavNo ratings yet
- 7) Add Maths TrigonometryDocument44 pages7) Add Maths TrigonometryRayyan TanveerNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics - Dynamics, Enhanced Etext - 9781119390985 - Exercise 85 - QuizletDocument2 pagesEngineering Mechanics - Dynamics, Enhanced Etext - 9781119390985 - Exercise 85 - QuizletAmirali SahebzamaniNo ratings yet
- AITS 1920 FT IV JEEA PAPER 1 Sol PDFDocument12 pagesAITS 1920 FT IV JEEA PAPER 1 Sol PDFNishit PNo ratings yet
- MOM Test 1 Sept 2015 - Scheme & SolutionDocument3 pagesMOM Test 1 Sept 2015 - Scheme & Solutionpiravi66No ratings yet
- FME CRANK Mechanism FinalDocument9 pagesFME CRANK Mechanism FinalMacrey BwaleiNo ratings yet
- Trigo Formulas PDFDocument3 pagesTrigo Formulas PDFthishaniNo ratings yet
- Basic Review of TrigonometryDocument3 pagesBasic Review of Trigonometryyassine rekikNo ratings yet
- Basic Review of Trig PDFDocument3 pagesBasic Review of Trig PDFChing RofalsNo ratings yet
- Frequency Analysis-Plethysmograph Waves: Plethysmograph Waveform (Pre-Exercise)Document1 pageFrequency Analysis-Plethysmograph Waves: Plethysmograph Waveform (Pre-Exercise)davidleraolNo ratings yet
- Exercicis EstructuresDocument8 pagesExercicis Estructurespochmax18No ratings yet
- TUGAS DESAIN PONDASI II - SULAIMAN SAPUTRA - 180501064-DikonversiDocument19 pagesTUGAS DESAIN PONDASI II - SULAIMAN SAPUTRA - 180501064-DikonversiMuhammad Dicky Zulkarnain SNo ratings yet
- Q4 W2Trigonometric Ratios of Special AnglesDocument27 pagesQ4 W2Trigonometric Ratios of Special Anglesrevilla.136521140284No ratings yet
- I. Solution: DL DL A B A B SDocument6 pagesI. Solution: DL DL A B A B SWilliam ProvidoNo ratings yet
- PHY2042 Experiment #5 - Newton's Second LawDocument3 pagesPHY2042 Experiment #5 - Newton's Second LawKelsey WNo ratings yet
- Physics 2230 Experiment #5 - Newton's Second LawDocument3 pagesPhysics 2230 Experiment #5 - Newton's Second LawKelsey WNo ratings yet
- WM C1602M 1YNNbV4Document15 pagesWM C1602M 1YNNbV4Lenovo IncognitoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7Document7 pagesTutorial 7snoozermanNo ratings yet
- T7.3 Example FrameDocument17 pagesT7.3 Example FrameUpdirahman MohamoudNo ratings yet
- Tugas Pengganti EAS PDFDocument33 pagesTugas Pengganti EAS PDFjefri arisNo ratings yet
- Unit TestDocument2 pagesUnit TestsionNo ratings yet
- Two Sample Hypothesis ExamplesDocument6 pagesTwo Sample Hypothesis ExamplesSRI RAMNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry P1 Unsolved - 231015 - 193252Document18 pagesTrigonometry P1 Unsolved - 231015 - 193252inaayaNo ratings yet
- 0914 Stress Transformation UpdateDocument24 pages0914 Stress Transformation UpdateAdian Weigen GohNo ratings yet
- Bim04 4to Semana02Document26 pagesBim04 4to Semana02Daiana Díaz GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Shearwall Checks: Safety Factor (LRFD)Document3 pagesShearwall Checks: Safety Factor (LRFD)ManuelGarciaNo ratings yet
- Tarea 5.2 Bishop Fellenius IMPDocument2 pagesTarea 5.2 Bishop Fellenius IMPLuis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Iii Ii IDocument11 pagesIii Ii ISarah Ayu AmaliaNo ratings yet
- 65° Triple Band Panel AntennaDocument2 pages65° Triple Band Panel AntennaАнтонNo ratings yet
- NA 4004 (T2) SolutionDocument7 pagesNA 4004 (T2) SolutionKhin Me Me MyintNo ratings yet
- Mastery Test 2 SolutionDocument6 pagesMastery Test 2 SolutionConie CatapanNo ratings yet
- Lab Exe GarlandDocument5 pagesLab Exe Garlandichiwaaa sanNo ratings yet
- Plumbnes Strake 2 - (12 Koordinat)Document1 pagePlumbnes Strake 2 - (12 Koordinat)yuwantoniNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of MaterialsDocument34 pagesMechanics of MaterialsCharn69% (16)
- Wednesday Paper 3Document6 pagesWednesday Paper 3avinsaini05No ratings yet
- Desain Tulangan Memanjang Balok (As-A) : Data BangunanDocument4 pagesDesain Tulangan Memanjang Balok (As-A) : Data BangunanerikNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.3Document4 pagesProblem 4.3Jae CNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3Ridho Bela NegaraNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Modal Testing 1-2Document29 pagesFundamentals of Modal Testing 1-2Ridho Bela NegaraNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Modal Testing 1-2-CompressedDocument29 pagesFundamentals of Modal Testing 1-2-CompressedRidho Bela NegaraNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Modal Testing 1-2Document31 pagesFundamentals of Modal Testing 1-2Ridho Bela NegaraNo ratings yet
- Rob HallDocument4 pagesRob HallRidho Bela NegaraNo ratings yet
- Sections Legends: Arts, Customs and Beliefs of Malaysia L Arts, Customs and Beliefs of Malaysia LDocument1 pageSections Legends: Arts, Customs and Beliefs of Malaysia L Arts, Customs and Beliefs of Malaysia LRidho Bela NegaraNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of The Temperature Profile Along Offshore Pipeline of An Oil and Gas Flow: Effect of Insulation MaterialsDocument8 pagesModeling and Simulation of The Temperature Profile Along Offshore Pipeline of An Oil and Gas Flow: Effect of Insulation MaterialsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Plane - Final.Document107 pagesMotion in A Plane - Final.Sahil KarandeNo ratings yet
- Gaskell 6th SolutionsDocument229 pagesGaskell 6th Solutionsrogue20200429No ratings yet
- Sri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology Course Material (Question Bank)Document3 pagesSri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology Course Material (Question Bank)rnranjinaNo ratings yet
- An Explicit Approximation Factor#Reynolds Relation Rough and Smooth PipesDocument2 pagesAn Explicit Approximation Factor#Reynolds Relation Rough and Smooth PipesAnonymous vWRpcHZcwNo ratings yet
- Wakefield Heat SinkDocument23 pagesWakefield Heat SinkNiko KraljNo ratings yet
- Day 1 - Harmonic Motion Notes PageDocument2 pagesDay 1 - Harmonic Motion Notes Pagecandela floresNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rocket NozzleDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Rocket NozzleleulmathersNo ratings yet
- A 3D Method To Evaluate Moisture Losses in A Low Pressure SteamDocument11 pagesA 3D Method To Evaluate Moisture Losses in A Low Pressure SteamMuhammad Junaid DarNo ratings yet
- XXXDocument33 pagesXXXjay danenjeyanNo ratings yet
- All Shure Mics Data SheetsDocument12 pagesAll Shure Mics Data SheetsRosana Mabel VillaNo ratings yet
- Force AnswersDocument11 pagesForce AnswersLelon OngNo ratings yet
- Strut and Tie Sample 03Document5 pagesStrut and Tie Sample 03Oliver AtomNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of Injection Characteristics, Hydrodynamics and PDFDocument8 pagesNumerical Simulation of Injection Characteristics, Hydrodynamics and PDFnacer zidiNo ratings yet
- Two-Phase Pressure Drops (ALF)Document7 pagesTwo-Phase Pressure Drops (ALF)Eng AlfNo ratings yet
- PIB English FeaturesDocument2 pagesPIB English FeaturesmanishbabuNo ratings yet
- Safety at Ultimate Limit State in Flexure: Xu Xu, MaxDocument7 pagesSafety at Ultimate Limit State in Flexure: Xu Xu, MaxMisa JCNo ratings yet
- C469C469M-14 Standard Test Method For Static Modulus of Elasticity and Poisson's Ratio of Concrete in CompressionDocument5 pagesC469C469M-14 Standard Test Method For Static Modulus of Elasticity and Poisson's Ratio of Concrete in CompressionAlabbas Fadhel100% (6)
- Staad EditorDocument25 pagesStaad EditorBãlã Ð Chøçølãtě Røměø100% (1)
- Laws of Motion AssignmnetDocument5 pagesLaws of Motion AssignmnetRyan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- XFlow Brochure 2011Document5 pagesXFlow Brochure 2011invisiblevision4No ratings yet
- Berthier PaperDocument7 pagesBerthier PaperJuan Manuel Hernandez LNo ratings yet
- ECIV 3316 - Chapter 05 - Shear in Beams + ExampleDocument30 pagesECIV 3316 - Chapter 05 - Shear in Beams + Examplebuffyto5377No ratings yet
- Lecture-5: Technological Properties of Metals Steel and Its ClassificationDocument51 pagesLecture-5: Technological Properties of Metals Steel and Its ClassificationSarojKumarSinghNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Worksheet DypisDocument2 pagesGrade 6 Worksheet DypisPehel MehtaNo ratings yet
- Momentum Absorption by Vegetation: Quart. 97Document16 pagesMomentum Absorption by Vegetation: Quart. 97Ivan RodrigoNo ratings yet
- RC One Way Slab Design (ACI318)Document2 pagesRC One Way Slab Design (ACI318)Bunkun15100% (1)
- Module 10 - Simple Harmonic MotionDocument6 pagesModule 10 - Simple Harmonic MotionSukhvinder SinghNo ratings yet