Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sse 2 - Finals
Sse 2 - Finals
Uploaded by
Alexie Anne MariñoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- TAP - School Beautification ProjectDocument5 pagesTAP - School Beautification ProjectMaestro Varix100% (7)
- UDL Lesson Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesUDL Lesson Plan TemplatePsiho LoguseNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log For Fundamentals of ABMDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Log For Fundamentals of ABMVanessa Lou Torejas100% (2)
- Differentiates Between Equations and InequalitiesDocument7 pagesDifferentiates Between Equations and InequalitiesMarc Galos100% (2)
- SLT Working Privately in GWGTN RegionDocument2 pagesSLT Working Privately in GWGTN Regioncdw27No ratings yet
- Cot DLL Filipino Q 2Document3 pagesCot DLL Filipino Q 2Dorothy Jean100% (5)
- Edu601 Lesson 6-11Document2 pagesEdu601 Lesson 6-11Jo MomNo ratings yet
- Cot Filipino Q 2Document3 pagesCot Filipino Q 2Jane Bunuan SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Compressed Escuela Normal ClassroommanagementDocument28 pagesCompressed Escuela Normal Classroommanagementjennybacay.12345No ratings yet
- Learning Task 5 Evero CarinapassDocument23 pagesLearning Task 5 Evero CarinapassPlatero Roland100% (1)
- Principles and Strategies of Teaching 2020 AND 2021Document9 pagesPrinciples and Strategies of Teaching 2020 AND 2021IGNACIO JULLIE MAENo ratings yet
- Assessment ReviewerDocument4 pagesAssessment ReviewerAngelica TañedoNo ratings yet
- Lesson DesignDocument3 pagesLesson DesignKen DonkohNo ratings yet
- Principles and Strategies of TeachingDocument19 pagesPrinciples and Strategies of Teachingnhicabonit7No ratings yet
- Unit 3 (Prof - Ed 8)Document2 pagesUnit 3 (Prof - Ed 8)CyanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On The Preparation of PIVOT I D E A Lesson Exemplars RM No. 296 s.2020Document61 pagesGuidelines On The Preparation of PIVOT I D E A Lesson Exemplars RM No. 296 s.2020Jonathan Marc Fule Castillo100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan PerdevDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan PerdevMuffy FernandezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An FEI Lesson.1109Document2 pagesAnatomy of An FEI Lesson.1109arudenstineNo ratings yet
- Y4 Week 8 or 9Document6 pagesY4 Week 8 or 9LINANo ratings yet
- Action Plan RDTDocument2 pagesAction Plan RDTadadNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson PlanNhico BryanNo ratings yet
- LP Uri NG Pangungusap g6Document4 pagesLP Uri NG Pangungusap g6Wynn Gargar TormisNo ratings yet
- TTL Lesson 6Document6 pagesTTL Lesson 6Katlyn MRNo ratings yet
- Wiggins Mctighe Ubd Nutshell PDFDocument4 pagesWiggins Mctighe Ubd Nutshell PDFNeda KahnNo ratings yet
- The Task Cycle (Autoguardado)Document14 pagesThe Task Cycle (Autoguardado)Nadia SimónNo ratings yet
- UMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: Ccss - Math.Content - Hsf.Bf.B.5Document3 pagesUMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: Ccss - Math.Content - Hsf.Bf.B.5api-335961271No ratings yet
- TEMPLATEDocument6 pagesTEMPLATECaryn MorataNo ratings yet
- DLL - TTSCUR FinalDocument5 pagesDLL - TTSCUR FinalKenneth AminullaNo ratings yet
- Teaching ApproachesDocument3 pagesTeaching Approachesapi-546696759No ratings yet
- Week H - Embodied Spirit3Document4 pagesWeek H - Embodied Spirit3JonalynNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6 (TTSC) - ALILIN, RENA ROSE S. BEED 3A DAYDocument5 pagesExercise 6 (TTSC) - ALILIN, RENA ROSE S. BEED 3A DAYJeremy NeriNo ratings yet
- NVSD Unit Planner 1Document2 pagesNVSD Unit Planner 1api-533726217No ratings yet
- Task October 15 IIDocument2 pagesTask October 15 IIMera Largosa ManlaweNo ratings yet
- Module 3A Lesson 2 RioDocument7 pagesModule 3A Lesson 2 RioRioVierraMadriagaMallaNo ratings yet
- Comparative EssayDocument2 pagesComparative Essayapi-335961418No ratings yet
- Accteach Prelims Chapter 1&2Document6 pagesAccteach Prelims Chapter 1&2KDumpNo ratings yet
- Accteach PrelimsDocument6 pagesAccteach PrelimsKDumpNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 MergedDocument9 pages1 2 3 4 MergedAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- UbD in A NutshellDocument4 pagesUbD in A NutshellTeachThoughtNo ratings yet
- Accteach Prelims Chapter 1&2Document7 pagesAccteach Prelims Chapter 1&2KDumpNo ratings yet
- Learning Episode: The Meaning of CurriculumDocument132 pagesLearning Episode: The Meaning of CurriculumMaela Pollen Elumba YemaNo ratings yet
- Cot Filipino Q 2Document4 pagesCot Filipino Q 2Jane Bunuan SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Teaching Learning Process and Curriculum Development With Adaptaion and ModificationDocument21 pagesTeaching Learning Process and Curriculum Development With Adaptaion and ModificationAmy F. CabfeoNo ratings yet
- DLL Philosophy QUARTER 2 WEEK 2Document3 pagesDLL Philosophy QUARTER 2 WEEK 2checkaliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9Document2 pagesLesson 9nkosiNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 3 (K-W-L)Document2 pagesLearning Task 3 (K-W-L)RHEA JOY VILLASNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument6 pagesMathematicsMatias, Emie Rose Q.No ratings yet
- Annotation-English 9 First Classroom Observation July 30, 2019Document3 pagesAnnotation-English 9 First Classroom Observation July 30, 2019Rey Salomon Vistal100% (4)
- UMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesUMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Templateapi-335961271No ratings yet
- UbD Workshop Part 3Document30 pagesUbD Workshop Part 3RossNo ratings yet
- DLL - Week - 10 - Statistics and ProbabilityDocument3 pagesDLL - Week - 10 - Statistics and ProbabilityRoboCopyNo ratings yet
- EDTM 312 LU5 Group AssignmentDocument4 pagesEDTM 312 LU5 Group Assignmentchakaolebogeng3No ratings yet
- Educ 6 PrelimsDocument2 pagesEduc 6 PrelimsDextroi HombrebuenoNo ratings yet
- DIASS DLL Week 2Document3 pagesDIASS DLL Week 2aireen rose manguiranNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Sorensen Classroom Observation Form January 15 2021Document8 pagesBenjamin Sorensen Classroom Observation Form January 15 2021api-380337066No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Filipino 6 Quarter 3Document3 pagesLesson Plan in Filipino 6 Quarter 3Wynn Gargar Tormis80% (5)
- Kit Oseias H. Castillo - TEACHING INTERN ONLINE DEMONSTRATION LESSONDocument3 pagesKit Oseias H. Castillo - TEACHING INTERN ONLINE DEMONSTRATION LESSONKit Oseias H. CastilloNo ratings yet
- Oc Week 1 DLL - F. DuncabDocument4 pagesOc Week 1 DLL - F. DuncabFatima DuncabNo ratings yet
- RSML - 5 - e - 8 Etsot - Eleot AlignmentDocument2 pagesRSML - 5 - e - 8 Etsot - Eleot AlignmentkhalafNo ratings yet
- UMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesUMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Templateapi-335961271No ratings yet
- OB26a Teacher Reflection For Math LessonDocument2 pagesOB26a Teacher Reflection For Math Lessonsherdan genistonNo ratings yet
- MICROECONOMICS LECTURE - To EditDocument11 pagesMICROECONOMICS LECTURE - To EditAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- PATHFIT To PrintDocument4 pagesPATHFIT To PrintAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Geog 1 - FinalsDocument10 pagesGeog 1 - FinalsAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Sse 1 - FinalsDocument3 pagesSse 1 - FinalsAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Sse 2 - FinalsDocument9 pagesSse 2 - FinalsAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Task Sheet 1.4 - 3Document3 pagesTask Sheet 1.4 - 3Jerel John CalanaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Study Essay 2Document4 pagesLesson Study Essay 2api-284319074No ratings yet
- Pass/Fail 85% F: Assessment, Scoring, and EvaluationDocument23 pagesPass/Fail 85% F: Assessment, Scoring, and EvaluationParag NaikNo ratings yet
- CN3121 Project 1 - 2011Document2 pagesCN3121 Project 1 - 2011Jing WangNo ratings yet
- E-Rancangan Pengajaran Harian: (Yussry@Zeynorene B. Tukimin) Guru Besar SK LengaDocument14 pagesE-Rancangan Pengajaran Harian: (Yussry@Zeynorene B. Tukimin) Guru Besar SK Lengasharkies1No ratings yet
- By Diane Rich: Bang, Bang! Gun Play, and Why Children Need ItDocument6 pagesBy Diane Rich: Bang, Bang! Gun Play, and Why Children Need Itapi-38412056No ratings yet
- ENTREP-DLL-Mar 20-24 Week 6Document3 pagesENTREP-DLL-Mar 20-24 Week 6Mary Baltazar BulataoNo ratings yet
- Isaac Lopez Integrated School: The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument5 pagesIsaac Lopez Integrated School: The Problem and Its BackgrounddaneNo ratings yet
- ECD SyllabusDocument1 pageECD SyllabusIt's MeNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q1 - W4Document6 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q1 - W4SHERYL SAUDANNo ratings yet
- Raz ld48 DaydadDocument12 pagesRaz ld48 DaydadNguyễn Anh MinhNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Praktikum EnglishDocument13 pagesJurnal Praktikum Englisharon hasanNo ratings yet
- Narrative On The Pod MonitoringDocument3 pagesNarrative On The Pod MonitoringHanz Albrech AbellaNo ratings yet
- Educational Psychology: An International Journal of Experimental Educational PsychologyDocument13 pagesEducational Psychology: An International Journal of Experimental Educational PsychologyFahimeh MoafianNo ratings yet
- Ipcrf-Individual-Development-Plan-Itable JMDocument2 pagesIpcrf-Individual-Development-Plan-Itable JMJohn Michael ItableNo ratings yet
- Week 2-3Document3 pagesWeek 2-3api-367840311No ratings yet
- Individual Differences in L2 AcquisitionDocument15 pagesIndividual Differences in L2 Acquisitionmajtwin100% (2)
- Tle dm7-8 q1 Mod2 SDOv1-MGKaDocument32 pagesTle dm7-8 q1 Mod2 SDOv1-MGKaAldea ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- My First Cot GR.3Document4 pagesMy First Cot GR.3Nardita CastroNo ratings yet
- Undergraduate Students' Perspectives On Digital Competence and Academic Literacy in A Spanish UniversityDocument2 pagesUndergraduate Students' Perspectives On Digital Competence and Academic Literacy in A Spanish UniversityFernando GuzmánNo ratings yet
- SPJ 4 - Quarter 4 - Learning Activity SheetsDocument44 pagesSPJ 4 - Quarter 4 - Learning Activity SheetsLovilyn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Technical University of Mombasa: TUM Is ISO 9001:2015 CertifiedDocument5 pagesTechnical University of Mombasa: TUM Is ISO 9001:2015 Certifiedjoel collinsNo ratings yet
- Activity-7 7Document3 pagesActivity-7 7John Michael PerezNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education: Academic Calendar 2008-2009Document6 pagesMaharashtra State Board of Technical Education: Academic Calendar 2008-2009manojNo ratings yet
- Student Spotlight Parent LetterDocument2 pagesStudent Spotlight Parent Letterapi-507162341No ratings yet
- III-Day 17Document4 pagesIII-Day 17Florita Lagrama100% (1)
- A Qualitative Study of Students With Behavioral PRDocument3 pagesA Qualitative Study of Students With Behavioral PRRefenej Tio100% (1)
Sse 2 - Finals
Sse 2 - Finals
Uploaded by
Alexie Anne MariñoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sse 2 - Finals
Sse 2 - Finals
Uploaded by
Alexie Anne MariñoCopyright:
Available Formats
FINAL TERM – SSE 2: HOW WE PLAN THE LESSON?
TEACHING APPROACHES IN SECONDARY EDUCATION IN SOCIAL
STUDIES • Lesson Plan serves bible every teacher; do not
enter the room without plan
WEEK 14: LESSON 1 - INSTRUCTIONAL
OBJECTIVES Competence
According to Gagne (1964), there are what we called Nine • Set of knowledge, skills and attributes required to
Levels of Instruction. successfully perform a permanent task stated in
specific terms
o It is very important to understand
learning competencies
o Mas malawak yung learning
competencies at maabot yung
instructional objectives.
Instructional Objectives
• It identifies what students are expected to do and
demonstrate now they do it
• It provides focus and direction for both teacher
and learners
o SMART
• The verb in the objectives describes the designed
performance expected of the learners
• Benjamin Bloom created a framework for writing
a. Gain objectives at many cognitive levels (It was revised
Attention – in 2001).
its is about Happens o When we are talking about time bound,
attracting or meanings, it always measurable in time
prior to
getting the (ex. 50-60 mins)
instruction/or
students’ • “Bloom’s Taxonomy”
attention before
b. Inform discussion
learner of
Objectives VERB + NOUN PHRASE (this is the topic, content, task)
c. Prior All of these
Learning levels are “A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing.” (1956
d. Present part of – Bloom – Orig ; 2001 - Revised)
Content - we learning
teach the plan/lesson
content plan.
e. Providing Meaning,
Guidance – lahat ‘yan ay
collaborative Happens plinaplano.
activities during
f. Practice / discussion
Direct
Performance
– about
applying the
content
g. Provide
Feedback –
this is about
appreciating
h. Assess
Performance Happens
i. Enhance after Ex. Nakabubuo ng timeline ng mga paglalakbay ng
Retention discussion / Espanyol sa Pilipinas hanggang sa pagkakatatag ng
and Transfer instruction Maynila at mga unang engkwentro ng mga Espanyol at
to the Job Pilipino.
Verb: Nakabubuo (cognitive – process dimension)
Noun Phrase: ng timeline…Pilipino (knowledge
dimension)
COGNITIVE PROCESS (Revised Bloom’s KNOWLEDGE DIMENSION
Taxonomy)
A. Factual – (ex. sino ang unang president ng 4th
• Remember • Analyze congress)
• Understanding • Evaluate B. Conceptual – application
• Apply • Create C. Procedural – (ex. economics) more on systematic
processes
D. Metacognitive – ginagamitan ng cognition
• HOW LEARNERS THINK?
• WHAT COGNITIVE PROCESS USED BY THE
STUDENTS?
A. FACTUAL KNOWLEDGE – the basic elements students
THE COGNITIVE PROCESS DIMENSION must know to be acquainted with a discipline or solve
problems in it
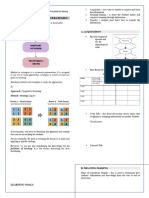
The Remember Under Apply Analyze Evaluation Create
Knowledge standing MAJOR TYPES AND EXAMPLES
Dimension SUBTYPES
Factual Aa. Knowledge of Technical vocabulary,
Conceptual Terminology musical symbols
Procedural Ab. Knowledge of specific Major natural resources,
Metacognitive details and elements reliable sources of
information
(nature, events, places,
COGNITIVE PROCESS dates, terms, documents,
objects)
1. Remember
• Factual
B. CONCEPTUAL KNOWLEDGE – the interrelationship
o ex. Natutukoy ang mga
among the basic elements within a larger structure that
pangyayaring…
enable them to function together
2. Understand
• Verb MAJOR TYPES AND EXAMPLES
• Context means from instructing SUBTYPES
messages, including.. Ba. Knowledge of Period of geological time,
o Naipapaliwanag classifications and forms of business
o Nailalarawan categories ownership
o Naiuugnay Bb. Knowledge of Pythagorean theorem, law
o Naipapapaliwanag principles and of supply and demand
3. Apply generalizations
• Carry on Bc. Knowledge of Theory of evolution,
o Nailalapat at kahulugan ng theories, models and structure of congress
structures
ekonomiyang naipapamuhay
bilang isang mag-aaral at
kasapi ng pamilya at • Categories
komunidad. o Stage of cultural evolution
4. Analyze o Economic systems
• Break material on its.. o Forms of government
o 4.1. Differentiating o SOGIE
o 4.2. Organizing o Regions
o 4.3. Attributing ▪ Regionalization si debatable
which talking about its
5. Evaluate geographical aspect and
• H culture
o 5.1. Checking • Theories, Models and Structures
o 5.2. Critiquing o Theory of evolution
▪ Nagtataya/evaluate o Big Bang Theory
6. Create o Circular Flow of Market System
• C o Ideologies
o 6.1, Creating – hypothesizing o Philosophies
o 6.2. Planning – Designing o Religious Beliefs
o 6.3 Producing – Conducting
▪ Andragogy
• Naisasagawa
• Nakapamum
ungkahi
• Nakagagawa
C. PROCEDURAL KNOWLEDGE – How to do something, WEEK 14: LESSON 2 – SUBTASKING THE
methods of inquiry, and criteria for using skills, algorithms,
COMPETENCE
techniques and methods
• Unpacking the learning competencies
SUBTYPES EXAMPLES
• Towards adhere learning standards
Ca. Knowledge of subject- Friction calculation
• Develop the knowledge, skills, and attributes to
specific skills and
algorithms achieve learning standards
Cb. Knowledge of Scientific Methods
LEARNING STANDARDS
subject-specific
techniques and methods • Provide level of doing competence indicate real-
Cc. Knowledge of criteria The criteria used to
life purpose of competence show literary
for determining when to determine when to apply
connection (enduring) of different competencies
use appropriate Newtons second law
stated in a broad and general way
procedures
• Process, Series, Steps, Techniques
o Historical Method
o Scientific Method
o Research Method
o Locate Places
o Computing for GDP
o Making a graph
D. METACOGNITIVE – Knowledge of cognition in general
as well as awareness and knowledge of one’s own
cognition
SUBTYPES EXAMPLES
Da. Strategic Knowledge Knowledge of outlining as
a means of capturing the
structure of a unit of
subject matter in a
textbook
Db. Knowledge about Knowledge of the
cognitive tasks, including cognitive demands of
appropriate contextual different tasks The competencies are needed to be classified if they are
and conditional broad or specific. (APCG and MELCS – the learning
knowledge competencies here is somehow broad).
Dc. Self-Knowledge Awareness of one’s own
knowledge level
MELCS
• inducing understanding
• Subject “wholeness”
• Measuring (calrity and competencies)
INSTRUCTIONAL ACTIVITIES
• Statement of the intended learning based on
standard and competencies
• These are specific to the tasks for the day and
allowing contexts to assessment.
o LC – 1 per week
CHARACTERS OF INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES
A. Connected to the standards and curriculum
based
B. Appropriate for the proficiency level
C. Measurable and anchor to the learning
competencies
D. Specific
E. Demonstrated what strand will be able to do.
HOW TO MAKE INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES?
• Simula sa basic
o Natutunan
o Naiiba
o Nailalarawan
o Naisusuri
o Napapahuluguhan
• Instructional Objectives will help to achieve the
Learning Comptencies
ASSESSMENT:
A. Diagnostic Assessment – recorded but not
graded
B. Formative Assessment – recorded but not
graded; tinitignan if yung bata ay hand ana sa
summative assessment
C. Summative Assessment – Recorded and graded
You might also like
- TAP - School Beautification ProjectDocument5 pagesTAP - School Beautification ProjectMaestro Varix100% (7)
- UDL Lesson Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesUDL Lesson Plan TemplatePsiho LoguseNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log For Fundamentals of ABMDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Log For Fundamentals of ABMVanessa Lou Torejas100% (2)
- Differentiates Between Equations and InequalitiesDocument7 pagesDifferentiates Between Equations and InequalitiesMarc Galos100% (2)
- SLT Working Privately in GWGTN RegionDocument2 pagesSLT Working Privately in GWGTN Regioncdw27No ratings yet
- Cot DLL Filipino Q 2Document3 pagesCot DLL Filipino Q 2Dorothy Jean100% (5)
- Edu601 Lesson 6-11Document2 pagesEdu601 Lesson 6-11Jo MomNo ratings yet
- Cot Filipino Q 2Document3 pagesCot Filipino Q 2Jane Bunuan SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Compressed Escuela Normal ClassroommanagementDocument28 pagesCompressed Escuela Normal Classroommanagementjennybacay.12345No ratings yet
- Learning Task 5 Evero CarinapassDocument23 pagesLearning Task 5 Evero CarinapassPlatero Roland100% (1)
- Principles and Strategies of Teaching 2020 AND 2021Document9 pagesPrinciples and Strategies of Teaching 2020 AND 2021IGNACIO JULLIE MAENo ratings yet
- Assessment ReviewerDocument4 pagesAssessment ReviewerAngelica TañedoNo ratings yet
- Lesson DesignDocument3 pagesLesson DesignKen DonkohNo ratings yet
- Principles and Strategies of TeachingDocument19 pagesPrinciples and Strategies of Teachingnhicabonit7No ratings yet
- Unit 3 (Prof - Ed 8)Document2 pagesUnit 3 (Prof - Ed 8)CyanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On The Preparation of PIVOT I D E A Lesson Exemplars RM No. 296 s.2020Document61 pagesGuidelines On The Preparation of PIVOT I D E A Lesson Exemplars RM No. 296 s.2020Jonathan Marc Fule Castillo100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan PerdevDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan PerdevMuffy FernandezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An FEI Lesson.1109Document2 pagesAnatomy of An FEI Lesson.1109arudenstineNo ratings yet
- Y4 Week 8 or 9Document6 pagesY4 Week 8 or 9LINANo ratings yet
- Action Plan RDTDocument2 pagesAction Plan RDTadadNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson PlanNhico BryanNo ratings yet
- LP Uri NG Pangungusap g6Document4 pagesLP Uri NG Pangungusap g6Wynn Gargar TormisNo ratings yet
- TTL Lesson 6Document6 pagesTTL Lesson 6Katlyn MRNo ratings yet
- Wiggins Mctighe Ubd Nutshell PDFDocument4 pagesWiggins Mctighe Ubd Nutshell PDFNeda KahnNo ratings yet
- The Task Cycle (Autoguardado)Document14 pagesThe Task Cycle (Autoguardado)Nadia SimónNo ratings yet
- UMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: Ccss - Math.Content - Hsf.Bf.B.5Document3 pagesUMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: Ccss - Math.Content - Hsf.Bf.B.5api-335961271No ratings yet
- TEMPLATEDocument6 pagesTEMPLATECaryn MorataNo ratings yet
- DLL - TTSCUR FinalDocument5 pagesDLL - TTSCUR FinalKenneth AminullaNo ratings yet
- Teaching ApproachesDocument3 pagesTeaching Approachesapi-546696759No ratings yet
- Week H - Embodied Spirit3Document4 pagesWeek H - Embodied Spirit3JonalynNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6 (TTSC) - ALILIN, RENA ROSE S. BEED 3A DAYDocument5 pagesExercise 6 (TTSC) - ALILIN, RENA ROSE S. BEED 3A DAYJeremy NeriNo ratings yet
- NVSD Unit Planner 1Document2 pagesNVSD Unit Planner 1api-533726217No ratings yet
- Task October 15 IIDocument2 pagesTask October 15 IIMera Largosa ManlaweNo ratings yet
- Module 3A Lesson 2 RioDocument7 pagesModule 3A Lesson 2 RioRioVierraMadriagaMallaNo ratings yet
- Comparative EssayDocument2 pagesComparative Essayapi-335961418No ratings yet
- Accteach Prelims Chapter 1&2Document6 pagesAccteach Prelims Chapter 1&2KDumpNo ratings yet
- Accteach PrelimsDocument6 pagesAccteach PrelimsKDumpNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 MergedDocument9 pages1 2 3 4 MergedAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- UbD in A NutshellDocument4 pagesUbD in A NutshellTeachThoughtNo ratings yet
- Accteach Prelims Chapter 1&2Document7 pagesAccteach Prelims Chapter 1&2KDumpNo ratings yet
- Learning Episode: The Meaning of CurriculumDocument132 pagesLearning Episode: The Meaning of CurriculumMaela Pollen Elumba YemaNo ratings yet
- Cot Filipino Q 2Document4 pagesCot Filipino Q 2Jane Bunuan SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Teaching Learning Process and Curriculum Development With Adaptaion and ModificationDocument21 pagesTeaching Learning Process and Curriculum Development With Adaptaion and ModificationAmy F. CabfeoNo ratings yet
- DLL Philosophy QUARTER 2 WEEK 2Document3 pagesDLL Philosophy QUARTER 2 WEEK 2checkaliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9Document2 pagesLesson 9nkosiNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 3 (K-W-L)Document2 pagesLearning Task 3 (K-W-L)RHEA JOY VILLASNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument6 pagesMathematicsMatias, Emie Rose Q.No ratings yet
- Annotation-English 9 First Classroom Observation July 30, 2019Document3 pagesAnnotation-English 9 First Classroom Observation July 30, 2019Rey Salomon Vistal100% (4)
- UMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesUMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Templateapi-335961271No ratings yet
- UbD Workshop Part 3Document30 pagesUbD Workshop Part 3RossNo ratings yet
- DLL - Week - 10 - Statistics and ProbabilityDocument3 pagesDLL - Week - 10 - Statistics and ProbabilityRoboCopyNo ratings yet
- EDTM 312 LU5 Group AssignmentDocument4 pagesEDTM 312 LU5 Group Assignmentchakaolebogeng3No ratings yet
- Educ 6 PrelimsDocument2 pagesEduc 6 PrelimsDextroi HombrebuenoNo ratings yet
- DIASS DLL Week 2Document3 pagesDIASS DLL Week 2aireen rose manguiranNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Sorensen Classroom Observation Form January 15 2021Document8 pagesBenjamin Sorensen Classroom Observation Form January 15 2021api-380337066No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Filipino 6 Quarter 3Document3 pagesLesson Plan in Filipino 6 Quarter 3Wynn Gargar Tormis80% (5)
- Kit Oseias H. Castillo - TEACHING INTERN ONLINE DEMONSTRATION LESSONDocument3 pagesKit Oseias H. Castillo - TEACHING INTERN ONLINE DEMONSTRATION LESSONKit Oseias H. CastilloNo ratings yet
- Oc Week 1 DLL - F. DuncabDocument4 pagesOc Week 1 DLL - F. DuncabFatima DuncabNo ratings yet
- RSML - 5 - e - 8 Etsot - Eleot AlignmentDocument2 pagesRSML - 5 - e - 8 Etsot - Eleot AlignmentkhalafNo ratings yet
- UMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesUMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Templateapi-335961271No ratings yet
- OB26a Teacher Reflection For Math LessonDocument2 pagesOB26a Teacher Reflection For Math Lessonsherdan genistonNo ratings yet
- MICROECONOMICS LECTURE - To EditDocument11 pagesMICROECONOMICS LECTURE - To EditAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- PATHFIT To PrintDocument4 pagesPATHFIT To PrintAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Geog 1 - FinalsDocument10 pagesGeog 1 - FinalsAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Sse 1 - FinalsDocument3 pagesSse 1 - FinalsAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Sse 2 - FinalsDocument9 pagesSse 2 - FinalsAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Task Sheet 1.4 - 3Document3 pagesTask Sheet 1.4 - 3Jerel John CalanaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Study Essay 2Document4 pagesLesson Study Essay 2api-284319074No ratings yet
- Pass/Fail 85% F: Assessment, Scoring, and EvaluationDocument23 pagesPass/Fail 85% F: Assessment, Scoring, and EvaluationParag NaikNo ratings yet
- CN3121 Project 1 - 2011Document2 pagesCN3121 Project 1 - 2011Jing WangNo ratings yet
- E-Rancangan Pengajaran Harian: (Yussry@Zeynorene B. Tukimin) Guru Besar SK LengaDocument14 pagesE-Rancangan Pengajaran Harian: (Yussry@Zeynorene B. Tukimin) Guru Besar SK Lengasharkies1No ratings yet
- By Diane Rich: Bang, Bang! Gun Play, and Why Children Need ItDocument6 pagesBy Diane Rich: Bang, Bang! Gun Play, and Why Children Need Itapi-38412056No ratings yet
- ENTREP-DLL-Mar 20-24 Week 6Document3 pagesENTREP-DLL-Mar 20-24 Week 6Mary Baltazar BulataoNo ratings yet
- Isaac Lopez Integrated School: The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument5 pagesIsaac Lopez Integrated School: The Problem and Its BackgrounddaneNo ratings yet
- ECD SyllabusDocument1 pageECD SyllabusIt's MeNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q1 - W4Document6 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q1 - W4SHERYL SAUDANNo ratings yet
- Raz ld48 DaydadDocument12 pagesRaz ld48 DaydadNguyễn Anh MinhNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Praktikum EnglishDocument13 pagesJurnal Praktikum Englisharon hasanNo ratings yet
- Narrative On The Pod MonitoringDocument3 pagesNarrative On The Pod MonitoringHanz Albrech AbellaNo ratings yet
- Educational Psychology: An International Journal of Experimental Educational PsychologyDocument13 pagesEducational Psychology: An International Journal of Experimental Educational PsychologyFahimeh MoafianNo ratings yet
- Ipcrf-Individual-Development-Plan-Itable JMDocument2 pagesIpcrf-Individual-Development-Plan-Itable JMJohn Michael ItableNo ratings yet
- Week 2-3Document3 pagesWeek 2-3api-367840311No ratings yet
- Individual Differences in L2 AcquisitionDocument15 pagesIndividual Differences in L2 Acquisitionmajtwin100% (2)
- Tle dm7-8 q1 Mod2 SDOv1-MGKaDocument32 pagesTle dm7-8 q1 Mod2 SDOv1-MGKaAldea ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- My First Cot GR.3Document4 pagesMy First Cot GR.3Nardita CastroNo ratings yet
- Undergraduate Students' Perspectives On Digital Competence and Academic Literacy in A Spanish UniversityDocument2 pagesUndergraduate Students' Perspectives On Digital Competence and Academic Literacy in A Spanish UniversityFernando GuzmánNo ratings yet
- SPJ 4 - Quarter 4 - Learning Activity SheetsDocument44 pagesSPJ 4 - Quarter 4 - Learning Activity SheetsLovilyn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Technical University of Mombasa: TUM Is ISO 9001:2015 CertifiedDocument5 pagesTechnical University of Mombasa: TUM Is ISO 9001:2015 Certifiedjoel collinsNo ratings yet
- Activity-7 7Document3 pagesActivity-7 7John Michael PerezNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education: Academic Calendar 2008-2009Document6 pagesMaharashtra State Board of Technical Education: Academic Calendar 2008-2009manojNo ratings yet
- Student Spotlight Parent LetterDocument2 pagesStudent Spotlight Parent Letterapi-507162341No ratings yet
- III-Day 17Document4 pagesIII-Day 17Florita Lagrama100% (1)
- A Qualitative Study of Students With Behavioral PRDocument3 pagesA Qualitative Study of Students With Behavioral PRRefenej Tio100% (1)