Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oxidative Stress: Objective: Methods
Oxidative Stress: Objective: Methods
Uploaded by
Achmad Gus FahmiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oxidative Stress: Objective: Methods
Oxidative Stress: Objective: Methods
Uploaded by
Achmad Gus FahmiCopyright:
Available Formats
Bali Medical Journal (Bali Med J) 2016, Volume 5, Number 3: 79-83
P-ISSN.2089-1180, E-ISSN.2302-2914
Gaharu Leaf Water Extract Reduce MDA and 8-OHdG Levels and Increase Activities SOD and
Catalase in Wistar Rats Provided Maximum Physical Activity
I Made Oka Adi Parwata1*, Ida Bagus Putra Manuaba1, I Wayan Putu Sutirtayasa2, I Wayan Wita2
1
Faculty Mathematics and Science Udayana University, Denpasar, Bali-Indonesia
2
Faculty of Medicine Udayana University, Denpasar, Bali-Indonesia
*Correspondence: E-mail: m.andita@yahoo.co.id
Background: Oxidative stress occurs due to an imbalance of the number of free radicals by the
number of endogenous antioxidant produced by the body i.e. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD),
Gluthathione Peroxidase (GPx), and Catalase. The imbalance between the number of free radicals and
antioxidants can be overcome with the endogenous antioxidant intake that exogenous oxidative
stress can be reduced. One of exogenous antioxidants is natural Gaharu leaf water extract.
Objective: This research focus on the effect of Gaharu leaf water extract in reducing MDA and 8-
OHdG and increase the activity of SOD and Catalase. Methods: This study was an experimental with
post only controls group design. Experiment was divided into 5 groups of wistar rats, each consisting
of 5 animals, i.e. negative control group without extract [K (-)], treatment 1 treated 50 mg/kg BW/day
of the extract (T1), treatment 2 treated 100 mg/kg BW/day of the extract (T2), treatment 3 treated 200
mg/ kg BW/day of the extract (T3), and positive control group [K (+)] treated with vitamin Cat a dose
50 mg/kg BW/day. All groups treated for 10 weeks. Every day, before treatment, each group was
given a maximum swimming activity for 1.5 hours for 10 weeks. ELISA was used to measure
MDA, 8-OHdG, SOD, and Catalase activities. Result: The research results showed that treatment of
extract of leaves of Gaharu with an higher dose from 50 mg/kg BW up to 200 mg/ kg BW significantly
decline (p <0.05) levels of MDA with the average ranging from 6.37±0.23, 5,56±0.27 and 4.32±0.27,
8-OHdG with a mean of 1.64±0.11, 1.26±0.46, and 1.09±0.17. On the other hand the treatment also
increase SOD activity with less ranging from 12.15±1.04, 15.70±2.02, and 18.84±1.51, and Catalase
ranging from 6,68±0.63, 8.20±1.14 and 9.29±0,79 in the blood of Wistar rats were given a maximum
activity compared to the negative control group. This is probably higher phenol compounds
(bioflavonoids) quantity content of the extract. These compounds synergistically affect their activity
through capture and neutralize the free radicals that oxidized the lipid to less that automatically MDA
production as the end result of oxidation lipid levels down, 8-OHdG down, the activity of SOD and
Catalase ride. Conclusion: Gaharu leaf water extract reduced oxidative stress of Wistar rats through
reduction of MDA and 8-OhdG mechanism. On the other hand, the extract increases SOD and Catalase
activity.
Keywords: Gaharu leaf water extract, SOD, MDA, 8-OHdG and Catalase
http://dx.doi.org/10.15562/bmj.v5i3.297
Cite This Article: Parwata, I., Manuaba, I., Yasa, I., Wita, I. 2016. Gaharu Leaf Extract Water Reduce
MDA and 8-OHdG Levels and Increase Activities SOD and Catalase in Wistar Rats Provided
Maximum Physical Activity. Bali Medical Journal 5(3): 79-83. DOI:10.15562/bmj.v5i3.297
Corresponding author: body oxygen consumption increased 20 times while
I Made Oka Adi Parwata the oxygen consumption of the muscle fibers
Address: Faculty Mathematics and Science expected to increase 100 folds. This can result in the
Udayana University, Denpasar, Bali-Indonesia body will huge lack of oxygen, known as hypoxia.
Email: m.andita@yahoo.co.id This resulted in an increase in oxygen consumption
increased production of free radicals which can
INTRODUCTION oxidize fat in muscle tissue (fat tissue oxidation
Maximum physical activity can trigger an muscle), causing damage to muscle cells.2
imbalance between production of free radicals and Start physical training physiological and
the body's antioxidant defense system known as biochemical response is complex.
oxidative stress1, during maximal exercise, whole Each movement begins with a rapid muscle
Open access: www.balimedicaljournal.org and www.ojs.unud.ac.id 79
Bali Medical Journal (Bali Med J) 2016, Volume 5, Number 3: 79-83
P-ISSN.2089-1180, E-ISSN.2302-2914
anaerobic metabolism. Strength comes from the bioflavonoid can prevent lipid peroxidation,
breakdown of ATP to ADP or AMP results and takes preventing DNA damage, stimulating the formation
place in the mitochondria. The energy release is of enzymatic antioxidants Superoxide Dismutase
accompanied by increasing flow of electrons in (SOD) , catalase and Glutathione peroxidase (GPx)
mitochondrial respiration circuit causes the as an anti-inflammatory and as a chelating agent of
formation of reactive oxygen (O2-) and H2O2 in an metal Cu and Fe. It inhibits advanced initiation and
effort to ATP formation.3 propagation reactions of radicals.7-8 However, the
Physical training tends to empty the ATP and mechanism in protecting endothelial dysfunction is
ADP which would stimulate the conversion of ADP not known with certainty.
catabolism and Xanthine dehydrogenase (XDH) into The aim of this study was to prove the ability
oxidase. Xanthine Oxidase (XOD) will form free of Gaharu leaf water extract in decreasing MDA and
radicals (O2-). Excessive formation of free radicals 8-OHdG and increase the activity of SOD and
that will cause an imbalance known as oxidative Catalase on Wistar rats which administered to a
stress damage with the end result of fat, proteins and maximum swimming activity of 1.5 hours per day
DNA.3 for 10 weeks.
Oxidative stress also occurs due to decreased
amount of oxygen and nutrients, causing micro METHODS
vascular damage. This situation is referred to Materials and Instrument
reperfusion injury. It can also lead to tissue damage Materials and instruments in this research
due to excess production of free radicals from the including : thirty white male rats, Wistar descent,
metabolism of fats and proteins stored in the body (weighing 200g – 250g, aged 2-4 months). Gaharu
due to lack of intake from outside the body.2 leaf extract (Gyrinops versteegii), ELISA Kits, SOD
Oxidation reactions involving free radicals Bio Vision K355 - 100, Bio Vision Catalase, ELISA
*OH can damage cell membranes and damaging the Kit K773-100, 8-OHdG ELISA Kit, DNA Damage
surrounding normal DNA composition which can Cell Bio labs STA-320, 1,1,3,3-tetraethoxypropane
result in a mutation. Mutations or DNA damage can (Sigma), thiobarbituric acid, phosphate and
lead to degenerative diseases such as cancer, heart methanol. UV-Vis double beam (Varian), analytic
disease, cataracts, premature aging and other.1 Digital Balance Scale, Memmert heating and dry
Compound 8-OHdG is a marker that indicates the oven, polypropylene tube, centrifuge, Buchi rotary
occurrence of DNA damage caused by free radicals evaporator, water bath, pyrex measuring cup, pyrex
excess. This is due to the oxidation of DNA test tubes, micropipette, a set of mouse cage.
constituent bases (guanosine). Oxidized guanosine
will form 8-OHdG. Deoxyguanosine (dG) is one of Procedure
the constituent bases of DNA and the oxidation 1. Manufacture of Gaharu leaf water extract
reaction when experiencing will be 8-hydroxy-2'- Total of 1000 grams Gaharu leaf powder is put in
deoxyguanosin (8-OHdG). 2 litres of hot water (60oC) for approximately 2
Guanosine can also undergo hydroxylation in hours while stirring, let it stand for 24 hours. Then,
response to normal metabolism or environmental filter extraction results. Liquid extract obtained was
pollution, especially heavy metals.4 Increased levels concentrated used freeze dryer extracts obtained
of 8-OHdG pathology associated with the disease thick. Viscous extract, was stored in -20oC for
include depression, cancer, diabetes, and further research.
hypertension.4-5 This is evidenced by several studies
found that 8-OHdG was significantly decreased in 2. Treatment of Mice
the group of pregnant women who are given the A total of 30 white male rats was divided into 5
sport compared with the group without exercise. groups, each of 6 rats. All groups of rats were given
The imbalance between the number of free a maximum activity of 1.5 hours of swimming every
radicals and antioxidants can be overcome with the day for 10 weeks. The groups been awarded the
exogenous antioxidant intake or reduced the maximum activity and each group was given the
exogenous oxidative stress. One of exogenous following treatment. Group I / negative control [K (-
antioxidants is natural Gaharu leaf water extract. )] is given only distilled water, group II (P1) Gaharu
This is evidenced overcome from in vitro analysis of leaf water extract given 50 mg/kg BW, group III
the water extract of leaves of Gaharu that have a high (P2) given Gaharu leaf water extract 100 mg/kg BW,
antioxidant capacity with IC50 value = 3.44 ppm, group IV (P3) given Gaharu leaf water extract 200
which means with a concentration of 3.44 ppm has mg/kg BW and group V / positive control [K (+)]
been able to inhibit 50% of reactive oxygen species Vitamin C given 50 mg/kg BW.9 After the treatment,
(ROS) and the content of phenolic compounds / blood was taken, apply in the test tube of blood
bioflavonoid = 14.980 mg GAE/100 g) that can be containing EDTA. Blood plasma were then analyzed
protected endothelial dysfunction.6 Phenolic levels of MDA, SOD of activity, Catalase activity
compounds including bioflavonoid can directly and levels of 8-OHdG.
capture superoxide radicals, peroxynitrite that
Open access: www.balimedicaljournal.org and www.ojs.unud.ac.id 80
Bali Medical Journal (Bali Med J) 2016, Volume 5, Number 3: 79-83
P-ISSN.2089-1180, E-ISSN.2302-2914
3. Analysis of MDA Analysis of the results showed that MDA
Measurement of MDA levels following the levels that leaf water extract of Gaharu with
procedure 10 A total of 0.5 ml of blood plasma was increasing doses ranging from 50 mg/kg BW up to
added 2.0 ml of cold Hcl (0.25 N) containing 15% 200 mg/ kg BW was able to significantly (p <0.05)
TCA, 0.38% TBA and 0.5% BHT. This mixture is lower levels of MDA with the average ranging from
heated 80°C for one hour. After boiling, the tubes 6.37 ± 0, 23, 5.56 ± 0.27 and 4.32 ± 0.27 compared
were placed into an ice bath to cool the samples. The to the negative control group without being
cooled samples were mixed well and applied to SEP- administered the extract with a mean of 6.82 ± 0.48.
Pak C18 column, then centrifuged at 3500 rpm for This is due to the quantity of the content of this class
10 minutes. Obtained supernatant absorbance was of compounds phenol /bioflavonoid which is more
measured spectrum photo metrically at 532 nm. Unit and work synergistically in the capture or neutralize
of measurement is nm / ml. free radicals (*OH) are usually to peroxide fat to less
that automatically MDA production as the final
4. Analysis of SOD activity result of the oxidation of PUFA and oxidative stress
A total of 0,08 ml of blood plasma was treated levels down can be prevented.11 The decrease in
with a mixture consisting of 2.90 ml of Na2CO3 MDA levels mentioned above can be seen in the
buffer containing 0.1mm EDTA (pH 10), 0:06 ml Table 1 and Figure 1.
xanthine, 10 mM, bovine serum albumin 00:03
(BSA) 0.5%, 2.5 mM NBT 0:03 ml. Furthermore, Table 1. The decrease of MDA Levels
the addition of xanthine oxidase (0:04 units). The Mean of
resulting absorbance after 30 minutes was measured MDA
Subject Group N F P
at a wave length of 560 nm. Furthermore, the Levels
regression curve of standard solutions made SOD (nm/mL)
Assay Kit Bio Vision with measurement unit U/mL. K (-) 5 6,82±0,48
Extract 50 mg 5 6,37±0,23
5. Analysis of Catalase Activity Extract 100 mg 5 5,56±0,27 70,1 0,0001
Measurements were performed by manual Extract 200 mg 5 4,32±0,27
procedure of Bio Vision Assay Kit. Catalase activity K (+) 5 3,60±0,39
was measured with magnitude of the reduction of
hydrogen peroxide. In quartz cuvette, the blood Table 2. The decrease of 8-OHdG Levels
plasma of 0.5 added to 2.0ml of K3PO4 buffer Mean of
(pH7.0) containing 10 mM hydrogen peroxide. 8-OHdG
Changes in absorbance at 240nm recorded every 15 Subject group N F P
Levels
seconds for one minute. Furthermore, the regression (ng/mL)
curve of standard solutions made CAT Assay Kit K (-) 5 1,92±0,61
Bio Vision. Unit of measurement is U /mg. Extract 50 mg 5 1,63±0,11
Extract 100 mg 5 1,26±0,46 4,62 0,008
6. Analysis of 8-OHdG levels Extract 200 mg 5 1,09±0,17
Measurement of 8-OHdG levels following the K (+) 5 0,89±0,55
procedure in product instruction 8-OHdG ELISA
Kit STA-320 Cell Bio-labs. Unit of measurement is
Analysis of the levels of 8-OHdG, shows that
ng/mL. the water extract of the leaves of Gaharu with
increasing doses ranging from 50 mg/kg BW up to
RESULTS 200 mg/kg BW was able to significantly (p <0.05)
Prior to the treatment of wistar rats (Rattus
lower levels of 8-OHdG with the average ranging
norvegicus L.) males adapted for 1 month.
from 1,63±0.11, 1.26±0.46 and 1.09±0.17 compared
Furthermore, given the maximum activity in the
to the negative control group without being
form of swimming 1.5 hours per-day for 10 weeks. administered the extract with a mean of 1.92 ± 0.61.
Having been awarded the maximum activity of mice This is due to the quantity of the content of this class
given water extract of leaves of Gaharu with
of compounds phenol /bioflavonoid which is more
increasing doses from 50 mg/kg BW, 100 mg/kg
and work synergistically in the capture or neutralize
BW and 200 mg/kg BW in the treatment group.
free radicals (*OH) that normally oxidize guanosine
These results were compared with the control
bases of the DNA becomes less automatic 8-OHdG
(-) with no feed Gaharu leaf water extract, only mice production as an end result of oxidation levels down
given distilled water alone, control (+) to give and DNA damage can be prevented. The decrease in
vitamin Cat a dose of 50 mg/ kg BW. Treatment of
8-OHdG levels mentioned above can be seen in the
the extract was carried out for 10 weeks, blood in the
table 2 and figure 2.
eye of mice subsequently retrieved and examined
SOD enzyme activity analysis showed that
the levels of MDA, 8-OHdG levels, enzyme activity
the results of leaf water extract of Gaharu with
of SOD and catalase enzyme activity. increasing doses ranging from 50 mg/kg BW up to
Open access: www.balimedicaljournal.org and www.ojs.unud.ac.id 81
Bali Medical Journal (Bali Med J) 2016, Volume 5, Number 3: 79-83
P-ISSN.2089-1180, E-ISSN.2302-2914
200 mg/kg BW was able to significantly (p <0.05) Table 4. The Increase of Catalase Activity
increase in SOD enzyme activity with a mean Mean of
ranging from 12.15 ± 1, 04, 15.70 ± 2.02 and 18.84 Subject Catalase
N F P
± 1.51 compared to the negative control group group Activity
without being administered the extract with a mean (U/mg)
of 10.25 ± 1.35. K (-) 5 6,10±0,76
Extract 50 5 6,68±0,63
Extract 100 5 8,20±1,14 46,22 0,000
Extract 200 5 9,28±0,79
K(+) 5 12,13±0,46
Figure 1.
The decrease of MDA Levels
Figure 3.
The Increase of SOD Activity
Figure 2.
The decrease of8-OHdG Levels
Table 3. The Increase of SOD Activity
Mean of Figure 4.
Subject SOD The Increase of Catalase Activity
N F P
group Activity
(U/mL) Catalase activity analysis showed that the
K (-) 5 10,25 results of Gaharu leaf water extract with increasing
Extract 50 5 12,15 doses ranging from 50 mg/kg BW up to 200 mg/kg
Extract 100 5 15,70 61,69 0,000 BW was able to significantly (p <0.05) increase the
Extract 200 5 18,84 activity of the enzyme catalase, with the average
K (+) 5 23,55 ranging from 6.68±0,63, 8.20±1.14 and 9.29±0.79
compared to the negative control group without
This is due to the quantity of the content of being administered the extract with a mean of
this class of compounds phenol / bioflavonoid which 6.1±0.76.
is more and work synergistically, can directly This is due to the quantity of the content of
capture or neutralize the SOD, peroxynitrite so this class of compounds phenol/bioflavonoid which
flavonod stimulate the formation of enzymatic is more and work synergistically, can directly
antioxidants SOD and endothelial dysfunction can capture or neutralize the free radical superoxide,
be reduced.6 The increase of SOD Activity peroxynitrites, bioflavonoid stimulate the formation
mentioned above can be seen in the table 3 and of enzymatic antioxidants catalase and endothelial
figure 3. dysfunction can be reduced.12-13 The decrease of
Open access: www.balimedicaljournal.org and www.ojs.unud.ac.id 82
Bali Medical Journal (Bali Med J) 2016, Volume 5, Number 3: 79-83
P-ISSN.2089-1180, E-ISSN.2302-2914
Catalase activity mentioned above can be seen in the Heavy Metals. Polish J. of Environ. Study.
table 4 and figure 4. 2009: 18 (6): 1131-39.
5. Gupta, R.K., Kesari, A.N., Kesari, S., Santosh,
CONCLUSION K.S., and Watal, G. Studies on glycemic and
Gaharu leaf water extract with increasing lipidemic effect of Murraya koenigii in
doses of 50 mg/kg BW, 100 mg/kg BW and 200 experimental animal. Journal of
mg/kg BW significantly (p <0.05) can reduce Ethnopharmacology. 2010. 112:305-311.
oxidative stress through the mechanism of reduction 6. Almey A., Khan AJ., Zahir S., Suleiman M.,
in MDA and 8-OHdG and SOD enzyme activity and Aisyah Rahim K. Total phenolic content and
the increase catalase in blood of Wistar rats given primary antioxidan activity of methanolic and
maximal activity. The higher the dose given greater ethanolic extract of aromatic plants’ leaves.
reduction in levels of MDA and 8-OHdG, and given International Food Research Journal. 2010: 17;
the higher dose the greater the increase in enzyme 1077-88.
activity of SOD and catalase. This is due to the 7. Product Mmanual. Superoxide Dismutase
content of phenolic compounds / flavonoids greater (SOD) Activity and Catalase Activity
will be stronger in the capture and neutralize free Colorimetric/Fluorometric. Assay Kit.
radical superoxide, hydroxyl and peroxynitrite that BioVision Inc. Milpitas, 2014. USA.
endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress can be 8. Akhlaghi M. and Brian B. Mechanisms of
prevented. flavonoid protection against myocardial
ischemia–reperfusion injury. Journal of
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2009.: 46;
To all those who have deigned to provide 309–17.
assistance and input to completing the study until the 9. Reagan-Shaw, S., M. Nihal, and N. Ahmad.
completion of this article. We would like to thank Dose Translation from Animal to Human
you profusely to Mr Promotor Prof. Dr. Ir. Ida Bagus Studies Revisited.The FASEB Journal Life
Putra Manuaba, M. Phill, Co-promotor Prof. Dr. dr. Sciences Forum. 2007: 22(-); 659-661.
I Wayan Wita, Sp. JP and Co-promotor II, Dr. dr. I 10. Kumar, S. Kumar, D. Manjusha, Saroha, K.
Wayan Putu Sutirtayasa, M.Sc., for all the advice Singh, N. dan Vashishta, B. Antioxidant and
and guidance so that research and this article could free radical scavenging potential of Citrullus
be resolved in time. colocynthis (l.) Schrad. methanolic fruit extract.
Acta Pharmacology. 2008: 58; 215–220.
REFERENCES 11. Forlenza, J.M. and G.E. Miller. Increased
1. Murray R K. et.al. Harper’s Illustrated Serum Levels of 8-Hydroxy-2-Deoxyguanosine
Biochemistry 28th ed. New York: Lange in Clinical Depression. Psychosomatic.2006:
Medical Publications. 2009.pg 155 – 459. 68; 1-7.
2. Sasaki M, Joh T. Oxidative stress and ischemia- 12. Cai, Y., Q. Luo, M. Sun and H. Corke.
reperfusion injury in gastrointestinal tract and Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Compounds
antioxidant, protective agents. J Clin Biochem of 112 Traditional Chinese Medicinal Plants
Nutr. 2007;40(1):1-12. Associated with Anticancer. Life Science. 2004:
3. Chevion S, Molan DS, Heled Y. Plasma 74(17); 2157 –84.
antioxidant status and cell injury after severe
physical exercise. PNAS. 2003: 100(9); 5119-
23.
4. Chabowska, S.A., A.Beck, R.Poreba,
R.Andrzejak, J.Antonowicz Juchniewicz.
Evaluation of DNA Damage in People
Occupationally Exposed to Arsenik and Some
Open access: www.balimedicaljournal.org and www.ojs.unud.ac.id 83
You might also like
- Croak by Gina Damico ExcerptDocument29 pagesCroak by Gina Damico ExcerptHoughton Mifflin Harcourt0% (1)
- Samuel Taylor ColeridgeDocument18 pagesSamuel Taylor ColeridgeHemant SinghNo ratings yet
- Comparative Effect of Aqueous Aloe Vera Extracts On Oxidative Stress in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Wistar RatsDocument6 pagesComparative Effect of Aqueous Aloe Vera Extracts On Oxidative Stress in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Wistar RatsEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Anti-Oxidoreductive Stress Effects of Iraqi Olea Europaea L. Leaves Extract Against Low Double Doses of Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in RatsDocument11 pagesAnti-Oxidoreductive Stress Effects of Iraqi Olea Europaea L. Leaves Extract Against Low Double Doses of Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in RatsVincentius KevinNo ratings yet
- Journal of Ethnopharmacology: Parminder Nain, Vipin Saini, Sunil Sharma, Jaspreet NainDocument7 pagesJournal of Ethnopharmacology: Parminder Nain, Vipin Saini, Sunil Sharma, Jaspreet NainAngie MenaNo ratings yet
- Mahe 01Document5 pagesMahe 01mahemezNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Assays On GPX and Sod in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Mice Given Yellow Velvet Leaf (Limnocharis Flava) Ethanol ExtractsDocument8 pagesEnzyme Assays On GPX and Sod in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Mice Given Yellow Velvet Leaf (Limnocharis Flava) Ethanol Extractsimam muhammadNo ratings yet
- Ekstrak Daun Salam (Eugenia Polyantha) EFEKTIF DALAM Menurunkan Kadar Malondialdehyde Pada Kondisi Tikus HiperlipidDocument10 pagesEkstrak Daun Salam (Eugenia Polyantha) EFEKTIF DALAM Menurunkan Kadar Malondialdehyde Pada Kondisi Tikus HiperlipidMuhammad Adhar GeslauwNo ratings yet
- Sutaryono, Sholikhah Deti A., Nurul HidayatiDocument9 pagesSutaryono, Sholikhah Deti A., Nurul HidayatiMayang TariNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Untuk Soal Pak WYDocument11 pagesJurnal Untuk Soal Pak WYPitra CharesnaNo ratings yet
- Graviola Annona Muricata lDocument10 pagesGraviola Annona Muricata lRuben GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Combination of Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Lithium, and Aripiprazole Reduces Oxidative Stress in Brain of Mice With ManiaDocument9 pagesCombination of Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Lithium, and Aripiprazole Reduces Oxidative Stress in Brain of Mice With ManiaIntanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2405844019365946 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S2405844019365946 Mainantonio loraNo ratings yet
- Geriatrics 07 00064 v2Document9 pagesGeriatrics 07 00064 v2dandiokasubantaraNo ratings yet
- Centella 05Document7 pagesCentella 05Uwais AlNo ratings yet
- Red Cabbage (Brassica Oleracea) Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy in RatsDocument7 pagesRed Cabbage (Brassica Oleracea) Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy in Ratsarmash mominNo ratings yet
- Chronic Cadmium Hepatooxidative in Rats: Treatment With Haruan Fish (Channa Striata) ExtractDocument5 pagesChronic Cadmium Hepatooxidative in Rats: Treatment With Haruan Fish (Channa Striata) Extractkirana_patrolinaNo ratings yet
- 456 PDFDocument6 pages456 PDFMary Rose UmayamNo ratings yet
- 9 PDFDocument7 pages9 PDFfaikaNo ratings yet
- Oral Rg1 Supplementation Strengthens Antioxidant Defense System Against Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rat Skeletal MusclesDocument7 pagesOral Rg1 Supplementation Strengthens Antioxidant Defense System Against Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rat Skeletal MusclesLuis Castro XtrmNo ratings yet
- Ijerph 16 00647 v3Document15 pagesIjerph 16 00647 v3claraNo ratings yet
- Effect of Antihipoglycemic Sechium Edule Jacq. Swartz. Etanol Extract On Histopathologic Changes in Hyperglycemic Mus Musculus LDocument8 pagesEffect of Antihipoglycemic Sechium Edule Jacq. Swartz. Etanol Extract On Histopathologic Changes in Hyperglycemic Mus Musculus LAnindita Putri WardaniNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0895398821001069 MainDocument4 pages1 s2.0 S0895398821001069 MainShierly ShafrillaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Purple Sweet Potato Ipomoea Ba 24953e1eDocument8 pagesEffect of Purple Sweet Potato Ipomoea Ba 24953e1e1005 Siti Ainunnisa Lingga WinariNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S175646461930622X MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S175646461930622X MainEli SahirohNo ratings yet
- E Ganistrus Lipid Lowering EffectDocument10 pagesE Ganistrus Lipid Lowering EffectRahayu UtamiNo ratings yet
- Intense and Exhaustive Exercise Induce Oxidative Stress in Skeletal MuscleDocument4 pagesIntense and Exhaustive Exercise Induce Oxidative Stress in Skeletal MuscleRoy WilsonNo ratings yet
- Basil Leaves (Ocimum Sanctum Linn.) Extract Decreases Total Cholesterol Levels in Hypercholesterolemia Sprague Dawley Rats ModelDocument7 pagesBasil Leaves (Ocimum Sanctum Linn.) Extract Decreases Total Cholesterol Levels in Hypercholesterolemia Sprague Dawley Rats ModelMiftahul HudaNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemic and Antioxidant Activities of Balinese Purple Sweet Potato (Ipomoea Batatas L) in Induced-Diabetic RatsDocument6 pagesHypoglycemic and Antioxidant Activities of Balinese Purple Sweet Potato (Ipomoea Batatas L) in Induced-Diabetic RatsAlfira Naya ZakiyahNo ratings yet
- Elderly Diet BackgroundDocument34 pagesElderly Diet BackgroundGUtkarshNo ratings yet
- Ijtk202358 363Document7 pagesIjtk202358 363Priyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant and Lipid Lowering Effects of Elaeocarpus Ganitrus in Cholesterol Fed RabbitsDocument9 pagesAntioxidant and Lipid Lowering Effects of Elaeocarpus Ganitrus in Cholesterol Fed RabbitsKuberBajgainNo ratings yet
- The Alterations of Antioxidant Enzyme Levels in The Blood Serum by Adding Alkaline Water Supplemented With Sodium Ascorbate During Acute Hyperthermic ExposureDocument6 pagesThe Alterations of Antioxidant Enzyme Levels in The Blood Serum by Adding Alkaline Water Supplemented With Sodium Ascorbate During Acute Hyperthermic ExposureValdrina AjetiNo ratings yet
- Mechanistic Role of Epigallocatechin 3 Gallate in Regulation of The Antioxidant Markers in Ethanol Induced Liver Damage in MiceDocument10 pagesMechanistic Role of Epigallocatechin 3 Gallate in Regulation of The Antioxidant Markers in Ethanol Induced Liver Damage in MiceAllan WanderaNo ratings yet
- 2013 Article 1220Document11 pages2013 Article 1220MeLissa AymNo ratings yet
- Pan 2015Document13 pagesPan 2015Fran CiNo ratings yet
- Summary BiokimDocument13 pagesSummary BiokimThurain LeoNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry: Hui-Yin Chen, Gow-Chin YenDocument9 pagesFood Chemistry: Hui-Yin Chen, Gow-Chin YenGREESTYNo ratings yet
- Hypoglicemic EffectDocument7 pagesHypoglicemic EffectErizal Dwi HandokoNo ratings yet
- 1 LipidperoxidationDocument8 pages1 LipidperoxidationAgharid Ali HusseinNo ratings yet
- Effect of The Long-Term Intake of An Egg PDFDocument7 pagesEffect of The Long-Term Intake of An Egg PDFMohammed HussienNo ratings yet
- Buah Asam Gelugur Dibuat TeaDocument7 pagesBuah Asam Gelugur Dibuat TeaabdiNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Ekstrak Rumput Laut (Euchema Sp.) Terhadap Histologi Sel Β Pankreas Pada Rattus Novergicus Galur Wistar Dengan Diabetes Mellitus Yang Di Injeksi Aloksan Kurniati Maya Sari, WdDocument8 pagesPengaruh Ekstrak Rumput Laut (Euchema Sp.) Terhadap Histologi Sel Β Pankreas Pada Rattus Novergicus Galur Wistar Dengan Diabetes Mellitus Yang Di Injeksi Aloksan Kurniati Maya Sari, Wdsri selfiana novita sariNo ratings yet
- 2 PBDocument6 pages2 PBYami ArsyaNo ratings yet
- Research Article Moringa Oleifera in Rats Subjected ToDocument10 pagesResearch Article Moringa Oleifera in Rats Subjected ToYaniNo ratings yet
- Antioxidants Defense Mechanism: December 2018Document37 pagesAntioxidants Defense Mechanism: December 2018NUR KINTAN APRILIANo ratings yet
- Invitro Anti Diabetic ActivityDocument6 pagesInvitro Anti Diabetic ActivityshashidharNo ratings yet
- Edith's SeminarDocument4 pagesEdith's SeminarFredNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant Activities of Aqueous Bitter Kola Garcinia Kola Seed Extract On WisDocument6 pagesAntioxidant Activities of Aqueous Bitter Kola Garcinia Kola Seed Extract On WisLilian EdeniNo ratings yet
- $RHZ3KN3Document39 pages$RHZ3KN3va.tmcbogorNo ratings yet
- Profil Kadar Mda (Malondialdehide) Sebagai Penanda Kerusakan Seluler Akibat Radikal Bebas Pada Tikus Yang Diberikan Air BeroksigenDocument6 pagesProfil Kadar Mda (Malondialdehide) Sebagai Penanda Kerusakan Seluler Akibat Radikal Bebas Pada Tikus Yang Diberikan Air BeroksigenMarta WangsadinataNo ratings yet
- 6BBL0325 2 TheoriesofAgeingRandomDamageDocument10 pages6BBL0325 2 TheoriesofAgeingRandomDamageVaidehi KatariaNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument11 pages1 SMAisah Cory PrasonoNo ratings yet
- Antidiabetic Effect of Potential Indian Medicinal Plants: A Target Specific In-Vitro StudyDocument14 pagesAntidiabetic Effect of Potential Indian Medicinal Plants: A Target Specific In-Vitro StudyRajendra YegnambhatlaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologyonline 1 - (2008)Document10 pagesPharmacologyonline 1 - (2008)kahren wayetNo ratings yet
- Potential Impact of Strawberry Leaves Extract On Neurotoxicity in RatsDocument7 pagesPotential Impact of Strawberry Leaves Extract On Neurotoxicity in RatsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Antifatigue Potential of Loquat Leaf Extract in Physical Stress in C2C12 Myotubes and in Vivo ModelsDocument12 pagesResearch Article: Antifatigue Potential of Loquat Leaf Extract in Physical Stress in C2C12 Myotubes and in Vivo ModelsjljsjoostenNo ratings yet
- PharmacognJ 14 5 469Document8 pagesPharmacognJ 14 5 469fita triastuti /ananda syifa ahmad syamilNo ratings yet
- Vijay EtalDocument6 pagesVijay EtaleditorijmrhsNo ratings yet
- Hasil Penelitian Dari PegaganDocument7 pagesHasil Penelitian Dari PegaganMuhammad YarhamNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Erick PrasetyaDocument14 pagesJurnal Erick PrasetyaEska MeditasiliukaNo ratings yet
- Doctor ZhivagoDocument3 pagesDoctor ZhivagoTaufiq XemoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of IUGR: Traditional Biometry: Elizabeth Platz, MD, and Roger Newman, MDDocument8 pagesDiagnosis of IUGR: Traditional Biometry: Elizabeth Platz, MD, and Roger Newman, MDBella DirkNo ratings yet
- A Little Bit About Shawn KimuliDocument1 pageA Little Bit About Shawn Kimuliapi-26150854No ratings yet
- Disagreeing PolitelylpDocument7 pagesDisagreeing PolitelylpRoseanne IkanNo ratings yet
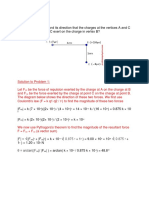
- Problem and Solution Electric FieldDocument10 pagesProblem and Solution Electric FieldSansen Diamante Colipano Jr.No ratings yet
- Project On Recruit Ment SlectionDocument6 pagesProject On Recruit Ment SlectionSunny KhushdilNo ratings yet
- Kneehigh TheaterDocument2 pagesKneehigh Theaterapi-706488422No ratings yet
- Digital Terrain Analysis in A GIS Environment. Concepts and DevelopmentDocument2 pagesDigital Terrain Analysis in A GIS Environment. Concepts and Developmentfox wolfNo ratings yet
- Gelorevoice Throat Lozenges: Batch NumberDocument2 pagesGelorevoice Throat Lozenges: Batch NumberWesam Al-TawilNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 10 Exam 4th QuarterDocument2 pagesMapeh 10 Exam 4th QuarterMaybelyn de los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Resilience To Academic Stress The Key Towards SuccessDocument4 pagesResilience To Academic Stress The Key Towards SuccessEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Cotización Criba 50Document2 pagesCotización Criba 50Grace MartinezNo ratings yet
- Sami BhaiDocument8 pagesSami BhaiNostalgic IlluzionsNo ratings yet
- Sonny Lo vs. KJS Eco-Formwork System Phil, Inc, GR No. 149420 (2003)Document2 pagesSonny Lo vs. KJS Eco-Formwork System Phil, Inc, GR No. 149420 (2003)Je S BeNo ratings yet
- Every Transfer of ImmovableDocument3 pagesEvery Transfer of ImmovableAdan HoodaNo ratings yet
- William - Shakespeare On The Double! Romeo and Juliet (Shakespeare On The Double!) (2006)Document243 pagesWilliam - Shakespeare On The Double! Romeo and Juliet (Shakespeare On The Double!) (2006)GogiGogos100% (1)
- "Behavioral and Experimental Economics": Written Exam For The M.Sc. in Economics 2010-IDocument4 pages"Behavioral and Experimental Economics": Written Exam For The M.Sc. in Economics 2010-ICoxorange94187No ratings yet
- MemoDocument33 pagesMemoNeha GillNo ratings yet
- Public Service RulesDocument9 pagesPublic Service RulesAnonymous uZbDBWsIcu100% (1)
- Statutory Interpretation: Katharine MathesonDocument28 pagesStatutory Interpretation: Katharine MathesonKofi Mc SharpNo ratings yet
- Winners List - Motor Car (ACG) : E-AuctionDocument20 pagesWinners List - Motor Car (ACG) : E-AuctionSameen SaleemNo ratings yet
- TMS 3701Document2 pagesTMS 3701nnshabalala290No ratings yet
- Organization of The Book: Part I: Foundations of Global StrategyDocument20 pagesOrganization of The Book: Part I: Foundations of Global StrategyDonart BerishaNo ratings yet
- Arya PDFDocument26 pagesArya PDFRahmawati JuliaNo ratings yet
- Simon The Sportsman: Activity TypeDocument3 pagesSimon The Sportsman: Activity TypeEkaterina DatsenkoNo ratings yet
- The Lost HeroDocument7 pagesThe Lost HeroSalim Akhtar0% (1)
- Unit 3 Module 1 The Menstrual CycleDocument20 pagesUnit 3 Module 1 The Menstrual CycleMARIANNE SORIANO100% (2)