Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scenario For DMIS
Scenario For DMIS
Uploaded by
Cleofe PavoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Undercover by John Bevere TagalogDocument5 pagesUndercover by John Bevere TagalogAngela Bainca Amper86% (21)
- Affirming Diversity Ch. 1Document39 pagesAffirming Diversity Ch. 1Stephanie Abraham83% (6)
- Bennett - Turning Frogs Into InterculturalistsDocument10 pagesBennett - Turning Frogs Into InterculturalistscamelslayerNo ratings yet
- Croak by Gina Damico ExcerptDocument29 pagesCroak by Gina Damico ExcerptHoughton Mifflin Harcourt0% (1)
- General and Specific ObjectivesDocument8 pagesGeneral and Specific ObjectivesBea Simagala95% (21)
- Kenneth Clark - Alternative Public SchoolsDocument15 pagesKenneth Clark - Alternative Public SchoolsChris StewartNo ratings yet
- Elearning in Aviation SuzanneDocument35 pagesElearning in Aviation SuzannejuanNo ratings yet
- Thesis PaperDocument12 pagesThesis Paperapi-711579758No ratings yet
- Diversity and Excellence in Higher Education: Is There A Con Ict?Document19 pagesDiversity and Excellence in Higher Education: Is There A Con Ict?Renan SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Personal IdentityDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Personal IdentityBoby Kurnia DitamaNo ratings yet
- Deconstructing Power Privilege and SilenDocument18 pagesDeconstructing Power Privilege and SilenPj InudomNo ratings yet
- DSJL EssayDocument6 pagesDSJL Essayapi-357321063No ratings yet
- 2 LectureDocument23 pages2 LectureAkbibi YazgeldiyevaNo ratings yet
- DiversityDocument81 pagesDiversityNanthiniNo ratings yet
- Eth305v 02 Mark098100Document11 pagesEth305v 02 Mark098100Anonymous lwUVg0100% (2)
- Ed 258 - w10 AssignmentDocument7 pagesEd 258 - w10 Assignmentapi-614812254No ratings yet
- Gamage 2009Document22 pagesGamage 2009Jersey FreshNo ratings yet
- DEANE 2015 Difference and School UniformsDocument10 pagesDEANE 2015 Difference and School Uniformssibo kanoNo ratings yet
- Critical Theory and Pedagogy GROUP 3Document6 pagesCritical Theory and Pedagogy GROUP 3josephmehr90No ratings yet
- Handout 1 - Racism Is Still Rife in South AfricaDocument2 pagesHandout 1 - Racism Is Still Rife in South AfricaandobandofilifandoNo ratings yet
- Educ606 Diversity EssayDocument7 pagesEduc606 Diversity Essayapi-578092724No ratings yet
- Kumashiro, K. Toward A Theory of Anti-Oppressive Education.Document29 pagesKumashiro, K. Toward A Theory of Anti-Oppressive Education.FABIOLA RAMIREZ100% (1)
- Critical Pedagogy and Teacher Education - BartolomeDocument26 pagesCritical Pedagogy and Teacher Education - BartolomeAbu UbaidahNo ratings yet
- Marginalized in EducationDocument19 pagesMarginalized in EducationAkiko Grace TanNo ratings yet
- CIT in Edu Unit1-4 Mid Term CompleteDocument21 pagesCIT in Edu Unit1-4 Mid Term CompleteUmar DrazNo ratings yet
- Soc 499 Proposal - Kayla ParksDocument35 pagesSoc 499 Proposal - Kayla Parksapi-598231935No ratings yet
- Multicultural Education: Lhinever T. Gilhang Bsed 4-5Document71 pagesMulticultural Education: Lhinever T. Gilhang Bsed 4-5Via CioneloNo ratings yet
- Final PaperDocument7 pagesFinal Paperapi-313065681No ratings yet
- Critical InquiryDocument23 pagesCritical InquiryEmily HNo ratings yet
- Intercultural Sesi 14Document9 pagesIntercultural Sesi 14Carmel Debora Siregar -No ratings yet
- Individual DifferncesDocument8 pagesIndividual Differncesjerry mae sacasanNo ratings yet
- What Does It Mean To Be A Morally Responsible Teacher in A Social and Political DemocracyDocument6 pagesWhat Does It Mean To Be A Morally Responsible Teacher in A Social and Political Democracyapi-289752254No ratings yet
- Emery TSOC 5000 Three Perspectives Essay 15SEP2021Document11 pagesEmery TSOC 5000 Three Perspectives Essay 15SEP2021emeryNo ratings yet
- Aiming Higher Together Strategizing Better Educational Outcomes For Boys and Young Men of ColorDocument93 pagesAiming Higher Together Strategizing Better Educational Outcomes For Boys and Young Men of Colorcorey_c_mitchellNo ratings yet
- CultureDocument20 pagesCultureSsewa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Democracy N Diversity ClassDocument24 pagesDemocracy N Diversity ClassAndrew RihnNo ratings yet
- Boling Final Paper Educ 2120Document9 pagesBoling Final Paper Educ 2120api-606897869No ratings yet
- University of Arizona Faculty Handbook "Diversity and Inclusiveness in The Classroom"Document20 pagesUniversity of Arizona Faculty Handbook "Diversity and Inclusiveness in The Classroom"The College FixNo ratings yet
- NAMEDocument11 pagesNAMERose Jane AdobasNo ratings yet
- Education PaperDocument8 pagesEducation Paperapi-643481686No ratings yet
- Lesson - Multicultural EducationDocument73 pagesLesson - Multicultural EducationAldous ManuelNo ratings yet
- Yellow Colorful Animated Illustration Science Theme Presentation - 20240226 - 211224 - 0000Document74 pagesYellow Colorful Animated Illustration Science Theme Presentation - 20240226 - 211224 - 0000dalynNo ratings yet
- Implicit Bias Against International Students: Student Name University Affiliation Professor Course DateDocument6 pagesImplicit Bias Against International Students: Student Name University Affiliation Professor Course DateKing Mashe UltimatelyNo ratings yet
- DIVERSITY OF LEARNERS WITH AR Reaction Paper #2-ROMMEL OBILLODocument2 pagesDIVERSITY OF LEARNERS WITH AR Reaction Paper #2-ROMMEL OBILLORommel ObilloNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Topics For Multicultural EducationDocument4 pagesResearch Paper Topics For Multicultural EducationyquyxsundNo ratings yet
- Education AssignmentDocument5 pagesEducation AssignmentFinch SlimesNo ratings yet
- Key Features That Can Impact The Experiences of Ethnic and Cultural Minority GroupsDocument7 pagesKey Features That Can Impact The Experiences of Ethnic and Cultural Minority GroupsDONNA MENESESNo ratings yet
- Diversity and Complexity in The ClassroomDocument11 pagesDiversity and Complexity in The ClassroomGiavannaMNo ratings yet
- KIRSCHNER INCLUSIVEEDUCATION SageEncycofClMgmt - 2015Document17 pagesKIRSCHNER INCLUSIVEEDUCATION SageEncycofClMgmt - 2015citra cityNo ratings yet
- Multicultural EducationDocument4 pagesMulticultural EducationAnggen SafutriNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 AssignmentDocument6 pagesUnit 6 Assignmentapi-564826175No ratings yet
- Chapter Three: The Multicultural ClassroomDocument16 pagesChapter Three: The Multicultural ClassroomSanja ShishinNo ratings yet
- Whenever A Serious Problem Arises in SocietyDocument9 pagesWhenever A Serious Problem Arises in SocietyafifahyulianiNo ratings yet
- EJ795237Document26 pagesEJ795237nusinNo ratings yet
- CDP Allyson PerryDocument13 pagesCDP Allyson Perryapi-488950470No ratings yet
- Kubota, Ryuko. Critical Multiculturalism and Second Language EducationDocument23 pagesKubota, Ryuko. Critical Multiculturalism and Second Language EducationanacfeNo ratings yet
- CRT in SpedDocument18 pagesCRT in Spedapi-299089301No ratings yet
- Social Justice and Educational Delights: Morwenna Griffiths University of EdinburghDocument12 pagesSocial Justice and Educational Delights: Morwenna Griffiths University of EdinburghAmandeep Singh RishiNo ratings yet
- Critical Multicultural Education: What Is It?Document25 pagesCritical Multicultural Education: What Is It?Marshella ManshorNo ratings yet
- American Racism: Systemic Racism in the United States of AmericaFrom EverandAmerican Racism: Systemic Racism in the United States of AmericaNo ratings yet
- Diversity in American Schools and Current Research Issues in Educational LeadershipFrom EverandDiversity in American Schools and Current Research Issues in Educational LeadershipNo ratings yet
- HGP Module 1 Activity SheetDocument2 pagesHGP Module 1 Activity SheetCleofe PavoNo ratings yet
- Oral Com FinalsDocument3 pagesOral Com FinalsCleofe PavoNo ratings yet
- 2023 Q4 School MEA Dashboard - FinalDocument31 pages2023 Q4 School MEA Dashboard - FinalCleofe PavoNo ratings yet
- As Diesel price-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageAs Diesel price-WPS OfficeCleofe PavoNo ratings yet
- September 13, 2023Document35 pagesSeptember 13, 2023Cleofe PavoNo ratings yet
- 2022 Travel Order TemplateDocument1 page2022 Travel Order TemplateCleofe PavoNo ratings yet
- Insurance Syllabus 2018Document14 pagesInsurance Syllabus 2018Bhell MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics Activities PDF VersionDocument2 pagesPhonetics Activities PDF VersionBounouara MokhtariaNo ratings yet
- Removing Baseline Wander in ECG WaveformsDocument3 pagesRemoving Baseline Wander in ECG WaveformsSohaib AkhterNo ratings yet
- Every Transfer of ImmovableDocument3 pagesEvery Transfer of ImmovableAdan HoodaNo ratings yet
- Simon The Sportsman: Activity TypeDocument3 pagesSimon The Sportsman: Activity TypeEkaterina DatsenkoNo ratings yet
- Bullying: by Cathlyn de Dios and Mary Yochabel FrancoDocument31 pagesBullying: by Cathlyn de Dios and Mary Yochabel FrancoKDNo ratings yet
- THE MG MODEL FOR THE ESTIMATION OF PEAK FLOOD FLOWS, Application To French RiversDocument11 pagesTHE MG MODEL FOR THE ESTIMATION OF PEAK FLOOD FLOWS, Application To French RiversGiacomo GiNo ratings yet
- Melc DLL Eng 7 Week 8 Q4 DoneDocument5 pagesMelc DLL Eng 7 Week 8 Q4 DoneJudith DacuaNo ratings yet
- Final Nancy121Document66 pagesFinal Nancy121Sahil SethiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ObDocument6 pagesDrug Study Obednaria100% (1)
- APAC LocalizationsDocument15 pagesAPAC LocalizationsDhinakaranNo ratings yet
- A Maqāma Collection by A Mamlūk Historian: Mu Ammad Al - Afadī (Fl. First Quarter of The 8th/14th C.)Document33 pagesA Maqāma Collection by A Mamlūk Historian: Mu Ammad Al - Afadī (Fl. First Quarter of The 8th/14th C.)mpomeranNo ratings yet
- Sugar Analysis Using Ion ChromatographyDocument7 pagesSugar Analysis Using Ion ChromatographyJohn QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Cath SAP 5Document47 pagesCath SAP 5Angel AliNo ratings yet
- Let Export Copy: Indian Customs Edi SystemDocument7 pagesLet Export Copy: Indian Customs Edi Systemsaikatpaul22No ratings yet
- Arya PDFDocument26 pagesArya PDFRahmawati JuliaNo ratings yet
- Sitaramarhi 1 PDFDocument33 pagesSitaramarhi 1 PDFnachNo ratings yet
- RZA V Imposters ComplaintDocument14 pagesRZA V Imposters ComplaintMatias SmithNo ratings yet
- NCUK International Foundation Year MapDocument2 pagesNCUK International Foundation Year Mapkumar.arasu8717No ratings yet
- Non Rigid Connector FPDDocument3 pagesNon Rigid Connector FPDIana RusuNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Parallelogram PracticalDocument5 pagesClass 11 Parallelogram Practicalpratyushpradhan929No ratings yet
- Hebrew GematriaDocument265 pagesHebrew GematriaNicolas Dominguez100% (6)
- Outline and Notes - Biography of The Dollar-KarminDocument7 pagesOutline and Notes - Biography of The Dollar-KarminBankingLinguisticCheckmatesNo ratings yet
- Preposition, Conjunction and ParticiplesDocument22 pagesPreposition, Conjunction and ParticiplesAudrey MonicaNo ratings yet
- XLNTrade TC - 2021 - Final - v.2 - 02112021 - With Signatures - FinalDocument7 pagesXLNTrade TC - 2021 - Final - v.2 - 02112021 - With Signatures - FinalCarlos Daniel Rios OcampoNo ratings yet
Scenario For DMIS
Scenario For DMIS
Uploaded by
Cleofe PavoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Scenario For DMIS
Scenario For DMIS
Uploaded by
Cleofe PavoCopyright:
Available Formats
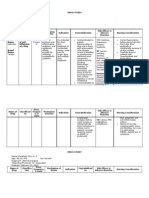
Scenario 1: This DMIS stage manifest as a disinterest in or avoidance of other cultures, or in naive
statements such as “Do they have toilets in Africa?” In educational settings, the denial stage may
manifest in statements such as “Those families just don’t value education” or “If they really cared about
their children they would show up to more school events.” In many cases, people at the denial stage are
not intentionally trying to denigrate other cultures or groups, but their naiveté may nevertheless be
hurtful to others or incline them to support unjust policies. They perceive others as less complex than
themselves, and thus they experience them as less human.
Scenario 2: In educational settings, this DMIS stage may manifest as parent protests or community
opposition campaigns against racial integration, out-of-district busing, equitable school funding, or
detracking (the elimination of academic tracks such as standard, college prep, and honors), or as the
expressed fear that greater racial diversity in the student population will inevitably lead to more in-
school behavioral problems, drug abuse, and violence.
Scenario 3: In educational settings, examples of this DMIS stage might include administrators
discouraging black students from forming a black-student group by encouraging them to join an existing
student group instead or responding to incidents of racial bias and bullying among students by discussing
the need for “respect” while avoiding direct discussions of racism. Another example would be the so-
called “food, flags, and fun” approach to diversity or multicultural education wherein educators
celebrate superficial aspects of cultures but avoid uncomfortable discussions about cultural differences
or prejudice.
Scenario 4: In educational settings, this DMIS stage may manifest in changes to the curriculum, such as
teaching students about non-white historical figures or having them reading multicultural literature
(rather than literature selected exclusively from the Western canon), or in programs such as LGBTQ+
student organizations that allow students to organize or educate their peers across cultural difference.
Scenario 5: This DMIS stage manifest when people from different cultural backgrounds can discuss their
cultural experiences and perspectives in ways that are conversant in and sensitive to the other culture
(Bennett has described this process as “mutual adaptation”), or when organizations embrace inclusive
policies and practices that create conditions for respectful and productive cross-cultural interaction and
teamwork among employees.
You might also like
- Undercover by John Bevere TagalogDocument5 pagesUndercover by John Bevere TagalogAngela Bainca Amper86% (21)
- Affirming Diversity Ch. 1Document39 pagesAffirming Diversity Ch. 1Stephanie Abraham83% (6)
- Bennett - Turning Frogs Into InterculturalistsDocument10 pagesBennett - Turning Frogs Into InterculturalistscamelslayerNo ratings yet
- Croak by Gina Damico ExcerptDocument29 pagesCroak by Gina Damico ExcerptHoughton Mifflin Harcourt0% (1)
- General and Specific ObjectivesDocument8 pagesGeneral and Specific ObjectivesBea Simagala95% (21)
- Kenneth Clark - Alternative Public SchoolsDocument15 pagesKenneth Clark - Alternative Public SchoolsChris StewartNo ratings yet
- Elearning in Aviation SuzanneDocument35 pagesElearning in Aviation SuzannejuanNo ratings yet
- Thesis PaperDocument12 pagesThesis Paperapi-711579758No ratings yet
- Diversity and Excellence in Higher Education: Is There A Con Ict?Document19 pagesDiversity and Excellence in Higher Education: Is There A Con Ict?Renan SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Personal IdentityDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Personal IdentityBoby Kurnia DitamaNo ratings yet
- Deconstructing Power Privilege and SilenDocument18 pagesDeconstructing Power Privilege and SilenPj InudomNo ratings yet
- DSJL EssayDocument6 pagesDSJL Essayapi-357321063No ratings yet
- 2 LectureDocument23 pages2 LectureAkbibi YazgeldiyevaNo ratings yet
- DiversityDocument81 pagesDiversityNanthiniNo ratings yet
- Eth305v 02 Mark098100Document11 pagesEth305v 02 Mark098100Anonymous lwUVg0100% (2)
- Ed 258 - w10 AssignmentDocument7 pagesEd 258 - w10 Assignmentapi-614812254No ratings yet
- Gamage 2009Document22 pagesGamage 2009Jersey FreshNo ratings yet
- DEANE 2015 Difference and School UniformsDocument10 pagesDEANE 2015 Difference and School Uniformssibo kanoNo ratings yet
- Critical Theory and Pedagogy GROUP 3Document6 pagesCritical Theory and Pedagogy GROUP 3josephmehr90No ratings yet
- Handout 1 - Racism Is Still Rife in South AfricaDocument2 pagesHandout 1 - Racism Is Still Rife in South AfricaandobandofilifandoNo ratings yet
- Educ606 Diversity EssayDocument7 pagesEduc606 Diversity Essayapi-578092724No ratings yet
- Kumashiro, K. Toward A Theory of Anti-Oppressive Education.Document29 pagesKumashiro, K. Toward A Theory of Anti-Oppressive Education.FABIOLA RAMIREZ100% (1)
- Critical Pedagogy and Teacher Education - BartolomeDocument26 pagesCritical Pedagogy and Teacher Education - BartolomeAbu UbaidahNo ratings yet
- Marginalized in EducationDocument19 pagesMarginalized in EducationAkiko Grace TanNo ratings yet
- CIT in Edu Unit1-4 Mid Term CompleteDocument21 pagesCIT in Edu Unit1-4 Mid Term CompleteUmar DrazNo ratings yet
- Soc 499 Proposal - Kayla ParksDocument35 pagesSoc 499 Proposal - Kayla Parksapi-598231935No ratings yet
- Multicultural Education: Lhinever T. Gilhang Bsed 4-5Document71 pagesMulticultural Education: Lhinever T. Gilhang Bsed 4-5Via CioneloNo ratings yet
- Final PaperDocument7 pagesFinal Paperapi-313065681No ratings yet
- Critical InquiryDocument23 pagesCritical InquiryEmily HNo ratings yet
- Intercultural Sesi 14Document9 pagesIntercultural Sesi 14Carmel Debora Siregar -No ratings yet
- Individual DifferncesDocument8 pagesIndividual Differncesjerry mae sacasanNo ratings yet
- What Does It Mean To Be A Morally Responsible Teacher in A Social and Political DemocracyDocument6 pagesWhat Does It Mean To Be A Morally Responsible Teacher in A Social and Political Democracyapi-289752254No ratings yet
- Emery TSOC 5000 Three Perspectives Essay 15SEP2021Document11 pagesEmery TSOC 5000 Three Perspectives Essay 15SEP2021emeryNo ratings yet
- Aiming Higher Together Strategizing Better Educational Outcomes For Boys and Young Men of ColorDocument93 pagesAiming Higher Together Strategizing Better Educational Outcomes For Boys and Young Men of Colorcorey_c_mitchellNo ratings yet
- CultureDocument20 pagesCultureSsewa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Democracy N Diversity ClassDocument24 pagesDemocracy N Diversity ClassAndrew RihnNo ratings yet
- Boling Final Paper Educ 2120Document9 pagesBoling Final Paper Educ 2120api-606897869No ratings yet
- University of Arizona Faculty Handbook "Diversity and Inclusiveness in The Classroom"Document20 pagesUniversity of Arizona Faculty Handbook "Diversity and Inclusiveness in The Classroom"The College FixNo ratings yet
- NAMEDocument11 pagesNAMERose Jane AdobasNo ratings yet
- Education PaperDocument8 pagesEducation Paperapi-643481686No ratings yet
- Lesson - Multicultural EducationDocument73 pagesLesson - Multicultural EducationAldous ManuelNo ratings yet
- Yellow Colorful Animated Illustration Science Theme Presentation - 20240226 - 211224 - 0000Document74 pagesYellow Colorful Animated Illustration Science Theme Presentation - 20240226 - 211224 - 0000dalynNo ratings yet
- Implicit Bias Against International Students: Student Name University Affiliation Professor Course DateDocument6 pagesImplicit Bias Against International Students: Student Name University Affiliation Professor Course DateKing Mashe UltimatelyNo ratings yet
- DIVERSITY OF LEARNERS WITH AR Reaction Paper #2-ROMMEL OBILLODocument2 pagesDIVERSITY OF LEARNERS WITH AR Reaction Paper #2-ROMMEL OBILLORommel ObilloNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Topics For Multicultural EducationDocument4 pagesResearch Paper Topics For Multicultural EducationyquyxsundNo ratings yet
- Education AssignmentDocument5 pagesEducation AssignmentFinch SlimesNo ratings yet
- Key Features That Can Impact The Experiences of Ethnic and Cultural Minority GroupsDocument7 pagesKey Features That Can Impact The Experiences of Ethnic and Cultural Minority GroupsDONNA MENESESNo ratings yet
- Diversity and Complexity in The ClassroomDocument11 pagesDiversity and Complexity in The ClassroomGiavannaMNo ratings yet
- KIRSCHNER INCLUSIVEEDUCATION SageEncycofClMgmt - 2015Document17 pagesKIRSCHNER INCLUSIVEEDUCATION SageEncycofClMgmt - 2015citra cityNo ratings yet
- Multicultural EducationDocument4 pagesMulticultural EducationAnggen SafutriNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 AssignmentDocument6 pagesUnit 6 Assignmentapi-564826175No ratings yet
- Chapter Three: The Multicultural ClassroomDocument16 pagesChapter Three: The Multicultural ClassroomSanja ShishinNo ratings yet
- Whenever A Serious Problem Arises in SocietyDocument9 pagesWhenever A Serious Problem Arises in SocietyafifahyulianiNo ratings yet
- EJ795237Document26 pagesEJ795237nusinNo ratings yet
- CDP Allyson PerryDocument13 pagesCDP Allyson Perryapi-488950470No ratings yet
- Kubota, Ryuko. Critical Multiculturalism and Second Language EducationDocument23 pagesKubota, Ryuko. Critical Multiculturalism and Second Language EducationanacfeNo ratings yet
- CRT in SpedDocument18 pagesCRT in Spedapi-299089301No ratings yet
- Social Justice and Educational Delights: Morwenna Griffiths University of EdinburghDocument12 pagesSocial Justice and Educational Delights: Morwenna Griffiths University of EdinburghAmandeep Singh RishiNo ratings yet
- Critical Multicultural Education: What Is It?Document25 pagesCritical Multicultural Education: What Is It?Marshella ManshorNo ratings yet
- American Racism: Systemic Racism in the United States of AmericaFrom EverandAmerican Racism: Systemic Racism in the United States of AmericaNo ratings yet
- Diversity in American Schools and Current Research Issues in Educational LeadershipFrom EverandDiversity in American Schools and Current Research Issues in Educational LeadershipNo ratings yet
- HGP Module 1 Activity SheetDocument2 pagesHGP Module 1 Activity SheetCleofe PavoNo ratings yet
- Oral Com FinalsDocument3 pagesOral Com FinalsCleofe PavoNo ratings yet
- 2023 Q4 School MEA Dashboard - FinalDocument31 pages2023 Q4 School MEA Dashboard - FinalCleofe PavoNo ratings yet
- As Diesel price-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageAs Diesel price-WPS OfficeCleofe PavoNo ratings yet
- September 13, 2023Document35 pagesSeptember 13, 2023Cleofe PavoNo ratings yet
- 2022 Travel Order TemplateDocument1 page2022 Travel Order TemplateCleofe PavoNo ratings yet
- Insurance Syllabus 2018Document14 pagesInsurance Syllabus 2018Bhell MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics Activities PDF VersionDocument2 pagesPhonetics Activities PDF VersionBounouara MokhtariaNo ratings yet
- Removing Baseline Wander in ECG WaveformsDocument3 pagesRemoving Baseline Wander in ECG WaveformsSohaib AkhterNo ratings yet
- Every Transfer of ImmovableDocument3 pagesEvery Transfer of ImmovableAdan HoodaNo ratings yet
- Simon The Sportsman: Activity TypeDocument3 pagesSimon The Sportsman: Activity TypeEkaterina DatsenkoNo ratings yet
- Bullying: by Cathlyn de Dios and Mary Yochabel FrancoDocument31 pagesBullying: by Cathlyn de Dios and Mary Yochabel FrancoKDNo ratings yet
- THE MG MODEL FOR THE ESTIMATION OF PEAK FLOOD FLOWS, Application To French RiversDocument11 pagesTHE MG MODEL FOR THE ESTIMATION OF PEAK FLOOD FLOWS, Application To French RiversGiacomo GiNo ratings yet
- Melc DLL Eng 7 Week 8 Q4 DoneDocument5 pagesMelc DLL Eng 7 Week 8 Q4 DoneJudith DacuaNo ratings yet
- Final Nancy121Document66 pagesFinal Nancy121Sahil SethiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ObDocument6 pagesDrug Study Obednaria100% (1)
- APAC LocalizationsDocument15 pagesAPAC LocalizationsDhinakaranNo ratings yet
- A Maqāma Collection by A Mamlūk Historian: Mu Ammad Al - Afadī (Fl. First Quarter of The 8th/14th C.)Document33 pagesA Maqāma Collection by A Mamlūk Historian: Mu Ammad Al - Afadī (Fl. First Quarter of The 8th/14th C.)mpomeranNo ratings yet
- Sugar Analysis Using Ion ChromatographyDocument7 pagesSugar Analysis Using Ion ChromatographyJohn QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Cath SAP 5Document47 pagesCath SAP 5Angel AliNo ratings yet
- Let Export Copy: Indian Customs Edi SystemDocument7 pagesLet Export Copy: Indian Customs Edi Systemsaikatpaul22No ratings yet
- Arya PDFDocument26 pagesArya PDFRahmawati JuliaNo ratings yet
- Sitaramarhi 1 PDFDocument33 pagesSitaramarhi 1 PDFnachNo ratings yet
- RZA V Imposters ComplaintDocument14 pagesRZA V Imposters ComplaintMatias SmithNo ratings yet
- NCUK International Foundation Year MapDocument2 pagesNCUK International Foundation Year Mapkumar.arasu8717No ratings yet
- Non Rigid Connector FPDDocument3 pagesNon Rigid Connector FPDIana RusuNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Parallelogram PracticalDocument5 pagesClass 11 Parallelogram Practicalpratyushpradhan929No ratings yet
- Hebrew GematriaDocument265 pagesHebrew GematriaNicolas Dominguez100% (6)
- Outline and Notes - Biography of The Dollar-KarminDocument7 pagesOutline and Notes - Biography of The Dollar-KarminBankingLinguisticCheckmatesNo ratings yet
- Preposition, Conjunction and ParticiplesDocument22 pagesPreposition, Conjunction and ParticiplesAudrey MonicaNo ratings yet
- XLNTrade TC - 2021 - Final - v.2 - 02112021 - With Signatures - FinalDocument7 pagesXLNTrade TC - 2021 - Final - v.2 - 02112021 - With Signatures - FinalCarlos Daniel Rios OcampoNo ratings yet