Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 5-14 Notes 2
Week 5-14 Notes 2
Uploaded by
navkkirangillCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Resting Membrane, Graded, Action Potentials AtfDocument4 pagesResting Membrane, Graded, Action Potentials AtfdaphneNo ratings yet
- Applied Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics, 5th EditionDocument1 pageApplied Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics, 5th Editionbencleese14% (7)
- Pad HPNDocument137 pagesPad HPNpmm21d229No ratings yet
- Cvs DrugsDocument106 pagesCvs DrugsIkoona ivanNo ratings yet
- 1CVS-2. ACEIs 1435 PDFDocument19 pages1CVS-2. ACEIs 1435 PDFMuath AlqarniNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Hypertension: Dr. R. PilvinieneDocument33 pagesDrugs Used in Hypertension: Dr. R. PilvinieneNewteNo ratings yet
- 2 5377779365079685362Document23 pages2 5377779365079685362ahmaNo ratings yet
- ReveweDocument119 pagesRevewehikmatullah rahimiNo ratings yet
- Cardio DrugsDocument68 pagesCardio DrugsIconMaicoNo ratings yet
- Part 3: Pharmacology Antihypertensives: SympatholyticsDocument13 pagesPart 3: Pharmacology Antihypertensives: SympatholyticsJovelyn BandiolaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDocument3 pagesPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تNo ratings yet
- Cronic Heart FailureDocument37 pagesCronic Heart FailureHanif RobbanizerNo ratings yet
- Treatment of CHF: Therapeutic UsesDocument2 pagesTreatment of CHF: Therapeutic UsesAsma AlfaouriNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyAnne Marie BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- 09 Treatment for Hypertension 1-12-2021 配布用Document17 pages09 Treatment for Hypertension 1-12-2021 配布用Lan NguyenNo ratings yet
- ANTIHYPERTENSIVEDocument32 pagesANTIHYPERTENSIVEKeziah TampusNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemDocument21 pagesDrugs Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemAudrey Beatrice ReyesNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs RTDocument41 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs RTMaherNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY Drugs Used in HypertensionDocument11 pagesSUMMARY Drugs Used in HypertensionPAULINE ANGELI DIEGONo ratings yet
- Terapi Farmakologi Gagal Jantung - Sept - 2020Document58 pagesTerapi Farmakologi Gagal Jantung - Sept - 2020FAUZAN ILHAM PRATAMANo ratings yet
- Clonidine: Imidazoline Derivative, PartialDocument2 pagesClonidine: Imidazoline Derivative, PartialAsma AlfaouriNo ratings yet
- Drugs SummaryDocument23 pagesDrugs Summaryapi-3832811100% (1)
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument56 pagesAntihypertensive Drugssultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Penatalaksanaan Penyulit Gagal JantungDocument17 pagesPenatalaksanaan Penyulit Gagal JantungarumNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibitors Simple NursingDocument2 pagesAce Inhibitors Simple NursingMM J30No ratings yet
- Antihypertensive - ABCDDocument5 pagesAntihypertensive - ABCDTingCheung100% (1)
- AntihipertensiDocument39 pagesAntihipertensiHarri HardiNo ratings yet
- Anti HypertensivesDocument23 pagesAnti HypertensivesLeena AlateeqNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Anti Hypertensive Agents (For BPT Students)Document17 pagesPharmacology of Anti Hypertensive Agents (For BPT Students)Dr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- Pharma Unit 1-2 Anti - Adrenergic DrugsDocument21 pagesPharma Unit 1-2 Anti - Adrenergic DrugsMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs1Document36 pagesCardiovascular Drugs1Ruchika BajajNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs: DR. DR Umi Kalssum MkesDocument58 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs: DR. DR Umi Kalssum MkesadilaalifnugrahaeniNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular DisordersDocument4 pagesPeripheral Vascular DisordersDawnmurph Dharlene Wag-eNo ratings yet
- AntihypertensivesDocument32 pagesAntihypertensivesJianne CaloNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs.Document35 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs.Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- 2.Ghafez-Adrenergic Antagonists 2023Document29 pages2.Ghafez-Adrenergic Antagonists 2023yasmin.rahmany03No ratings yet
- Anti Hypertension: Dr. Putrya Hawa, M.BiomedDocument24 pagesAnti Hypertension: Dr. Putrya Hawa, M.BiomedputryaNo ratings yet
- AkshayDocument35 pagesAkshaySheryl VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Chronic Heart FailureDocument2 pagesTreatment of Chronic Heart FailureShannon RamsumairNo ratings yet
- Cardio ReviewerDocument21 pagesCardio ReviewerCreciabullecerNo ratings yet
- CVD and HTNDocument60 pagesCVD and HTNZsazsa100% (1)
- Penanganan Krisis HipertensiDocument36 pagesPenanganan Krisis Hipertensisuho exoNo ratings yet
- 4 Adrenergic and Anti-Adrenergic DrugsDocument51 pages4 Adrenergic and Anti-Adrenergic DrugsLoai Mohammed IssaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Agents in Heart Failure: Ayman Khdair, Ph.D. Wayne State University, Michigan, USADocument41 pagesPharmacologic Agents in Heart Failure: Ayman Khdair, Ph.D. Wayne State University, Michigan, USAJalil HaddadinNo ratings yet
- Antihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DDocument28 pagesAntihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Management of Heart Failure: DR Sindwa KanyimbaDocument29 pagesDrugs Used in The Management of Heart Failure: DR Sindwa Kanyimbaedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For CHF & Angina PDFDocument15 pagesDrugs For CHF & Angina PDFAbdullah ElsayedNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument85 pagesHypertensionmelkamu AssefaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Anti HypertensionDocument40 pagesLecture 6 Anti HypertensionMNGS StudioNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument43 pagesHypertensionAbin PNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument29 pagesHypertensionkadir.dallenmae.d.bcsiNo ratings yet
- HPNDocument32 pagesHPNkaren GoNo ratings yet
- Pharma Unit 8 - Anti - Adrenergic Drugs - 2 of 2Document21 pagesPharma Unit 8 - Anti - Adrenergic Drugs - 2 of 2MIbrahimNo ratings yet
- PP Drug Classes and IndicationsDocument67 pagesPP Drug Classes and IndicationspninthemakinNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemDocument70 pagesDrugs Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemRayne Bonifacio100% (2)
- Cardiotonics - DR Anoosha BhandarkarDocument60 pagesCardiotonics - DR Anoosha BhandarkaranooshabhandarkarNo ratings yet
- HYPERTENSION Priya FINAL PPT 2Document14 pagesHYPERTENSION Priya FINAL PPT 2Priya Tiwari100% (1)
- Cardiac Medications:: What's With The Mixing & Matching?Document97 pagesCardiac Medications:: What's With The Mixing & Matching?TinaHoNo ratings yet
- Antianginal DrugsDocument19 pagesAntianginal DrugsAnusha ZubairNo ratings yet
- DysrhythmiasDocument67 pagesDysrhythmiashhh hhhNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Cardiovascular and Renal Systems Ed 6-20-22Document117 pagesWeek 4 Cardiovascular and Renal Systems Ed 6-20-22sultanmsajidmNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Acute Management of Open Fractures Proposal of A New Multidisciplinary AlgorithmDocument5 pagesAcute Management of Open Fractures Proposal of A New Multidisciplinary AlgorithmLuigi Paolo Zapata DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Microspheresdocx 2021 03 25 16 55Document6 pagesMicrospheresdocx 2021 03 25 16 55Ravirajsinh GohilNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument1 pageGeneric NameKaryl Marie Rodas JaminNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Gastroretentive Drug Delivery SystemDocument8 pagesThesis On Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systemreneejonesanchorage100% (2)
- Computer in Community Pharmacy HDocument13 pagesComputer in Community Pharmacy HMayan Khan100% (2)
- Course Structure Format: Year: 1 Semester: IDocument17 pagesCourse Structure Format: Year: 1 Semester: IVaishali PathakNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases of The Skin and EyeDocument37 pagesCommunicable Diseases of The Skin and Eyemonica claritoNo ratings yet
- Clin Tox Lab 1Document4 pagesClin Tox Lab 1Czariana Cassidy MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Route of AdministrationDocument17 pagesRoute of AdministrationFatema OsamaNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Concept MapDocument1 pageSchizophrenia Concept MapAlma Janella TOSINO100% (2)
- Mood and SuicideDocument36 pagesMood and SuicideCaroline Alagadmo100% (1)
- Visvesvaraya Technological University: Jnana Sangama, Belagavi-590018Document25 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University: Jnana Sangama, Belagavi-590018Kevin Raj SNo ratings yet
- Update Stok 02 Juni 2023Document27 pagesUpdate Stok 02 Juni 2023Riyanto DwNo ratings yet
- Prep 22-27Document2 pagesPrep 22-27soubi_yodi100% (1)
- Glaucoma in Dog A Case Report-Dr. Jibachha SahDocument8 pagesGlaucoma in Dog A Case Report-Dr. Jibachha SahDr.Jibachha Sah,Vet.physician,author, & motivatorNo ratings yet
- Solution 1Document5 pagesSolution 1Amruta MahajanNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Drug WithdrawalDocument13 pagesPsychotropic Drug WithdrawalViviani ReisNo ratings yet
- AtracuriumDocument1 pageAtracuriumMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- S. B. No. 2573: Second Regular SessionDocument13 pagesS. B. No. 2573: Second Regular SessionmkoguicoNo ratings yet
- Routes of Drug Administration KsTUDocument23 pagesRoutes of Drug Administration KsTUadjei philemonNo ratings yet
- Proceedings ICoMP Vol1Document377 pagesProceedings ICoMP Vol1Anisa SafutriNo ratings yet
- Aerosol Delivery DevicesDocument68 pagesAerosol Delivery DevicesINGRID YISEL IDROBO AGREDONo ratings yet
- BUD AppendixDocument48 pagesBUD AppendixOrnielNo ratings yet
- E Library For PharmacyDocument27 pagesE Library For PharmacyMuhammad Ali0% (1)
- Chemotherapy For Gynecologic CancerDocument69 pagesChemotherapy For Gynecologic CancerBEREKET100% (1)
- Ampi+Salbactum Amo+ Clavulanate Piper+Tazobactam: ST ST ND ND ND ND TH ST ND TH TH TH RD RD RD TH THDocument1 pageAmpi+Salbactum Amo+ Clavulanate Piper+Tazobactam: ST ST ND ND ND ND TH ST ND TH TH TH RD RD RD TH THAnnieNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For Postpartum MothersDocument5 pagesDrug Study For Postpartum MothersnnicakoNo ratings yet
- Acne DissertationDocument6 pagesAcne DissertationPaySomeoneToDoMyPaperUK100% (1)
Week 5-14 Notes 2
Week 5-14 Notes 2
Uploaded by
navkkirangillOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 5-14 Notes 2
Week 5-14 Notes 2
Uploaded by
navkkirangillCopyright:
Available Formats
Cont..
Potassium chloride
Indication for use
• Treatment or prevention of hypokalemia
α1- adrenergic antagonists: Doxazosin
• treatment of mild alkalosis
Indications for use
Mechanism of action
• hypertension, urinary outflow obstruction, symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia
• Mimics endogenous potassium ions
Desired effects
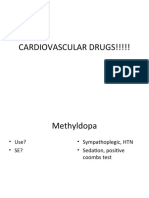
Mechanisms of Action
• Maintain potassium balance
• Acts by selectively blocking the alpha 1-adrenergic receptors in the vascular smooth muscle
Adverse effects
• Nausea and vomiting, hyperkalaemia
• Dilates peripheral blood vessels, ↓ peripheral resistance, ↓ BP -
Desired effects
• Decreased BP
Calcium Channel Blockers
• Exert a number of beneficial effects on the heart and Adverse effects
blood vessels by blocking calcium ion channels • Dizziness, weakness, drowsiness, headache, orthostatic hypotension, palpitations, chest pain, edema, dysrhythmias, nausea and vomit
• Widely used in the treatment of hypertension and other diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain
cardiovascular diseases
Nursing implications
Calcium channel blockers: Nifedipine • Orthostatic hypotension
Indications for use β1- receptors in heart muscle cells
- Hypertension, angina, migraine prophylaxis adrenergic blockers (“olols”): Metoprolol
Indications for use
Mechanism of action
• Hypertension, angina, MI
• Acts by selectively blocking calcium channels in
myocardial and vascular smooth muscle, including that in
Mechanisms of Action
the coronary arteries
• Acts by selectively blocking the beta1 adrenergic β1- receptors in heart muscle cells
• ↓oxygenusebyheart,↑CO,↓BP
• ↓ BP, ↓ myocardial O2 demand, ↓ elevated renin plasma levels, -
receptor
Desired effect
• Decreased BP in hypertension
Desired effects
• Decreased BP, heart rate
Adverse effects
• Headache, dizziness, drowsiness, lightheadedness,
Adverse effects
dysrhythmias, nausea, vomiting, hypotension, tachycardia,
• Insomnia, dizziness, headaches, HF, palpitations, dysrhythmias, cardiac arrest, hypotension, bradycardia,
palpitations, diarrhea, constipation, nocturia, polyuria
pulmonary/peripheral edema, chest pain, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, constipation hiccups,
bronchospasm, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia purpura
Nursing implications
• grapefruit juice, ECG, vital signs (BP & HR)
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers
• blocks the renin - angiotensin aldosterone syndrome to prevent the intense vasoconstriction caused by angiotensin 2
• Decrease blood volume which enhances their antihypertensive effect
ACE inhibitors (“prils”): Enalapril
Indications for use
• Hypertension, HF, left ventricular dysfunction
wout
convert
Mechanisms of Action
• Inhibits angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) Prevents conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II resulting in dilation of
arterial and venous vessels Angiotensin II strong vasoconstrictor
/
2
Desired effects
-
• Decreased BP in hypertension
1
Adverse effects
• Dizziness, headache, nausea and vomiting, dry cough, diarrhea, hypotension, chest pain, tachycardia, dysrhythmias, syncope, angina,
orthostatic hypotension, tinnitus, proteinuria, agranulocytosis, neutropenia, ↓ Na+ and ↑ K+ and ↑ Cr+
·
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs): Losartan -
S
Indications for use
• Hypertension, patients who cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors ARB BLOCKS
bind -2
Mechanism of Action
• Selectively blocks the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor found in tissues
Blocks the vasoconstricting and aldosterone- secreting effects of angiotensin II
of
Desired effects
• Decreased BP
Adverse effects
• Dizziness, insomnia, headache, hypotension, diarrhea, dyspepsia, constipation, dry mouth, thrombocytopenia angioedema,
cough, hyperkalemia, hypoglycemia
You might also like
- Resting Membrane, Graded, Action Potentials AtfDocument4 pagesResting Membrane, Graded, Action Potentials AtfdaphneNo ratings yet
- Applied Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics, 5th EditionDocument1 pageApplied Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics, 5th Editionbencleese14% (7)
- Pad HPNDocument137 pagesPad HPNpmm21d229No ratings yet
- Cvs DrugsDocument106 pagesCvs DrugsIkoona ivanNo ratings yet
- 1CVS-2. ACEIs 1435 PDFDocument19 pages1CVS-2. ACEIs 1435 PDFMuath AlqarniNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Hypertension: Dr. R. PilvinieneDocument33 pagesDrugs Used in Hypertension: Dr. R. PilvinieneNewteNo ratings yet
- 2 5377779365079685362Document23 pages2 5377779365079685362ahmaNo ratings yet
- ReveweDocument119 pagesRevewehikmatullah rahimiNo ratings yet
- Cardio DrugsDocument68 pagesCardio DrugsIconMaicoNo ratings yet
- Part 3: Pharmacology Antihypertensives: SympatholyticsDocument13 pagesPart 3: Pharmacology Antihypertensives: SympatholyticsJovelyn BandiolaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDocument3 pagesPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تNo ratings yet
- Cronic Heart FailureDocument37 pagesCronic Heart FailureHanif RobbanizerNo ratings yet
- Treatment of CHF: Therapeutic UsesDocument2 pagesTreatment of CHF: Therapeutic UsesAsma AlfaouriNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyAnne Marie BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- 09 Treatment for Hypertension 1-12-2021 配布用Document17 pages09 Treatment for Hypertension 1-12-2021 配布用Lan NguyenNo ratings yet
- ANTIHYPERTENSIVEDocument32 pagesANTIHYPERTENSIVEKeziah TampusNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemDocument21 pagesDrugs Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemAudrey Beatrice ReyesNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs RTDocument41 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs RTMaherNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY Drugs Used in HypertensionDocument11 pagesSUMMARY Drugs Used in HypertensionPAULINE ANGELI DIEGONo ratings yet
- Terapi Farmakologi Gagal Jantung - Sept - 2020Document58 pagesTerapi Farmakologi Gagal Jantung - Sept - 2020FAUZAN ILHAM PRATAMANo ratings yet
- Clonidine: Imidazoline Derivative, PartialDocument2 pagesClonidine: Imidazoline Derivative, PartialAsma AlfaouriNo ratings yet
- Drugs SummaryDocument23 pagesDrugs Summaryapi-3832811100% (1)
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument56 pagesAntihypertensive Drugssultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Penatalaksanaan Penyulit Gagal JantungDocument17 pagesPenatalaksanaan Penyulit Gagal JantungarumNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibitors Simple NursingDocument2 pagesAce Inhibitors Simple NursingMM J30No ratings yet
- Antihypertensive - ABCDDocument5 pagesAntihypertensive - ABCDTingCheung100% (1)
- AntihipertensiDocument39 pagesAntihipertensiHarri HardiNo ratings yet
- Anti HypertensivesDocument23 pagesAnti HypertensivesLeena AlateeqNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Anti Hypertensive Agents (For BPT Students)Document17 pagesPharmacology of Anti Hypertensive Agents (For BPT Students)Dr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- Pharma Unit 1-2 Anti - Adrenergic DrugsDocument21 pagesPharma Unit 1-2 Anti - Adrenergic DrugsMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs1Document36 pagesCardiovascular Drugs1Ruchika BajajNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs: DR. DR Umi Kalssum MkesDocument58 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs: DR. DR Umi Kalssum MkesadilaalifnugrahaeniNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular DisordersDocument4 pagesPeripheral Vascular DisordersDawnmurph Dharlene Wag-eNo ratings yet
- AntihypertensivesDocument32 pagesAntihypertensivesJianne CaloNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs.Document35 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs.Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- 2.Ghafez-Adrenergic Antagonists 2023Document29 pages2.Ghafez-Adrenergic Antagonists 2023yasmin.rahmany03No ratings yet
- Anti Hypertension: Dr. Putrya Hawa, M.BiomedDocument24 pagesAnti Hypertension: Dr. Putrya Hawa, M.BiomedputryaNo ratings yet
- AkshayDocument35 pagesAkshaySheryl VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Chronic Heart FailureDocument2 pagesTreatment of Chronic Heart FailureShannon RamsumairNo ratings yet
- Cardio ReviewerDocument21 pagesCardio ReviewerCreciabullecerNo ratings yet
- CVD and HTNDocument60 pagesCVD and HTNZsazsa100% (1)
- Penanganan Krisis HipertensiDocument36 pagesPenanganan Krisis Hipertensisuho exoNo ratings yet
- 4 Adrenergic and Anti-Adrenergic DrugsDocument51 pages4 Adrenergic and Anti-Adrenergic DrugsLoai Mohammed IssaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Agents in Heart Failure: Ayman Khdair, Ph.D. Wayne State University, Michigan, USADocument41 pagesPharmacologic Agents in Heart Failure: Ayman Khdair, Ph.D. Wayne State University, Michigan, USAJalil HaddadinNo ratings yet
- Antihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DDocument28 pagesAntihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Management of Heart Failure: DR Sindwa KanyimbaDocument29 pagesDrugs Used in The Management of Heart Failure: DR Sindwa Kanyimbaedward kaumbaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For CHF & Angina PDFDocument15 pagesDrugs For CHF & Angina PDFAbdullah ElsayedNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument85 pagesHypertensionmelkamu AssefaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Anti HypertensionDocument40 pagesLecture 6 Anti HypertensionMNGS StudioNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument43 pagesHypertensionAbin PNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument29 pagesHypertensionkadir.dallenmae.d.bcsiNo ratings yet
- HPNDocument32 pagesHPNkaren GoNo ratings yet
- Pharma Unit 8 - Anti - Adrenergic Drugs - 2 of 2Document21 pagesPharma Unit 8 - Anti - Adrenergic Drugs - 2 of 2MIbrahimNo ratings yet
- PP Drug Classes and IndicationsDocument67 pagesPP Drug Classes and IndicationspninthemakinNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemDocument70 pagesDrugs Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemRayne Bonifacio100% (2)
- Cardiotonics - DR Anoosha BhandarkarDocument60 pagesCardiotonics - DR Anoosha BhandarkaranooshabhandarkarNo ratings yet
- HYPERTENSION Priya FINAL PPT 2Document14 pagesHYPERTENSION Priya FINAL PPT 2Priya Tiwari100% (1)
- Cardiac Medications:: What's With The Mixing & Matching?Document97 pagesCardiac Medications:: What's With The Mixing & Matching?TinaHoNo ratings yet
- Antianginal DrugsDocument19 pagesAntianginal DrugsAnusha ZubairNo ratings yet
- DysrhythmiasDocument67 pagesDysrhythmiashhh hhhNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Cardiovascular and Renal Systems Ed 6-20-22Document117 pagesWeek 4 Cardiovascular and Renal Systems Ed 6-20-22sultanmsajidmNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Acute Management of Open Fractures Proposal of A New Multidisciplinary AlgorithmDocument5 pagesAcute Management of Open Fractures Proposal of A New Multidisciplinary AlgorithmLuigi Paolo Zapata DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Microspheresdocx 2021 03 25 16 55Document6 pagesMicrospheresdocx 2021 03 25 16 55Ravirajsinh GohilNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument1 pageGeneric NameKaryl Marie Rodas JaminNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Gastroretentive Drug Delivery SystemDocument8 pagesThesis On Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systemreneejonesanchorage100% (2)
- Computer in Community Pharmacy HDocument13 pagesComputer in Community Pharmacy HMayan Khan100% (2)
- Course Structure Format: Year: 1 Semester: IDocument17 pagesCourse Structure Format: Year: 1 Semester: IVaishali PathakNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases of The Skin and EyeDocument37 pagesCommunicable Diseases of The Skin and Eyemonica claritoNo ratings yet
- Clin Tox Lab 1Document4 pagesClin Tox Lab 1Czariana Cassidy MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Route of AdministrationDocument17 pagesRoute of AdministrationFatema OsamaNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Concept MapDocument1 pageSchizophrenia Concept MapAlma Janella TOSINO100% (2)
- Mood and SuicideDocument36 pagesMood and SuicideCaroline Alagadmo100% (1)
- Visvesvaraya Technological University: Jnana Sangama, Belagavi-590018Document25 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University: Jnana Sangama, Belagavi-590018Kevin Raj SNo ratings yet
- Update Stok 02 Juni 2023Document27 pagesUpdate Stok 02 Juni 2023Riyanto DwNo ratings yet
- Prep 22-27Document2 pagesPrep 22-27soubi_yodi100% (1)
- Glaucoma in Dog A Case Report-Dr. Jibachha SahDocument8 pagesGlaucoma in Dog A Case Report-Dr. Jibachha SahDr.Jibachha Sah,Vet.physician,author, & motivatorNo ratings yet
- Solution 1Document5 pagesSolution 1Amruta MahajanNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Drug WithdrawalDocument13 pagesPsychotropic Drug WithdrawalViviani ReisNo ratings yet
- AtracuriumDocument1 pageAtracuriumMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- S. B. No. 2573: Second Regular SessionDocument13 pagesS. B. No. 2573: Second Regular SessionmkoguicoNo ratings yet
- Routes of Drug Administration KsTUDocument23 pagesRoutes of Drug Administration KsTUadjei philemonNo ratings yet
- Proceedings ICoMP Vol1Document377 pagesProceedings ICoMP Vol1Anisa SafutriNo ratings yet
- Aerosol Delivery DevicesDocument68 pagesAerosol Delivery DevicesINGRID YISEL IDROBO AGREDONo ratings yet
- BUD AppendixDocument48 pagesBUD AppendixOrnielNo ratings yet
- E Library For PharmacyDocument27 pagesE Library For PharmacyMuhammad Ali0% (1)
- Chemotherapy For Gynecologic CancerDocument69 pagesChemotherapy For Gynecologic CancerBEREKET100% (1)
- Ampi+Salbactum Amo+ Clavulanate Piper+Tazobactam: ST ST ND ND ND ND TH ST ND TH TH TH RD RD RD TH THDocument1 pageAmpi+Salbactum Amo+ Clavulanate Piper+Tazobactam: ST ST ND ND ND ND TH ST ND TH TH TH RD RD RD TH THAnnieNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For Postpartum MothersDocument5 pagesDrug Study For Postpartum MothersnnicakoNo ratings yet
- Acne DissertationDocument6 pagesAcne DissertationPaySomeoneToDoMyPaperUK100% (1)