Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geo
Geo
Uploaded by
Nikoleta Konrádová0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
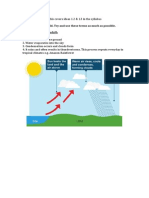
4 views2 pagesFronts occur where two different air masses meet and mix. There are three types of fronts: cold fronts, warm fronts, and occluded fronts, classified based on temperature. Seasonal winds include monsoons, which reverse direction between summer and winter due to uneven land and sea surface heating. Local winds occur on smaller scales and include sea and land breezes as well as mountain and valley winds. There are three main types of rainfall: frontal/depressional rainfall from colliding air masses; convective rainfall from rapid air uplift; and orographic rainfall when moist air is forced over high terrain.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFronts occur where two different air masses meet and mix. There are three types of fronts: cold fronts, warm fronts, and occluded fronts, classified based on temperature. Seasonal winds include monsoons, which reverse direction between summer and winter due to uneven land and sea surface heating. Local winds occur on smaller scales and include sea and land breezes as well as mountain and valley winds. There are three main types of rainfall: frontal/depressional rainfall from colliding air masses; convective rainfall from rapid air uplift; and orographic rainfall when moist air is forced over high terrain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesGeo
Geo
Uploaded by
Nikoleta KonrádováFronts occur where two different air masses meet and mix. There are three types of fronts: cold fronts, warm fronts, and occluded fronts, classified based on temperature. Seasonal winds include monsoons, which reverse direction between summer and winter due to uneven land and sea surface heating. Local winds occur on smaller scales and include sea and land breezes as well as mountain and valley winds. There are three main types of rainfall: frontal/depressional rainfall from colliding air masses; convective rainfall from rapid air uplift; and orographic rainfall when moist air is forced over high terrain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
ATMOSPHERE
- fronts=zone/area where 2 different types of air mass meet&mix
COLD&WARM FRONTS
- classification of airfronts acc. to temperature: 1. COLD F.=occurs when cold polar air meets warm tropical air -
warm air rises, condenses from tall/high clouds (this process is short but very intensive w/thunder and lightnings
2. WARM F.= occurs when tropical air meets cold polar air – warm air slowly rises and creates long period of rain
which is steady&gently
3. OCCLUDED F.=occurs when warm&cold front meet and mix
- classification acc. to source region: 1. the Arctic front=separates Arctic air mass from Polar air mass
2. the Polar f.= separates Polar air mass from Tropical air mass
3. the Equatorial f.= separates Tropical air mass from Equatorial air mass
SEASONAL WINDS
monsoon circulation
- monsoon=is derived from mausin meaning season and it is wind whose direction is completely reversed from 1
season to the next
- land surfaces heat in summer and cool in winter much faster than water surf., the unequal temperatures cause
significant differences in pressure over continental&oceanic areas
- reasonal reversal of wind direc. between oceanic surf. and neighboring lands develops in many parts of the Earth
but monsoon effect, due to its great size, is most typical in South&South-East Asia
- importance of monsoons in Asia
SUMMER MONSOON=blows from ocean surf. to land s. and brings precipitation (very important for growing of rice)
WINTER M.=blows from land surf. to ocean surf. and brings dry sunny weather (important for turism)
LOCAL WINDS
- occur in smaller areas on daily timescale/periodically throughout year
LAND&SEA BREEZE – monsoons in small scale
sea breeze=occurs during summer day, wind blows from water surf. to land s. bcs water s. is cooler than land s. (high
pressure/low p.)
land breeze=occurs during clear night, wind blows from land s. to water s. bcs land s. is cooler than water s. (high
p./low p.)
MOUNTAIN&VALLEY WINDS
valley wind=occurs during sunny day, it´s warm rising air along slopes-bcs sun heats slopes very quickly and there´s
low pressure
mountain wind=occurs during night, it´s cold sinking air along slopes- bcs slopes cool down very quickly during night
and there´s high p.
fohn (fohn wind formation)=warm sinking air in high mountains, especially in northern slopes of the Alps
RAINFALL
- condensation takes place when water vapour changes into tiny water droplets/particles of ice; it occurs when
saturated, cooled to below its dew point (temperature at which water vapour saturates from air mass into
liquid/solid usually forming rain, snow, frast, dew; it occurs when air mass has humidity 100%) and there are small
particles of matter such as dust in air
- forms of condensation are cloud, mist, fog/frost (ice particles)
precipitation= large water droplets (rain) and ice particles (snow, hail) that fall to ground
- 3 TYPES OF RAINFALL (acc. to process of formation)
1. FRONTAL/DEPRESSION/CYCLONE – resulting from meeting of 2 different air masses; long term precipitation,
usually gently
2. COVECTIONAL – air uplift causes condensation of water vapour, fast development of clouds; short intensive
precipitation
3. OROGRAPHIC/RELIEF – humid air mass, when forced to rise to overcome relief barrier, cools and produces
precipitation over windward side of slope
- prefixes&suffixes used to describe clouds: CIRRUS, ALTUS, FOG, NIMBUS, CUMULUS, STRATUS
You might also like
- ATPL - EASA2016 - MeteorologyDocument70 pagesATPL - EASA2016 - MeteorologyNuno Arnaud100% (2)
- 8 - Cluster 4 - Weather - Manitoba - Grade 5 Science Unit - Distance LearningDocument36 pages8 - Cluster 4 - Weather - Manitoba - Grade 5 Science Unit - Distance LearningZabrinaNo ratings yet
- Flight Doc NotationsDocument1 pageFlight Doc Notationsdard100% (1)
- On Planetary WindsDocument57 pagesOn Planetary WindsTenzin DemaNo ratings yet
- Weather Climate NotesDocument61 pagesWeather Climate NotesRene Ramilo100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Notes - 34622175 - 2024 - 05 - 01 - 03 - 58Document18 pagesLecture 3 Notes - 34622175 - 2024 - 05 - 01 - 03 - 58forreading1820No ratings yet
- Hydrometeorological HazardsDocument26 pagesHydrometeorological HazardsMr GameplayNo ratings yet
- Land Breeze andDocument6 pagesLand Breeze andDeleteafter ThismlbbNo ratings yet
- Met 05Document4 pagesMet 05janine GoncalvesNo ratings yet
- Climate and Weather Patterns (Lessons) 1Document5 pagesClimate and Weather Patterns (Lessons) 1patcris moncadaNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Factors Affecting ClimateDocument16 pagesPresentation - Factors Affecting ClimateAltoverosDihsarlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - ClimateDocument10 pagesChapter 2 - ClimateJOSHUA TAN LI EN (4R52023)No ratings yet
- Seismic Design Criteria For Soil LiquefactionDocument8 pagesSeismic Design Criteria For Soil LiquefactionJim SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document6 pagesLesson 7ricapearl.zorillaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 AssignmentDocument12 pagesWeek 2 AssignmentKenneth Ryan EbaldoneNo ratings yet
- The AtmosphereDocument28 pagesThe AtmosphereJulie Amor ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Weather and Climate 1Document5 pagesModule 3: Weather and Climate 1LaurenNo ratings yet
- 5 Ch2 - ClimateDocument5 pages5 Ch2 - ClimateMARIA ISABILLE DUALLO MUSONGNo ratings yet
- Meteorology ReviewerDocument6 pagesMeteorology ReviewerRyanNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study GuideDocument2 pagesExam 1 Study GuideafdsghfhjgNo ratings yet
- Classification of Air Masses and Fronts - Geography Optional - UPSC - Digitally LearnDocument14 pagesClassification of Air Masses and Fronts - Geography Optional - UPSC - Digitally LearnPrakhar BilloreNo ratings yet
- Air MassesDocument22 pagesAir MassesPrince MpofuNo ratings yet
- Climate and Global Systems Earth SciDocument6 pagesClimate and Global Systems Earth SciClarence DeitaNo ratings yet
- Land and Sea Breezes Monsoon Cold and Warm Fronts ItczDocument40 pagesLand and Sea Breezes Monsoon Cold and Warm Fronts ItczJeric ValdezNo ratings yet
- Weather Study Guide Earth ScienceDocument11 pagesWeather Study Guide Earth Sciencefailures12No ratings yet
- Weather StudiesDocument17 pagesWeather StudiesMuz SitholeNo ratings yet
- Meteo 0 Module Week 9 12 SemifinalDocument11 pagesMeteo 0 Module Week 9 12 Semifinalalyssainojosa9No ratings yet
- Geografía Tema 4Document12 pagesGeografía Tema 4Rocío MadolellNo ratings yet
- ClimateDocument38 pagesClimatecharlesmaniulitNo ratings yet
- Weather NotesDocument6 pagesWeather NotesAwesomeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Climate ChangeDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 Climate Changemaleeha baburNo ratings yet
- MeteorologyDocument10 pagesMeteorologyAMAZING GREATNESSNo ratings yet
- Weather Systems Vocab Updated 12-31-14Document5 pagesWeather Systems Vocab Updated 12-31-14api-260201978No ratings yet
- Weather Climate NotesDocument68 pagesWeather Climate Notesmrlu1sandNo ratings yet
- Geo Weather Quiz Notes1Document3 pagesGeo Weather Quiz Notes1Michelle LiNo ratings yet
- Ak HW HFST 2Document10 pagesAk HW HFST 2akbarshahbasaratNo ratings yet
- For WebsiteDocument2 pagesFor Websiteapi-290916666No ratings yet
- W15 Q2 LESSON 6.1 Understanding TyphoonsDocument18 pagesW15 Q2 LESSON 6.1 Understanding TyphoonsAndrina Binogwal TocgongnaNo ratings yet
- g6 Factors Affecting The ClimateDocument35 pagesg6 Factors Affecting The ClimateserwelaslebronNo ratings yet
- Monsoon Season 1Document2 pagesMonsoon Season 1adi bachtiarNo ratings yet
- Air MassDocument34 pagesAir MassRahul DekaNo ratings yet
- Discuss How The Global Wind Pattern Is FormedDocument9 pagesDiscuss How The Global Wind Pattern Is FormedJonelou CusipagNo ratings yet
- Meterology 1.3-2.5 and 10Document6 pagesMeterology 1.3-2.5 and 10nishant85408No ratings yet
- Earth Science 061307Document24 pagesEarth Science 061307Keith Elizer MarayagNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 PDFDocument6 pagesLecture 2 PDFaliNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes!: Candidates Should Be Able ToDocument13 pagesLearning Outcomes!: Candidates Should Be Able ToThe ExistingNo ratings yet
- GR 12 Climatology Part 1Document50 pagesGR 12 Climatology Part 1Oluwatooyin OyegbileNo ratings yet
- Mass 369104ngsDocument5 pagesMass 369104ngsPhftNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Weather and ClimateDocument3 pages1st Year Weather and ClimateBrYan GoNo ratings yet
- Weather 17Document47 pagesWeather 17Adrian QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document28 pagesCH 2ADIL DURRANINo ratings yet
- A Summary of The Hydrologic Cycle: Lecture One Definition of HYDROLOGYDocument7 pagesA Summary of The Hydrologic Cycle: Lecture One Definition of HYDROLOGYAnonymous aE0YYlCOKNo ratings yet
- Tropical Cyclones and Factors Influencing Climate: By: Onen LailaDocument12 pagesTropical Cyclones and Factors Influencing Climate: By: Onen LailaHadad LwazeNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure, Breezes, Monsoons, ITCZDocument47 pagesAir Pressure, Breezes, Monsoons, ITCZmichaelaapilat026No ratings yet
- What Is It-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesWhat Is It-WPS OfficeYanna HerasNo ratings yet
- Precipiation and Rainfall Types and Their Characteristic FeaturesDocument3 pagesPrecipiation and Rainfall Types and Their Characteristic FeaturesJejomae Isberto CalisingNo ratings yet
- METDocument5 pagesMETD PrasathNo ratings yet
- Name: Syeda Rubab Roll No# BSSEC-19-78Document4 pagesName: Syeda Rubab Roll No# BSSEC-19-78c saadNo ratings yet
- GR 12 Climatology Part 2Document40 pagesGR 12 Climatology Part 2Oluwatooyin OyegbileNo ratings yet
- Week 21 Learning PacketDocument12 pagesWeek 21 Learning PacketAizel Nova AranezNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Lecture NotesDocument47 pagesModule 4 Lecture Notesrz2853No ratings yet
- Introduction To ClimatologyDocument36 pagesIntroduction To ClimatologyMehak SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Climate ServicesDocument23 pagesClimate ServicesPeEjay EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- By Dr. Md. Mahfuzur RahmanDocument15 pagesBy Dr. Md. Mahfuzur RahmanRifat RomanNo ratings yet
- TS or CB Clouds or AIR MASS THUNDERSTORMSDocument11 pagesTS or CB Clouds or AIR MASS THUNDERSTORMSLiwan ChristopherNo ratings yet
- On CycolneDocument37 pagesOn CycolneMoshin Khan100% (1)
- Ppt. Presentation-Weather DisturbancesDocument36 pagesPpt. Presentation-Weather DisturbancesDanFel Pajimula100% (5)
- Learn About HurricanesDocument2 pagesLearn About Hurricanesapi-255930635No ratings yet
- Wind WeatherDocument9 pagesWind WeatheroffshorearmadaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Physics Review - Includes Cloud Physics and Cloud DynamicsDocument5 pagesCloud Physics Review - Includes Cloud Physics and Cloud DynamicsJames WallaceNo ratings yet
- WX-950 Stormscope-CompressedDocument47 pagesWX-950 Stormscope-CompressedViniciusppaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper 1Document3 pagesReaction Paper 1chadionisioNo ratings yet
- 3 CrosswordDocument1 page3 Crossworddio..No ratings yet
- Weather Review Sheet AnswersDocument3 pagesWeather Review Sheet Answersapi-270626148No ratings yet
- Forecasting at Meteorological Centers of IMDDocument34 pagesForecasting at Meteorological Centers of IMDnarachasNo ratings yet
- Anticyclone and Other Pressure SystemsDocument18 pagesAnticyclone and Other Pressure SystemsSalvador Jr. Besares67% (3)
- Marcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabDocument5 pagesMarcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabShiyas Basheer100% (1)
- WeatherDocument2 pagesWeatherAvtar DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 4: Understanding Typhoons: ScienceDocument33 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 4: Understanding Typhoons: ScienceCharity Bantigue100% (9)
- METEOROLOGYDocument37 pagesMETEOROLOGYfarras cantikaNo ratings yet
- HS Earth Science Chapter 20 Power PointDocument36 pagesHS Earth Science Chapter 20 Power PointMichael McPeakNo ratings yet
- On That Tragic Day in IranDocument3 pagesOn That Tragic Day in IranLone WolfNo ratings yet
- Subiecte Clasa A VIII-A 2018Document3 pagesSubiecte Clasa A VIII-A 2018Oana-Violeta Si Cornel SelaruNo ratings yet
- El Nino and La NinaDocument13 pagesEl Nino and La NinashilpaogaleNo ratings yet
- Indian Monsoons: Breeze On A Large ScaleDocument7 pagesIndian Monsoons: Breeze On A Large ScaleVikram DasNo ratings yet
- Rosa Del Viento de La Estacion MACHUPICCHODocument2 pagesRosa Del Viento de La Estacion MACHUPICCHOQuispe Huarayo UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Met Ocean Ant II E-Learning 6Document16 pagesMet Ocean Ant II E-Learning 6AndhikaNo ratings yet
- Soal LatihanDocument5 pagesSoal LatihanHizkia RusdimanNo ratings yet
- Song of The RainDocument4 pagesSong of The RainGajendra SinghNo ratings yet