Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes
Notes
Uploaded by
Ismail AkbarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Crystal Healer: Volume 2: Harness the power of crystal energy. Includes 250 new crystalsFrom EverandThe Crystal Healer: Volume 2: Harness the power of crystal energy. Includes 250 new crystalsNo ratings yet
- Arbitration Award Writing - Lecture Notes - CombinedDocument114 pagesArbitration Award Writing - Lecture Notes - CombinedILTERIS DOGAN100% (1)
- Particles Mastery BookletDocument25 pagesParticles Mastery Bookletapi-42242870050% (2)
- StahlDocument9 pagesStahlTaoman50% (2)
- 1.3 & 1.4 Lecture PPT (Exercises Answer) 12.5.2022Document14 pages1.3 & 1.4 Lecture PPT (Exercises Answer) 12.5.2022Thara PhyoNo ratings yet
- Assumption College of NabunturanDocument4 pagesAssumption College of NabunturanAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- CH1 NotesDocument11 pagesCH1 Notesaharshika557No ratings yet
- Folio Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Document34 pagesFolio Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Nurul Syafiqa MahadhirNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocument36 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsYard BirdNo ratings yet
- 01matterinoursurrounding 240206102143 4bb18095Document19 pages01matterinoursurrounding 240206102143 4bb18095atharv artsNo ratings yet
- Tagore International School Vasant Vihar, N. DelhiDocument2 pagesTagore International School Vasant Vihar, N. DelhiAnant IssarNo ratings yet
- Topic - The States of MatterDocument4 pagesTopic - The States of MatterReshma Seeth-SieunarineNo ratings yet
- State of MatterDocument14 pagesState of MatterAlvinNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Module 1 AnswersDocument6 pagesGen Chem 2 Module 1 AnswersSharmaine Joyce RegioNo ratings yet
- The Particle Model of MatterDocument12 pagesThe Particle Model of Matter18811301255No ratings yet
- VJVVJVJJVJVJDocument10 pagesVJVVJVJJVJVJamanda dNo ratings yet
- 9 PPT Matter in Our Surroundings LatestDocument53 pages9 PPT Matter in Our Surroundings Latestvbxjbp8hd5No ratings yet
- World of MatterDocument14 pagesWorld of MatterAding SamNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 1-8Document7 pagesUnit 1 1-8b52352986No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding NotesAanvi TripathiNo ratings yet
- Ebookneonclasseschemistryeng 2Document63 pagesEbookneonclasseschemistryeng 2rameshNo ratings yet
- NSC U4 Matter. (Part Ii)Document10 pagesNSC U4 Matter. (Part Ii)Amaia TeranNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Chap01 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument5 pages09 Science Chap01 Matter in Our SurroundingsRopsonNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surrounding QRDocument48 pagesMatter in Our Surrounding QRomvjanapureNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 IMF Part3Document12 pagesChap 1 IMF Part3lyza shane bernalNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings ( Prashant Kirad ) (1)Document41 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings ( Prashant Kirad ) (1)nidhimathapati123No ratings yet
- PDF Bio ch3Document19 pagesPDF Bio ch3DHRUV JAINNo ratings yet
- MixturesDocument25 pagesMixturesJoma Guerra ina moNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument12 pagesRevision Notes On Matter in Our SurroundingsRudra aminNo ratings yet
- 6resource 131602210601 53Document156 pages6resource 131602210601 53No ExcuseNo ratings yet
- Nelson 9 Unit C c05-01 PDFDocument4 pagesNelson 9 Unit C c05-01 PDFshailytutorials scienceNo ratings yet
- Colloid: By: Nia Pramais OctavianiDocument35 pagesColloid: By: Nia Pramais OctavianidshineNo ratings yet
- Ch-1, Cl-9, Matter in Our SurroundingDocument37 pagesCh-1, Cl-9, Matter in Our SurroundingSoumalyaNo ratings yet
- 2024 - Science - Y1 - PPT2 - Separation Tech - Magnet, Using Solvent and FiltrationDocument21 pages2024 - Science - Y1 - PPT2 - Separation Tech - Magnet, Using Solvent and Filtrationcate.yim11No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Structure of The AtomDocument42 pagesChapter 2: Structure of The AtomThanabalan MunuswamyNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Chem Simplified Notes s2Document130 pagesForm 1 Chem Simplified Notes s2micah isabokeNo ratings yet
- The Particulate NatureDocument123 pagesThe Particulate Naturewidya sariNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 - Matter in Our Surrondings - NewDocument73 pagesChapter - 1 - Matter in Our Surrondings - NewRashmi GuptaNo ratings yet
- ES Module 3 - Quarter 1 - Types of SolidsDocument13 pagesES Module 3 - Quarter 1 - Types of SolidsAnalynAsuncionAtaydeNo ratings yet
- 2.1 (A) Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument12 pages2.1 (A) Kinetic Theory of MatterwannwaNo ratings yet
- All About Matter: November 20, 2017Document2 pagesAll About Matter: November 20, 2017Aaliyah Joize LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Ram Gelo de Luna Haway - ACTIVITY NO. 1 (General Chemistry)Document5 pagesRam Gelo de Luna Haway - ACTIVITY NO. 1 (General Chemistry)Ram Gelo HawayNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - MATTER (Combined PPT) Class VII Help NotesDocument72 pagesCHAPTER - MATTER (Combined PPT) Class VII Help NotesPriyanca JunejaNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Form 4 VersionDocument17 pagesStates of Matter Form 4 VersionNirvana SuggieNo ratings yet
- POLARITY AT WORK - WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesPOLARITY AT WORK - WPS OfficePsychopompNo ratings yet
- 12.1 Types of MixturesDocument6 pages12.1 Types of MixturesOmar AlwaerNo ratings yet
- (CSEC Chemistry) Section A Notes and ESQsDocument191 pages(CSEC Chemistry) Section A Notes and ESQsNathaniel WhyteNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Big IdeaDocument32 pagesSolutions: Big Ideaits.amy.zhangNo ratings yet
- F1 Chapter 5 MatterDocument13 pagesF1 Chapter 5 Matteralya sophiaNo ratings yet
- COLLOIDSDocument20 pagesCOLLOIDSNarciso sorianoNo ratings yet
- Conformed SCI-8 Quarter3 Module 1Document11 pagesConformed SCI-8 Quarter3 Module 1Thea Marie VilladolidNo ratings yet
- Ngss Particle Model PDFDocument2 pagesNgss Particle Model PDFDarwinEspinoza100% (1)
- Delhi Public School Class 9 - Chemistry Chapter 1: Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument8 pagesDelhi Public School Class 9 - Chemistry Chapter 1: Matter in Our SurroundingsShirin PanditaNo ratings yet
- Chapt 5 MarshakDocument21 pagesChapt 5 Marshak周牮No ratings yet
- Class Ix Chemistry Notes Session 1 L1Document3 pagesClass Ix Chemistry Notes Session 1 L1jeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- CHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0105 FDDocument16 pagesCHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0105 FDKhayh Jhyv Hyasynth A. VillagraciaNo ratings yet
- The Separation Method For Removing of Colloidal Particles From Raw WaterDocument8 pagesThe Separation Method For Removing of Colloidal Particles From Raw WaterAnonymous Hy5Ir9QXNo ratings yet
- ColloidsDocument7 pagesColloidsAfree Awan MohamedNo ratings yet
- Written IN General Chemistry: Maharlika Highway, Brgy. Campetic, Palo, LeyteDocument54 pagesWritten IN General Chemistry: Maharlika Highway, Brgy. Campetic, Palo, LeyteJireh Mae CorderoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry S1 L1Document116 pagesIGCSE Chemistry S1 L1Antonia Putri Sri Nova YolandhaNo ratings yet
- Oil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandOil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Prague Wednesday AM - AcquirerDocument85 pagesPrague Wednesday AM - AcquirerbenNo ratings yet
- Switchgears Catalog PDFDocument81 pagesSwitchgears Catalog PDFS. M. Touhidur Rahman0% (1)
- Electrical Component Locator - Nissan Sentra 1993Document47 pagesElectrical Component Locator - Nissan Sentra 1993Alessandro BaffaNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument3 pagesTutorialSivanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Jubiliant MSDSDocument12 pagesJubiliant MSDShimanshushah871006No ratings yet
- Notes On Modern PhilosophyDocument20 pagesNotes On Modern PhilosophyÜmit YılmazNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Petroleum Limited ProjectDocument6 pagesPakistan Petroleum Limited ProjectRandum PirsonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitled박준수No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Calculation For Fire Protec7Document3 pagesHydraulic Calculation For Fire Protec7RaviNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Bahasa Inggris Sma HortatorDocument6 pagesLatihan Soal Bahasa Inggris Sma HortatorIsna FitrianiNo ratings yet
- 067Document28 pages067Nouman AsgharNo ratings yet
- Avaya SBCE Deploying On An AWS Platform 8.1.x December 2020Document64 pagesAvaya SBCE Deploying On An AWS Platform 8.1.x December 2020Vicky NicNo ratings yet
- Frequency Dictionary en 82 765Document1,403 pagesFrequency Dictionary en 82 765mmbkr_No ratings yet
- Question2 p2 Aqa Combined Jun 2019Document5 pagesQuestion2 p2 Aqa Combined Jun 2019Justin Lloyd CasilaganNo ratings yet
- What Is An Echinoderm?Document18 pagesWhat Is An Echinoderm?isuru PereraNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Philosophical AnthropologyDocument8 pagesThe Nature of Philosophical AnthropologyPaul HorriganNo ratings yet
- Gen Physics 2 - Module 7 Electric Circuits - Answer SheetDocument7 pagesGen Physics 2 - Module 7 Electric Circuits - Answer SheetDrei DreiNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On AutomationDocument32 pagesSeminar Report On AutomationDusmanta moharanaNo ratings yet
- 4 SOEE5010 QuestionnaireDocument2 pages4 SOEE5010 QuestionnairePrince JuniorNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Contract: Section 1. General Conditions of ContractDocument55 pagesPart 1 Contract: Section 1. General Conditions of ContractRun FastNo ratings yet
- 13500-0004 BiladylTriladyl Es 120814Document2 pages13500-0004 BiladylTriladyl Es 120814Fabio FerreiraNo ratings yet
- AAASteele BioDocument21 pagesAAASteele Bioceice2013100% (1)
- Lecture 9 - Capcity and Level of Service - IIDocument43 pagesLecture 9 - Capcity and Level of Service - IIBasoz Arif AhmadNo ratings yet
- Compare-Contrast Essay Writing: All: Most: SomeDocument10 pagesCompare-Contrast Essay Writing: All: Most: SomeGayatri Maniksha ParsekarNo ratings yet
- Anusha Dadwani - ResumeDocument2 pagesAnusha Dadwani - Resumeapi-458585393No ratings yet
- Extention FuelManSystem - InstallGuideDocument10 pagesExtention FuelManSystem - InstallGuidekavireeshgh_007No ratings yet
- IC5 Level Intro - Scope - and - SequenceDocument4 pagesIC5 Level Intro - Scope - and - Sequencematerial didacticoNo ratings yet
- Video - Digital Video Recorder 440/480 SeriesDocument3 pagesVideo - Digital Video Recorder 440/480 SeriesMonir UjjamanNo ratings yet
Notes
Notes
Uploaded by
Ismail AkbarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes
Notes
Uploaded by
Ismail AkbarCopyright:
Available Formats
3
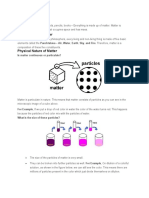
01. 1 Particulate Nature of Matter
Everything is made of particles. Rock, air, and water look very different. But
they have one big thing in common: they are all made of very tiny pieces,
far too small to see. For the moment, we will call these pieces particles.
alt
In rock and other solids, the particles are not free to move around. But in
liquids and gases, they move freely. As they move they collide with each
other, and bounce off in all directions.
from
here to
here
01. 2 Particulate Nature of Matter
There is evidence all around you that things are made of particles, and that
they move around in liquids and gases. Look at these examples.
Cooking smells can spread out into You often see dust and smoke
the street. dancing in the air, in bright sunlight.
01. 3 Diffusion
Place a crystal of potassium manganate(VII) in a beaker of water. The
colour spreads through the water. Why? First, particles leave the crystal – it
dissolves. Then they mix among the water particles.
water
particle
particles from
the crystal mix
among the
water particles
the crystal
The colour spreads through the water.
Why? First, particles leave the crystal – it
dissolves.
Abul Fazal 01 States of Matter
Bilal Hameed Marginalizer
4
2
01. 4 Diffusion
Diffusion is the overall movement of particles from a high concentration to
a low concentration due to random movement of particles.
particles mix by colliding with each other and bouncing off in all directions. This
mixing process is called diffusion.
alt
The overall result is the flow of particles from where they are more concentrated
to where they are less concentrated, until they are evenly spread out.
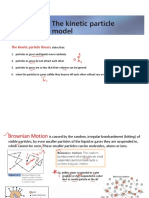
01. 5 Kinetic Theory of Particles
The kinetic theory helps to explain the way in which matter behaves. The
evidence is consistent with the idea that all matter is made up of tiny
particles. This theory explains the physical properties of matter in terms of
the movement of its constituent particles.
• All matter is made up of tiny, moving particles, invisible to the naked eye. Different
substances have different types of particles (atoms, molecules or ions) which have
different sizes.
• The particles move all the time. The higher the temperature, the faster they move on
average.
• Heavier particles move more slowly than lighter ones at a given temperature.
01. 6 Diffusion - Example
Place a crystal of potassium manganate(VII) in a beaker of water. The
colour spreads through the water. Why? First, particles leave the crystal – it
dissolves. Then they mix among the water particles.
water
particle
particles from
the crystal mix
among the
water particles
the crystal
01 States of Matter Abul Fazal
Marginalizer Bilal Hameed
You might also like
- The Crystal Healer: Volume 2: Harness the power of crystal energy. Includes 250 new crystalsFrom EverandThe Crystal Healer: Volume 2: Harness the power of crystal energy. Includes 250 new crystalsNo ratings yet
- Arbitration Award Writing - Lecture Notes - CombinedDocument114 pagesArbitration Award Writing - Lecture Notes - CombinedILTERIS DOGAN100% (1)
- Particles Mastery BookletDocument25 pagesParticles Mastery Bookletapi-42242870050% (2)
- StahlDocument9 pagesStahlTaoman50% (2)
- 1.3 & 1.4 Lecture PPT (Exercises Answer) 12.5.2022Document14 pages1.3 & 1.4 Lecture PPT (Exercises Answer) 12.5.2022Thara PhyoNo ratings yet
- Assumption College of NabunturanDocument4 pagesAssumption College of NabunturanAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- CH1 NotesDocument11 pagesCH1 Notesaharshika557No ratings yet
- Folio Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Document34 pagesFolio Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Nurul Syafiqa MahadhirNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocument36 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsYard BirdNo ratings yet
- 01matterinoursurrounding 240206102143 4bb18095Document19 pages01matterinoursurrounding 240206102143 4bb18095atharv artsNo ratings yet
- Tagore International School Vasant Vihar, N. DelhiDocument2 pagesTagore International School Vasant Vihar, N. DelhiAnant IssarNo ratings yet
- Topic - The States of MatterDocument4 pagesTopic - The States of MatterReshma Seeth-SieunarineNo ratings yet
- State of MatterDocument14 pagesState of MatterAlvinNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Module 1 AnswersDocument6 pagesGen Chem 2 Module 1 AnswersSharmaine Joyce RegioNo ratings yet
- The Particle Model of MatterDocument12 pagesThe Particle Model of Matter18811301255No ratings yet
- VJVVJVJJVJVJDocument10 pagesVJVVJVJJVJVJamanda dNo ratings yet
- 9 PPT Matter in Our Surroundings LatestDocument53 pages9 PPT Matter in Our Surroundings Latestvbxjbp8hd5No ratings yet
- World of MatterDocument14 pagesWorld of MatterAding SamNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 1-8Document7 pagesUnit 1 1-8b52352986No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding NotesAanvi TripathiNo ratings yet
- Ebookneonclasseschemistryeng 2Document63 pagesEbookneonclasseschemistryeng 2rameshNo ratings yet
- NSC U4 Matter. (Part Ii)Document10 pagesNSC U4 Matter. (Part Ii)Amaia TeranNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Chap01 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument5 pages09 Science Chap01 Matter in Our SurroundingsRopsonNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surrounding QRDocument48 pagesMatter in Our Surrounding QRomvjanapureNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 IMF Part3Document12 pagesChap 1 IMF Part3lyza shane bernalNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings ( Prashant Kirad ) (1)Document41 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings ( Prashant Kirad ) (1)nidhimathapati123No ratings yet
- PDF Bio ch3Document19 pagesPDF Bio ch3DHRUV JAINNo ratings yet
- MixturesDocument25 pagesMixturesJoma Guerra ina moNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument12 pagesRevision Notes On Matter in Our SurroundingsRudra aminNo ratings yet
- 6resource 131602210601 53Document156 pages6resource 131602210601 53No ExcuseNo ratings yet
- Nelson 9 Unit C c05-01 PDFDocument4 pagesNelson 9 Unit C c05-01 PDFshailytutorials scienceNo ratings yet
- Colloid: By: Nia Pramais OctavianiDocument35 pagesColloid: By: Nia Pramais OctavianidshineNo ratings yet
- Ch-1, Cl-9, Matter in Our SurroundingDocument37 pagesCh-1, Cl-9, Matter in Our SurroundingSoumalyaNo ratings yet
- 2024 - Science - Y1 - PPT2 - Separation Tech - Magnet, Using Solvent and FiltrationDocument21 pages2024 - Science - Y1 - PPT2 - Separation Tech - Magnet, Using Solvent and Filtrationcate.yim11No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Structure of The AtomDocument42 pagesChapter 2: Structure of The AtomThanabalan MunuswamyNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Chem Simplified Notes s2Document130 pagesForm 1 Chem Simplified Notes s2micah isabokeNo ratings yet
- The Particulate NatureDocument123 pagesThe Particulate Naturewidya sariNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 - Matter in Our Surrondings - NewDocument73 pagesChapter - 1 - Matter in Our Surrondings - NewRashmi GuptaNo ratings yet
- ES Module 3 - Quarter 1 - Types of SolidsDocument13 pagesES Module 3 - Quarter 1 - Types of SolidsAnalynAsuncionAtaydeNo ratings yet
- 2.1 (A) Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument12 pages2.1 (A) Kinetic Theory of MatterwannwaNo ratings yet
- All About Matter: November 20, 2017Document2 pagesAll About Matter: November 20, 2017Aaliyah Joize LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Ram Gelo de Luna Haway - ACTIVITY NO. 1 (General Chemistry)Document5 pagesRam Gelo de Luna Haway - ACTIVITY NO. 1 (General Chemistry)Ram Gelo HawayNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - MATTER (Combined PPT) Class VII Help NotesDocument72 pagesCHAPTER - MATTER (Combined PPT) Class VII Help NotesPriyanca JunejaNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Form 4 VersionDocument17 pagesStates of Matter Form 4 VersionNirvana SuggieNo ratings yet
- POLARITY AT WORK - WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesPOLARITY AT WORK - WPS OfficePsychopompNo ratings yet
- 12.1 Types of MixturesDocument6 pages12.1 Types of MixturesOmar AlwaerNo ratings yet
- (CSEC Chemistry) Section A Notes and ESQsDocument191 pages(CSEC Chemistry) Section A Notes and ESQsNathaniel WhyteNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Big IdeaDocument32 pagesSolutions: Big Ideaits.amy.zhangNo ratings yet
- F1 Chapter 5 MatterDocument13 pagesF1 Chapter 5 Matteralya sophiaNo ratings yet
- COLLOIDSDocument20 pagesCOLLOIDSNarciso sorianoNo ratings yet
- Conformed SCI-8 Quarter3 Module 1Document11 pagesConformed SCI-8 Quarter3 Module 1Thea Marie VilladolidNo ratings yet
- Ngss Particle Model PDFDocument2 pagesNgss Particle Model PDFDarwinEspinoza100% (1)
- Delhi Public School Class 9 - Chemistry Chapter 1: Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument8 pagesDelhi Public School Class 9 - Chemistry Chapter 1: Matter in Our SurroundingsShirin PanditaNo ratings yet
- Chapt 5 MarshakDocument21 pagesChapt 5 Marshak周牮No ratings yet
- Class Ix Chemistry Notes Session 1 L1Document3 pagesClass Ix Chemistry Notes Session 1 L1jeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- CHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0105 FDDocument16 pagesCHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0105 FDKhayh Jhyv Hyasynth A. VillagraciaNo ratings yet
- The Separation Method For Removing of Colloidal Particles From Raw WaterDocument8 pagesThe Separation Method For Removing of Colloidal Particles From Raw WaterAnonymous Hy5Ir9QXNo ratings yet
- ColloidsDocument7 pagesColloidsAfree Awan MohamedNo ratings yet
- Written IN General Chemistry: Maharlika Highway, Brgy. Campetic, Palo, LeyteDocument54 pagesWritten IN General Chemistry: Maharlika Highway, Brgy. Campetic, Palo, LeyteJireh Mae CorderoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry S1 L1Document116 pagesIGCSE Chemistry S1 L1Antonia Putri Sri Nova YolandhaNo ratings yet
- Oil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandOil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Prague Wednesday AM - AcquirerDocument85 pagesPrague Wednesday AM - AcquirerbenNo ratings yet
- Switchgears Catalog PDFDocument81 pagesSwitchgears Catalog PDFS. M. Touhidur Rahman0% (1)
- Electrical Component Locator - Nissan Sentra 1993Document47 pagesElectrical Component Locator - Nissan Sentra 1993Alessandro BaffaNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument3 pagesTutorialSivanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Jubiliant MSDSDocument12 pagesJubiliant MSDShimanshushah871006No ratings yet
- Notes On Modern PhilosophyDocument20 pagesNotes On Modern PhilosophyÜmit YılmazNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Petroleum Limited ProjectDocument6 pagesPakistan Petroleum Limited ProjectRandum PirsonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitled박준수No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Calculation For Fire Protec7Document3 pagesHydraulic Calculation For Fire Protec7RaviNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Bahasa Inggris Sma HortatorDocument6 pagesLatihan Soal Bahasa Inggris Sma HortatorIsna FitrianiNo ratings yet
- 067Document28 pages067Nouman AsgharNo ratings yet
- Avaya SBCE Deploying On An AWS Platform 8.1.x December 2020Document64 pagesAvaya SBCE Deploying On An AWS Platform 8.1.x December 2020Vicky NicNo ratings yet
- Frequency Dictionary en 82 765Document1,403 pagesFrequency Dictionary en 82 765mmbkr_No ratings yet
- Question2 p2 Aqa Combined Jun 2019Document5 pagesQuestion2 p2 Aqa Combined Jun 2019Justin Lloyd CasilaganNo ratings yet
- What Is An Echinoderm?Document18 pagesWhat Is An Echinoderm?isuru PereraNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Philosophical AnthropologyDocument8 pagesThe Nature of Philosophical AnthropologyPaul HorriganNo ratings yet
- Gen Physics 2 - Module 7 Electric Circuits - Answer SheetDocument7 pagesGen Physics 2 - Module 7 Electric Circuits - Answer SheetDrei DreiNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On AutomationDocument32 pagesSeminar Report On AutomationDusmanta moharanaNo ratings yet
- 4 SOEE5010 QuestionnaireDocument2 pages4 SOEE5010 QuestionnairePrince JuniorNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Contract: Section 1. General Conditions of ContractDocument55 pagesPart 1 Contract: Section 1. General Conditions of ContractRun FastNo ratings yet
- 13500-0004 BiladylTriladyl Es 120814Document2 pages13500-0004 BiladylTriladyl Es 120814Fabio FerreiraNo ratings yet
- AAASteele BioDocument21 pagesAAASteele Bioceice2013100% (1)
- Lecture 9 - Capcity and Level of Service - IIDocument43 pagesLecture 9 - Capcity and Level of Service - IIBasoz Arif AhmadNo ratings yet
- Compare-Contrast Essay Writing: All: Most: SomeDocument10 pagesCompare-Contrast Essay Writing: All: Most: SomeGayatri Maniksha ParsekarNo ratings yet
- Anusha Dadwani - ResumeDocument2 pagesAnusha Dadwani - Resumeapi-458585393No ratings yet
- Extention FuelManSystem - InstallGuideDocument10 pagesExtention FuelManSystem - InstallGuidekavireeshgh_007No ratings yet
- IC5 Level Intro - Scope - and - SequenceDocument4 pagesIC5 Level Intro - Scope - and - Sequencematerial didacticoNo ratings yet
- Video - Digital Video Recorder 440/480 SeriesDocument3 pagesVideo - Digital Video Recorder 440/480 SeriesMonir UjjamanNo ratings yet