Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Hole Revision
Science Hole Revision
Uploaded by
s23Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Hole Revision
Science Hole Revision
Uploaded by
s23Copyright:
Available Formats
1.
1 structure and function of the cell
1. What are three functions of all cells?
2. Describe What are the three key points of cell theory?
3. Scientists discover new kinds of life in the deep ocean every year. What does the cell theory tell them must
be true about every new organism?
4. in Argument from Evidence Use evidence to explain how advancements in technology influenced cell theory.
5. Compare and contrast the structure and function of a unicellular organism to that of a multicellular organism.
6. Use Models On a separate piece of paper, draw two circles of the same size. In the first circle, draw a small,
simple picture of something that is big enough to see without magnification. In the second circle, draw it
again under 5x magnification. If it is too big to fit in the circle, draw only the part of the object that fits inside.
7. Hooke and Van Leeuwenhoek made their discoveries around the same time. More than 150 years later,
Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow all made breakthroughs within a few years of each other. What are some
possible reasons for the sudden development of the cell theory after such a long break?
1.2 cell structure
1. Why do cells have so many different organelles and structures?
2. What are the main differences between cell walls and cell membranes?
3. Are there more tissues or more organs in your body? Explain your reasoning.
What are three differences between plant cells and animal cells?
1.3 obtaining and removing materials
1. Why do cells need to maintain homeostasis?
2. How is facilitated diffusion different from diffusion?
3. What would happen to a cell placed in extremely salty water?
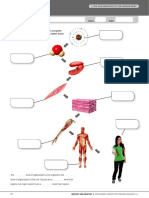
4. Fill in the Venn diagram with the following terms: exocytosis, diffusion, endocytosis, osmosis
5. How could disease-causing bacteria get inside a cell without damaging the cell membrane?
1.4 cell division
1. Why is it important for the cells in your body to go through the cell cycle?
2. How does a plant cell accomplish cytokinesis?
3. When you look at cells under a microscope, how can you recognize cells that are dividing
4. Why does the cell need to replicate its DNA during interphase?
5. Why does the cell need to replicate its DNA during interphase?
6. What would happen to a cell that didn't replicate its DNA before cell division?
7. What happens during cytokinesis? Use a separate piece of paper to sketch and label a diagram of an animal
cell undergoing cytokinesis.
1.5 photosynthesis
1. Where does a plant get the energy necessary to drive the chemical reaction in photosynthesis?
2. Make Generalizations How do you know an organism is a heterotroph? Name three heterotrophs.
3. Why are most plants green?
4. What are the raw materials, or reactants, for Stage 2 of photosynthesis, and where do these materials come
from?
5. Energy and Matter How does chlorophyll help the functioning of chloroplasts?
6. The concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has been gradually increasing for many years. How
might this increase affect photosynthesis?
7. What are the roles of light, carbon dioxide, and water in the production of food and oxygen?
8. Would you expect a plant to produce less oxygen on a sunny day or a cloudy day? Explain.
1.6 cellular respiration
1. Identify Where does cellular respiration take place in the cell?
2. Define What are two examples of useful products made by fermentation?
3. On a separate piece of paper, sketch and label a diagram showing the relationship between photosynthesis
and cellular respiration.
4. Do plants and animals both use cellular respiration?
5. Apply Concepts How do heterotrophs get energy? Explain.
6. A classmate states that both energy and matter can be created during photosynthesis and cellular
respiration. Is this true? Explain.
https://quizlet.com/733495451/elevate-science-course-2-topic-1-flash-cards/
https://quizlet.com/618310988/test?funnelUUID=113a2947-1816-4b06-b1bb-18bb715733e3
You might also like
- Focus Smart Plus Science M3 - Teacher GuideDocument79 pagesFocus Smart Plus Science M3 - Teacher GuideJittipat DaleNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 As v1.0Document19 pagesGeneral Biology 1 As v1.0John Rex100% (4)
- Class 9 Biology Foundation Bharati BhawanDocument175 pagesClass 9 Biology Foundation Bharati Bhawans88% (8)
- Cell TheoryDocument32 pagesCell TheorySumana BasuNo ratings yet
- Bio Adv CC CH 03 - Cell Biology - Answer Keys (10.03.15)Document29 pagesBio Adv CC CH 03 - Cell Biology - Answer Keys (10.03.15)Margie OpayNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell Theory Structure and Function of OrganellesDocument12 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell Theory Structure and Function of OrganellesYkhay ElfanteNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 LM General Biology 1 Module1Document13 pagesGrade 12 LM General Biology 1 Module1altheajade jabanNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Module 1 Week 1Document8 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Module 1 Week 1Melanie OrayNo ratings yet
- Sallim Herniza P. Week 1 General Biology 1 SW1Document8 pagesSallim Herniza P. Week 1 General Biology 1 SW1Nurhaliza KuhutanNo ratings yet
- GR 7 Module 2 For StudentsDocument16 pagesGR 7 Module 2 For StudentsPatricia Mae Rolls SantillanNo ratings yet
- The Basics of BiologyDocument127 pagesThe Basics of BiologyMonica SevillaNo ratings yet
- QTR 2 Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsDocument16 pagesQTR 2 Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsNick Bantolo100% (7)
- Gen Bio 1 - Q1 - W1 - Las 1 PDFDocument14 pagesGen Bio 1 - Q1 - W1 - Las 1 PDFI am stupd100% (1)
- Elsq2 W1&2 - Fabrigas-11abmcharityDocument4 pagesElsq2 W1&2 - Fabrigas-11abmcharityFabrigasBennetNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument7 pagesCellsizabella maryNo ratings yet
- Teaching Specialized Field-DawangDocument19 pagesTeaching Specialized Field-DawangNoven DawangNo ratings yet
- 10 Cell Structure and Function PDFDocument42 pages10 Cell Structure and Function PDFJay Anne RulesNo ratings yet
- APEX Life ReproductionDocument104 pagesAPEX Life Reproductionzerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1Anis PuadahNo ratings yet
- Cell Test Review AnswersDocument4 pagesCell Test Review AnswersMelva GuerraNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 18-19 Cells Reference PPT1Document68 pagesGen Bio 1 18-19 Cells Reference PPT1Ciena GaddiNo ratings yet
- Cell Assignment: .ONE Markers - ONE Liners - ONE Word AnswersDocument8 pagesCell Assignment: .ONE Markers - ONE Liners - ONE Word Answersnaman mahawerNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology & BiochemistryDocument320 pagesCell Biology & BiochemistryVai SanNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Q1 Mod1Document30 pagesBIOLOGY Q1 Mod1Karen Mae CastilloNo ratings yet
- Opening Prayer: Heavenly FatherDocument45 pagesOpening Prayer: Heavenly FatherHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- The Discovery and Binding Mechanisms of Life: Activity 1Document3 pagesThe Discovery and Binding Mechanisms of Life: Activity 1Zaira McHargue50% (2)
- BioEOC PracticekeyDocument21 pagesBioEOC PracticekeyEnerya AbalosNo ratings yet
- 2copy Shs Life Science WorksheetsDocument86 pages2copy Shs Life Science WorksheetsDodong Dingdong100% (1)
- Term Paper On Cell DiversityDocument5 pagesTerm Paper On Cell Diversitydhjiiorif100% (1)
- Bio 100 A Virtual Labs Unit OneDocument7 pagesBio 100 A Virtual Labs Unit OneTammy SmithNo ratings yet
- Bio 100 A Virtual Labs Unit One and TwoDocument14 pagesBio 100 A Virtual Labs Unit One and TwoTammy Smith92% (12)
- Cell BiologyDocument104 pagesCell BiologyADARSH RNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument45 pagesBIOLOGYBenmashour BiaoNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life EditedDocument22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life EditedQuerubin SalesNo ratings yet
- Bio Lo Gym 2 Cell Structure FunctionDocument24 pagesBio Lo Gym 2 Cell Structure FunctionMarmorn ArborshateNo ratings yet
- Science11 - Q1 - Mod1 - GeneralBiology1-Part 1Document38 pagesScience11 - Q1 - Mod1 - GeneralBiology1-Part 1Jordan DingayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Bio Test Study Guide BDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Bio Test Study Guide BRachel FrankenfieldNo ratings yet
- Biology RevisionDocument9 pagesBiology RevisionAINo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument18 pagesCell TheoryAika NaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Self-Learning Packet Preliminaries Module #2-Events in The Cell TheoryDocument9 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Self-Learning Packet Preliminaries Module #2-Events in The Cell TheoryGi GiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)Document24 pagesModule 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)greggcllam619076100% (7)
- Zoology 232 NotesDocument36 pagesZoology 232 NotesKevinNo ratings yet
- 2cells and MicrosDocument5 pages2cells and MicrosyurugachavaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in Biology 1: Quarter 1 Week 1Document10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in Biology 1: Quarter 1 Week 1Ryan NegadNo ratings yet
- Progress Indicators: Learning Objective: To Understand The Structure of Animal and Plant CellsDocument49 pagesProgress Indicators: Learning Objective: To Understand The Structure of Animal and Plant CellsnidhiNo ratings yet
- Module 9 - Weeks 1,2Document15 pagesModule 9 - Weeks 1,2Jomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module1: Postulates of The Cell TheoryDocument12 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module1: Postulates of The Cell TheoryAyessa Karyl Ganir100% (1)
- Cell Bio Chapter 1Document22 pagesCell Bio Chapter 1GuteNo ratings yet
- GED23 (Life Science) PDFDocument25 pagesGED23 (Life Science) PDFtahireslNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Semester I Final Exam Study Guide - Bio23Document4 pagesKami Export - Semester I Final Exam Study Guide - Bio23Ryan FungNo ratings yet
- TB3BIOANDGEOUND1Document10 pagesTB3BIOANDGEOUND1Núria Real TortosaNo ratings yet
- Science7 q2 Week5 Refined FinalDocument13 pagesScience7 q2 Week5 Refined FinalRonalynAlonsabeBernadasNo ratings yet
- Module BIO IIDocument7 pagesModule BIO IIBrandon DacanayNo ratings yet
- 2015 Biology Eoc Study GuideDocument99 pages2015 Biology Eoc Study GuidedkissamNo ratings yet
- In 1665Document6 pagesIn 1665Loraine Andrei DeLeonNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 Cell Theory October 5,2020 Nick Andrew v. BoholDocument4 pagesActivity No. 1 Cell Theory October 5,2020 Nick Andrew v. BoholNick Andrew boholNo ratings yet
- Bio Module 2Document9 pagesBio Module 2Cecile MusaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Topic 1 Past Paper QuestionsDocument9 pagesBIOLOGY Topic 1 Past Paper QuestionsLoraine NNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document9 pagesModule 1Ivan PaulinoNo ratings yet
- High School Biology: Comprehensive Content for Cell & Molecular BiologyFrom EverandHigh School Biology: Comprehensive Content for Cell & Molecular BiologyNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Lab 9Document35 pagesAP Biology Lab 9WutWut0% (1)
- Biomolecules WorksheetDocument4 pagesBiomolecules WorksheetJana ArafaNo ratings yet
- Medical Technology in The Philippines: Problems, Resources, and NeedsDocument24 pagesMedical Technology in The Philippines: Problems, Resources, and NeedsJr BalagtasNo ratings yet
- Zoology (Book)Document26 pagesZoology (Book)sme olaplNo ratings yet
- Micróbios e PinturasDocument7 pagesMicróbios e PinturasElvis P. SalesNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Purine & Pyrimidine NucleotidesDocument38 pagesMetabolism of Purine & Pyrimidine NucleotidesShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Immunoprophylaxix (Dr. Ankita Garg)Document21 pagesImmunoprophylaxix (Dr. Ankita Garg)Intan PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Lithothamnion MuelleriDocument21 pagesLithothamnion MuelleriSophia SousaNo ratings yet
- HEMATURIADocument9 pagesHEMATURIAAndreina AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and Binomial NomenclatureDocument3 pagesTaxonomy and Binomial NomenclatureMa. Cassandra A. RamosNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/22 May/June 2019Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/22 May/June 2019Nyasha MtemeriNo ratings yet
- 2015 Issue 2Document80 pages2015 Issue 2Fareesha KhanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and Variations: By: Dr. Anand ManiDocument113 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and Variations: By: Dr. Anand ManiIndu YadavNo ratings yet
- h20 01 Breadth in BiologyDocument36 pagesh20 01 Breadth in Biologyirene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Proteins, Biology For Engineers DRPDocument6 pages1.3 Proteins, Biology For Engineers DRPShreya shresthNo ratings yet
- Managing GMP, HSE and HTA Regulations in Multiproduct ATMP ManufacturingDocument28 pagesManaging GMP, HSE and HTA Regulations in Multiproduct ATMP Manufacturingalnzeer omerNo ratings yet
- 3 PracticalDocument47 pages3 PracticalT NNo ratings yet
- PolyketideDocument49 pagesPolyketidearisadennis2000No ratings yet
- Anxiety and Depression in Staff of Mental Units - The Role of BurnoutDocument307 pagesAnxiety and Depression in Staff of Mental Units - The Role of BurnoutOsamaNo ratings yet
- Biology Experiment 3 Study of Flowering PlantDocument9 pagesBiology Experiment 3 Study of Flowering PlantanuvaNo ratings yet
- Parasitic Diseases Low Resolution 7th EditDocument616 pagesParasitic Diseases Low Resolution 7th EditLusungu S. Lupenza100% (1)
- NHL Diffuse PatientDocument58 pagesNHL Diffuse PatientHoang DoanNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin & Derivatives: DR. S. Irfan RazaDocument30 pagesHemoglobin & Derivatives: DR. S. Irfan RazaSyed Irfan Raza100% (1)
- Biomath FinalDocument25 pagesBiomath FinalJomar RabajanteNo ratings yet
- Childhood MedulloblastmaDocument17 pagesChildhood MedulloblastmaIrenaNo ratings yet
- PMFIAS NCERT Biology 6 12 Compilation PFDocument224 pagesPMFIAS NCERT Biology 6 12 Compilation PFAmit DixitNo ratings yet
- Botony II (EM) BLM 21-22Document62 pagesBotony II (EM) BLM 21-22Nishith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Octocorals: Marine Ecology Progress Series December 2011Document20 pagesSexual Reproduction in Octocorals: Marine Ecology Progress Series December 2011Emmanuel MejiasNo ratings yet
- 1-1 BQ Problemas Primer Parcial Lehninger EstudiantesDocument5 pages1-1 BQ Problemas Primer Parcial Lehninger EstudiantesBerenice UlloaNo ratings yet