Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Publication - Orchid Culture
Publication - Orchid Culture
Uploaded by
dove DonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Publication - Orchid Culture
Publication - Orchid Culture
Uploaded by
dove DonCopyright:
Available Formats
Care of orchids Diseases
Leaf Spot: Triangular blackish spot with yellowish reddish discoloura-
Watering is required at 3-4 days interval. Sprinkler and misting system is
tion at edge and base. Carbendazim (@ 2-3g/L water)/ Thiophanate-
good. Fertilizer mix of N, P and K @ 30:10:20 or 30:10:10 at pre flowering
methyl (2g/L water) is sprayed.
stage and 10:20:20 at flowering stage is applied as basal dose as well as foliar
Bacterial soft and Brown rot: Brown patches on the leaves with yellow
sprays. Fertilizer application frequency is 7-14 days starting from 30 days
ring surrounding the patch. Streptomycin Sulphate (0.5g/L water) + Cop-
after planting. The concentration of fertilizer solution for sprays should be
per Oxychloride (2g/L water) is sprayed.
very low (2g/L water). Various fertilizer mix are available containing NPK
Black rot: Circular reddish brown spot appear on the leaves. Copper Ox-
and other micro nutrients like zinc, copper, iron, boron and manganese . Pot-
ting mix containing bark required more nitrogenous fertilizer. Light, tempera-
ture and humidity should be maintained as per the type of orchid .
ychloride (2g/L water) is sprayed.
Stem Rot: Water soaked lesion on the stem and turns brown in colour.
Rotting of stem occur. Spray bavistin (2g/L water)/ Copper Oxychloride
Orchid Culture
Propagation (2g/L water).
for Cut Flower and Pot Plant Production:
Most common method is division of basal clumps into small units from the
mother plant and planting in separate packets or containers. Some orchids like
Dendrobium produces small rooted plantlets at the nodal points of pseudo- a complete technology guide
bulbs. These are called off shoots or kiekis. Stem cuttings for orchids like
Venda are most common. Well developed top growth stem of 30-40 cm
length with 2-3 aerial roots are separated.
Orchid potting media
Coconut husk Saw dust
Acknowledgement: We sincerely thank to Dr. Narendra Prakash, Director, ICAR RC
Brick chips NEH Region for his guidance and to all who contributed directly or indirectly for pre-
Charcoal chips paring this manuscript.
Disclaimer: Some contents and photos might have taken from difference sources to
make the topic more elaborative for farmer’s easy understanding and for welfare of
Flowering and Harvesting farmers. Sources/ person are hereby well acknowledged.
Orchid flowers are cut when all most all the flowers or at least 50-80%
flowers are open. Otherwise unopened buds will wilt if cut at early stage. Year 2018 Publication No. 58
After harvesting by cutting at the base of the flower stalk/peduncle, ap-
prox. 0.75-1.0 cm of base of the flower stalk is cut off and immediately put Prepared & Designed by: Biswajit Das
into bucket containing water and preservative. Pulsing with 5% sucrose, Dr. Biswajit Das, Principal Scientist, Horticulture, ICAR RC, Tripura Centre
holding solution silver nitrate 25mg/L water + 8-hydroxy quinoline sul- H. Lambisana Devi
Published by :
phate (8-HQS) 400 mg/L water + Sucrose 5% and vase solution of 2% su-
crose and 200mg/L water 8-HQC. Wrapping materials are 50 gauge poly- The Joint Director, ICAR RC for NEH, Tripura Centre B. K. Kandpal
ethylene paper or cellophane paper. Vase life is around 15-20 days.
For more details please contact:
Plant Protection
Dr. B. K. Kandpal
Insect Pests Joint Director
Snail and Slug: Separated from the plants manually. ICAR Research Complex for NEH Region,
Termite and Ants: Damages the media. Drenching of chlorpyri- Tripura Centre, Lembucherra, Tripura (West) - 799210
phos (1-1.5ml/L water). E-mail : jd.tripura@Icar.gov.in
Aphid: Suck cell sap from the tender stacks and shoots. Foliar
spray of imidacloprid (1ml/L water)/dimethoate (1.5ml/L water)/ Dr. Biswajit Das
thimet(1.5ml/L water). Principal Scientist, Horticulture
Mite: Small spider like insects makes webs and suck cell saps. ICAR RC, Tripura Centre
Leaves become brownish to brick red. Foliar spray of dicofol or
E-mail: biswajitsom_dr@yahoo.co.in Indian Council of Agricultural Research
propergite (1.5 ml/L water). Copyright ©: ICAR-NEH Region, Tripura Centre. ICAR Research Complex for NEH Region
White Fly: White small flies also suck sap and leaves become dis- Tripura Centre, P.O. Lembucherra-799210
torted. Spray thiomethoxame (1-1.5ml/L water).
Orchids are most attractive flowers with diversity in plant characters, Potting Media Repotting
flower colour, size, shape and blooming time. North Eastern India is the hot
Potting media is prepared combining soil, sand, cocochips, leaf Repotting is very essential after every 1-2 years when there is over growth
spot of orchids naturally growing in the undisturbed forest areas. Over the
mould, tree dried bark, saw dust, brick pieces, charcoal dust/chips, of roots and clumps or plant.
years, a well organized commercial orchid culture has been developed in
wood pieces and dried cow dung/vermicompost.
Sikkim. However in Tripura, orchid culture for commercial purpose on a At this stage, medium become old and powdery. Air space are
large scale has not been adopted by the flower growers. In the recent years, A good mixture of coco peat, bark and brick pieces (1:1:1) tightly blocked and holds water for longer time which is detrimental to the
selected farmers have started orchid culture in the state. Considering the bundled with coconut husk is good for Dendrobium. orchid plants. Orchid roots also become brown.
suitable agro-climatic conditions of Tripura and scope of orchid culture
for livelihood improvement, different type of orchids have been collected at Coco chips, coco peat and brick pieces (3:3:1) or charcoal chips, leaf Dendrobium and Phelaenopsis are repotted annually, Cattleya in 2nd
ICAR Research Complex for NEH Region, Tripura Centre for their rela- mould, loamy soils and sand are also mixed for Cymbidium. year and Vanda in 3rd year.
tive performance evaluation in the state. Brick chips, coco chips, leaf mould (1:1:1) and flat stone pieces are Orchid plant is taken out of the old medium along with the dense
used for Cattleya. clinging root network. Extra areal as well as basal roots are trimmed
Climatic Suitability
All the media components are well treated with formalin 40% (1.5- and clumps are separated from the mother plant.
Orchids are found in tropical, subtropical and in temperate areas. In gen-
2%) separately. Formalin is drenched into theheap @ 200-250ml/10L Repotting is done in another container filled with fresh media. All
eral, favourable temperature requirement is 15-300C in day and 10-200C in
water and the heap is covered with black polyethylene sheet for 7 these repotted plants are kept under shade for few days.
night depending upon the orchid species. Tropical orchids like Dendrobi-
days. Media is then turned and left for 4-6 days. Such treated soil is
um, Vanda and Phelaenopsis require 21-290C in day and 18-210C in night.
Whereas, Cattleya and Oncidium require 18-210C in day and 12-170C in
free from all types of soil born insects-diseases. Protected Structures
night. Relative humidity should be40-75% RH. Grows well under low in- Planting
tensity light and partial shade. Moderate to heavy rainfall with moist grow- High quality orchid for cut flower as well as pot plants is grown under natu-
ing conditions. The climate of Tripura is characterized by tropical hot and Orchids are planted in containers or some are tied on the tree trunk/ rally ventilated shade nets houses or polyhouses of varying dimensions
humid summer (RH:60-80%), mild winter and experiences heavy rainfall branches. Orchid can be planted directly on the ground in the pit con- (generally 300 -500m2 area and central height of 5-6m). The structure may
during the monsoon season. Temperature ranges from 20-350C in summer taining orchid media. be fully made of nets with 75% shade nets on the roof and 50% shade net or
and rainy season and 5-220C in winter. Rain forests are distributed in all transparent uv stabilized poly ethylene sheet covered roof top with black
parts of the state and different species of orchids grows naturally on forest Containers may be earthen pot, ceramic pot, plastics pot, wooden shade net celling for partial shade and side cover with green or black shade
trees. logs, wooden frame made baskets, galvanized wire baskets and bam- nets. Benches are constructed for making the stage for keeping orchid con-
boo made baskets. These are soaked in water for 1-2 hrs before filling tainers. Concrete piles of 1.5 x 1.5 inch thickness and 3-4 feet long are fixed
Suitable Orchids for Tripura in the container. on the ground at 3.5-4 feet width and 2.5-3 feet gap just opposite to each
Coconut husk made blocks containing charcoal chips are also used other along the line. Dimension of the benches may be adjusted depending
Orchid species collected are Dendrobium, Cattleya, Cymbidium, Vanda, specially for Dendrobium. upon the area of the polyhouse, so that 4 numbers of benches may be con-
Mokara and Phelaenopsis apart from some local wild collections. The most structed keeping 3 feet gap among the benches for easy movement. Piles are
suitable species for Tripura is Dendrobium for good quality cut flower pro- There should be sufficient holes for water drainage from the media inserted 1 feet deep into the ground and 2-3feetis kept above the ground.
duction. There are many colour and size variation in this species. Variety and for hanging purpose light weight containers are used. Flat stone Concrete beams are fixed with bolts horizontally along the width on the top
Sonia 17 and Sonia 28 have been found to be very good in terms of flower or broken clay pot pieces are put at the base of the container and then, of the pillars and 4-5 numbers of iron or wooden frames or thick wire are
spike length (40-55 cm) and flower size. Other colour ranges are pink, filled with coconut husk chips, charcoal and brick chips on after an- laid horizontally along the length and width at equal spacing to keep the
white, orange, yellow and red etc. and flowering is continued through out other. orchid containers. Spacing of these frames may be adjusted according to the
the year. Vase life is approx. 15-20 days and also has a long pot flower life Finally saw dust is put on these media. Small plantlets or off shoots size of the container or coconut husk blocks containing orchid plants. Sprin-
for about 45-50 days. Cymbidium species requires cool temperature (7- are carefully planted in pots or even cuttings of root and stem are also kler or mist irrigation pipes may also be laid along the length. Containers or
100C) to set flower bud and in the winter and flowering takes place in inserted into the potting mix. At the time of planting the stem should coconut blocks are placed 20-25 cm apart on the benches particularly during
spring season. Similarly, Cattleya species is cool temperature orchid and be erected upward and may be supported with bamboo stick. flowering time.
flowering takes place in winter. Flowering during August was also recorded
under Tripura condition with pot flower life of about 35-45 days.
Phalaenopsis can be grown in warm climate, however, requires low tem-
perature (120C) for flower initiation. Under Tripura condition, pick flower-
ing is during spring. Vanda is another warm climate orchid and Mokara is a
hybrid orchid under Vanda. Though, Dendrobium has been found to be
very good for cut flower, however, all these orchid species are very much
suitable for cut as well as pot plant purpose. Each orchid pot plant is sold
for Rs. 500-1000 depending on the size of plant and pot.
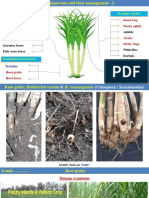
Orchids in bloom
Different Types of
Repotting
Planting
Naturally ventilated net house for Dendrobium
Continue…..
You might also like
- Sean Burke - Online Algae WebquestDocument4 pagesSean Burke - Online Algae Webquestapi-386190429100% (2)
- In Search of The Sacred Silk Cotton TreeDocument173 pagesIn Search of The Sacred Silk Cotton TreeLyall Winston Small80% (5)
- Orchid Cultivation PDFDocument2 pagesOrchid Cultivation PDFNars BabieraNo ratings yet
- Icar-Iihr Rose Varieties For Open Field: Insect Pests Symptoms Management Practices ThripsDocument2 pagesIcar-Iihr Rose Varieties For Open Field: Insect Pests Symptoms Management Practices ThripsReddyNo ratings yet
- AnthuriumDocument9 pagesAnthuriumHexaNotes100% (2)
- RAWE PRESENTATION-Insect, Pest & DiseaseDocument14 pagesRAWE PRESENTATION-Insect, Pest & DiseaseanujagriNo ratings yet
- WaterhycinthDocument7 pagesWaterhycinthEvan AzerNo ratings yet
- Package of Practice StrawberryDocument28 pagesPackage of Practice Strawberrypankaj kumarNo ratings yet
- TN 52 Moringa Water TreatmentDocument3 pagesTN 52 Moringa Water TreatmentPACITA LESTOJAS100% (1)
- Coconut DiseasesDocument32 pagesCoconut Diseasesmohamed ismailNo ratings yet
- Facilities Management: Submitted To: Dr. Mayanka Gupta Submitted By: Srishti MishraDocument25 pagesFacilities Management: Submitted To: Dr. Mayanka Gupta Submitted By: Srishti MishraSRISHTI MISHRANo ratings yet
- Betel Leaves Plant CareDocument4 pagesBetel Leaves Plant CareshriraghavNo ratings yet
- Botanical Pesticide FinalllDocument30 pagesBotanical Pesticide FinalllBenedict GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument5 pagesInternship ReportNavneet YadavNo ratings yet
- Organic Liquid FertilizersDocument2 pagesOrganic Liquid FertilizersSarwar M. RasheedNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Skeletonized LeavesDocument3 pagesLab Manual Skeletonized LeavesBrent Aren Bersabe SumadsadNo ratings yet
- Guide To OrchidsDocument7 pagesGuide To OrchidsShay GinsbourgNo ratings yet
- Betel Leaves EditedDocument8 pagesBetel Leaves EditednihanNo ratings yet
- Diseases of CoconutDocument16 pagesDiseases of CoconutTaushif AhammedNo ratings yet
- Cashew Nut FullDocument17 pagesCashew Nut FullKadipo BandaNo ratings yet
- 10 5923 J Plant 20180801 01 PDFDocument7 pages10 5923 J Plant 20180801 01 PDFmeriemNo ratings yet
- Some Tips For The Cultivation of VandasDocument3 pagesSome Tips For The Cultivation of VandasPrejith SampathNo ratings yet
- GerberaDocument32 pagesGerberaDr. Priyanka NandiNo ratings yet
- Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia Crassipes) As A Organic ManureDocument4 pagesWater Hyacinth (Eichhornia Crassipes) As A Organic Manuresukesh sNo ratings yet
- Micropropagation From Nodal Explants of Rose (Rosa Hybrida L.) at Different Concentration of BAP (6-Benzyl Amino Purine)Document4 pagesMicropropagation From Nodal Explants of Rose (Rosa Hybrida L.) at Different Concentration of BAP (6-Benzyl Amino Purine)Sokkunthea TholNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Rose CultivationDocument8 pagesRecent Advances in Rose CultivationamitNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble FertilizerDocument5 pagesWater Soluble FertilizerHarsh KotechaNo ratings yet
- Ento Unit 5 Note Upto 1st Term Exam PortionDocument39 pagesEnto Unit 5 Note Upto 1st Term Exam PortionAmitChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Plant Care SheetDocument11 pagesPlant Care SheetСтефан СтефановNo ratings yet
- Package of Practices in WheatDocument12 pagesPackage of Practices in WheatNibedita KhatuaNo ratings yet
- Ipm Vegetable Crops 26022015Document80 pagesIpm Vegetable Crops 26022015nabajyotib054No ratings yet
- Mesta 1.0Document5 pagesMesta 1.0Sharath.H sharuNo ratings yet
- Micropropagation of Mokara Orchid by Temporary Immersion System TechniqueDocument5 pagesMicropropagation of Mokara Orchid by Temporary Immersion System TechniqueMarco CordobaNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Propagation in Pteridophytes A ReviewDocument7 pagesIn Vitro Propagation in Pteridophytes A Reviewathira vijayanNo ratings yet
- Betel Vine CultivationDocument55 pagesBetel Vine CultivationDr.Eswara Reddy Siddareddy100% (1)
- DENNERLE Dennerle Plants PDFDocument20 pagesDENNERLE Dennerle Plants PDFmaztortonNo ratings yet
- Ojsadmin, 05 A Practical Guide For SuccessfulDocument6 pagesOjsadmin, 05 A Practical Guide For Successfulankush prakashNo ratings yet
- RhizobiumDocument23 pagesRhizobiumDipti PriyaNo ratings yet
- 30 Couroupitaagnano Deleted PDFStuffDocument9 pages30 Couroupitaagnano Deleted PDFStuffAnu GraphicsNo ratings yet
- KNR Agriculture CatalogDocument80 pagesKNR Agriculture Cataloganothermeii6No ratings yet
- Bio Protocol1108Document4 pagesBio Protocol1108Surendra MeenaNo ratings yet
- PCP Unit - IIIDocument26 pagesPCP Unit - IIIParthasarathiNo ratings yet
- Pest of Roses1Document11 pagesPest of Roses1Mukesh ShahNo ratings yet
- D.Bala Raju SMS Plant Protection KVK, KurnoolDocument29 pagesD.Bala Raju SMS Plant Protection KVK, KurnoolBalaraju DesuNo ratings yet
- k0199 70Document2 pagesk0199 70bingus sNo ratings yet
- W5 Lecture 4 SlidesDocument15 pagesW5 Lecture 4 SlidesDr-Ashay DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Terbacil in Orange SeedlingsDocument10 pagesMetabolism of Terbacil in Orange SeedlingsSh1vaNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Isolation of Protoplasts From Mesophyll Cells of Dendrobium Queen PinkDocument5 pagesA Study On The Isolation of Protoplasts From Mesophyll Cells of Dendrobium Queen Pinkkahkashan kazmiNo ratings yet
- Zantedeschia Manual: Scientific Name-Albomaculata Jucanda Family-Araceae Origin - South AfricaDocument8 pagesZantedeschia Manual: Scientific Name-Albomaculata Jucanda Family-Araceae Origin - South AfricagridinsergiuNo ratings yet
- Okra Production Guide - Beta - 356244Document2 pagesOkra Production Guide - Beta - 356244Kristine Joy PoliquitNo ratings yet
- Plant Protection Cardamom: Presented byDocument26 pagesPlant Protection Cardamom: Presented byaditya rajNo ratings yet
- Coconut DiseaseDocument10 pagesCoconut DiseaseummuzzzNo ratings yet
- Hydroponic Herb GardenDocument3 pagesHydroponic Herb GardenAbdul RazakNo ratings yet
- T.N. Fernando, S. A. Ariadurai, A. G. B. Aruggoda, C. K. Disanayaka and S. KulathungeDocument4 pagesT.N. Fernando, S. A. Ariadurai, A. G. B. Aruggoda, C. K. Disanayaka and S. Kulathungenilanthi fernandoNo ratings yet
- Rambey 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 122 012058Document11 pagesRambey 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 122 012058ist.nfNo ratings yet
- Guayabano Production GuideDocument7 pagesGuayabano Production GuideJobert ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Invitro Axillary Bud Proliferation PDFDocument8 pagesInvitro Axillary Bud Proliferation PDFShailaja SharmaNo ratings yet
- Culture Guide Gerbera DuroraDocument2 pagesCulture Guide Gerbera DuroraAlexandruNo ratings yet
- IndianLotus AMulti purposeAquaticOrnamentalPlant.Document4 pagesIndianLotus AMulti purposeAquaticOrnamentalPlant.Smit kalamkarNo ratings yet
- Dandelion: A Grower's GuideDocument4 pagesDandelion: A Grower's Guidemiyoko KoNo ratings yet
- Botany Practicals Question Bank Final 2020-21Document12 pagesBotany Practicals Question Bank Final 2020-21DIPANSHUNo ratings yet
- Get Ink & Wash Florals: Stunning Botanical Projects in Watercolor & Ink 1st Edition Camilla Damsbo Brix PDF Full ChapterDocument24 pagesGet Ink & Wash Florals: Stunning Botanical Projects in Watercolor & Ink 1st Edition Camilla Damsbo Brix PDF Full Chapterbastidaney100% (6)
- Major Test - Full Syllabus-1 - English - 12-Apr-2023 - StudentDocument34 pagesMajor Test - Full Syllabus-1 - English - 12-Apr-2023 - StudentSuman LattaNo ratings yet
- Heli Forklift CPC CPQ CPQD CPCD 2 5t 3t 3 5t Parts ManualDocument22 pagesHeli Forklift CPC CPQ CPQD CPCD 2 5t 3t 3 5t Parts Manualtimothyfisher200593ati100% (75)
- Difference Between Algae & Bryophytes Table - EasybiologyclassDocument7 pagesDifference Between Algae & Bryophytes Table - EasybiologyclassUPASI TRF VandiperiyarNo ratings yet
- Bio - Assignment - 1 (Reproduction in Flowering Plants)Document2 pagesBio - Assignment - 1 (Reproduction in Flowering Plants)VatsalNo ratings yet
- SeedWorks Standard Presentation VegetableDocument33 pagesSeedWorks Standard Presentation VegetableJenesa DelacruzNo ratings yet
- 4 Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pages4 Bahasa InggrisSyaila Affani NasutionNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 12 NotesDocument46 pagesBiology Class 12 Notesbalamuruganbro45No ratings yet
- BOT 101 Lecture Note On SpermatophytesDocument36 pagesBOT 101 Lecture Note On SpermatophytesAtoloye Favour100% (1)
- Crop Protection2Document22 pagesCrop Protection2skrt skrtNo ratings yet
- Practical Manual Pests of Field Crops and Their ManagementDocument37 pagesPractical Manual Pests of Field Crops and Their ManagementMahendra100% (6)
- Plant Identification BasicsDocument12 pagesPlant Identification BasicsARKASNo ratings yet
- Teak Tree - Rishika JainDocument8 pagesTeak Tree - Rishika JainHarsimran ChadhaNo ratings yet
- English Practice 41Document5 pagesEnglish Practice 41Bùi ThưNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants Revision Notes For Class 11 Biology CH 6Document30 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants Revision Notes For Class 11 Biology CH 6Anubhav MamgainNo ratings yet
- Terminal Five 2023Document32 pagesTerminal Five 2023jovic9002No ratings yet
- Cytokinins History:: 1. Tobacco Pith CultureDocument4 pagesCytokinins History:: 1. Tobacco Pith CulturedawoodNo ratings yet
- PC-FT 403: Lecture (1) byDocument21 pagesPC-FT 403: Lecture (1) byFT 19 Suparno DasNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Notes NeoDocument130 pagesAgriculture Notes NeoGodzila BwNo ratings yet
- Aula 2Document29 pagesAula 2Ana Patricia MartinsNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Tissues - Revision WRKSHT - 23-24Document3 pagesGrade 9 - Tissues - Revision WRKSHT - 23-24Yashvi PatelNo ratings yet
- Solution MT 4 Brahmastra 26 03 2023Document34 pagesSolution MT 4 Brahmastra 26 03 2023Vaibhav Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Biology Practicals Class XIIDocument37 pagesBiology Practicals Class XIIAnand Krishna PuthilenNo ratings yet
- Baba Bodse Junior College: Section A Q.1.Choose Correct Option: 4MDocument2 pagesBaba Bodse Junior College: Section A Q.1.Choose Correct Option: 4MsupriyaNo ratings yet
- Relationships Between Organisms LectureDocument23 pagesRelationships Between Organisms LectureGourav DasNo ratings yet
- Identifikasi Morfologi Dan Anatomi Tipe StomataDocument9 pagesIdentifikasi Morfologi Dan Anatomi Tipe StomataDella AndreanaNo ratings yet
- Oasis GK Key Book MinDocument146 pagesOasis GK Key Book MinJaishree RamNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 DLL ESP 6 Q1 Week 3abcDocument7 pagesGrade 6 DLL ESP 6 Q1 Week 3abcGeizel ReubalNo ratings yet