Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic Cell
Cells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic Cell
Uploaded by
gafir1230Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Science7 q2 Mod4 Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument34 pagesScience7 q2 Mod4 Asexual and Sexual ReproductionRomeo Dela Rosa100% (7)
- Developmental Psychology (PDE 102)Document125 pagesDevelopmental Psychology (PDE 102)Anita Lawal100% (4)
- Mitosis Vs Meiosis PracticeDocument3 pagesMitosis Vs Meiosis Practiceapi-293001217No ratings yet
- 11 - Chapter 1 PDFDocument20 pages11 - Chapter 1 PDFDr Shikha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellshaji1234554No ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- CellDocument6 pagesCellHONEYLYN CASINGNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- Module 3-P. E. CellsDocument4 pagesModule 3-P. E. CellsRylle SimonNo ratings yet
- Class9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesDocument7 pagesClass9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesabhishekNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes EukaryotesDocument4 pagesProkaryotes EukaryotesSayyeda SumaiyahNo ratings yet
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- Cellular Diversity (Lec, 4)Document21 pagesCellular Diversity (Lec, 4)Maryum JavedNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDocument14 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDaniella Pasilbas SabacNo ratings yet
- Biomedical 01Document26 pagesBiomedical 01api-3706483No ratings yet
- CH 1 Notes Cell Basic Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCH 1 Notes Cell Basic Unit of LifetsudheraNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument20 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesKerubin Mamaril67% (3)
- Cell Biology - Unit - 1Document19 pagesCell Biology - Unit - 1shivangipurohitNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesDocument8 pagesCell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesdaddysharkNo ratings yet
- Organelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)Document6 pagesOrganelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)vscolegit shoppeNo ratings yet
- Leture Slides Biol For Engg. NS2001Document75 pagesLeture Slides Biol For Engg. NS2001vikash1221149No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and EukaryoticDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and EukaryoticG- 6 ODL Trisha Mae Clemente100% (1)
- Farmasi 1Document50 pagesFarmasi 1Suci Umniyah RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document4 pagesCell (Biology)Marella SatorreNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument14 pagesCell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediarycasiquinNo ratings yet
- Botany Full PDF EMDocument72 pagesBotany Full PDF EMAbinaya PalaniNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Document2 pagesDepartment of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Chimmy ChangaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles LectureDocument54 pagesCell Organelles LectureAlthea Aubrey AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes & EukaryotesDocument10 pagesProkaryotes & EukaryotesJogie De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Navigation SearchDocument14 pagesCell (Biology) : Navigation Searchsamz95100% (1)
- 1.2 IntroductionDocument8 pages1.2 IntroductionmiftahNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- Cell - Study NotesDocument16 pagesCell - Study NotesrockyajeetNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Basic Cell BiologyDocument116 pagesUnit-I Basic Cell Biologyvishav sharmaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument8 pagesCellsAnchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument45 pagesCELLKimberly Clarisse VegaNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 3Document22 pagesLecturer 3Rao ChandNo ratings yet
- EUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Document2 pagesEUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Alea AicoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsCrocky CookNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument5 pages1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesJosh Miguel BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document14 pagesCell (Biology)gigiuobohoNo ratings yet
- Cells NotesDocument7 pagesCells Notesshinde.sampada1923No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesRahul ManhasNo ratings yet
- G.Bio. AL-Saeeda (18 - 41)Document24 pagesG.Bio. AL-Saeeda (18 - 41)naaaa7733770No ratings yet
- Arsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesArsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleАрсений ВасильченкоNo ratings yet
- 01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFDocument5 pages01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFsonali voraNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellsjodeoiraluis josonNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic&Eukaryotic DIFFERENCESDocument7 pagesProkaryotic&Eukaryotic DIFFERENCESChristian John Sitjar Dumo100% (1)
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument26 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsKirito HatakuNo ratings yet
- 7 - Cell ModelDocument6 pages7 - Cell ModelshailaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellDocument49 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic CellArthe RajarajanNo ratings yet
- CeluarDocument7 pagesCeluarJef PerezNo ratings yet
- Struckture of ProkaryoticDocument5 pagesStruckture of ProkaryoticAuni NaemiNo ratings yet
- Tour of The CellDocument60 pagesTour of The Celladisty sncNo ratings yet
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCell As A Unit of LifeRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Botany InformationDocument19 pagesBotany InformationJana Mohamed Mohamed Asaad Ibrahim AwadNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document57 pagesBio Chapter 2Xue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document3 pagesGeneral Biology 2Sean CaloyloyNo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument4 pagesLevels of OrganizationSwayangdipta TalapatraNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument48 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryotesunifeb128075No ratings yet
- Animal Cells Vs Plant CellsDocument6 pagesAnimal Cells Vs Plant CellsEszterNo ratings yet
- 01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFDocument6 pages01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- CH14 OL SummaryDocument32 pagesCH14 OL Summaryzuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Sba Controlled Test 1Document13 pagesGrade 12 Sba Controlled Test 1aphelelembhele065No ratings yet
- NCERT Solution: Plant KingdomDocument7 pagesNCERT Solution: Plant KingdomJonathan Tolentino MercadoNo ratings yet
- RTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 21 2008Document9 pagesRTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 21 2008iwan93No ratings yet
- CGL Mock in EnglishDocument64 pagesCGL Mock in EnglishViral IndiaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Sex, Gender, and CultureDocument58 pagesBasic Concepts of Sex, Gender, and CultureKipi Waruku BinisutiNo ratings yet
- Biology Genetics LMDocument79 pagesBiology Genetics LMguadie workuNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Biology How Do Organisms Reproduce NotesDocument12 pagesCBSE Class 10 Biology How Do Organisms Reproduce NotesAnonymous rePT5rCrNo ratings yet
- Midterm Study GuideDocument4 pagesMidterm Study GuideAlejandra MartinezNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Genetics TestDocument2 pagesAP Bio Genetics TestHunterNo ratings yet
- FYP PresentationDocument17 pagesFYP PresentationNor AfiliaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument26 pagesReproduction in OrganismsRakesh S. GourNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7MALTI MAHESH VASHISTHNo ratings yet
- Agro-Technology. Thompson, R. Paul. Cambridge, 2011Document260 pagesAgro-Technology. Thompson, R. Paul. Cambridge, 2011Tiago OliveiraNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 BiologyWorksheetsDocument36 pagesCBSE Class 12 BiologyWorksheetsHarshitNo ratings yet
- Mutasi Gonosom ManusiaDocument20 pagesMutasi Gonosom ManusiaMaharRkpNo ratings yet
- Xii Botany Chapters Quick Recap Ppt-1Document66 pagesXii Botany Chapters Quick Recap Ppt-1Varun muttevi. roll no:-60No ratings yet
- Biology F5 Chapter 6 KSSM NotesDocument8 pagesBiology F5 Chapter 6 KSSM NotesTimothy DenisNo ratings yet
- Science Animal PortfolioDocument9 pagesScience Animal PortfolioCrys TalNo ratings yet
- Sexual and Asexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesSexual and Asexual ReproductionDennisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - MutationDocument7 pagesChapter 7 - MutationblaNo ratings yet
- Science LMS For Grade 8Document15 pagesScience LMS For Grade 8Leah BordalloNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10th - CH 9 Heredity and Evolution Science Study RankersDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10th - CH 9 Heredity and Evolution Science Study Rankersp_manjulaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Template 1Document37 pagesThesis Template 1Rene MolinaNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: The Plant KingdomDocument3 pagesSummary Sheets: The Plant KingdomAreeba Inam RaoNo ratings yet
- 17-1 Teachers EditionDocument5 pages17-1 Teachers EditionRamyRamia ElzantNo ratings yet
Cells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic Cell
Cells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic Cell
Uploaded by
gafir1230Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic Cell
Cells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic Cell
Uploaded by
gafir1230Copyright:
Available Formats
Lab.
Animal cell
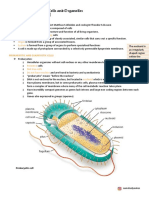
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things
Type of cells
1.Prokaryotic cell
2. Eukaryotic cell
Prokaryotic cells are the cells that do not have a true nucleus and membrane-
bound organelles.
Eukaryotic cells
are much larger and profoundly different from prokaryotic cells, with
a complex interior organization. All cells alive today except bacteria
and archaea are of this new kind. Eukaryotic cells have a system of
interior membranes and membrane-bounded organelles that subdivide
the interior into functional compartments
Compares between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotes Prokaryotes
Type of Cell Always unicellular Unicellular and multi-cellular
Cell size Ranges in size from 0.2 μm – Size ranges from 10 μm – 100
2.0 μm in diameter μm in diameter
Cell wall Usually present; chemically When present, chemically
complex in nature simple in nature
Nucleus Absent. Instead, they have Present
a nucleoid region in the cell
Ribosomes Present. Smaller in size and Present. Comparatively larger
spherical in shape in size and linear in shape
DNA arrangement Circular Linear
Mitochondria Absent Present
Cytoplasm Present, but cell organelles Present, cell organelles
absent present
Endoplasmic reticulum Absent Present
Plasmids Present Very rarely found in eukaryotes
Ribosome Small ribosomes Large ribosomes
Lysosome Lysosomes and centrosomes Lysosomes and centrosomes
are absent are present
Cell division Through binary fission Through mitosis
Flagella The flagella are smaller in size The flagella are larger in size
Reproduction Asexual Both asexual and sexual
Example Bacteria and Archaea Plant and Animal cell
Types of Animal Cells
Animals are multicellular organisms, and as such, their body is comprised of
several cells (about trillions of cells).
Tissue : A group of cells performing a specific function is called. Animal cells
in a tissue may be held through cell junctions, e.g. tight junctions gap junctions,
and desmosomes.The animal body has several types of cells. Examples of
common animal cell types include (skin cells, muscle cells, blood cells, fat
cells nerve cells, sex cells, and stem cells).
a. Skin cells are cells that make up the skin or epithelial tissue.
b. Muscle cells (also called myocytes) are cells that make up muscular
tissue.
c. Blood cells are the cellular elements of the blood. They are the red blood cells
and white blood cells.
d. Fat cells (also called adipocytes) are cells of the adipose tissue
e. Nerve cells (also called neurons) are cells of nervous tissue.
f. Sex cells are cells involved in sexual reproduction. In males, the sperm cell is
the mature and functional sex cell In females, the egg cell is the sex cell.
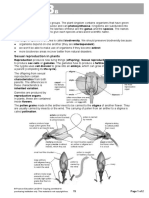
Cell Division
Mitosis
Mitosis is a form of eukaryotic cell division that produces two daughter cells
with the same genetic component as the parent cell. Chromosomes replicated
during the S phase are divided in such a way as to ensure that each daughter cell
.receives a copy of every chromosome.
It is divided into five stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase and
telophase.
Meiosis
Meiosis is the form of eukaryotic cell division that produces haploid sex cells or
gametes (which contain a single copy of each chromosome) from diploid cells
(which contain two copies of each chromosome). The process takes the form of
one DNA replication followed by two successive nuclear and cellular divisions
(Meiosis I and Meiosis II). As in mitosis, meiosis is preceded by a process of
DNA replication that converts each chromosome into two sister chromatids
You might also like
- Science7 q2 Mod4 Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument34 pagesScience7 q2 Mod4 Asexual and Sexual ReproductionRomeo Dela Rosa100% (7)
- Developmental Psychology (PDE 102)Document125 pagesDevelopmental Psychology (PDE 102)Anita Lawal100% (4)
- Mitosis Vs Meiosis PracticeDocument3 pagesMitosis Vs Meiosis Practiceapi-293001217No ratings yet
- 11 - Chapter 1 PDFDocument20 pages11 - Chapter 1 PDFDr Shikha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellshaji1234554No ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- CellDocument6 pagesCellHONEYLYN CASINGNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- Module 3-P. E. CellsDocument4 pagesModule 3-P. E. CellsRylle SimonNo ratings yet
- Class9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesDocument7 pagesClass9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesabhishekNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes EukaryotesDocument4 pagesProkaryotes EukaryotesSayyeda SumaiyahNo ratings yet
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- Cellular Diversity (Lec, 4)Document21 pagesCellular Diversity (Lec, 4)Maryum JavedNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDocument14 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDaniella Pasilbas SabacNo ratings yet
- Biomedical 01Document26 pagesBiomedical 01api-3706483No ratings yet
- CH 1 Notes Cell Basic Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCH 1 Notes Cell Basic Unit of LifetsudheraNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument20 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesKerubin Mamaril67% (3)
- Cell Biology - Unit - 1Document19 pagesCell Biology - Unit - 1shivangipurohitNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesDocument8 pagesCell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesdaddysharkNo ratings yet
- Organelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)Document6 pagesOrganelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)vscolegit shoppeNo ratings yet
- Leture Slides Biol For Engg. NS2001Document75 pagesLeture Slides Biol For Engg. NS2001vikash1221149No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and EukaryoticDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and EukaryoticG- 6 ODL Trisha Mae Clemente100% (1)
- Farmasi 1Document50 pagesFarmasi 1Suci Umniyah RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document4 pagesCell (Biology)Marella SatorreNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument14 pagesCell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediarycasiquinNo ratings yet
- Botany Full PDF EMDocument72 pagesBotany Full PDF EMAbinaya PalaniNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Document2 pagesDepartment of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Chimmy ChangaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles LectureDocument54 pagesCell Organelles LectureAlthea Aubrey AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes & EukaryotesDocument10 pagesProkaryotes & EukaryotesJogie De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Navigation SearchDocument14 pagesCell (Biology) : Navigation Searchsamz95100% (1)
- 1.2 IntroductionDocument8 pages1.2 IntroductionmiftahNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- Cell - Study NotesDocument16 pagesCell - Study NotesrockyajeetNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Basic Cell BiologyDocument116 pagesUnit-I Basic Cell Biologyvishav sharmaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument8 pagesCellsAnchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument45 pagesCELLKimberly Clarisse VegaNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 3Document22 pagesLecturer 3Rao ChandNo ratings yet
- EUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Document2 pagesEUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Alea AicoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsCrocky CookNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument5 pages1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesJosh Miguel BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document14 pagesCell (Biology)gigiuobohoNo ratings yet
- Cells NotesDocument7 pagesCells Notesshinde.sampada1923No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesRahul ManhasNo ratings yet
- G.Bio. AL-Saeeda (18 - 41)Document24 pagesG.Bio. AL-Saeeda (18 - 41)naaaa7733770No ratings yet
- Arsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesArsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleАрсений ВасильченкоNo ratings yet
- 01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFDocument5 pages01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFsonali voraNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellsjodeoiraluis josonNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic&Eukaryotic DIFFERENCESDocument7 pagesProkaryotic&Eukaryotic DIFFERENCESChristian John Sitjar Dumo100% (1)
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument26 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsKirito HatakuNo ratings yet
- 7 - Cell ModelDocument6 pages7 - Cell ModelshailaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellDocument49 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic CellArthe RajarajanNo ratings yet
- CeluarDocument7 pagesCeluarJef PerezNo ratings yet
- Struckture of ProkaryoticDocument5 pagesStruckture of ProkaryoticAuni NaemiNo ratings yet
- Tour of The CellDocument60 pagesTour of The Celladisty sncNo ratings yet
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCell As A Unit of LifeRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Botany InformationDocument19 pagesBotany InformationJana Mohamed Mohamed Asaad Ibrahim AwadNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document57 pagesBio Chapter 2Xue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document3 pagesGeneral Biology 2Sean CaloyloyNo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument4 pagesLevels of OrganizationSwayangdipta TalapatraNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument48 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryotesunifeb128075No ratings yet
- Animal Cells Vs Plant CellsDocument6 pagesAnimal Cells Vs Plant CellsEszterNo ratings yet
- 01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFDocument6 pages01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- CH14 OL SummaryDocument32 pagesCH14 OL Summaryzuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Sba Controlled Test 1Document13 pagesGrade 12 Sba Controlled Test 1aphelelembhele065No ratings yet
- NCERT Solution: Plant KingdomDocument7 pagesNCERT Solution: Plant KingdomJonathan Tolentino MercadoNo ratings yet
- RTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 21 2008Document9 pagesRTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 21 2008iwan93No ratings yet
- CGL Mock in EnglishDocument64 pagesCGL Mock in EnglishViral IndiaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Sex, Gender, and CultureDocument58 pagesBasic Concepts of Sex, Gender, and CultureKipi Waruku BinisutiNo ratings yet
- Biology Genetics LMDocument79 pagesBiology Genetics LMguadie workuNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Biology How Do Organisms Reproduce NotesDocument12 pagesCBSE Class 10 Biology How Do Organisms Reproduce NotesAnonymous rePT5rCrNo ratings yet
- Midterm Study GuideDocument4 pagesMidterm Study GuideAlejandra MartinezNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Genetics TestDocument2 pagesAP Bio Genetics TestHunterNo ratings yet
- FYP PresentationDocument17 pagesFYP PresentationNor AfiliaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument26 pagesReproduction in OrganismsRakesh S. GourNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7MALTI MAHESH VASHISTHNo ratings yet
- Agro-Technology. Thompson, R. Paul. Cambridge, 2011Document260 pagesAgro-Technology. Thompson, R. Paul. Cambridge, 2011Tiago OliveiraNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 BiologyWorksheetsDocument36 pagesCBSE Class 12 BiologyWorksheetsHarshitNo ratings yet
- Mutasi Gonosom ManusiaDocument20 pagesMutasi Gonosom ManusiaMaharRkpNo ratings yet
- Xii Botany Chapters Quick Recap Ppt-1Document66 pagesXii Botany Chapters Quick Recap Ppt-1Varun muttevi. roll no:-60No ratings yet
- Biology F5 Chapter 6 KSSM NotesDocument8 pagesBiology F5 Chapter 6 KSSM NotesTimothy DenisNo ratings yet
- Science Animal PortfolioDocument9 pagesScience Animal PortfolioCrys TalNo ratings yet
- Sexual and Asexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesSexual and Asexual ReproductionDennisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - MutationDocument7 pagesChapter 7 - MutationblaNo ratings yet
- Science LMS For Grade 8Document15 pagesScience LMS For Grade 8Leah BordalloNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10th - CH 9 Heredity and Evolution Science Study RankersDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10th - CH 9 Heredity and Evolution Science Study Rankersp_manjulaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Template 1Document37 pagesThesis Template 1Rene MolinaNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: The Plant KingdomDocument3 pagesSummary Sheets: The Plant KingdomAreeba Inam RaoNo ratings yet
- 17-1 Teachers EditionDocument5 pages17-1 Teachers EditionRamyRamia ElzantNo ratings yet