Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1st Year
1st Year
Uploaded by
fiker23swOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1st Year
1st Year
Uploaded by
fiker23swCopyright:
Available Formats
1. In the sum A + B = C, vector A has a magnitude of 12.0 m and is angled 40.
0◦ counter
clockwise from the +x direction, and vector C has magnitude of 15.0 m and is angled 20.0◦
counter clockwise from the -x direction. What are (a) the magnitude and (b) the angle (relative
to +x) of B?
2. A vector B, when added to the vector C = 3.0i+4.0j, yields a resultant vector that is in the
positive y direction and has a magnitude equal to that of C. What is the magnitude of B?
3. A penny is dropped from the top of the Sears Tower in Chicago. Considering that the height
of the building is 427 m and ignoring air resistance, find the speed with which the penny strikes
the ground. The penny starts from y = 0.
4. A tennis ball is struck such that it leaves the racket horizontally with a speed of 28.0 m/s.
The ball hits the court at a horizontal distance of 19.6 m from the racket. What is the height of
the tennis ball when it leaves the racket?
5. A golf ball is hit at a speed of 35.0 m/s at 50.0◦ above the horizontal toward a large brick
wall whose base is 80.0 m from the point where the ball is launched. (a) At what height does
the ball strike the wall? (b) What is the speed of the ball when it hits? (c) When the ball hit the
wall was it still rising or was it descending?
6. From her bedroom window a girl drops a water–filled balloon to the ground, 6.0 m below.
If the balloon is released from rest, how long is it in the air?
7. A small mass moves on a circular path of radius 2.50 m with constant speed; it makes one
revolution every 3.20 s. (a) what is the speed of the mass? (b) What is the magnitude of its
centripetal acceleration?
8. A 20 cm long tendon was found to stretch 40 mm by a force of 14 N. Assuming the tendon
was approximately circular and has a diameter of 9 mm. calculate
i) Tensile stress and Strain
ii) Young’s modulus under tensile stress
9. What is the principle behind hydraulic brakes used in automobiles?
A) Bernoulli’s theorem
B) Pascal’s law
C) Newton’s law
D) Archimedes’ principle
10. Explain briefly
i) Newton’s first law of motion
ii) Newton’s second law of motion
iii) Newton’s third law of motion
11. A small mass moves on a circular path of radius 2.5 m with constant speed, it makes one
revolution every 3.20 sec. a) what is the speed of the mass? b) What is the magnitude of its
centripetal acceleration?
12. A car has kinetic energy K. What will be the effect on its kinetic energy if its velocity is
doubled?
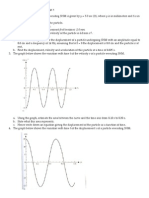
13. A particle oscillates with a simple harmonic motion (SHM) along the x-axis. Its position
varies with time according to the equation (X= (2m) cos (πt + π/4), where t is in seconds
and the angles in the parentheses are in radians.
A) Determine the amplitude, frequency, and period of the motion.
B) Calculate the velocity and acceleration of the object at any time t.
C) Determine the maximum speed and maximum acceleration of the object.
14. Atoms in a solid are not stationary, but vibrate about their equilibrium positions. Typically,
the frequency of vibration is about f = 2.0×1012 Hz, and the amplitude is about 1.1 × 10−11
m. For a typical atom, what is its (a) maximum speed and (b) maximum acceleration?
15. Write the four basic characteristics of waves which are important in determining the size
of waves, the speed of waves, etc.
16. Two sphere: 4 cm apart, attract each other with a force of 1.2 *10-9 N. Determine the
magnitude of the charge on each, if one has twice the charge (of the opposite sign) as the
other.
17. Write the main contribution of Physics in health science and medical imaging?
18. Equation of continuity………….
You might also like
- Solution Manual For A First Course in Abstract Algebra 8th Edition John B Fraleigh Neal Brand 2Document38 pagesSolution Manual For A First Course in Abstract Algebra 8th Edition John B Fraleigh Neal Brand 2sennitgladwyn17p68o100% (17)
- Governor's Study Group On Efficiency in State GovernmentDocument12 pagesGovernor's Study Group On Efficiency in State GovernmentMike Cason67% (3)
- Waves 1Document5 pagesWaves 1Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamNo ratings yet
- Igcse RevisionDocument62 pagesIgcse RevisionAnh_Hipton100% (3)
- 14 NMDocument17 pages14 NMArvindGovaNo ratings yet
- All Semester Activities PDFDocument19 pagesAll Semester Activities PDFIan Gerardo Memije NuñezNo ratings yet
- Problems 15 Serway 6 eDocument16 pagesProblems 15 Serway 6 eAndre CVNo ratings yet
- PHYF 115 Tutorial QuestionsDocument25 pagesPHYF 115 Tutorial QuestionsSattishZeeNo ratings yet
- Sheet 0 Oscillatory MotionsDocument2 pagesSheet 0 Oscillatory MotionsOmer GadNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Final Term Spring 2019-20. - 2Document2 pagesAssignment For Final Term Spring 2019-20. - 219-40122-1No ratings yet
- Asignment 1 - Phy210Document3 pagesAsignment 1 - Phy210MOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRINo ratings yet
- Tutoring QuestionsDocument7 pagesTutoring QuestionsJulieneNo ratings yet
- Advanced Higher Mechanics Tutorial 6Document2 pagesAdvanced Higher Mechanics Tutorial 6veluarasuNo ratings yet
- Work SheetDocument3 pagesWork SheetMikî Mań0% (1)
- CAPE Physics Unit I MarathonDocument26 pagesCAPE Physics Unit I MarathonLeighton ThompsonNo ratings yet
- R (4.0 CM + (2.5 CM/S) I + (5.0 CM/S) T J: - (A) Find The Magnitude and Direction of The Dot's AverageDocument4 pagesR (4.0 CM + (2.5 CM/S) I + (5.0 CM/S) T J: - (A) Find The Magnitude and Direction of The Dot's AverageOlojo Oluwasegun EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Problems 1,, Straightforward, Intermediate,: y (X, T) (0.800 M) Sin (0.628 (X - VT) )Document10 pagesChapter 16 Problems 1,, Straightforward, Intermediate,: y (X, T) (0.800 M) Sin (0.628 (X - VT) )Aldo Novaz CostradaNo ratings yet
- Extra Exercise Chapter One: System of Units: - BT, Where T Refers To Time. What AreDocument5 pagesExtra Exercise Chapter One: System of Units: - BT, Where T Refers To Time. What AreAina AdamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions Phy 101 DR AkinyemiDocument2 pagesTutorial Questions Phy 101 DR Akinyemisamuelakpuri5No ratings yet
- Repaso Bachillerato - EjerciciosDocument5 pagesRepaso Bachillerato - EjerciciosAnonymous qmwoKAfNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Muhammed IfkazNo ratings yet
- Annual Examination Physics (Theory) Code - B: Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70Document4 pagesAnnual Examination Physics (Theory) Code - B: Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70Sumathi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- XI Physics IMP Short QuestionsDocument4 pagesXI Physics IMP Short QuestionsAshfaque Memon100% (1)
- Tutorial Fundaamental PhysicsDocument2 pagesTutorial Fundaamental PhysicsIzyan Mohd SubriNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET NO. 5 - Simple Harmonic MotionDocument2 pagesWORKSHEET NO. 5 - Simple Harmonic MotionMark SmithNo ratings yet
- Physics HHHHDocument4 pagesPhysics HHHHsatishNo ratings yet
- PCS125 Tutorial QuestionsDocument52 pagesPCS125 Tutorial Questionsfurbac321No ratings yet
- SHM and Waves Problem SetDocument5 pagesSHM and Waves Problem SetbananacrunchNo ratings yet
- Problems 16 SerwayDocument11 pagesProblems 16 SerwayKitz DerecoNo ratings yet
- 1 0wave1 11 2activityDocument10 pages1 0wave1 11 2activityNisa Hj MohamadNo ratings yet
- Sample FinalDocument15 pagesSample FinalGeoff HattNo ratings yet
- 3U Exam ReviewDocument5 pages3U Exam ReviewShivansh DharNo ratings yet
- Physics (Theory) Class - Xi Course Code-042Document10 pagesPhysics (Theory) Class - Xi Course Code-042Puneet KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice ProblemDocument2 pagesPhysics Practice ProblemnurulalomadorNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 Su 20 105 ADocument2 pagesAssignment-1 Su 20 105 AMd. Imran AhmedNo ratings yet
- I-Taalem Task - Chapter 8Document3 pagesI-Taalem Task - Chapter 8ruzaimi98No ratings yet
- 11 Physics SPDocument4 pages11 Physics SPvikas vyasNo ratings yet
- Affiliated To Central Board of Secondary EducationDocument18 pagesAffiliated To Central Board of Secondary Educationdeetchu10No ratings yet
- B.Tech (ME) T2105 - T1105Document2 pagesB.Tech (ME) T2105 - T1105mohammedafreeed700No ratings yet
- Physics 1 2016-17 Quiz3Document6 pagesPhysics 1 2016-17 Quiz3Khoa TrầnNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment I PHY 105/PHY 2105 PhysicsDocument1 pageHome Assignment I PHY 105/PHY 2105 PhysicsMd. Imran AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ref Phy 9Document1,351 pagesRef Phy 9mkumar0% (2)
- Motion in Two & Three Dimensions: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsDocument7 pagesMotion in Two & Three Dimensions: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsRomou AlsaaqNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 AssignmentDocument1 pageUnit 2 AssignmentSagar YadavNo ratings yet
- Phys 1011 Worksheet II 2015Document6 pagesPhys 1011 Worksheet II 2015MeklitNo ratings yet
- Gr11 Physics FpeDocument42 pagesGr11 Physics FpeHoàn Nguyễn NgọcNo ratings yet
- MidtermPractice (UnknownDate)Document4 pagesMidtermPractice (UnknownDate)Mansoor Al TunijiNo ratings yet
- End of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CDocument4 pagesEnd of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CChristina ZhangNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - KinematicsDocument4 pagesTutorial 3 - KinematicsDanny MutamboNo ratings yet
- NUPOC Study GuideDocument26 pagesNUPOC Study GuideAmrit Pal Singh RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Assignment I - PHY 101 - A PDFDocument1 pageAssignment I - PHY 101 - A PDFmkNo ratings yet
- Final Exam W07Document5 pagesFinal Exam W07Malik ANo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument4 pagesPHYSICSAarav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion Problems With Answers FINALDocument15 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion Problems With Answers FINALAngelNo ratings yet
- General Physics Worksheet OneDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics Worksheet OnejadedstillharmonyNo ratings yet
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch13 Test BankDocument14 pagesWolfson Eup3 Ch13 Test Bankifghelpdesk100% (1)
- Tutorials 3 - Motion in One Dimension and Two DimensionsDocument6 pagesTutorials 3 - Motion in One Dimension and Two DimensionsSamson ManyanyeNo ratings yet
- Wave Properties CrevDocument7 pagesWave Properties CrevFatah BanyunukiNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Explain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorFrom EverandExplain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Electric Power Steering ReportDocument454 pagesElectric Power Steering Reportangel tomas guerrero de la rubiaNo ratings yet
- The Complete Buyers Guide To A Semantic LayerDocument17 pagesThe Complete Buyers Guide To A Semantic LayerSujit SadagopanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 QuestionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 2 QuestionsPham Thi Hong ThuyNo ratings yet
- Device Comment 12/6/2021 Data Name: COMMENTDocument17 pagesDevice Comment 12/6/2021 Data Name: COMMENTRio WicakNo ratings yet
- Big Data Analytics (2017 Regulation)Document8 pagesBig Data Analytics (2017 Regulation)cskinitNo ratings yet
- Building MaterialsDocument13 pagesBuilding MaterialsDeeana MoraaNo ratings yet
- 18 Cognitive Bias ExamplesDocument55 pages18 Cognitive Bias Examplesbogzi100% (1)
- Definition of Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument9 pagesDefinition of Strategic Human Resource ManagementAnkush RanaNo ratings yet
- FiltersDocument4 pagesFiltersESRANo ratings yet
- NLL INT Extra Practice KeyDocument2 pagesNLL INT Extra Practice KeyMagdalena ZglińskaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Design ThinkingDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Design Thinkingrawasthi29No ratings yet
- Department of Social Welfare Services: Republic of The Philippines City of CebuDocument2 pagesDepartment of Social Welfare Services: Republic of The Philippines City of CebuadoptifyNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Topic - Salts 2Document5 pagesCH 2 Topic - Salts 2siratNo ratings yet
- Installation & User Guide PC HP RP5800 On VIDASDocument41 pagesInstallation & User Guide PC HP RP5800 On VIDASHadi AlbitarNo ratings yet
- MicroondasDocument196 pagesMicroondasSaid A Herrera LNo ratings yet
- Fan ArrangementDocument3 pagesFan ArrangementSantoshNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Economics Formula Sheet.Document38 pagesStatistics For Economics Formula Sheet.VivekNo ratings yet
- IEC Standard Symbols Packing and InstructionDocument11 pagesIEC Standard Symbols Packing and InstructionPumps RnDNo ratings yet
- sjzl20096163-ZXMSG5200 (V3.1) Multiplex Service Gateway Configuration Manual (CLI)Document204 pagessjzl20096163-ZXMSG5200 (V3.1) Multiplex Service Gateway Configuration Manual (CLI)muhammadtariq730100% (1)
- IV. Choose The Word That Has The Stress Pattern Different From That of The Other Words. (10pts)Document7 pagesIV. Choose The Word That Has The Stress Pattern Different From That of The Other Words. (10pts)sad mindNo ratings yet
- PRC ApplicationDocument1 pagePRC ApplicationJericho CabungcalNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Manual For Alpha Series AmplifiersDocument156 pagesInstallation and Operation Manual For Alpha Series AmplifiersMogtaba OsmanNo ratings yet
- HS3251 Professional English-II Notes 04 - by WWW - Notesfree.inDocument126 pagesHS3251 Professional English-II Notes 04 - by WWW - Notesfree.inrakulkavi4No ratings yet
- Modelling of Primary FragmentationDocument10 pagesModelling of Primary FragmentationRamancoronaNo ratings yet
- Rimaoctavia - 20180350107 - Farmasi - Unit 8Document2 pagesRimaoctavia - 20180350107 - Farmasi - Unit 8rimaocta02No ratings yet
- 7th FINA World Junior SwimmingDocument17 pages7th FINA World Junior SwimmingAlvaro Covarrubias BascuñateNo ratings yet