Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F. L. Vargas College, Inc.: Course Sem/AY Module No. Lesson Title Week Duration Date Description of The Lesson
F. L. Vargas College, Inc.: Course Sem/AY Module No. Lesson Title Week Duration Date Description of The Lesson
Uploaded by
princessp.pagaddu05Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F. L. Vargas College, Inc.: Course Sem/AY Module No. Lesson Title Week Duration Date Description of The Lesson
F. L. Vargas College, Inc.: Course Sem/AY Module No. Lesson Title Week Duration Date Description of The Lesson
Uploaded by
princessp.pagaddu05Copyright:
Available Formats
F. L. VARGAS COLLEGE, INC.
Tuguegarao City, Cagayan, Philippines
Telefax # (078) 396-1347
Self-Paced Learning Module (SLM)
Course Forensic 1 - Forensic Photography
Sem/AY Second Semester/2021-2022
Module No. 3
Lesson Title Properties of Light and Photography
Week
2
Duration
Date March 7-18, 2022
Description This lesson will tackle the light and its properties focusing on the photographic rays
of the use in modern photography. This lesson will also provide activities and exercises to
Lesson demonstrate learned knowledge the concept of light as an element of photography
Learning Outcomes
Intended Students should be able to meet the following intended learning outcomes:
Learning • Explain the concept of light.
Outcomes • Discuss the photographic rays use in modern photography.
• Establish its properties and sources.
Targets/ At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Objectives • Discuss light characteristic.
• elaborate the photographic rays use in modern photography.
• identify properties and mediums of light.
Student Learning Strategies
Online Activities A. Online Discussion via Google Meet
(Synchronous/ You will be directed to attend in at least one hour class discussion on the history
Asynchronous) and elements of photography. To have access to the Online Discussion, refer to
this link:
Section 2-A https://meet.google.com/tjg-otwu-kdh
Section 2-B https://meet.google.com/nys-fhgh-umt
Section 2-C https://meet.google.com/jhd-qban-sqr
Section 2-D https://meet.google.com/mks-mfrk-dqm
The online discussion will happen on your given schedule from 5:00-6:30.
COURSE FACILITATOR: ROLAND N. RESURRECCION
F. L. VARGAS COLLEGE, INC.
Tuguegarao City, Cagayan, Philippines
Telefax # (078) 396-1347
(For further instructions, refer to your Google Classroom and see the schedule of
activities for this module)
B. Learning Guide Questions:
1. What is light and its role in photography?
2. Compare the different properties of light?
3. Distinguish the modern photographic rays use in police work?
Note: The insight that you will post on online discussion forum using Learning
Management System (LMS) will receive additional scores in class participation.
Lecture Guide
PHOTOGRAPHIC RAYS:
ITS NATURE AND CHARACTERISTICS
Everyone knows light. It excites the retina of the eye. Light
makes things visible. There is no exaggeration to say that man cannot
live without light. Same things are true in photography, because light is
needed to produce a photograph.
LIGHT
- It is a form of electromagnetic radiation which travels in wave
motion.
- It is a wavelength of radiant energy capable of visual detection.
Offline Activities - It is a radiant energy which emanates from heat.
(e-Learning/Self- - Light moves in straight lines from its source, but it can be bent
Paced) and scattered by objects placed in its path.
- It travels at a speed of about 186, 000 miles per second in air or
300, 000 km/sec in an open space but differs in wavelength and
frequency. It can be bud or reflected. It takes about 8 minutes
for the light to travel from the sun to reach the earth.
• Aloh Roemer (Denmark) – he measured the speed of light
in 1676.
Optics is the study of light. It is concerned with the nature of light and the way
it behaves in optical instruments. Light is a form of energy and so an object may
only produce light when there is energy present.
COURSE FACILITATOR: ROLAND N. RESURRECCION
F. L. VARGAS COLLEGE, INC.
Tuguegarao City, Cagayan, Philippines
Telefax # (078) 396-1347
THEORIES OF LIGHT
1. Wavelength Theory
- The wavelength of the light is the most pertinent,
particularly in the design of lenses.
- It is best illustrated by the dropping of stone in a pond of
still water.
- The series of wave which travels outward from the
center point are just a like wave that travels in all
direction from a source with equal velocity.
- This theory maybe used to illustrate reflection,
interference, refraction, diffraction and polarization.
- James Clerk Maxwell – A British scientist who discovered
wavelength structure of light after 20 years or research.
2. Quantum Theory
- Max Plank theorized in 1900 that light might be made up of little bundles
of energy named quanta
- A quantum of light is called photon, when photon strikes a light sensitive
surface, it gives energy of electrons within the metal explain the
photoelectric current.
- It is used to explain X-radiation and photo-electricity.
The different energies in the electromagnetic spectrum are the
following: cosmic rays; gamma rays; x-rays; UV rays; visible light; infra-red
rays; heat rays; Hertzian waves, and the alternating current oscillation.
Visible Spectrum - a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum
where the visible light is found, the portion of the electromagnetic
spectrum that affect the human sense of sight. Visible light includes all
those radiation having a wavelength ranging from 400 – 700 mu.
FOUR PHOTGRAPHIC RAYS OF MODERN PHOTOGRAPHY
1. X-rays – 01 to 30 nm.(nanometer)
2. Ultra-violet rays- 3- to 400 nm. (nanometer)
3. Visible light – 400 t0 700 nm. (nanometer)
4. Infra-red rays- 700 to 1000+ nm. (nanometer)
Note: 1 meter (m) of length
Equals: 1,000,000,000.00 nanometers (nm) in length
GENERAL TYPES OF LIGHT
1. Visible Light
- Lights with a wavelength of 400-700 nm.
COURSE FACILITATOR: ROLAND N. RESURRECCION
F. L. VARGAS COLLEGE, INC.
Tuguegarao City, Cagayan, Philippines
Telefax # (078) 396-1347
2. Invisible Light
- Lights with shorter or longer wavelengths.
WHITE LIGHT
When the wavelengths between 400-700 nn are presented to
the eye in nearly equal quantity, we get the sensation or perception of
colorless or white light. If a narrow beam of white light is allowed to
pass through a prism it will bend the light of shorter wavelength thus
spreading them out into visible spectrum. These are the color of the
rainbow.
White is the sum total of all the colors of the rainbow while black
is the absence of all colors.
If we divide the wavelength of visible light into three, we will
produce blue, green and red colors.
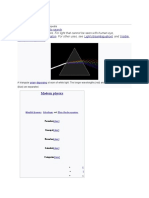
Separation of White
Light into Colored Light
Light from many
sources, such as the
Sun, appears white.
When white light
passes through a prism,
however, it separates
into a spectrum of
different colors. The
prism separates the
light by refracting, or
bending, light of
different colors at
different angles. Red
light bends the least
and violet light bends
the most.
PROPERTIES OF LIGHT
1. Reflection
- It is the deflection or bouncing back of light when it hits a
surface.
COURSE FACILITATOR: ROLAND N. RESURRECCION
F. L. VARGAS COLLEGE, INC.
Tuguegarao City, Cagayan, Philippines
Telefax # (078) 396-1347
a. Regular reflection- happens when light hits a flat, smooth
and shiny surface.
b. Irregular or diffused reflection- occurs when light hits a
rough or uneven but glossy object.
2. Refraction
- The bending of light when passing from one medium to
another.
3. Diffraction
- The bending of light when it hits a sharp edge of an opaque
object.
- It is also the separation of the colors of light.
Sample:
1. light striking spider wave, your eyes can see different
colors of light like rainbow.
2. Rainbow is the effect of light diffusion due to
atmospheric vapor.
4. Interference
- Color can be produced by interference of light waves in thin
film like soap bubbles or a film of oil floating in water.
5. Rectilinear
- The nature of light that normally travels in straight line.
6. Absorption
- The nature of light to be absorbed in the process of dark
surfaces.
7. Filtration
- The character of light to be altered from its colorless into
visible state.
8. Polarization
- The process by which the vibration of light are confined to
definite plane, the speed of light can be measured.
It is the blocking of unwanted light, it is best seen in sun
glasses to minimize the effects of light in the eyes.
COURSE FACILITATOR: ROLAND N. RESURRECCION
F. L. VARGAS COLLEGE, INC.
Tuguegarao City, Cagayan, Philippines
Telefax # (078) 396-1347
9. Fluorescence
- This happens when molecules of the fluorescent material
absorb energy at one wavelength and radiate it at another
wavelength.
QUALITIES OF LIGHT
1. Intensity
- It refers to the strength of light. This varies according to the output of
light source and the distance from the source.
2. Direction
- Where there is a single source, the direction is clearly defined. Where
there are multiple sources or the light is diffused as on a cloudy day, the
direction is less evident or totally absent.
3. Color
- Light varies in color depending upon its source and the substance
through which it passes. Natural sunlight has a different color mixture
from incandescent lighting or electronic flash, and the color of sunlight
itself varies depending upon the atmospheric conditions and time of
the day. The following are the characteristics of color: hue, saturation
and brightness.
Mediums of Light
Objects that influence the intensity of light as they may reflect
absorb or transmit.
Mediums of light maybe classified as:
- Transparent Objects – Materials, which allow light to pass through
so that objects on the other side, can be distinguished. Mediums that
merely slow down the speed of light but allow to pass freely in other
respects, transmit 90% or more of the incident light.
- Translucent Objects – Those that allow light to pass through but
diffuse the flow of light so that objects on the other side cannot be
distinctly seen. Mediums that allow light to pass through it in such
a way that the outline of the source of light is not clearly visible,
transmit 50% or less of the incident light.
- Opaque Objects – A medium that divert or absorb light, but does
not allow lights to pass though, they absorb most of the light while
reflecting some of it.
COURSE FACILITATOR: ROLAND N. RESURRECCION
F. L. VARGAS COLLEGE, INC.
Tuguegarao City, Cagayan, Philippines
Telefax # (078) 396-1347
THE RAT LAW
When incident light hits a medium, three things might happen,
the light maybe:
A. Reflected
B. Absorbed
C. Transmitted
SOURCES OF LIGHT
1. NATURAL LIGHT
- Those coming from nature like the sun, moon, stars, other
heavenly bodies, lighting, fire, etc.
- The intensity of the sunlight falling on an open space varies
depending on the weather condition, time of the day, or even
time of the year.
- For a more accurate exposure setting at daylight, only one
characteristic is considered- the kind of shadow casted by an
object in an open space.
a. Bright sunlight- a lighting condition where objects in open
space cast a deep and uniform or distinct shadow.
b. Hazy sunlight- objects in open space cast a transparent
shadow.
c. Dull sunlight- open objects in space cast no shadow.
- Cloudy bright- objects in an open space cast no shadow
but objects are far distances are clearly visible.
- Cloudy dull- objects in open space cast no shadow and
visibility of distant objects are already limited.
2. ARTIFICIAL LIGHT
- Light sources of this category are man-made and are divided
into the continuous radiation and the short duration.
a. Continuous radiation
- Those that can give illumination continuously.
b. Short Duration
- It gives a brief flash of light produced by a burning metallic
wire (flash bulb) or an electrical discharge through a gas-
filled tube (electronic flash)
- The flash bulb is no longer available in the market but the
electronic flash remains very popular.
- Because it is battery-powered, it is more convenient for field
work where AC current is not available.
COURSE FACILITATOR: ROLAND N. RESURRECCION
F. L. VARGAS COLLEGE, INC.
Tuguegarao City, Cagayan, Philippines
Telefax # (078) 396-1347
FORENSIC LIGHT SOURCES
1. Ultra violet lamp
- It comes in variety of shapes, sizes and power.
- Some units are portable battery operated and are easily
carried and can meet the rugged and rigorous demand for
field work.
2. LASER- Light Amplification through Simulated Emission of
Radiation
- By illuminating certain items with LASER, they would
fluoresce or could be made to stand out in sharp contrast
from their background.
- This was especially significant in locating dried
biological items.
- It provided a way for the criminalist to finally see, locate,
and visually record evidence that they know that they
had been missing
- They are quite expensive.
3. Alternative Light Source (ALS)
- Far more expensive alternative to forensic LASER.
- It uses a variety of band pass filters to provide a high
intensity beam of non-coherent light.
4. Forensic Light Sources (FLS)
- Applied to a wide variety of relatively inexpensive light
sources which use filtered white light.
Performance Tasks
COURSE FACILITATOR: ROLAND N. RESURRECCION
F. L. VARGAS COLLEGE, INC.
Tuguegarao City, Cagayan, Philippines
Telefax # (078) 396-1347
PT 1
Directions: In not less than fifty (50) words, explain whether photography is possible without light
(20 points).
PT 2
Directions: State and explain the four (4) photographic rays of modern photography (40 points).
PT 3
Directions: State and explain the so-called RAT Law (30 points).
Understanding Directed Assess
COURSE FACILITATOR: ROLAND N. RESURRECCION
F. L. VARGAS COLLEGE, INC.
Tuguegarao City, Cagayan, Philippines
Telefax # (078) 396-1347
Rubric for Designing Lesson Plan (PT 2)
Learning Resources
COURSE FACILITATOR: ROLAND N. RESURRECCION
F. L. VARGAS COLLEGE, INC.
Tuguegarao City, Cagayan, Philippines
Telefax # (078) 396-1347
Books
Delizo, D. B. G. (2019). Criminalistics: Textbook and review materials. Crimzone Enterprises.
Manlusoc, A.C. Yang, B.T. and Bolante, R. B. (2011). Forensic photography.: Wiseman Publishing
Inc.
Robinson E. (2016) Crime scene photography. Academic Press
Marsh, N. (2014) Forensic Photography: a practitioner's guide. John Wiley & Sons, LTD
Internet Resources
Nola Taylor Redd (2022, February 1). How fast does light travel? | The speed of light.
https://www.space.com/15830-light-speed.html
Ryan (n.d.). (2022, February 1). Theories of light. http://www.angelfire.com/sc3/light/
Theories,html
Shaw Academy.(2022, February). The importance of light in photography.
https://blog.shawacademy.com/light-in-photography/
COURSE FACILITATOR: ROLAND N. RESURRECCION
You might also like
- Aramco Evaluation QuestionsDocument21 pagesAramco Evaluation QuestionsKunal Singh100% (11)
- LightDocument2 pagesLightelorran0% (2)
- Ophthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneFrom EverandOphthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan Form 2Document10 pagesScience Yearly Lesson Plan Form 2NorelyanaAli100% (2)
- 2nd Notes On Forensic PhotographyDocument10 pages2nd Notes On Forensic PhotographyEdward John Quibot FajardoNo ratings yet
- Chap16 LightDocument20 pagesChap16 LightJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- LIGHTDocument4 pagesLIGHTNerrio Christian Art NerioNo ratings yet
- Light - WikipediaDocument89 pagesLight - WikipediaRaj ThakurNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document11 pagesModule 2Lee DabinNo ratings yet
- LIGHT 7 Es APARENTE MIRASOLDocument8 pagesLIGHT 7 Es APARENTE MIRASOLMirasol Aparente100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Spectrum and Visible LightDocument14 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum and Visible LightDreian Calaoagan PalalayNo ratings yet
- Optics Learning ModuleDocument30 pagesOptics Learning ModuleManas DashNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Optics: Pre Pared By: Je Nno S - La Ntaya, OdDocument27 pagesTheoretical Optics: Pre Pared By: Je Nno S - La Ntaya, OdDyra Kim QuintanaNo ratings yet
- All About LightsDocument8 pagesAll About LightsAl LyNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS II LAS Wave OpticsDocument19 pagesPHYSICS II LAS Wave Opticsel janeNo ratings yet
- Despre Lumina in Limba EnglezaDocument7 pagesDespre Lumina in Limba EnglezaDia0505No ratings yet
- Week 7 FotoDocument6 pagesWeek 7 FotoGiesel PalomoNo ratings yet
- Fors211 Photo Lesson 3 (Light)Document34 pagesFors211 Photo Lesson 3 (Light)Almar MamarintaNo ratings yet
- Light and Sources of LightDocument12 pagesLight and Sources of LightPraneetha DumsapurNo ratings yet
- Light WavesDocument12 pagesLight WavesMpforgeNo ratings yet
- LAS SCIE8 Q1.Wk5 6Document6 pagesLAS SCIE8 Q1.Wk5 6Edie Lyn CatapangNo ratings yet
- Salas PSQ4W3L1-2Document22 pagesSalas PSQ4W3L1-2riaNo ratings yet
- Light Notes 1Document31 pagesLight Notes 1api-233194737No ratings yet
- Module 2 in Forensic Photography Chapter 2Document9 pagesModule 2 in Forensic Photography Chapter 2escasinasjeralyn42No ratings yet
- Light: Modern PhysicsDocument5 pagesLight: Modern PhysicsJef PerezNo ratings yet
- LightDocument2 pagesLightriNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 3 - Module 5 Your Light Is My Life!Document203 pagesScience Quarter 3 - Module 5 Your Light Is My Life!Ma. Teresa BajaoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics: Many Properties of Light Can Be Understood by Using A Wave Model of LightDocument7 pagesGrade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics: Many Properties of Light Can Be Understood by Using A Wave Model of LightjomardsamNo ratings yet
- LIGHTDocument37 pagesLIGHTalexymersNo ratings yet
- GenPhysics2 - Q2 Module 2Document19 pagesGenPhysics2 - Q2 Module 2Jasmin SorianoNo ratings yet
- Las Q3 Module 4 2Document2 pagesLas Q3 Module 4 2Jerome VitalNo ratings yet
- AMANREPORTDocument18 pagesAMANREPORTAMAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Light: Electromagnetic Radiation Light (Disambiguation) Visible Light (Disambiguation)Document19 pagesLight: Electromagnetic Radiation Light (Disambiguation) Visible Light (Disambiguation)AnandNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Light and ColorDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Light and ColorManuelNo ratings yet
- Photographic RaysDocument6 pagesPhotographic RaysPrecious ImperialNo ratings yet
- Forensic 1 Lesson 1-2Document3 pagesForensic 1 Lesson 1-2Trisha Joy Serdoncillo LuibNo ratings yet
- A4 Science 10 WEEK 2 Qtr. 2 2020-2021Document5 pagesA4 Science 10 WEEK 2 Qtr. 2 2020-2021ANDREW SALUNDAGUIT100% (1)
- Fiber Optics CommunicationsDocument8 pagesFiber Optics CommunicationsKuronix ArcayaNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document16 pagesSession 2KithminiNo ratings yet
- Phy. Sci. Quarter 4 M34 PDFDocument18 pagesPhy. Sci. Quarter 4 M34 PDFAshlyn WilsonNo ratings yet
- Iluminacion (Texto en Ingles)Document10 pagesIluminacion (Texto en Ingles)jonathan lopezNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Anna AutosavedDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic Anna AutosavedShaniah SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Radiant Energy & Nuclear EnergyDocument42 pagesRadiant Energy & Nuclear EnergyChristine Marielle Claroniño ApoNo ratings yet
- Lesson2 1-LightDocument4 pagesLesson2 1-LightGrace06 LabinNo ratings yet
- Lesson: Light References: Science 7LM, Science 7 TG, Materials: Visual Aids, Activity SheetDocument3 pagesLesson: Light References: Science 7LM, Science 7 TG, Materials: Visual Aids, Activity Sheetjoan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- Leica Elements of Optics RVD Basic Booklet 2012 enDocument21 pagesLeica Elements of Optics RVD Basic Booklet 2012 enRicardo GuimaraesNo ratings yet
- Me 324 Photonic ThermalDocument12 pagesMe 324 Photonic ThermalAnonymous 1VhXp1No ratings yet
- Light: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument22 pagesLight: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchJohn Vincen AnastacioNo ratings yet
- 4 Lesson Plan On LightsDocument4 pages4 Lesson Plan On LightsJustine Collamar GanabNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument94 pagesOpticsshahadaljobouryNo ratings yet
- Light: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument4 pagesLight: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchRonaldNo ratings yet
- SCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLDocument42 pagesSCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLErick Wangila WanyonyiNo ratings yet
- Science 10 SECOND QuarterDocument152 pagesScience 10 SECOND QuarterAPPLE GRACE MARIE SEBASTIAN100% (1)
- Zwinkels - 2015 - Light Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument9 pagesZwinkels - 2015 - Light Electromagnetic SpectrumFirda SyavieraNo ratings yet
- Interior Lighting Design The Fundamentals: David G. Weatherly, PE, LEED AP, LCDocument44 pagesInterior Lighting Design The Fundamentals: David G. Weatherly, PE, LEED AP, LCEzekiel Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Doon Public SchoolDocument18 pagesDoon Public SchoolManish HarneNo ratings yet
- Police Photography (Lights)Document6 pagesPolice Photography (Lights)Rj Mel King DonggonNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment 7Document1 pageFormative Assessment 7bashadelacruz7No ratings yet
- I. Introductory Concept: SHS - Physical ScienceDocument13 pagesI. Introductory Concept: SHS - Physical SciencePau FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Dual Role of Sunlight Plant Physiology by Hopkins 4EDocument14 pagesDual Role of Sunlight Plant Physiology by Hopkins 4EneharikagartiaNo ratings yet
- Sia83 3notesDocument5 pagesSia83 3notesAmaechi ZalNo ratings yet
- SpectroscopyetextDocument23 pagesSpectroscopyetextTejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Title I, Chapter 2)Document6 pagesModule 3 (Title I, Chapter 2)princessp.pagaddu05No ratings yet
- Module 4 (Title I, Chapter 3)Document2 pagesModule 4 (Title I, Chapter 3)princessp.pagaddu05No ratings yet
- Criminal Law Module 1Document4 pagesCriminal Law Module 1princessp.pagaddu05No ratings yet
- Module 2Document6 pagesModule 2princessp.pagaddu05No ratings yet
- Eros and Psyche Print 2 PDFDocument8 pagesEros and Psyche Print 2 PDFNizzy Hope Nulada CartagoNo ratings yet
- Reliability of Core Analysis & PVT Data-3Document1 pageReliability of Core Analysis & PVT Data-3Aditya KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Concept Note - C Financing MechanismsDocument17 pagesConcept Note - C Financing Mechanismst.ahmadzadeNo ratings yet
- NJSTR-2021 8 21Document9 pagesNJSTR-2021 8 21SAFIYANU AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Learn Astrology PDFDocument45 pagesLearn Astrology PDFRajagopal Rao85% (20)
- Assignment 1 2 PumpDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 2 PumpAnkit0% (1)
- TDE9540 09 WhitePaperDocument56 pagesTDE9540 09 WhitePaperdarkoskr84No ratings yet
- Hanwa Injection Substation Maintainance Ceck ListDocument18 pagesHanwa Injection Substation Maintainance Ceck ListMubarak Aleem100% (1)
- Poster PresentationDocument1 pagePoster PresentationPilla SatishNo ratings yet
- 2019 AAA Green Car GuideDocument217 pages2019 AAA Green Car GuideIslam MohamedNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid PDFDocument24 pagesAmniotic Fluid PDFJoshua Ty CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy and Steel Properties: Electron (-)Document10 pagesMetallurgy and Steel Properties: Electron (-)Ashish ManeNo ratings yet
- DGA Comparison Between Ester and Mineral Oils: C. Perrier, M. Marugan, M. Saravolac A. BeroualDocument4 pagesDGA Comparison Between Ester and Mineral Oils: C. Perrier, M. Marugan, M. Saravolac A. BeroualJhon Fredy Vallejo GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Analytic Representation of Oscillations, Excitability, and Traveling Waves in A Realistic Model of The Belousov-Zhabotinskii ReactionDocument12 pagesAnalytic Representation of Oscillations, Excitability, and Traveling Waves in A Realistic Model of The Belousov-Zhabotinskii Reactionrodolfo castilloNo ratings yet
- Challenges To IoT-Enabled Predictive Maintenance For Industry 4.0Document13 pagesChallenges To IoT-Enabled Predictive Maintenance For Industry 4.0BrunoNo ratings yet
- Phalogenics - Phalogenics Male Enhancement Reviews - Phalogenics Male Enhancement - Official Site !Document2 pagesPhalogenics - Phalogenics Male Enhancement Reviews - Phalogenics Male Enhancement - Official Site !Phalogenics Male EnhancementNo ratings yet
- Dual Drive Booster For A Two-Spool Turbofan: High Shaft Power Offtake Capability For Mea and Hybrid Aircraft ConceptsDocument10 pagesDual Drive Booster For A Two-Spool Turbofan: High Shaft Power Offtake Capability For Mea and Hybrid Aircraft ConceptsNguyễn Đức HuyNo ratings yet
- Vertu Reader Instruction ManualDocument4 pagesVertu Reader Instruction ManualRodrigo PossariNo ratings yet
- Druidic Guerilla Ranger - GM BinderDocument7 pagesDruidic Guerilla Ranger - GM BinderАлексей ЖуравлевNo ratings yet
- Model-Based Strategic PlanningDocument18 pagesModel-Based Strategic PlanningBintang ramadhanNo ratings yet
- Tna Training Brochure (EN)Document3 pagesTna Training Brochure (EN)Bindu PanickerNo ratings yet
- Hick's Law Lab 1Document6 pagesHick's Law Lab 1Merna SamieNo ratings yet
- CAPE Unit 1 Trig NotesDocument19 pagesCAPE Unit 1 Trig NotesAndre MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Summary ReportDocument24 pagesSummary ReportRonniNo ratings yet
- PPT01-Introduction To Big DataDocument34 pagesPPT01-Introduction To Big DataTsabitAlaykRidhollahNo ratings yet
- Recipe Book Part 1Document19 pagesRecipe Book Part 1Justine Keira AyoNo ratings yet
- Titanic: in Disasters Like The Sinking of The, Who Should Be Saved First?Document1 pageTitanic: in Disasters Like The Sinking of The, Who Should Be Saved First?Jay BautistaNo ratings yet
- Common Female Ancestor Test 2: African L2 Haplogroups Pereira Et Al (2001)Document7 pagesCommon Female Ancestor Test 2: African L2 Haplogroups Pereira Et Al (2001)Mwiinga JnrNo ratings yet