Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IGCSE 0610 - EYES Sense Organs NOTES (2023-2025)
IGCSE 0610 - EYES Sense Organs NOTES (2023-2025)
Uploaded by
ckqx1234Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IGCSE 0610 - EYES Sense Organs NOTES (2023-2025)
IGCSE 0610 - EYES Sense Organs NOTES (2023-2025)
Uploaded by
ckqx1234Copyright:
Available Formats
IGCSE 0610 - EYES Sense organs
NOTES (2023-2025)
In dim light the pupil dilates (widens) in order to allow as much light into the eye as possible
↳ radical muscle contracts and circular muscle relaxes
In bright light the pupil constricts (narrows) in order to prevent too much light entering the eye
and damaging the retina
↳ circular muscle contracts and radial muscle relaxes
Pupil
The pupil is controlled by the circular muscle and the radial muscle
↳ They work opposite and against each other which are examples of antagonistic muscles
Rods & Cones
Photoreceptors of the retina
Includes :
↳ Rod cells - allows to see in the dark but a not differentiate colours and movement
Rod cells are found all over the retina - except blind spot and fovea
↳ Cone cells - allows to see colour but not in the dark
IGCSE 0610 - EYES Sense organs NOTES (2023-2025) 1
There are 3 types of cone cells which are sensitive to different colours of light (red, blue and
green)
The fovea is an area on the retina where almost all of the cone cells are found
Very few at the peripheral retina
Blind spot - an area where the optic nerve attaches to the retina
↳ there are no light-sensitive cells at all in this area
Accommodation
The ability of the eye to change the thickness of the lens according to the distance of light from
an object by using contraction and relaxation of the ciliary muscles and the suspensory ligament
↳ To focus on distant objects
Lens is pulled in all directions to become thinner - this allows the light to be focused on the retina
slightly
Ciliary muscle relaxed
Suspensory ligament tight
↳ To focus on nearer objects
The lens becomes thicker - this allows the light to be focused on the retina stronger
Ciliary muscle tightens
Suspensory ligament relaxes
Suspensory
Position Ciliary muscles Muscle tension Lens shape Refraction
ligaments
Relaxed / Light is refracted
Near Contracts Low Fat / thicker
loosens strongly
Contracts / Light is refracted
Distant Relaxed High Thin
tightens slightly
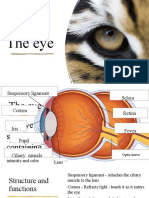
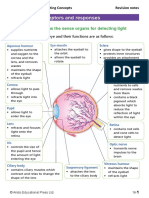
Parts of the eye
IGCSE 0610 - EYES Sense organs NOTES (2023-2025) 2
Cornea – refracts light - same function as the lens
Iris – controls how much light enters the pupil
Lens – focuses light on to the retina - same function as the cornea
Retina – contains light receptors, some sensitive to light of different colours
Optic nerve – carries impulses to the brain
IGCSE 0610 - EYES Sense organs NOTES (2023-2025) 3
IGCSE 0610 - EYES Sense organs NOTES (2023-2025) 4
You might also like
- Section 13 of HMADocument11 pagesSection 13 of HMAria rajeevNo ratings yet
- Government of Kerala: Income CertificateDocument1 pageGovernment of Kerala: Income CertificatethanseelnnNo ratings yet
- Institute of Engineering: Tribhuvan UniversityDocument41 pagesInstitute of Engineering: Tribhuvan UniversityShooting Star100% (2)
- Bata, Bata, Pa'no Ka Ginawa? Character AnalysisDocument2 pagesBata, Bata, Pa'no Ka Ginawa? Character AnalysisRain GoNo ratings yet
- Trial SBP SPM 2013 Biology SKEMA K3Document12 pagesTrial SBP SPM 2013 Biology SKEMA K3Cikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Characteristics of Living Things: Cambridge IGCSE BiologyDocument19 pagesCharacteristics of Living Things: Cambridge IGCSE BiologyKassyKasNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light (3.2.1) CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 Save My ExamsDocument1 pageReflection of Light (3.2.1) CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 Save My ExamsMuhammadAbdullah32No ratings yet
- BIO F4 Paper 1Document28 pagesBIO F4 Paper 1Zalina RoslanNo ratings yet
- 2023 Chemistry 0620 Specimen PapersDocument66 pages2023 Chemistry 0620 Specimen PapersClevxyNo ratings yet
- Mock Teaching Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesMock Teaching Lesson Planapi-400225241No ratings yet
- Biology F4 KSSM Textbook PDFDocument191 pagesBiology F4 KSSM Textbook PDFShu Tao OoiNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE PMR Notes and ExperimentsDocument221 pagesSCIENCE PMR Notes and ExperimentsAzlina Ahmad100% (1)
- Scheme of Work and Suggested Activities Formula A pt3 KSSM Science Form 2Document20 pagesScheme of Work and Suggested Activities Formula A pt3 KSSM Science Form 2Bestah Joewellster Teo100% (1)
- IT Sci F3 Topical Test 1 (E)Document6 pagesIT Sci F3 Topical Test 1 (E)Nad Ramli0% (1)
- Form 5 Biology Chapter 1 Transport (D)Document42 pagesForm 5 Biology Chapter 1 Transport (D)Marcus LeeNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Biology Peka ReportDocument3 pagesHow To Write A Biology Peka Reportsarah_aufaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Chapter 2 Powerpoint SlidesDocument124 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 2 Powerpoint SlidesADAM LOHNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Science Chapter 3 NotesDocument12 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 3 NotesAnonymous klhru5ENo ratings yet
- HCF and LCMDocument8 pagesHCF and LCMilkayNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion LatihanDocument5 pagesForce and Motion LatihanMohamad Tarmizi100% (1)
- SPM 4551 2006 Biology k3 BerjawapanDocument10 pagesSPM 4551 2006 Biology k3 Berjawapanpss smk selandarNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationDocument22 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationChew Han Hoong0% (2)
- SPM Biology Form 4 Chapter 2.1 Cell Structures and Functions (ALL 12 Structures of Plant Cell and Animal Cell)Document4 pagesSPM Biology Form 4 Chapter 2.1 Cell Structures and Functions (ALL 12 Structures of Plant Cell and Animal Cell)Felicia LingNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Coordinated Sciences Biological MoleculesDocument9 pagesIGCSE Coordinated Sciences Biological MoleculesSeonaid McDonaldNo ratings yet
- 2022 Specimen Paper 3 Instructions For Teachers ExaminersDocument32 pages2022 Specimen Paper 3 Instructions For Teachers ExaminersNor Hasmaliza0% (1)
- ModulDocument39 pagesModulThanabalan MunuswamyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Kohinoor BegumNo ratings yet
- Biology Section 2 Lesson 8Document59 pagesBiology Section 2 Lesson 8GLADSON SHABINNo ratings yet
- 1 Compressed Notes BioDDocument23 pages1 Compressed Notes BioDLIM ZHI SHUENNo ratings yet
- Lower 6 - Tutorial 3Document1 pageLower 6 - Tutorial 3Yvonne RagguettNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument25 pagesChapter 4 PDFChuahSiewHoonNo ratings yet
- Form 1-Science NotesDocument19 pagesForm 1-Science Notescikguanuar72% (18)
- SPM Biology 2007 k2Document22 pagesSPM Biology 2007 k2pss smk selandar67% (3)
- Nor Diana Binti HassanDocument2 pagesNor Diana Binti HassanFazwadi Haliah100% (1)
- Respirasi-SOALAN STRUKTURDocument6 pagesRespirasi-SOALAN STRUKTURkhairul afzal mokhtarNo ratings yet
- ICC Cricket World CupDocument3 pagesICC Cricket World Cupsanjayd2005No ratings yet
- Story On KSSM 27 June 2021Document3 pagesStory On KSSM 27 June 2021Nabila HadiNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 Biology Answering TechniquesDocument3 pagesPaper 3 Biology Answering Techniquesriyashree100% (1)
- Continuous Variation MethodDocument1 pageContinuous Variation Methoddalilac100% (1)
- Respiration ExperimentDocument5 pagesRespiration ExperimentAlexanderNo ratings yet
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Physics AnswersDocument14 pagesSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Physics AnswersChinWynn.com80% (5)
- SOUND NOTES-physics-SCIENCE SECONDARY CHECKPOINTDocument5 pagesSOUND NOTES-physics-SCIENCE SECONDARY CHECKPOINTsusan hiraNo ratings yet
- Bio Practical DiagramsDocument3 pagesBio Practical DiagramsmjNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Global Perspectives 0457/13Document4 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Global Perspectives 0457/13Asnehdeep SudanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Structure and Functions of The EyeDocument12 pagesLesson 2 The Structure and Functions of The EyeNguyễn Gia LộcNo ratings yet
- SENSE ORGANS, Grade 9Br Bio. MR MUSIMA.Document5 pagesSENSE ORGANS, Grade 9Br Bio. MR MUSIMA.Said SakerNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Sense Organs Eyes Skin and TongueDocument33 pagesUnit 2 Sense Organs Eyes Skin and TongueBONGISIPHO HLOPHENo ratings yet
- Specific Objectives Notes Practical: Section ADocument14 pagesSpecific Objectives Notes Practical: Section AaWDwaDNo ratings yet
- The Main Parts of The Eye and Their FunctionDocument5 pagesThe Main Parts of The Eye and Their FunctionJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Starter: - Task: What Is The Function of An Eye? - Watch Video On Evolution of EyeDocument21 pagesStarter: - Task: What Is The Function of An Eye? - Watch Video On Evolution of EyekathyNo ratings yet
- The EYE NotesDocument6 pagesThe EYE NotesSchool ApplicationNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument9 pagesThe EyeJada MillerNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Sense OrganDocument8 pages3.2 Sense OrganMod HollNo ratings yet
- Sense OrganDocument13 pagesSense OrganChai MingzeNo ratings yet
- The Eye - PrintedDocument4 pagesThe Eye - PrintedGabriel RiderNo ratings yet
- RBA Eye Grade 4 6 10x1Document12 pagesRBA Eye Grade 4 6 10x1Felixdino09No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Sense Organs - Eye - For UploadingDocument79 pagesChapter 14 Sense Organs - Eye - For UploadingmukarrumofficalNo ratings yet
- EYE Notes IgcseDocument3 pagesEYE Notes IgcseTay HermyNo ratings yet
- The-EyeDocument26 pagesThe-EyeBaciu Florina GabrielaNo ratings yet
- 5 Assessment and Diagnostic Procedures For Visual and Eye DisordersDocument5 pages5 Assessment and Diagnostic Procedures For Visual and Eye DisordersNica EnriquezNo ratings yet
- The Eye - Biology OnlyDocument30 pagesThe Eye - Biology Onlyfarmerllama.gkNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument9 pagesThe Human Eyegiana 4e100% (1)
- Eye Optics and AccommodationDocument14 pagesEye Optics and AccommodationJúnior AlvesNo ratings yet
- Ch16 Notes eDocument5 pagesCh16 Notes eJulius CruelNo ratings yet
- Wedding Program Template 13Document2 pagesWedding Program Template 13Ameyaw EffahNo ratings yet
- Panaguiton, Jr. Vs DOJ - G.R. No. 167571 - Nov 25, 2008Document9 pagesPanaguiton, Jr. Vs DOJ - G.R. No. 167571 - Nov 25, 2008Boogie San JuanNo ratings yet
- Aquino v. Mariano, 129 SCRA 532Document2 pagesAquino v. Mariano, 129 SCRA 532Bibi JumpolNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting - Kieso - Chapter 1Document46 pagesIntermediate Accounting - Kieso - Chapter 1Steffy AmoryNo ratings yet
- Preventive Actions of Police: A Project Proposal Made byDocument23 pagesPreventive Actions of Police: A Project Proposal Made bynupur jhodNo ratings yet
- The Gorgon's HeadDocument3 pagesThe Gorgon's HeadReden Macaraeg Juego100% (1)
- Window & Door System: Let'S Build A Better FutureDocument4 pagesWindow & Door System: Let'S Build A Better FutureAmir AlićNo ratings yet
- Carl Zeiss Jena Apo TessarDocument28 pagesCarl Zeiss Jena Apo TessarElla Antonella0% (1)
- At The HotelDocument38 pagesAt The HotelДіана БатраковаNo ratings yet
- Fellowship Cover LetterDocument5 pagesFellowship Cover Letterxjfahwegf100% (1)
- 2008olbrycht Alex OpisDocument23 pages2008olbrycht Alex OpisHamid Reza SorouriNo ratings yet
- Micom P40 Agile: Grid SolutionsDocument12 pagesMicom P40 Agile: Grid SolutionsAdetunji TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Chemistry Assignment 2Document4 pagesIndustrial Chemistry Assignment 2Meeqat SuharwardyNo ratings yet
- Certificate & Acknowledgment.Document5 pagesCertificate & Acknowledgment.Ravindra ThakurNo ratings yet
- Git Bash UsermanualDocument12 pagesGit Bash UsermanualtechbirdNo ratings yet
- MS Access - Working With QueriesDocument69 pagesMS Access - Working With QueriesbogsbestNo ratings yet
- University Management SystemDocument4 pagesUniversity Management Systemnavayuga83% (6)
- PSS2020 345Document11 pagesPSS2020 345Fergus BurnsNo ratings yet
- Administering Enema: Low Enema - 30 CM (12 Inches)Document2 pagesAdministering Enema: Low Enema - 30 CM (12 Inches)さいと フエンテ かずもとNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Editors Introductory ChapterDocument13 pagesChapter 1 Editors Introductory Chapterroxebag437No ratings yet
- Schunk, 2001. Self-Regulation Through Goal SettingDocument4 pagesSchunk, 2001. Self-Regulation Through Goal SettingNani Maciel100% (1)
- Improper Landscapes of Desire: Alternative Routes Towards (Un) Satisfaction in The Narrative of Ena Lucía PortelaDocument10 pagesImproper Landscapes of Desire: Alternative Routes Towards (Un) Satisfaction in The Narrative of Ena Lucía PortelayunlectorNo ratings yet
- GMS 691 Week 2Document23 pagesGMS 691 Week 2Mit DaveNo ratings yet
- A.C. No. 7054 - Que Vs Atty. Revilla - Case DigestDocument3 pagesA.C. No. 7054 - Que Vs Atty. Revilla - Case DigestSarah Jade Layug100% (2)
- Rebel Robin SurvivingDocument11 pagesRebel Robin Survivingbinengo24No ratings yet
- CumiDocument56 pagesCumiRahul NairNo ratings yet