Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bsee 23 Pos
Bsee 23 Pos
Uploaded by
orbesochristianneCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sicilian CourseDocument69 pagesSicilian Coursejuliamagister100% (1)
- 3rd Grade Ela ReviewDocument4 pages3rd Grade Ela Reviewapi-377242371100% (1)
- Engpro ReviewerDocument3 pagesEngpro ReviewerPrincess Gabrielle BrotonelNo ratings yet
- Major 3 IreneDocument23 pagesMajor 3 IreneJude Cedric ReyesNo ratings yet
- ELE123 Structure of English LessonsDocument110 pagesELE123 Structure of English LessonsRain Raven Barlizo LabanzaNo ratings yet
- Virtual Training Handbook I - English Communication Skill TrainingDocument18 pagesVirtual Training Handbook I - English Communication Skill TrainingAlfred Mc Donald Dillupac100% (1)
- Such As Business in Business MeetingDocument15 pagesSuch As Business in Business MeetingPhoebe Cates Tayanes ViscaynoNo ratings yet
- Bus Com 10Document19 pagesBus Com 10Elijah ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech in EnglishDocument30 pagesParts of Speech in EnglishRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter2grammaticalmetalanguage 121204161708 Phpapp02Document6 pagesChapter2grammaticalmetalanguage 121204161708 Phpapp02Cristine Joy R. QuizonNo ratings yet
- Virtual Training Handbook I - English Communication Skill TrainingDocument68 pagesVirtual Training Handbook I - English Communication Skill TrainingMarella OrqueroNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument4 pagesPurposive CommunicationASTRA FAYE QUEENA DELENANo ratings yet
- Partsof Speechin English GrammarDocument16 pagesPartsof Speechin English GrammarToledo, Denise Klaire M.100% (1)
- Part of SpeechDocument20 pagesPart of SpeechGewie Shane Blanco SumayopNo ratings yet
- Noun - PronounDocument19 pagesNoun - PronounAlula FarzanaNo ratings yet
- English Language TerminologyDocument59 pagesEnglish Language TerminologyDinesh PrabuNo ratings yet
- 3 Grade Reading & Language Arts CCGPS Study Guide: Nouns Nouns AbbreviationsDocument5 pages3 Grade Reading & Language Arts CCGPS Study Guide: Nouns Nouns Abbreviationsapi-327816044No ratings yet
- Grammatical-Categories 2.5Document12 pagesGrammatical-Categories 2.5arl somarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Structures Content WordsDocument28 pagesChapter 1 Structures Content WordsJOHN LACETER URIAN ORATANo ratings yet
- Your essential LPAT last minute revision notes - SELECTED - 複製Document5 pagesYour essential LPAT last minute revision notes - SELECTED - 複製Bryan WongNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Assessment of Grammar Midterm CoverageDocument4 pagesTeaching and Assessment of Grammar Midterm CoverageRoselyn AlbisoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Introduction and NounsDocument3 pagesUnit 1. Introduction and NounsEmz GelogoNo ratings yet
- Types of NounsDocument5 pagesTypes of NounsAlexis ViernesNo ratings yet
- LET English Major LanguageDocument39 pagesLET English Major LanguageJustin Jones NotarteNo ratings yet
- English LecturesDocument6 pagesEnglish LecturesAndrei Sy JaviertoNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesParts of Speechjerica tanaNo ratings yet
- Biru Hijau Imut Ceria Tugas Presentasi Kelompok - 20240317 - 230007 - 0000Document24 pagesBiru Hijau Imut Ceria Tugas Presentasi Kelompok - 20240317 - 230007 - 0000saputsaput251No ratings yet
- EC Second Semester FinalsDocument10 pagesEC Second Semester Finalschrisbel.simonNo ratings yet
- Winch 9780195529098 SCDocument37 pagesWinch 9780195529098 SCArti SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument10 pagesParts of SpeechSaikat SahaNo ratings yet
- BSEd 1A - Structure of English Final Requirement.Document20 pagesBSEd 1A - Structure of English Final Requirement.Claire Azucenas ApatanNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument18 pagesParts of SpeechSakunthala RajeshNo ratings yet
- Noun ReportDocument16 pagesNoun ReportAlleina UwUNo ratings yet
- English - CompleteDocument24 pagesEnglish - Completegarciaandrea236No ratings yet
- LET English Major LanguageDocument25 pagesLET English Major LanguageSharmaine Llasus FerrarezNo ratings yet
- READING SKILL iiDocument3 pagesREADING SKILL iizineNo ratings yet
- NounsDocument44 pagesNounsRoger Donoso BarralNo ratings yet
- 8 Parts of SpeechDocument4 pages8 Parts of SpeechTrisha CalmaNo ratings yet
- Contranstive Analysis (Aprida Simbolon 17120272)Document13 pagesContranstive Analysis (Aprida Simbolon 17120272)Cindi Novera ManullangNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument13 pagesParts of SpeechCherish PimmaengNo ratings yet
- Eng 001Document5 pagesEng 001Eldon JulaoNo ratings yet
- English Proficiency ReviewerDocument4 pagesEnglish Proficiency ReviewerlenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-Structure of EnglishDocument17 pagesLesson 1-Structure of EnglishMay Rhea Siapno LopezNo ratings yet
- CEBGADocument28 pagesCEBGACZYSTYNo ratings yet
- CEBallDocument70 pagesCEBallCZYSTYNo ratings yet
- Nouns: Action VerbDocument15 pagesNouns: Action VerbJerica PalomariaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Elfrida BakaraDocument34 pagesGrammar Elfrida BakaraLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- NounDocument15 pagesNounVanshNo ratings yet
- English: 1. Concrete Noun - Noun That CanDocument4 pagesEnglish: 1. Concrete Noun - Noun That CanIrish VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- NounDocument11 pagesNounPalak BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- P.eng Part 2Document5 pagesP.eng Part 2Shubham kumarNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesParts of SpeechKenneth ReyesNo ratings yet
- Signals of Syntactic StructureDocument4 pagesSignals of Syntactic StructureJohn Kelvin RodilNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - MamadDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 1 - MamadJehan BaruaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Terms and What They MeanDocument4 pagesGrammar Terms and What They Meanmuslimuser610No ratings yet
- Grammar - Parts of SpeechDocument17 pagesGrammar - Parts of Speechcaptainnkumar1043100% (1)
- LET Material (Language) 1. Structure of English Basic English Structures and RulesDocument35 pagesLET Material (Language) 1. Structure of English Basic English Structures and RulesCherrie Myth MonaresNo ratings yet
- LET English Major LanguageDocument35 pagesLET English Major LanguageJeremiah FameronagNo ratings yet
- Person Animal Place Thing Idea: Identifying A NounDocument4 pagesPerson Animal Place Thing Idea: Identifying A NounKryzl Rey del FierroNo ratings yet
- English Plus 1 Year 5: Starter Unit: Affirmative and Negative StatementsDocument12 pagesEnglish Plus 1 Year 5: Starter Unit: Affirmative and Negative StatementsAsmohaina Mohamed100% (1)
- Use of English Continuidad. 18-24 Mayo AKDocument3 pagesUse of English Continuidad. 18-24 Mayo AKLucía RiveroNo ratings yet
- Participles, Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument4 pagesParticiples, Gerunds and InfinitivesAhmet Celal KavcarNo ratings yet
- LM-0354 Gramatica Inglesa III PresenDocument6 pagesLM-0354 Gramatica Inglesa III PresenLuis MongeNo ratings yet
- Janez Ore (Nik: University of Ljubljana, LjubljanaDocument8 pagesJanez Ore (Nik: University of Ljubljana, Ljubljanagoran trajkovskiNo ratings yet
- Elementary Unit 12bDocument2 pagesElementary Unit 12bViviana LeguizamoNo ratings yet
- Intervention Material in English 9 AdverbDocument13 pagesIntervention Material in English 9 AdverbCharycel de Guzman100% (2)
- Verb Tenses, Affirmative, Negative & InterrogativeDocument12 pagesVerb Tenses, Affirmative, Negative & InterrogativeNadya OctavianaNo ratings yet
- ENHANCED ENGLISH7 - Q1 - LAS - Wk5Document5 pagesENHANCED ENGLISH7 - Q1 - LAS - Wk5Dauis National High SchoolNo ratings yet
- PDF Basic German Jolene Wochenske Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Basic German Jolene Wochenske Ebook Full Chapterotto.gliem566100% (4)
- Teste Diagnostico de Ingles 5º AnoDocument3 pagesTeste Diagnostico de Ingles 5º AnoMónica SantosNo ratings yet
- SBI PO Preliminary Model Paper 15Document36 pagesSBI PO Preliminary Model Paper 15Deepak SinhaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of The Language of ScienceDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of The Language of ScienceKurt OrfanelNo ratings yet
- English Basic Grammar by Color Association Metodo Opaa WwwenglearningsolutioncomarDocument17 pagesEnglish Basic Grammar by Color Association Metodo Opaa WwwenglearningsolutioncomarengleasolNo ratings yet
- 2015.458637.teach Yourself Hindustani TextDocument356 pages2015.458637.teach Yourself Hindustani TextIalmisry100% (1)
- French 3 Semester 1 Review Au LaboDocument4 pagesFrench 3 Semester 1 Review Au Laboapi-290605652No ratings yet
- Pokus NG PandiwaDocument4 pagesPokus NG PandiwaMaritess MacalingaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate English Grammar "Summarize Chapter 13: Adjective Clause"Document20 pagesIntermediate English Grammar "Summarize Chapter 13: Adjective Clause"Arga SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Short Test 2A: GrammarDocument1 pageUnit 3 Short Test 2A: GrammarIzabella Tar100% (1)
- Grammar of The Hawaiian Language PDFDocument168 pagesGrammar of The Hawaiian Language PDFdolphinsofshamballaNo ratings yet
- Cappello Cambridge Celta Assignment 2 Language Related Task PDF FreeDocument9 pagesCappello Cambridge Celta Assignment 2 Language Related Task PDF Freeheh199179No ratings yet
- GEO246 Topic 5Document2 pagesGEO246 Topic 5hihihihiNo ratings yet
- Tutkish Grammar Academic Edition Yüksel Göknel 2012Document436 pagesTutkish Grammar Academic Edition Yüksel Göknel 2012goknelyukselNo ratings yet
- Complete The Chart With The English Tenses: Structure and Use. Add ExamplesDocument5 pagesComplete The Chart With The English Tenses: Structure and Use. Add ExamplesAlondra VázquezNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test 1 Parts of SpeechDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test 1 Parts of SpeechANISA LIA AMOYELNo ratings yet
- Present TensesDocument18 pagesPresent TensesAisura GatauovaNo ratings yet
- Semantic: Final ExaminationDocument6 pagesSemantic: Final ExaminationFebriRotamaSilaban100% (1)
- Talking About Self (Materi X)Document10 pagesTalking About Self (Materi X)Erlangga PutraNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SentencesDocument10 pagesDirect and Indirect SentencesClorindaDonellaNo ratings yet
Bsee 23 Pos
Bsee 23 Pos
Uploaded by
orbesochristianneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bsee 23 Pos
Bsee 23 Pos
Uploaded by
orbesochristianneCopyright:
Available Formats
BSEE 23: STRUCTURE OF ENGLISH Collective noun
Word Categories - words that denote groups' collection or
multitude of something. These nouns are
Parts of speech
used as singular e.g., team, army, concert
- Every language consists on its basic - It can be confusing whether to use plural or
elements that are called words. As a singular verbs with collective nouns,
building is made by bricks; language is whether it points to the group working as
made by words. individuals or collectively in unison
- First, we will know about a word. A word is a - When a class unit is working in unison, a
speech sound or a combination of sound singular verb should be appropriate to use
having a particular meaning for an idea, - When they act separately, it is a must to use
object or thought and has a spoken or the plural verbs and pronouns
written form.
Concrete noun
- There are nine parts of speech in the
English grammar: noun, pronoun, verb, - the things which we can see or touch
adverb, adjective, preposition, conjunction, physically. This noun contrast with abstract
interjection and determiners. Some writes category of noun. For example: tree,
and websites count only eight parts of hammer, and pen. We can see them feel
speech and place determiner under the them or touch them. Some time we name it
category of adjectives material noun
- However, advance studies count determiner
Abstract noun
as a separate part of speech. These nine
parts of speech indicate how the words - things you cannot see or touch. Abstract
function within the sentence. An individual nouns do not have physical existence.
word may function as more than one part of These nouns are difficult to guess.
speech when used in various sentences Sometime learners get confused with
NOUN abstract noun and adjectives. Abilities and
emotions are abstract noun e.g., bravery,
- Everything is donated by a name and that joy, determination etc.
naming word is called a noun
Compound noun
Proper noun
- are nouns made up of more than one word.
- given name of a person, or a specific place For example: court-martial, pickpocket,
or thing. A proper noun always starts with a water bottle. Some compound nouns are
CAPITAL letter. All days and months are two words (e.g., peace pipe), some are
proper noun and start with capital letters hyphenated (e.g., play-off), and some have
(e.g., Sunday, March, and December). become single words (e.g., eye-opener)
Name of all person, name of countries,
Countable noun
name of oceans is counted in category of
proper nouns (e.g., Aaron, Japan, Atlantic) - noun that can be counted in numbers like
Common noun one pen, two cars with both a singular and a
plural form. (E.g., dog/dogs, pie/pies).
- the word used for a class of person, place,
Uncountable noun
or thing (e.g., person, city, and dog).
Common nouns are not capitalized unless - a noun without a plural form for example:
used in start of a sentence. There are some oxygen, patience. Such nouns do not
exceptions like in poetry where every word include counting. All abstract noun falls
of new line is capitalized. Something that is under the uncountable category of nouns
personified in poetry is also capitalized e.g.,
"So Nature incites them in their hearts"
(Prologue- Geoffrey Chaucer)
Gender of noun 4. Direct address
Masculine – Name of a person or thing is directly addressed
– Example: Dr. Smith, the pain in my leg is
- Duke
unbearable
- Mister
- Uncle Objective
- Grandfather
1. Direct object (Accusative
Feminine
- a word or phrase denoting the receiver of
- Duchess the action of a verb. (What, whom)
- Mistress - Example: my brother loaned me five dollars
- Auntie
2. Indirect object (dative)
- Grandmother
- the noun, noun phrase and pronoun that
Neuter
the action of a verb is performed for or
- Table directed to. (To whom, for what)
- Umbrella - Example: My brother loaned me five dollars.
- Cap
3. Object of the preposition
- Chair
- the noun or pronoun governed by the
Common
preposition in a prepositional phrase.
- Person - Example: When we got to the beach, we
- Parent knew we had chosen the right destination.
- Child
Possessive
- Spouse
- nouns that show ownership or a direct
Case of noun
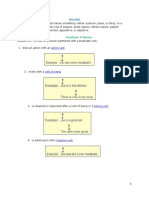
connection. Typically, singular possessive
- Refers to a manner of categorizing nouns, nouns use an apostrophe (‘) and the letter s
pronouns, adjectives, participles and at the end of the word to take the
numerals according to their traditionally possessive form.
corresponding grammatical functions within - For singular nouns, add apostrophe and “s”
a given phrase, clause, or sentence (‘s) for singular possessive. For plural
nouns, add only apostrophe (‘)
Nominative - For proper nouns ending in “s”, “z”, or “x”,
1. Subject of a verb add apostrophe
- . Of phrase is placed after a noun.
- the subject of a sentence - For compound possessive, both nouns are
- Example: people seek freedom possessive when the different entities
possess something separately. Only the last
noun is possessive when the different
2. Predicate nominative
entities share something, possessing it
- the noun that completes a linking and mean collectively.
the same as the subject.
PRONOUN
- Example: the anti-terrorism bill is already a
law - defined as a word that replaces a noun in a
sentence. It takes place of a noun.
3. Appositive
- Antecedent: a word which a pronoun stands
- a noun explains that another noun it follows or replaces. Ante = before
- Example: Father Randy, our family friend,
is a priest.
is NOT true with reflexive pronouns
because it will cause change in meaning, if
you remove them in sentences
Personal pronoun
Demonstrative pronoun
- Used as a simple substitute for proper
nouns. They serve as stunt doubles of - Demonstrative pronouns show, point, or
grammar which enable us to avoid too much exhibit. These are this, that, these, those.
repetition of proper noun passages. - Example: These are the items I bought after
- Personal pronouns have cases, number and spending 3 hours in the grocery.
person.
Indefinite pronoun
- Gender: The pronoun antecedent which
refers to the noun that the pronoun replaces - do not refer to any person or thing
can be masculine, feminine, or neutral. specifically like few, some, all, none.
- Example: Casey went to people’s park. She - Example: Only few committed to attend the
went to the park online meeting.
- Case: refers to the functions of a pronoun in
a sentence; nominative, objective or Interrogative pronoun
possessive. Since nouns can function as - Used to make questions. These are who,
both subject and object so can pronouns. whose, what, which.
- Example: She is an actress. The director - Example: Who is making that noise?
called her. That house over there is ours.
- Number: The number of a pronoun Distributive pronoun
depends on its antecedent.
- Denote persons or things of group or by
- Example: Richard and Raymond Gutierrez
group. They can be neither, either, each,
are both actors. They are also siblings in
etc.
real life.
- Person: refers to the point of view, or Neither
relationship of the speaker and the pronoun
antecedent. - is a pronoun that implies a negative
- First person: refers to the person speaking. meaning. Keep in mind that when 'neither' is
- Second Person refers to the person who is used as the subject pronoun of the
being spoken to. sentence, the verb that follows it must be
- Third Person refers to what or who is being singular
spoken about. Either
Reflexive pronoun - used to refer to two options or alternatives,
- The doer of the action in a sentence is also indicating that one or the other is applicable
the receiving end of that action. It can be or desirable. It is used with singular verbs
direct object, indirect object or object of the only when it is used as the subject pronoun
preposition of the sentence.
- Reflexive pronouns are mostly compound Each
personal pronouns
- used to refer to two or more people or
Intensive pronoun things, indicating that an action or property
- It precedes the noun which is often the noun applies to them individually. It can be used
immediately before the pronoun. They used with either a singular or a plural verb based
for emphasis. on the pronoun or noun it refers to.
- Example: the actress herself received the Reciprocal pronoun
awards
- Since intensive pronouns are used only for - Pronouns which express mutual or
emphasis, they can be removed without reciprocated relationship such as each other
affecting the meaning of the sentence. This and one another. When you want to refer
two people, most likely you use “each Interrogative adjective
other”. When you refer to more than two
- Pose a question and need a noun or
people, you will likely use “one another.”
pronoun by their side. Some of these are
- Example: We gave each other a hug after
what, which, and whose.
winning the dance competition.
Indefinite adjective
Relative pronoun
- adjectives point to non-specific items. Some
- Pronouns which join to clauses and relate or
of these are any, few, many, no and
refer back to their antecedent. These are
several
who, which, that, what, as, but, etc.
- Ex: The man who claimed he can stop a Personal adjective
calamity was mocked by the people.
- These are the personal titles used by a
Possessive pronoun noun.
- The man who claimed he can stop a Forms of adjective
calamity was mocked by the people.
- Ex; Those books are hers. Gradable
ADJECTIVE - Positive
- Comparative
- words which modify noun or pronoun - Superlative
Descriptive adjective Non gradable
- describes the nature, quality or attribute of a - Absolute
noun. It is also known as “Adjective of - Absolute adjectives:
Quality.” - True
- Ex; The pitiful dog got trapped in a filthy - Complete
cage. - Flawless
Numeric adjective - Final
- Alive
- It shows approximate amount of noun - Dead
- Also known as adjective of quantity - Full
- Types:
1.Definite: tells exact number
a. cardinal- counting number
b. ordinal- shows order, ranking or
sequence.
2. indefinite- tells inexact number (many,
all)
3, distributive- part of a whole (both,
another)
Demonstrative adjective
- describes the number and location of noun
or pronoun.
- Ex; Would you like these shoes?
Possessive adjective
- tells ownership and is usually followed by a
noun. Some of these adjectives are his,
her, my, our, their and your.
- Ex; Is that their house?
You might also like
- Sicilian CourseDocument69 pagesSicilian Coursejuliamagister100% (1)
- 3rd Grade Ela ReviewDocument4 pages3rd Grade Ela Reviewapi-377242371100% (1)
- Engpro ReviewerDocument3 pagesEngpro ReviewerPrincess Gabrielle BrotonelNo ratings yet
- Major 3 IreneDocument23 pagesMajor 3 IreneJude Cedric ReyesNo ratings yet
- ELE123 Structure of English LessonsDocument110 pagesELE123 Structure of English LessonsRain Raven Barlizo LabanzaNo ratings yet
- Virtual Training Handbook I - English Communication Skill TrainingDocument18 pagesVirtual Training Handbook I - English Communication Skill TrainingAlfred Mc Donald Dillupac100% (1)
- Such As Business in Business MeetingDocument15 pagesSuch As Business in Business MeetingPhoebe Cates Tayanes ViscaynoNo ratings yet
- Bus Com 10Document19 pagesBus Com 10Elijah ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech in EnglishDocument30 pagesParts of Speech in EnglishRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter2grammaticalmetalanguage 121204161708 Phpapp02Document6 pagesChapter2grammaticalmetalanguage 121204161708 Phpapp02Cristine Joy R. QuizonNo ratings yet
- Virtual Training Handbook I - English Communication Skill TrainingDocument68 pagesVirtual Training Handbook I - English Communication Skill TrainingMarella OrqueroNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument4 pagesPurposive CommunicationASTRA FAYE QUEENA DELENANo ratings yet
- Partsof Speechin English GrammarDocument16 pagesPartsof Speechin English GrammarToledo, Denise Klaire M.100% (1)
- Part of SpeechDocument20 pagesPart of SpeechGewie Shane Blanco SumayopNo ratings yet
- Noun - PronounDocument19 pagesNoun - PronounAlula FarzanaNo ratings yet
- English Language TerminologyDocument59 pagesEnglish Language TerminologyDinesh PrabuNo ratings yet
- 3 Grade Reading & Language Arts CCGPS Study Guide: Nouns Nouns AbbreviationsDocument5 pages3 Grade Reading & Language Arts CCGPS Study Guide: Nouns Nouns Abbreviationsapi-327816044No ratings yet
- Grammatical-Categories 2.5Document12 pagesGrammatical-Categories 2.5arl somarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Structures Content WordsDocument28 pagesChapter 1 Structures Content WordsJOHN LACETER URIAN ORATANo ratings yet
- Your essential LPAT last minute revision notes - SELECTED - 複製Document5 pagesYour essential LPAT last minute revision notes - SELECTED - 複製Bryan WongNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Assessment of Grammar Midterm CoverageDocument4 pagesTeaching and Assessment of Grammar Midterm CoverageRoselyn AlbisoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Introduction and NounsDocument3 pagesUnit 1. Introduction and NounsEmz GelogoNo ratings yet
- Types of NounsDocument5 pagesTypes of NounsAlexis ViernesNo ratings yet
- LET English Major LanguageDocument39 pagesLET English Major LanguageJustin Jones NotarteNo ratings yet
- English LecturesDocument6 pagesEnglish LecturesAndrei Sy JaviertoNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesParts of Speechjerica tanaNo ratings yet
- Biru Hijau Imut Ceria Tugas Presentasi Kelompok - 20240317 - 230007 - 0000Document24 pagesBiru Hijau Imut Ceria Tugas Presentasi Kelompok - 20240317 - 230007 - 0000saputsaput251No ratings yet
- EC Second Semester FinalsDocument10 pagesEC Second Semester Finalschrisbel.simonNo ratings yet
- Winch 9780195529098 SCDocument37 pagesWinch 9780195529098 SCArti SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument10 pagesParts of SpeechSaikat SahaNo ratings yet
- BSEd 1A - Structure of English Final Requirement.Document20 pagesBSEd 1A - Structure of English Final Requirement.Claire Azucenas ApatanNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument18 pagesParts of SpeechSakunthala RajeshNo ratings yet
- Noun ReportDocument16 pagesNoun ReportAlleina UwUNo ratings yet
- English - CompleteDocument24 pagesEnglish - Completegarciaandrea236No ratings yet
- LET English Major LanguageDocument25 pagesLET English Major LanguageSharmaine Llasus FerrarezNo ratings yet
- READING SKILL iiDocument3 pagesREADING SKILL iizineNo ratings yet
- NounsDocument44 pagesNounsRoger Donoso BarralNo ratings yet
- 8 Parts of SpeechDocument4 pages8 Parts of SpeechTrisha CalmaNo ratings yet
- Contranstive Analysis (Aprida Simbolon 17120272)Document13 pagesContranstive Analysis (Aprida Simbolon 17120272)Cindi Novera ManullangNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument13 pagesParts of SpeechCherish PimmaengNo ratings yet
- Eng 001Document5 pagesEng 001Eldon JulaoNo ratings yet
- English Proficiency ReviewerDocument4 pagesEnglish Proficiency ReviewerlenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-Structure of EnglishDocument17 pagesLesson 1-Structure of EnglishMay Rhea Siapno LopezNo ratings yet
- CEBGADocument28 pagesCEBGACZYSTYNo ratings yet
- CEBallDocument70 pagesCEBallCZYSTYNo ratings yet
- Nouns: Action VerbDocument15 pagesNouns: Action VerbJerica PalomariaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Elfrida BakaraDocument34 pagesGrammar Elfrida BakaraLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- NounDocument15 pagesNounVanshNo ratings yet
- English: 1. Concrete Noun - Noun That CanDocument4 pagesEnglish: 1. Concrete Noun - Noun That CanIrish VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- NounDocument11 pagesNounPalak BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- P.eng Part 2Document5 pagesP.eng Part 2Shubham kumarNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesParts of SpeechKenneth ReyesNo ratings yet
- Signals of Syntactic StructureDocument4 pagesSignals of Syntactic StructureJohn Kelvin RodilNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - MamadDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 1 - MamadJehan BaruaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Terms and What They MeanDocument4 pagesGrammar Terms and What They Meanmuslimuser610No ratings yet
- Grammar - Parts of SpeechDocument17 pagesGrammar - Parts of Speechcaptainnkumar1043100% (1)
- LET Material (Language) 1. Structure of English Basic English Structures and RulesDocument35 pagesLET Material (Language) 1. Structure of English Basic English Structures and RulesCherrie Myth MonaresNo ratings yet
- LET English Major LanguageDocument35 pagesLET English Major LanguageJeremiah FameronagNo ratings yet
- Person Animal Place Thing Idea: Identifying A NounDocument4 pagesPerson Animal Place Thing Idea: Identifying A NounKryzl Rey del FierroNo ratings yet
- English Plus 1 Year 5: Starter Unit: Affirmative and Negative StatementsDocument12 pagesEnglish Plus 1 Year 5: Starter Unit: Affirmative and Negative StatementsAsmohaina Mohamed100% (1)
- Use of English Continuidad. 18-24 Mayo AKDocument3 pagesUse of English Continuidad. 18-24 Mayo AKLucía RiveroNo ratings yet
- Participles, Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument4 pagesParticiples, Gerunds and InfinitivesAhmet Celal KavcarNo ratings yet
- LM-0354 Gramatica Inglesa III PresenDocument6 pagesLM-0354 Gramatica Inglesa III PresenLuis MongeNo ratings yet
- Janez Ore (Nik: University of Ljubljana, LjubljanaDocument8 pagesJanez Ore (Nik: University of Ljubljana, Ljubljanagoran trajkovskiNo ratings yet
- Elementary Unit 12bDocument2 pagesElementary Unit 12bViviana LeguizamoNo ratings yet
- Intervention Material in English 9 AdverbDocument13 pagesIntervention Material in English 9 AdverbCharycel de Guzman100% (2)
- Verb Tenses, Affirmative, Negative & InterrogativeDocument12 pagesVerb Tenses, Affirmative, Negative & InterrogativeNadya OctavianaNo ratings yet
- ENHANCED ENGLISH7 - Q1 - LAS - Wk5Document5 pagesENHANCED ENGLISH7 - Q1 - LAS - Wk5Dauis National High SchoolNo ratings yet
- PDF Basic German Jolene Wochenske Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Basic German Jolene Wochenske Ebook Full Chapterotto.gliem566100% (4)
- Teste Diagnostico de Ingles 5º AnoDocument3 pagesTeste Diagnostico de Ingles 5º AnoMónica SantosNo ratings yet
- SBI PO Preliminary Model Paper 15Document36 pagesSBI PO Preliminary Model Paper 15Deepak SinhaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of The Language of ScienceDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of The Language of ScienceKurt OrfanelNo ratings yet
- English Basic Grammar by Color Association Metodo Opaa WwwenglearningsolutioncomarDocument17 pagesEnglish Basic Grammar by Color Association Metodo Opaa WwwenglearningsolutioncomarengleasolNo ratings yet
- 2015.458637.teach Yourself Hindustani TextDocument356 pages2015.458637.teach Yourself Hindustani TextIalmisry100% (1)
- French 3 Semester 1 Review Au LaboDocument4 pagesFrench 3 Semester 1 Review Au Laboapi-290605652No ratings yet
- Pokus NG PandiwaDocument4 pagesPokus NG PandiwaMaritess MacalingaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate English Grammar "Summarize Chapter 13: Adjective Clause"Document20 pagesIntermediate English Grammar "Summarize Chapter 13: Adjective Clause"Arga SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Short Test 2A: GrammarDocument1 pageUnit 3 Short Test 2A: GrammarIzabella Tar100% (1)
- Grammar of The Hawaiian Language PDFDocument168 pagesGrammar of The Hawaiian Language PDFdolphinsofshamballaNo ratings yet
- Cappello Cambridge Celta Assignment 2 Language Related Task PDF FreeDocument9 pagesCappello Cambridge Celta Assignment 2 Language Related Task PDF Freeheh199179No ratings yet
- GEO246 Topic 5Document2 pagesGEO246 Topic 5hihihihiNo ratings yet
- Tutkish Grammar Academic Edition Yüksel Göknel 2012Document436 pagesTutkish Grammar Academic Edition Yüksel Göknel 2012goknelyukselNo ratings yet
- Complete The Chart With The English Tenses: Structure and Use. Add ExamplesDocument5 pagesComplete The Chart With The English Tenses: Structure and Use. Add ExamplesAlondra VázquezNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test 1 Parts of SpeechDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test 1 Parts of SpeechANISA LIA AMOYELNo ratings yet
- Present TensesDocument18 pagesPresent TensesAisura GatauovaNo ratings yet
- Semantic: Final ExaminationDocument6 pagesSemantic: Final ExaminationFebriRotamaSilaban100% (1)
- Talking About Self (Materi X)Document10 pagesTalking About Self (Materi X)Erlangga PutraNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SentencesDocument10 pagesDirect and Indirect SentencesClorindaDonellaNo ratings yet