Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Climate of The Past
Climate of The Past
Uploaded by
Joyce Ann0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views22 pagesThe document summarizes evidence of past climates from geological records such as corals, tree rings, ice cores, pollen grains, and glaciers. It then describes several periods of climate change in the geologic past from the Cenozoic era to the present. These include the Paleocene epoch where volcanic ash dissipated and temperatures rose after an asteroid explosion, the Eocene with rapid warming from tectonic activity, and the Pleistocene with rapid glacier formation until temperatures rose again in the 20th century during the industrial revolution.
Original Description:
Original Title
CLIMATE OF THE PAST
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes evidence of past climates from geological records such as corals, tree rings, ice cores, pollen grains, and glaciers. It then describes several periods of climate change in the geologic past from the Cenozoic era to the present. These include the Paleocene epoch where volcanic ash dissipated and temperatures rose after an asteroid explosion, the Eocene with rapid warming from tectonic activity, and the Pleistocene with rapid glacier formation until temperatures rose again in the 20th century during the industrial revolution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views22 pagesClimate of The Past
Climate of The Past
Uploaded by
Joyce AnnThe document summarizes evidence of past climates from geological records such as corals, tree rings, ice cores, pollen grains, and glaciers. It then describes several periods of climate change in the geologic past from the Cenozoic era to the present. These include the Paleocene epoch where volcanic ash dissipated and temperatures rose after an asteroid explosion, the Eocene with rapid warming from tectonic activity, and the Pleistocene with rapid glacier formation until temperatures rose again in the 20th century during the industrial revolution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 22
Presented by:
JOYCE ANN MARIE AMARILLE
CLIMATES
G E OL OGIC LIVING
E V E NTS I N T H INGS I N OF THE
R O CK S ROCKS PAST
CLIMATES
OF THE
PAST
•
•
CLIMATES •
OF THE •
•
PAST •
Corals build their hard skeletons
from calcium carbonate, a mineral
extracted from sea water. The
carbonate contains isotopes of
oxygen, as well as trace metals, that
can be used to determine the
temperature of the water in which the
coral grew.
Coral from Galapagos
Since tree growth is
influenced by climatic conditions,
patterns in tree-ring widths,
density, etc. reflect variations in
climate.
• Ice accumulates from
snowfall compressed over
many thousands of years.
• Ice cores contain dust, air
bubbles, or isotopes of oxygen,
that can be used to interpret
the past climate of that area.
• “the gold standard” of paleo
climatologists.
• Pollen grains are well preserved in
the sediment layers of ponds, lakes or
the ocean.
• Analysis of pollen grains in each layer
tell us what kinds of plants were
growing at the time the sediment was
deposited. Inferences can then be
made about the climate based on the
types of plants found each layer.
Pollen spores from the
Florida Everglades
• Scientists have recorded 169
glaciers from around the world.
• Study of glacier length over time
indicates the change in
temperature.
Aerial view of glaciers
• Direct measurements of
temperature from boreholes drilled
into the Earth’s crust.
• Changes in temperature have slowly
diffused downward, warming or
cooling layers meters below the
surface.
*Asteroid explosion causing
widespread forest fires.
*Explosion causes dust sucked
in the air resulting to warmer
temperatures.
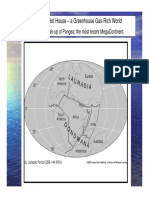
Cenozoic – Paleocene epoch
*volcanic ash clouds dissipated
and temperatures rose rapidly
paving the way in repopulating the
Earth.
Eocene epoch
*tectonic activity and volcanic
eruptions causes rapid rise in
temperature.
Oligocene epoch
*weakening of greenhouse
effect thus temperatures drop
rapidly.
MIOCENE EPOCH
*abrupt cooling and formation
of glaciers
PLEISTOCENE
*rapid rate of formation of
glaciers
*warm air cannot travel due to
formation of continents
*rise in temperature causes
the glaciers to melt and rise of
sea levels.
*paving the way for savannahs
and organisms to repopulate.
20th CENTURY – INDUSTRIAL
REVOLUTION
*rise in global temperature because
of high CO2 emissions brought
about by factories and man-made
activities
https://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-
nature/everything-you-ever-wanted-know-about-earths-
past-climates-180968797/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TwIPj8GtHo0
https://www.slideshare.net/cdenef/climate-change-in-
the-past-palaeoclimate
You might also like
- Action Plan For Waste DisposalDocument12 pagesAction Plan For Waste DisposalLea Paquibot33% (3)
- Oil and Gas Notes PDFDocument25 pagesOil and Gas Notes PDFstarway india100% (1)
- 5.3 and 5.4 Climate Change Exam QuestionsDocument10 pages5.3 and 5.4 Climate Change Exam QuestionsÖykü TuralNo ratings yet
- 2 Environmental EpidemiologyDocument33 pages2 Environmental EpidemiologyRatna Ismail80% (5)
- GS 503: Biostratigraphy & Paleoecology: Lecture 2: Climate Archives, Data & ModelDocument23 pagesGS 503: Biostratigraphy & Paleoecology: Lecture 2: Climate Archives, Data & Modelmd shohagul islamNo ratings yet
- Felix Changes in World ClimateDocument36 pagesFelix Changes in World ClimateKimberly RodriguezNo ratings yet
- NIrmal PPT Ice Age FinalDocument16 pagesNIrmal PPT Ice Age FinalNirmal MahapatraNo ratings yet
- History of Life On EarthDocument43 pagesHistory of Life On EarthNadia CzeredreckiNo ratings yet
- 6 - Studying Clues To Past ClimateDocument12 pages6 - Studying Clues To Past Climateshabad700No ratings yet
- HYDROTHERMALDocument2 pagesHYDROTHERMALMike GuerzonNo ratings yet
- W PaleoclimatologyDocument15 pagesW PaleoclimatologyGonzalo DaccoNo ratings yet
- Hothouse Intro 2010Document30 pagesHothouse Intro 2010cherNo ratings yet
- What Is Climate ?Document6 pagesWhat Is Climate ?Jaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 5: Developing of The Biosphere: Urey and Miller ExperimentDocument26 pagesModule 5: Developing of The Biosphere: Urey and Miller ExperimentFrederick JoshsonNo ratings yet
- GeonewsDocument4 pagesGeonewsapi-299813057No ratings yet
- Dasar Dasar Kimia PerairanDocument30 pagesDasar Dasar Kimia PerairanAnggi DwiNo ratings yet
- Environmental and Vedic Period by P. N. PhadkeDocument134 pagesEnvironmental and Vedic Period by P. N. Phadkeparidnyaa100% (1)
- GWDennis AveryDocument32 pagesGWDennis AverySteven.Republitarian6409No ratings yet
- L12 - Chemistry of The AtmosphereDocument40 pagesL12 - Chemistry of The AtmosphereHaneul KImNo ratings yet
- Earthscience Reviewer Q1Document21 pagesEarthscience Reviewer Q1sleighangeloNo ratings yet
- Global Warming and Climate ChangeDocument46 pagesGlobal Warming and Climate ChangeTaleb AbboudNo ratings yet
- Group 3:volcanoes and The Interior of The EarthDocument35 pagesGroup 3:volcanoes and The Interior of The EarthTrinna AbrigoNo ratings yet
- Paleoclimatology Geology NotesDocument15 pagesPaleoclimatology Geology NotesakbarsohailshaikhNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and The OzoneDocument43 pagesClimate Change and The OzoneFelyn Dee EncontroNo ratings yet
- Evidence For Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesEvidence For Plate TectonicsKoray Saliah0% (1)
- Degroot - Little Ice Age LessonsDocument13 pagesDegroot - Little Ice Age Lessonsshu chuangNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Topic2ClimateChangeDocument40 pagesUNIT 1 Topic2ClimateChangeIlayda UludagNo ratings yet
- Climate Change - Bacc1aDocument74 pagesClimate Change - Bacc1aangelikaNo ratings yet
- 142 Sol Amazing Facts Round RobinDocument5 pages142 Sol Amazing Facts Round RobinIchal PuzoNo ratings yet
- ATS351 Lecture13Document38 pagesATS351 Lecture13scribd.b012bdNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Week 1Document6 pagesEarth Science Week 1Aeila WpNo ratings yet
- Module 10 Mans Impact On The EnvironmentDocument53 pagesModule 10 Mans Impact On The Environmentayn pizzaNo ratings yet
- CoralsDocument11 pagesCoralsapi-343679675No ratings yet
- P E T M: Aleocene Ocene Hermal AximumDocument12 pagesP E T M: Aleocene Ocene Hermal AximumabhishekNo ratings yet
- Chapt 23 MarshakDocument32 pagesChapt 23 Marshak周牮No ratings yet
- 14.L 37 38 Cenozoic Climate Part 1Document30 pages14.L 37 38 Cenozoic Climate Part 1THE TERMINATORNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles: Why Are Biogeochemical Cycles Essential To Long-Term Life On Earth?Document29 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles: Why Are Biogeochemical Cycles Essential To Long-Term Life On Earth?Ralph Ian MalvarNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1: Global Climate Change: Evidence, Causes and ConsequencesDocument38 pagesUNIT-1: Global Climate Change: Evidence, Causes and ConsequencesroshanNo ratings yet
- 2 Continents Sources of SedimentDocument58 pages2 Continents Sources of Sedimentikhsansyah pratamaNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument59 pagesClimate Changeerickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Made By:-Krishan KumarDocument28 pagesGlobal Warming: Made By:-Krishan KumarPraveen ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- History of Life On EarthDocument3 pagesHistory of Life On Earthcabusorapauline5No ratings yet
- Changes in World Climate: Lesson 13.3Document42 pagesChanges in World Climate: Lesson 13.3ACAD COOR SCIENCENo ratings yet
- Why Earth Is HabitableDocument26 pagesWhy Earth Is Habitablestormfury150% (2)
- Condensation and Cloud FormationDocument34 pagesCondensation and Cloud FormationPatrick CelsoNo ratings yet
- Climate & Climate ChangeDocument43 pagesClimate & Climate ChangeAngel Joy AspillaNo ratings yet
- Speleothems and Lake SedimentsDocument2 pagesSpeleothems and Lake Sedimentslomba fotoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Kay Maam JDocument6 pagesReviewer Kay Maam JChloe EisenheartNo ratings yet
- 5.1. Oceanic, Atmospheric and Hydrologic CyclesDocument96 pages5.1. Oceanic, Atmospheric and Hydrologic CyclesPirathiish RajanNo ratings yet
- Paleoceanography and Thermohaline CirculationDocument2 pagesPaleoceanography and Thermohaline Circulationlomba fotoNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time Scale - PPTX (Autosaved)Document47 pagesGeologic Time Scale - PPTX (Autosaved)Kristina DavidNo ratings yet
- L5 CCST9023 ClimateDocument84 pagesL5 CCST9023 ClimateDaniel RadcliffNo ratings yet
- Energy RevisionDocument28 pagesEnergy Revisionapi-407286530100% (2)
- Climate Change VocabularyDocument3 pagesClimate Change VocabularymohammedNo ratings yet
- Biosteering in Petroleum ExplorationDocument36 pagesBiosteering in Petroleum Explorationshubham panchalNo ratings yet
- History of The EarthDocument7 pagesHistory of The EarthnayemNo ratings yet
- Địa chấn tổngDocument466 pagesĐịa chấn tổngNhi VoNo ratings yet
- Sedimentation and Oil/Gas FormationDocument33 pagesSedimentation and Oil/Gas FormationTriều TrầnNo ratings yet
- COR 009 Perodical-1Document3 pagesCOR 009 Perodical-1Margie MarklandNo ratings yet
- Structure of The EarthDocument58 pagesStructure of The EarthManasiNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument21 pagesGlobal WarmingVickyVigneshNo ratings yet
- Lecture Introduction To Petroleum GeologyDocument15 pagesLecture Introduction To Petroleum Geologykurddoski28No ratings yet
- Sudden Spring: Stories of Adaptation in a Climate-Changed SouthFrom EverandSudden Spring: Stories of Adaptation in a Climate-Changed SouthRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- SDGs in BangladeshDocument35 pagesSDGs in Bangladeshmoshiul rockyNo ratings yet
- Green BLDG Swapneel PDFDocument21 pagesGreen BLDG Swapneel PDFKulal SwapnilNo ratings yet
- Austria PowerpointDocument6 pagesAustria PowerpointSammie WainainaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle PowerPointDocument17 pagesCarbon Cycle PowerPointAssignment JamNo ratings yet
- Environmental-Awareness-by - MVDocument20 pagesEnvironmental-Awareness-by - MVFatima Valencia GecosoNo ratings yet
- Allocation and Usage of Water For Irrigation Governance in Sta. Cruz River Watershed, Laguna, PhilippinesDocument19 pagesAllocation and Usage of Water For Irrigation Governance in Sta. Cruz River Watershed, Laguna, PhilippinesJhanina CapicioNo ratings yet
- Nicole Reiff Resume 2019Document2 pagesNicole Reiff Resume 2019Nikki ReiffNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 - Lec-2Document19 pagesCh-2 - Lec-2Tural GojayevNo ratings yet
- HB - Site Analysis MumbaiDocument1 pageHB - Site Analysis MumbaiIsha SinghNo ratings yet
- Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication: EnvironmentDocument20 pagesOxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication: EnvironmentMosor VladNo ratings yet
- STSTSTS2015Document4 pagesSTSTSTS2015AidhONo ratings yet
- LEED v4.1 Residential Single Family Rating System 1.2020Document69 pagesLEED v4.1 Residential Single Family Rating System 1.2020Azzreiz AzzarainNo ratings yet
- MRFDocument6 pagesMRFMiriam Cocos100% (1)
- Abiotic and Biotic Factors DFDocument2 pagesAbiotic and Biotic Factors DFNancy MmlndNo ratings yet
- "Soil Quality: Why and How?" Rashmi C. M. and PradeepDocument4 pages"Soil Quality: Why and How?" Rashmi C. M. and PradeepRashmi C M RashmiNo ratings yet
- Indicators Todd Litman 2023Document117 pagesIndicators Todd Litman 2023Pedro DeckerNo ratings yet
- Notes Natural VegetationDocument3 pagesNotes Natural VegetationannaNo ratings yet
- 396ce15005 PPT On Rain Water HarvestingDocument11 pages396ce15005 PPT On Rain Water HarvestingHP PAVILIONNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management A Case Study of Jaipur City IJERTCONV4IS23003Document4 pagesSolid Waste Management A Case Study of Jaipur City IJERTCONV4IS23003manjuNo ratings yet
- MicroplasticDocument2 pagesMicroplasticjayashri ganesanNo ratings yet
- Literary Criticism ActivityDocument3 pagesLiterary Criticism ActivityJunrey De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3745-16 Stack Height RequirementsDocument6 pagesChapter 3745-16 Stack Height RequirementsAnaibar TarikNo ratings yet
- Hard&Soft Landscape ElementsDocument13 pagesHard&Soft Landscape Elementsbluemirage11100% (1)
- 6 Ecology1Document20 pages6 Ecology1Bhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Paola SassiDocument21 pagesPaola Sassisehgal91No ratings yet
- 20 Đề thi thử tốt nghiệp THPT năm 2021 - có đáp ánDocument131 pages20 Đề thi thử tốt nghiệp THPT năm 2021 - có đáp ánThanh NganNo ratings yet
- Design of Trash Trap System in Tanduyan River, Barangay Tanduyan, Ajuy, IloiloDocument21 pagesDesign of Trash Trap System in Tanduyan River, Barangay Tanduyan, Ajuy, IloiloConie CatapanNo ratings yet