Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formatif F4
Formatif F4
Uploaded by
Mia nina Marn najmiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Bio Module 2 PhotoMasterDocument23 pagesBio Module 2 PhotoMasterh33% (3)
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-FunctionsDocument23 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-FunctionsEmer Perez50% (2)
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanElizer100% (9)
- Model Answers: Chapter 2 Cell Biology and OrganizationDocument4 pagesModel Answers: Chapter 2 Cell Biology and Organizationsyed ali100% (1)
- Handout 2: Amity International School, Noida Class Ix Biology Chapter: The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesHandout 2: Amity International School, Noida Class Ix Biology Chapter: The Fundamental Unit of LifeayaanNo ratings yet
- Cells Activity QuestionsDocument2 pagesCells Activity QuestionsMusab AlbarbariNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: Name: - Class: - DateDocument7 pagesWorksheet: Name: - Class: - DateKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument8 pagesBIOENERGETICSSarah CalventasNo ratings yet
- Module 5 EALSDocument9 pagesModule 5 EALSKleffer YnanNo ratings yet
- BIO KPM Textbook ExercisesDocument33 pagesBIO KPM Textbook ExercisesJs TeoNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological OrganizationsDocument23 pagesLevels of Biological OrganizationsYuu KieNo ratings yet
- Student Booklet 8 Sci Student Activiry BookletDocument14 pagesStudent Booklet 8 Sci Student Activiry Bookletthe.efroNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4Document9 pagesBiology Form 4Ashlyn OoiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesRahul ManhasNo ratings yet
- Sallim Herniza P. Week 1 General Biology 1 SW1Document8 pagesSallim Herniza P. Week 1 General Biology 1 SW1Nurhaliza KuhutanNo ratings yet
- Biology Y10 Ch2Document7 pagesBiology Y10 Ch2zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- G9 - NCERT - The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument7 pagesG9 - NCERT - The Fundamental Unit of LifeYour mother Is fatNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument15 pagesBiologyChit su su zawNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument6 pagesCell Organelles WorksheetAndi ImanNo ratings yet
- Bio1 Lesson 1 NotesDocument7 pagesBio1 Lesson 1 Notesykanemoto81No ratings yet
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Document21 pagesAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.No ratings yet
- m2 DraftDocument4 pagesm2 DraftMae lea AndoloyNo ratings yet
- g11 Els OrganellesDocument3 pagesg11 Els OrganellesJarod PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Document17 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Dette Dominic Ballano67% (3)
- Short Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFDocument6 pagesShort Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFTanUeiHorngNo ratings yet
- M3 - Exercise 4. Plant and Animal CellDocument10 pagesM3 - Exercise 4. Plant and Animal CellVanessa RafaelNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Activity in Chapter 2. Exploring The CellDocument4 pagesAssessment and Activity in Chapter 2. Exploring The CellArmie Rose FaldasNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and FunstionsDocument4 pagesEukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and FunstionsCiara PanenNo ratings yet
- B.S 8.1 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesB.S 8.1 Lesson PlanNiranjan UniqueNo ratings yet
- General Biology Cells1Document6 pagesGeneral Biology Cells1Kristine CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Chapter IvDocument20 pagesChapter IvLaila Abdullah AmparoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure CH 1 CH 2 Ver 2Document22 pagesCell Structure CH 1 CH 2 Ver 2FaizNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Differences Between Light and Electron MicroscopeDocument14 pagesCell Structure: Differences Between Light and Electron Microscopeshen doweNo ratings yet
- Ch2. Notes - CellsDocument7 pagesCh2. Notes - Cellsmelodyau.seNo ratings yet
- Ex 3 Anaphysio PDFDocument6 pagesEx 3 Anaphysio PDFJayren Ramos TanghalNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument2 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Lifegamingayush4608No ratings yet
- 9th Unit 1Document17 pages9th Unit 1[36] IX-B P.Vishnu Vardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cell Growth and ReproductionDocument5 pagesCell Growth and ReproductionIsrael EsmileNo ratings yet
- Cell PortfolioDocument7 pagesCell PortfolioChhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cl6001 Module 1Document11 pagesCl6001 Module 1reshalyavikaumadi19No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Cell Structure and OrganizationDocument32 pagesChapter 2: Cell Structure and Organizationaida maroNo ratings yet
- Types of Cell PDFDocument20 pagesTypes of Cell PDFDave Billona100% (1)
- Science 7 Animals and Plant Cells 3Document33 pagesScience 7 Animals and Plant Cells 3Welfredo Jr YuNo ratings yet
- Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesCell: The Basic Unit of LifePradyun DSNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesDelhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionSaket TNo ratings yet
- CH 6 BioDocument5 pagesCH 6 BioedwarddameNo ratings yet
- CH - 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Text Book ExercisesDocument6 pagesCH - 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Text Book ExercisesUnkown HumanNo ratings yet
- Act 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportDocument7 pagesAct 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportAmy BalicagNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure AND Cell OrganisationDocument54 pagesCell Structure AND Cell OrganisationAngel Cascayan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 CellDocument109 pagesChapter 8 CellhafsaNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio Quiz 1Document3 pagesCell Bio Quiz 1raphaelNo ratings yet
- Cells Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCells Revision NotesmarzybarNo ratings yet
- Life Science 1Document5 pagesLife Science 1api-381391951No ratings yet
- O Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsDocument10 pagesO Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsTakudzwa ZvidzaNo ratings yet
- The Science of Cytology Cell Theory: The Principle Core of BiologyDocument6 pagesThe Science of Cytology Cell Theory: The Principle Core of Biologyhendrix obciana100% (1)
- CELLDocument17 pagesCELLdina ahmedNo ratings yet
- Rganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument26 pagesRganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationGasterNo ratings yet
- VPHYS 3 200 General Physiology 1 Sem 2021-2022 Laboratory Exercise Written ReportDocument4 pagesVPHYS 3 200 General Physiology 1 Sem 2021-2022 Laboratory Exercise Written ReportRated SPGNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Topic 1 Past Paper QuestionsDocument9 pagesBIOLOGY Topic 1 Past Paper QuestionsLoraine NNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Nutrient Losses Throughout The Blood FlowDocument2 pagesNutrient Losses Throughout The Blood FlowGwenethVineEscalanteNo ratings yet
- Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 2005 PDFDocument773 pagesAnnual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 2005 PDFditabokNo ratings yet
- Electrical Steel - PoscoDocument193 pagesElectrical Steel - PoscoJesus Verduzco100% (2)
- Physical Science Lesson 1Document2 pagesPhysical Science Lesson 1Mary Ann TolibaoNo ratings yet
- References For Human Hair PDFDocument2 pagesReferences For Human Hair PDFAbdelkader ZerroukNo ratings yet
- Past Year CHM510Document5 pagesPast Year CHM510May LeeNo ratings yet
- True Final Oral Presentation ScriptDocument2 pagesTrue Final Oral Presentation ScriptPich'y C. YiengveerachonNo ratings yet
- Design of S El Superstructure ElementsDocument75 pagesDesign of S El Superstructure Elementsyilkal kassahunNo ratings yet
- Marcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabDocument5 pagesMarcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabShiyas Basheer100% (1)
- Inventory StatusDocument19 pagesInventory StatusMuhaiminul IslamNo ratings yet
- Ansi 61Document3 pagesAnsi 61emperor_vamsiNo ratings yet
- VSD Program Guide v2Document43 pagesVSD Program Guide v2David BEN HAIMNo ratings yet
- 220 - Válvula de GloboDocument1 page220 - Válvula de GloboRafael SalazarNo ratings yet
- Batch No: Wurth SR No: 1 Date: 2/1/2018 Tested For: PAHARPUR Test Type: Tensile - Rod/Tube Basic Load/Displacement GraphDocument7 pagesBatch No: Wurth SR No: 1 Date: 2/1/2018 Tested For: PAHARPUR Test Type: Tensile - Rod/Tube Basic Load/Displacement GraphkasvikrajNo ratings yet
- MSDS Blasocut: Blaser Swisslube IncDocument4 pagesMSDS Blasocut: Blaser Swisslube InczaqNo ratings yet
- Halogen Boiling Point 10.1.1.510.8630Document6 pagesHalogen Boiling Point 10.1.1.510.8630NITIN P SHAHNo ratings yet
- Cells and Microscopes. Ms CooperDocument33 pagesCells and Microscopes. Ms CooperzeeNo ratings yet
- Distillation Technology and Need of Simultaneous Design and Control A ReviewDocument24 pagesDistillation Technology and Need of Simultaneous Design and Control A ReviewHesam AhmadianNo ratings yet
- Design of A Cryogenic Grinding System For SpicesDocument10 pagesDesign of A Cryogenic Grinding System For Spicesdeepakkumar2626No ratings yet
- Pet Fiber Spinning MethodDocument15 pagesPet Fiber Spinning Methodsuresh shobanatNo ratings yet
- BM1 ProcessDocument55 pagesBM1 Processeduardo_umNo ratings yet
- I SEM Backlog 12-11-2021Document46 pagesI SEM Backlog 12-11-2021Îdíøt Bøy SâtyäNo ratings yet
- Chol 440 - 576 XL-1000 - Xsys0009 - 70 - GDocument4 pagesChol 440 - 576 XL-1000 - Xsys0009 - 70 - GMatibar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Teknik Eksplorasi-Eksplorasi GeokimiaDocument27 pagesTeknik Eksplorasi-Eksplorasi GeokimiaAndry FerdianNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical ReactionsDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Chemical ReactionsHema lathaNo ratings yet
- A Citizen's Guide To BioremediationDocument2 pagesA Citizen's Guide To BioremediationRenatoNo ratings yet
- WinWave Power Point PresentationDocument34 pagesWinWave Power Point PresentationpatrizziamarieNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Di Deionised WaterDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Di Deionised Watercgjp120391No ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument5 pagesPhysical Sciencecatherine aleluyaNo ratings yet
- PolymerDocument30 pagesPolymerBarang TeknikNo ratings yet
Formatif F4
Formatif F4
Uploaded by
Mia nina Marn najmiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formatif F4
Formatif F4
Uploaded by
Mia nina Marn najmiCopyright:
Available Formats
1
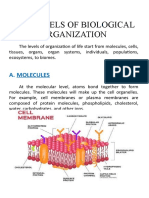
FORMATIVE PRACTICE FORM 4 • Plant cells have large vacuoles, whereas
C2 Cell Biology and Organisation animal cells do not (if there is, the size is small).
• Plant cells do not have centrioles whereas
FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 2.1 animal cells do.
1. State one structural difference between the
rough endoplasmic reticulum and the mooth
endoplasmic reticulum.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes
attached it whereas smooth endoplasmic FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 2.2
reticulum does not have any ribosomes
attached to it
1. What is the function of the contractile
vacuole in a Paramecium sp.?
2. Why is the use of an electron microscope
Contractile vacuoles are involved in
important in studying cells?
osmoregulation.
Light microscope usually has a magnification
2. How does the Amoeba sp. move?
of 1000x. On the other hand, the lectron
microscope is able to magnify a cell as much as
Amoeba sp. moves by extending its
2000000x.
pseudopodium (false feet)
Without an electron microscope, cell structures
This is followed by cytoplasmic streaming into
cannot be seen clearly because the light
the extended pseudopodium.
microscopes can only observe certain cell
components, such as cell membrane, cell wall,
3. How does the Amoeba sp. reproduce when
nucleus, cytoplasm, and chloroplast only
the environment is unfavourable?
3. Chloroplast is found in some plant cells only.
• Amoeba sp. forms spores.
Give one example of a plant cell that does not
• In the spores, mitosis takes place multiple
have chloroplast and give your reasons.
times to form daughter cells.
-Onion cell because onions grow in the ground.
• Once environmental conditions improve, the
-Onions obtain food from their storage organs
spores will germinate and release daughter
which are onion bulbs.
cells.
4. Compare and contrast animal cells and
plant cells
4. Predict what will happen to the contractile
Similarities:
Both cells have nucleus, cytoplasm, plasma vacuole if the Paramecium sp. is placed in a
membrane, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, concentrated salt solution.
endoplasmic reticulums and ribosomes. The contracting rate of the contractile vacuole
will decrease.
Differences:
• Plant cells have a fixed cell shape whereas
animal cells do not have.
• Plant cells have cell walls whereas animal
cells do not.
• Plant cells have chloroplasts whereas animal
cells do not.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
2
FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 2.3 3. Stems, twigs and flowers are organs in a
plant. Describe how stems, twigs and flowers
function in the shoot system.
1. State the components of cells found in high
density in cells that secrete protein products.
Trunk and branches make up the support
system of plants to support leaves at a vertical
Rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes and
position to allow maximum absorption of
Golgi apparatus.
sunlight during photosynthesis. Flowers are
involved in reproduction.
2. Briefly describe the structure and function
of the nerve tissue.
4. Predict what will happen if the organisation
level of cells does not exist in an organism.
A nerve tissue is made of cell body and nerve
The organism is not able to carry out a lot of
fibres that are called dendrites and axons.
functions that are needed for its survival.
Nerve tissues coordinate and control bodily
activities.
SUMMAT IVE PRACT ICE 2
3. Explain why the palisade mesophyll cell
contains a lot of chloroplast. 1. Why is chloroplast only found in plant cells
and not in animal cells?
A large number of chloroplasts can absorb more
light for photosynthesis. This is because chloroplast is used to produce
food during photosynthesis. Animal cells do
4. Fat cells have three adaptive characteristics not produce food
to allow the storage of fat. Describe the three
characteristics. 2. Explain the asexual reproduction of Amoeba
sp.
Fat cells contain very little cytoplasm but have
high fat content. Fat cells contain very few • Amoeba sp. undergoes binary fission.
mitochondria because it does not need a lot of • When Amoeba sp. has expanded to a certain
energy. Fat cells can expand to store more fat. size, the nucleus will divide mitotically.
• Then, cytokinesis takes place.
Formative Practice 2.4 • Two Amoeba sp. that possesses the same
1. State arrangement of sequence in the genetic composition are formed.
organisation of cells in a multicellular
organism. 3. An aphid is a small insect which sucks sap in
plants. An aphid puts its mouth in the stem
Cell →Tissue→ Organ→ System→ of a plant and sucks its nutrients. Name the
Multicellular organism liquid obtained from the plant and explain
why aphids are mostly found in the daytime.
2. The skin is the largest organ in the body. Phloem sap. Photosynthesis takes place during
Why is skin classified as an organ? the day. Therefore more sugar is produced and
is absorbed by the aphid.
Skin is classified as an organ because skin is
made up of epithelial tissues, connective
tissues, nerve tissues and muscle tissues that
work together to carry out the functions of skin
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
3
4. Figure 1 shows a plant cell • No ATPs are produced, which then hinders
the active transportation of ions into plant
cells.
8. Explain how an Amoeba sp. can survive in
fresh water that is hypotonic to the
cytoplasm of the organism.
• Through osmoregulation.
State the characteristics of P and its function • Osmoregulation in Amoeba sp. involves
contractile vacuoles.
P is cell wall. P is built from cellulose which is • Water will be absorbed into Amoeba sp. via
strong and fibrous as well as fully permeable. osmosis.
The function of cell wall is to maintain plant • Water collects in the contractile vacuoles
cell shape. until they reach the maximum size.
• Then, the contractile vacuoles will contract
5. X is a digestive organ consisting of cells with to expel water from Amoeba sp. As such,
a high concentration of rough endoplasmic Amoeba sp. does not overexpand and burst
reticulum for protein digestion. What is X?
Explain your answer. 9. Figure 2 shows one cell that can be seen
through an electron microscope.
X is stomach. The rough endoplasmic
reticulum carries proteins produced by
ribosomes. Stomach is an organ that
synthesises enzymes in large amounts for
protein breakdown.
6. Plant cells undergo process X to form xylem
vessels. Name process X. Explain how xylem
vessels are specialised in transporting water
and mineral salts.
Process X is differentiation. Xylem forms (a) (i) Name structure K.
hollow connected tubes. This ensures the
continuous transport of water and mineral salts K – Golgi apparatus
(ii) State the function of structures K and N.
7. Arif is a farmer. He uses a weed killer to
control the weed population growth on his K – The centre for processing, packaging and
farm. Weed killers can stop the transportion transportation of carbohydrate, protein and
of certain minerals in plants through the glycoprotein
hair root tissue. Explain why. N – Contains chlorophyll to trap sunlight for
photosynthesis
• Herbicides contains respiratory poisons.
• Herbicides will destroy respiratory enzymes
that will stop cellular respiration.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
4
(b) Explain how L mantains the turgidity of 11. Figure 3 shows the structure of a leaf.
the cell
• L is vacuole. Cell sap inside the vacuole
contains water, dissolved substances and
mineral salts.
• When water enters the vacuole, the vacuole
expands.
• The vacuole and cytoplasm will push
towards the plasma membrane and cell
wall. This will produce turgor pressure
within the cell and maintain cell turgidity.
10. State the differences between the following: (a) Name the cells labelled P and R.
(a) meristematic tissue with plant
epidermal tissue, P: Mesophyll cell R: Epidermal cell
• The meristematic tissue is a tissue that has (b) State the functions of cells P and R.
small cells, compact cytoplasm and many
nuclei. This tissue carries out cell division. • P contains a large number of chloroplasts
• The epidermal tissue has cells with large for maximum absorption of sunlight for
vacuoles and a thin layer of cytoplasm. This photosynthesis.
tissue covers the surface of plants to protect it • R protects plant tissues from mechanical
from injury and loss of water. injury.
(b) cell and tissue, (c) Explain the role of cell Q in increasing the
rate of photosynthesis.
• Cell is the basic unit of all life.
• Tissue is a group of cells that have a certain • When light intensity and carbon dioxide
structure and carry out a certain function. concentration are high, guard cells (Q cell)
curve outwards.
(c) epithelial tissue and muscle tissue. • This causes the stomata to open and allow
more carbon dioxide to enter the leaves
• The epithelial tissue is made up of one or
more layers of cells that cover the surface or (d) S contains two types of tissue.
body cavity and protects it from injury and (i) Name the two tissues
drying up.
• The muscle tissue is made up of muscle cells Xylem and phloem
and muscle fibres that can contract and relax
to produce movement. (ii)Explain the adaptive features of tissues in
S that help in the transportation of materials
in plants.
• Xylem is made up of vessel elements and
tracheids that are connected from one end
to the other.
• Vessel elements do not contain any
cytoplasm.
• •The cell walls are impregnated with
ligninThese characteristics allow xylem to
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
5
transport water and mineral salts 13. Figure 4 shows a unicellular organism that
throughout the entire plant. lives in a fresh water pond.
• Phloem consists of sieve tubes that are
arranged from one end to the other end.
Sieve tubes contain sieve plates that allow
the continuous transportation of organic
compounds
ESSAY QUEST IONS
12. Using an example of a unicellular organism,
explain the five living processes of this
organism. (a) Explain the function of X in
osmoregulation.
Example of unicellular organism is Amoeba sp.
Five life processes of unicellular organisms are • X is the contractile vacuole that controls the
as follows: water content in a unicellular organism.
• Excess water within the cell will enter the
• MOVEMENT contractile vacuole through osmosis.
Amoeba sp. extends its pseudopodium through • This will cause contractile vacuole to
the flow of cytoplasm to move. expand.
• The vacuole will then contract to expel
• NUTRITION water from the organism
Ingests through phagocytosis by extending its
pseudopodium to engulf food particles. Food is (b) Predict what will happen if a cell does not
kept inside food vacuoles and hydrolysed by have a Golgi apparatus. Explain your
enzymes before being absorbed. • Respiration answer.
Gaseous exchange of oxygen and carbon
dioxide through plasma membrane by If a cell does not have Golgi apparatus, protein
diffusion. from rough endoplasmic reticulum: • will not
be processed and modified
• EXCRETION • will not be separated according to their
Excretory products such as carbon dioxide and respective destinations
ammonia are excreted via diffusion. Cellular • will not be packaged into vesicles
osmotic pressure is controlled by contractile hus, protein cannot be transported to other parts
vacuoles. of the cell or secreted by the cell as extracellular
enzymes
• REPRODUCTION
Reproduces via asexual reproduction, which is (c) For each of the following cell, explain the
binary fission and spore formation relationship between structure and function.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
6
• Cell P is root hair cell. • The second factor is the high rate of cell
• Root hair cells are normal epidermal division in epithelial cells, which means
cells with long projections. mutations are more likely to happen
• This allows the root hair to seep spontaneously due to an error during
between soil particles to reach water DNA replication.
that surrounds soil particles. • Both factors contribute to the higher
• Long and thin projections increase the chances of cancer occurring in the
total surface area of the cell to absorb epithelial tissue
water and mineral salts. The thin and
semipermeable plasma membrane 15. The damage to the cartilage disc between the
allows water to diffuse through it into vertebrae of the spine is difficult to repair by
the cytoplasm via osmosis their own cells. What is the latest technology
that can be used to develop new cartilage
tissues?
Cells of new cartilage tissue can be generated
through embryonic stem cell injections to parts
of the damaged cartilage discs.
Visit https://www. regenexx.com/stem-cell-
disc-treatment/ to see how this procedure is
carried out.
• Q is a red blood cell. The red blood cell
does not have a nucleus. It is shaped like
a biconcave disc and flat.
• This increases the cell’s total surface
area and allows oxygen to diffuse faster
into the cell.
• Red blood cells are elastic. This allows
the cells to move though very thin
capillaries.
• Red blood cells also contain a red
pigment known as haemoglobin that
transports oxygen throughout the entire
body.
ENRICHMENT
14. Many cancers start with the epithelial tissue.
This includes lung cancer, colon cancer and
skin cancer. What are the two characteristics
of this tissue that can cause cancer?
• The epithelial tissue that lines the lungs,
colon or the skin is the outermost layer
of the skin or of the organ. As such, the
epithelial tissue is the first tissue to be
exposed to any substances that can
cause cancer compared to other tissues.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
1
FORMATIF QUOESTION F4
C7 : Cellular Respiration
The number of mitochondrion in the muscle
cells of an athlete increases after intensive
training. Explain how this contributes to the
Conduct a group discussion about the energy achievement of the athlete as compared with
requirements in the metabolic process. those who do not undergo intensive training.
FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 7.1
1. Give five examples of the necessity of energy
in a metabolic process.
• Maintaining body temperature at the optimal
temperature of 37 °C.
• Muscle contractions to enable movement.
• Cell division whereby new cells are produced
for growth and development.
• Absorption of digested food through active
transport.
• Synthesis of lipids, hormones, proteins and
enzymes
2. State the main substrate in the production of
energy.
Carbohydrate (glucose). FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 7.2
3. State the meaning of cellular respiration and 1. State the meaning of aerobic respiration.
the types of cellular respiration.
Aerobic respiration is the breakdown of
• Cellular respiration is the oxidation process glucose in the presence of oxygen to produce
of organic molecules through a few stages to chemical energy
release energy.
• The main substrate for cellular respiration is 2. Suggest another substrate apart from
glucose. glucose that can be used by cells for cellular
• There are two types of cellular respiration: Respiration.
aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration
Fructose, galactose
4. Explain how humans, animals and plants
acquire glucose to produce energy 3. State the word equation for aerobic
respiration.
In humans and animals, glucose is obtained
through the breakdown of carbohydrates Glucose + oxygen →carbon dioxide + water +
whereas in plants, glucose is produced through energy
photosynthesis.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
2
4. Describe the processes involved in aerobic 2. Give three examples of microorganisms and
respiration to produce energy food produced by the fermentation process.
• Sugar breakdown (glycolysis) takes place Organism: Saccharomyces Product of
in the cytoplasm. fermentation: CO2, ethanol Example: wine,
• Glucose (6-carbon) is broken down to two beer
pyruvate molecules (3-carbon).
• In the next stage, pyruvate is oxidised Organism: Aspergillus Product of
through a series of reactions to produce fermentation: lactic acid Example: soy sauce
carbon dioxide, water and energy.
• This stage takes place in the mitochondrion Organism: Acetobacter Product of
fermentation: Acetic acid Example: vinegar
3. While helping your father to cut the grass at the
Some bacteria can only survive in anaerobic farm, you come across a snake. Terrified, you
conditions. Predict what can happen to this run away from the snake. Explain the cellular
type of bacteria when oxygen is supplied. respiration that takes place in the muscle
cells of your legs.
• When you sprint, the lungs and blood
supply are unable to supply oxygen quickly
enough to meet the demands of the muscles
to produce ATP.
• In this condition, the muscle cells undergo
fermentation, whereby ATP is produced
without oxygen.
• Fermentation in muscle cells produces
lactic acid
Why is aerobic respiration more suitable for
yeast compared with fermentation? 4. State the differences between aerobic
respiration and fermentation
• Aerobic respiration involves the complete
breakdown of organic substances in the
presence of oxygen whereas fermentation
involves incomplete breakdown of organic
substances in the presence of limited oxygen
or absence of oxygen.
• Aerobic respiration takes place in cytoplasm
and mitochondria but fermentation only
FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 7.3
takes place in the cytoplasm.
• Aerobic respiration produces water whereas
1. State where the process of fermentation fermentation does not.
usually occurs. • In aerobic respiration, glucose is oxidised
completely into carbon dioxide and water
Human muscle cells, some bacteria, yeasts and
plants.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
3
whereas in fermentation, glucose is oxidised • By doing so, the runner uses existing
to ethanol or lactic acid. oxygen efficiently.
• However, lactic acid is accumulated
SUMMAT IVE PRACT ICE 7 because the oxygen supply to the muscles is
insufficient.
1. What are the uses of alcohol fermentation • On the other hand, long distance runners
products? who run at a slower speed are able to
dispose off the lactic acid accumulated in
Ethanol is used in the production of beer and the early stages of running.
wine. Carbon dioxide is used in breadmaking to • Long distance runners cannot hold their
help the dough rise. breath because lactic acid accumulation
causes rapid muscle fatigue.
2. Why do muscles carry out cellular • As such, long distance runners need to
respiration that produces lactic acid during breath throughout the race.
vigorous training?
6. Photograph 1 shows the activities by two
To provide the energy needed as well as individuals, P and Q.
enabling an individual to carry out activities.
3. Why does cellular respiration in muscles
that produce lactic acid supply less energy
compared to aerobic respiration?
This is because glucose oxidation is incomplete
and a part of the chemical energy is still tied in
the lactic acid molecule.
(a) (i) Based on Photograph 1, identify the
4. Explain why an individual usually feels tired respiration that occurs in the muscles of
faster compared with an athlete, when both individuals P and Q.
of them are running together.
P: Aerobic respiration. Q: Fermentation
• An athlete usually has more mitochondria
(ii) State the products of respiration in P and
in the muscle cells.
Q.
• Increased uptake of oxygen and oxidation
of lactic acid reduces muscle fatigue.
P: Carbon dioxide, water and energy
Q: Lactic acid and energy
5. A 100-metre sprinter usually holds his breath
while running compared with a long-distance
runner. After running, the sprinter needs seven
litres of oxygen to remove the lactic acid in his
muscle cells. Explain this difference between
the sprinter and the long-distance runner.
• 100 m runners complete the race fast by
holding their breath.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
4
(b) During the 100-metre sprint on Sports Day, (b) Compare aerobic respiration with
a pupil experienced muscle cramps and had to fermentation.
stop running. Explain why muscle cramps
happen. Similarities:
• Both are cellular respiration.
When a person sprints, their muscle cells • Both take place in animal and plant cells.
undergo fermentation in the absence of oxygen • Both produce energy in the form of ATPs.
to produce ATPs. Muscles produce lactic acid • Both use glucose as the main substrate.
that is toxic. Lactic acid causes cramps and
muscle pain
(c) Paddy plants grown in waterlogged areas
have tolerance to ethanol compared with
other plants.
(i) State the type of fermentation that occurs in
paddy plant cells.
Alcohol fermentation
(ii) Write the word equation for the
fermentation process that occurs in the
paddy plant cells.
Glucose → Ethanol + carbon dioxide + energy
(iii) Suggest another cell that can carry out
the fermentation process as in question c(ii).
Yeast
ESSAY QUESTIONS
(c) Microorganisms such as yeast and bacteria
7. (a) Explain why energy is required in usually play an important role in the
metabolic processes. fermentation process to produce food. Explain
why yoghurt can spoil if it is not kept in the
• To maintain body temperature at the optimum refrigerator.
temperature of 37 °C.
• For division as well as growth and • The sugar in milk is oxidised by bacteria
development of cells. such as Lactobacillus and Streptococcus into
lactic acid that solidifies the milk and
produces a sour taste until curd is formed.
• When kept in the fridge, the low temperature
controls bacterial activity from reproducing
and spoiling the product.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
5
• If kept at room temperature, the curd will 10. While conducting an experiment using yeast,
spoil as bacteria will continue to grow and Mei Ling found that if grape juice is kept with
oxidise the milk sugar. yeast in a covered container, the yeast will
slowly break down the glucose in the grapes.
ENRICHMENT However if the container does not contain any
oxygen, the yeast will break down the glucose
at a faster rate, and the alcohol content in the
8. A person who is not used to exercising will
container will rise very fast. At the end of the
experience muscle cramps when doing
experiment, Mei Ling found that the
vigorous exercise because of the accumulation
breakdown rate of glucose becomes slow again
of lactic acid in the cells. However, for high-
even though there are some grapes that have not
performance athletes, such problems do not
been oxidised. Explain Mei Ling’s
occur because their bodies have a high
observation.
tolerance for lactic acid. In your opinion, how
do high performance athletes overcome the
• If the container still contains oxygen, the
problem of lactic acid accumulation? Give
yeast will undergo aerobic respiration to
your reasoning.
produce carbon dioxide, water and energy.
• The rate of glucose breakdown is slow
• Someone who rarely exercises will
because the production of energy is high in
experience muscle cramps when they do
oxygenated conditions.
heavy exercises because the number of
mitochondria in their cells are very few. • However, when the container no longer
contains oxygen, the yeast will respire
• Therefore, during vigorous exercise,
anaerobically to produce ethanol, carbon
complete cellular respiration does not take
dioxide and energy.
place and a lot of lactic acid will be formed.
• The energy produced will be little, thus the
• To overcome this problem, an athlete needs
yeast has to break down glucose faster to
to undergo consistent training to produce
provide sufficient energy.
more mitochondria in their cells.
• The fast rate of glucose breakdown causes an
• The high number of mitochondria can help
increase in the rate of alcohol production.
an athlete’s cellular respiration.
• Subsequently, the rate of breakdown
• Faster uptake of oxygen and oxidation of
decreases as the high level of alcohol
lactic acid can reduce muscle fatigue during
accumulation is toxic and can inhibit yeast
vigorous activities
growth.
9. Studies have shown that intake of sodium • If the alcohol content reaches 14%, the yeast
bicarbonate or baking powder (baking soda) will die.
can increase muscle efficiency during intense
activities that involve muscle fermentation. 11. Susan tried to make bread using dry yeast
Give your justification. bought from a shop. When she mixed the yeast
with plain flour, she found that her bread did
not rise after half an hour. Explain how you
• This is because baking powder has a high pH
can help Susan solve her problem.
that is able to neutralise the lactic acid
produced by muscles during exercise.
• Susan should add a little lukewarm water
• This increases muscle efficiency because
into the dry yeast before mixing it into the
lactic acid causes muscle fatigue.
flour.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
6
• This step is to activate the dry yeast which is
in a dormant state when its environment is
dry.
• The activated yeast will undergo respiration
by breaking down the carbohydrates in the
flour and releasing carbon dioxide.
• Carbon dioxide causes the bread to expand
and rise.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
1
FORMATIVE PRACTICES FORM 4 The main cells in gastric glands are chief cells
C9 : NUTRITION AND THE HUMAN that secrete pepsinogen, parietal cells that
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. secrete hydrochloric acid and goblet cells that
secrete mucus
4. The small intestine secretes a few types of
Chew slowly a small piece of bread. Observe enzymes to complete the digestion process.
the taste when you first started chewing and Explain how these enzymes complete the
after a few minutes of chewing. Is there any digestion process.
difference in the taste of the bread?
The enzymes that are involved in the digestion
process in the small intestine are trypsin,
amylase, erepsin, sucrose, maltase, lactase and
lipase.
Function of enzyme:
Trypsin—hydrolyses polypeptide to peptide
Amylase—hydrolyses starch to maltose
Erepsin—hydrolyses peptides to amino acids
Chemical digestion involves enzyme-catalysed Sucrase—hydrolyses sucrose to glucose and
hydrolysis reaction. For example, an enzyme is fructose
needed in the decomposition of starch into Maltase—hydrolyses maltose and glucose
glucose. Lactase—hydrolyses lactose to glucose and
galactose
Lipase—hydrolyses lipids to fatty acids and
FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 9.1
glycerol
1. Explain the importance of the digestion
process for humans.
A gastroenterologist is a medical specialist who
specialises in the human digestive system
The food consumed by humans is in the form
of large and complex molecules. The food
needs to be broken down to a smaller and
simpler form that can diffuse into the blood Gather information about the absorption of
vessels and transported to body cells. alcohol and drugs
2. Name the structures in the alimentary canal
that are involved in food digestion.
The structures that are involved in the digestion
process are mouth, teeth, oesophagus, stomach,
duodenum, small and large intestines
3. Name the main cells in the gastric glands
and explain the functions of these cells.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
2
FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 9.2
Liver cirrhosis is a type of liver disease caused
1. Name the main structures for the by factors such as alcoholic drinks, toxic
absorption of digested food. substances and hepatitis. Liver cells are
replaced by scarred cells that can cause
The main structure in food absorption is villi failure in the liver functions. Hepatitis is an
inflammation of the liver caused by viral
2. Name the structure in the villus involved in infection, toxic substances or autoimmune
the transporting of the following nutrients: reaction (Photograph 9.1)
(a) amino acids
Blood capillaries
Conduct a research on the various functions of
(b) vitamins A and E the liver and produce a scrap book
Lacteal FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 9.3
3. Explain the adaptations of the small 1. State the meaning of assimilation.
intestine to increase the surface area for
absorption of nutrients. Assimilation refers to the use of absorbed
nutrients to synthesise complex compounds.
Long small intestine. The inner layer of the
small intestine is highly folded and covered 2. Explain the functions of the liver in the
with villi to increase surface area for nutrient assimilation of digested food.
absorption. There are many microvilli found on
the epithelial surface of the villi. The functions of liver in assimilation:
• Carbohydrate metabolism Glucose is
4. Explain how the following substances can oxidised to yield energy. Most of the
be transported across the plasma excess glucose are converted to glycogen
membrane. and stored in the liver.
(a) Glucose, galactose and amino acids • Protein metabolism Liver cells use amino
acids to synthesise plasma proteins and
Glucose, galactose and amino acids are enzymes.
actively transported across the epithelial cell • Storage of nutrients Besides storing
to the blood vessels by carrier proteins glycogen, the liver provides a place to
against the concentration gradient store vitamins and mineral salts.
• Detoxification The liver serves as a filter
(b) Fatty acids and glycerol and detoxifies dangerous particles such as
drugs, alcohol and other foreign
Fatty acids and glycerols diffuse across the substances
plasma membrane into the lacteal through
simple diffusion.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
3
This process enables the body to retain
The large intestine has a huge population of water.
bacteria. There are more than 1000 different • The absorption of vitamins maintains
species of bacteria in the large intestine and a health.
healthy balance between beneficial and less
beneficial bacteria is very important for health 4. Explain the formation process of faeces.
and a stable environment in the alimentary
canal. Formation of faeces:
• After the absorption of nutrients in the
small intestine, the remaining mixture
enters the colon.
What is the effect of antibiotics on the large • The remainder mixture consists of water,
intestine’s bacterial population? undigested food, bacteria, dead cells and
cellulose.
• The movement of undigested food is
facilitated by peristalsis.
• In the colon, the absorption of mineral salts
and water takes place until faeces are
formed
Nutritionists are specialists in the field of
FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 9.4 nutrition who advise specific individuals on
suitable diets.
1. State the main function of the large
intestine.
Plan meals based on Pinggan Sihat Malaysia
The main functions of the large intestine are for different individuals such as obese
water and vitamin reabsorption, and faeces individuals, cancer patients and heart patients.
formation
2. What are the substances absorbed in the
large intestine?
Water, minerals, the metabolic by-products of
bacteria such as vitamin B, K and folic acid
3. Explain the importance of water
absorption and vitamins in the large
intestine.
The significance of water and vitamin
absorption:
• The absorption of water in the large
intestine helps to form semi-solid faeces.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
4
stomach ulcer and complications in bowel
movement
Do a case study about the following health
issues related eating habits: • diabetes type 2 •
SUMMAT IVE PRACT ICE 9
obesity • acid reflux • pica
1. Some people cannot drink milk because it
causes diarrhoea and a bloated stomach.
Explain why.
• The intestinal juice of the individual may
possibly not contain or lacks lactase to
digest milk sugar (lactose) in the small
intestine.
• As a result, the bacteria in the large intestine
FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 9.5 will digest the lactose to yield fatty acids
and methane which causes diarrhoea and
bloating.
1. In your opinion, why is fibre important in
• The individual is advised to drink lactose-
the defaecation process. Explain your
free milk.
answer.
2. Amin had some meat dishes for lunch.
• The intake of a high-fibre diet facilitates the Explain how the protein is digested in
movement of faeces and prevents health
Amin’s stomach.
conditions such as constipation, colon
cancer, rectal cancer and haemorrhoids.
• The gastric glands in the stomach secrete
• Some of the functions of fibres are to gastric juice.
stimulate peristalsis, absorb and dispose off • Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid and
toxins, regulate glucose absorption pepsin
especially in diabetic patients, and increase • The medium in the stomach is acidic and
the bacterial population in the large intestine optimum for enzyme action.
• Protein is hydrolysed into polypeptides by
2. Predict the effect of modifying digestive pepsin.
organs such as gastric bypass on human
health 3. An individual has the following eating habits:
• Gastric bypasses involves the reduction of Overeating in a short period of time
the stomach’s size using diverse operative followed by intentional throwing up
methods. on purpose after each meal.
• Among the short-term side effects are acid
reflux, nausea and vomiting, dilated Explain how this eating habit can affect the
oesaphagus, prohibition of certain types of health of this individual.
foods, risk of infection and body weight gain
or loss. • The individual suffers from bulimia.
• Long-term side effects include nausea and • To retain his/her body mass, the patient
dizziness, low blood sugar, malnutrition, induces purging.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
5
• The patient also experiences stress and (d) A student enjoys eating a lot of oranges.
anxiety. Explain the effect of eating too many oranges
• The patient suffers from an imbalance of on the digestion of starch in X
mineral ions in the blood.
• This causes damage to the alimentary canal. The acid in oranges reduces the pH value in the
duodenum. This slows down starch digestion.
4. Figure 1 shows the alimentary canal in humans.
ESSAY QUEST IONS
5. Explain the processes that fat molecules
undergo starting from the duodenum until
it is finally used by body cells.
• Lipid digestion begins in the duodenum.
• Bile salts produced by the liver emulsify
fats into lipid droplets.
• Pancreas secretes pancreatic juice which
contains lipase into the duodenum.
• Lipase hydrolyses lipid droplets to fatty
(a) Name structures X and Y.
acids and glycerol.
• Lipid + water →Glycerol + fatty acids
X: Duodenum Y: Pancreas
• Absorption of fatty acids and glycerol
occurs in the small intestine.
(b) (i) The enzymes in X are only effective in
• In the epithelial cells of villi, the
an alkaline environment. Explain how an
condensation of fatty acid and glycerol
alkaline environment is maintained in X.
forms lipid.
• Lipid droplets are absorbed into the
• The bile and pancreatic juice are alkaline. lacteals of villi.
• These liquids help to neutralize the acids • Lipid is transported from the lacteal by the
from the stomach. lymphatic system into the thoracic duct
and finally enters the blood flow through
(ii) Explain how Y is involved in the digestion the left subclavian vein.
of carbohydrates in X. • Assimilation occurs in the cells.
• Cells use lipids to form the complex
• Y secretes pancreatic juice that contains compounds of the plasma membrane
digestive enzymes into X.
• Pancreatic amylase hydrolyses starch to
maltose
(c) Name the enzyme found in Z. Explain
how this enzyme functions in the digestion of
proteins.
Pepsin hydrolyses protein to polypeptides
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
6
6. A teenager had the following for his breakfast • The lumen of the artery becomes narrow.
This will make it difficult for blood to flow.
Buttered bread – 2 pieces The condition will increase blood pressure
Hard-boiled eggs – 2 (hypertension)
Fresh milk – 1 glass • If the arterial lumen that becomes narrow is
Apple – 1
the coronary artery (artery in the heart), this
Explain what happens to the final digested may cause a heart attack due to the lack of
products of his breakfast in his body cells. oxygen supply to the cardiac muscles.
• If the cholesterol hardens and clogs the
• Bread contains carbohydrate. The digestion coronary artery, heart attack or coronary
of carbohydrate produces glucose. thrombosis (lack of oxygen supply to the
• Glucose is transported to body cells and the heart) may occur, resulting in damage to
liver to be oxidised during cellular parts of the heart. This can turn fatal if
respiration to yield energy. pumping of the heart stops.
• Excess glucose is converted into glycogen • Excess cholesterol may also lead to
for storage. gallstone formation.
• The final product of butter is fatty acids and
glycerol. (b) Suggest suitable types of food for
• Lipid is oxidised to produce energy. someone who wants to reduce weight and
• Some of the lipids are stored in adipose reduce the risk of contracting
tissues. cardiovascular disease. Explain your
• The final product of proteins (egg and milk) answer.
is amino acids.
• Amino acids are carried to body cells for • Foods with less carbohydrates and fats.
enzyme synthesis and repair of damaged Less carbohydrate will be converted to fats.
tissues. • Foods with less fats and cholesterol. Less
• Apple and milk provide vitamin and cholesterol will be deposited on the arterial
mineral salts. walls blocking the arteries. Blood flow in
• Vitamins such as vitamin B are used as the heart will also not be blocked.
cofactors. Generally, vitamins and mineral
salts maintain optimum health. (c) Explain the processes of starch digestion,
• Apple also provides undigested fibre that absorption and assimilation in the human
facilitates defaecation. body.
• The hydrolysis of starch by salivary
7. (a) Explain why a diet rich in fats is not good amylase produces maltose. Next, the
for health. hydrolysis of maltose by maltase produces
glucose. The final product of starch is
A diet rich in fat is not good for health for the glucose. Glucose is absorbed through the
following reasons: ileum epithelial cells and then absorbed into
• A diet with a high content of fat and oily the blood circulatory system through blood
foods may cause high blood pressure and capillaries.
lead to cardiovascular diseases. • Glucose is then transported by the hepatic
• Excess fat will be deposited in the arterial portal vein to the liver.
walls (atherosclerosis) causing blocked • Assimilation occurs in the liver. Depending
arteries. on the body’s needs, glucose in the liver is
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
7
oxidised, excess glucose is converted into 9. How are drinks with added artificial
glycogen to be stored in the liver or changed sweeteners produced and marketed?
to fats to be transported to other body parts
for storage. • Artificial sweeteners such as saccharine,
• From the liver, some of the glucose is aspartame and sucralose provide a sweet
carried in the blood circulatory system to taste to the drinks, but contribute only a
the heart and then pumped to the whole small caloric value.
body. • Sucralose is made from modified sucrose
• In body cells, glucose is oxidised to yield whereby three hydroxyl groups of the
energy, water and carbon dioxide. sucrose molecule are substituted by
• Energy is used for chemical processes in the chlorine atoms.
cell, for example, muscle contraction and • Sucralose stimulates taste buds (sweet)
protein synthesis. Excess glucose is stored such as sucrose but it is not digested by
in the muscles. enzymes.
• Therefore, sucralose does not give any
caloric value to food.
ENRICHMENT • Sucralose is more stable compared to other
artificial sweeteners.
8. Medicines in the form of capsules are not
broken down in the stomach but absorbed
easily by the small intestine. When the blood
sample of the patient is taken and analysed, it is
found that the molecular structure of this
medicine is different from its original
molecular structure. Explain why.
• The drug/medicine may have been
modified by the liver.
• The medicine that is absorbed through the
small intestine is transported by blood to the
liver.
• In the liver, any toxic components in the
medicine is metabolised and converted into
a less toxic form which is easily excreted
through the kidney.
• Thus, the original molecular structure of the
medicine swallowed is different from the
one found in the blood
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
8
10. Nowadays, many individuals prefer ready-to- • Sodium nitrates and artificial colourings
eat or frozen food products due to their busy that make fast foods appear fresh and
lifestyles. Predict the health risks that may attractive have been associated with various
arise if these foods are taken continuously cancers. Some of the preservatives are
for a long period of time and in large actually carcinogenic (cause of cancer).
quantities • Besides, substances that are used as volume
enhancers such as cellulose and potassium
The ingredients in fast or frozen foods usually bromate may disturb the nutrient-absorbing
contain a lot of fats, salt, sugar and processed system in the body. This contributes to
chemicals. various problems of the digestive system.
• Most of the fats found in fast or frozen
foods are trans fats. Trans fats are fats that
naturally exist in liquid form but have been
modified to become solids. Trans fats make
fast food last longer. However, trans fats
can also increase the bad cholesterol (LDL)
level and decrease the good cholesterol
(HDL) level. This increases the risks of
heart diseases and causes clogged arteries.
Some fast foods contain red meat and
cheese which naturally consists of saturated
fats but can increase bad cholesterol.
• Salt is usually used as flavour enhancer and
as a preservative. A serving of fast food
contains more salt than what our body
needs on a daily basis. This may increase
cholesterol level, and blood pressure. The
high salt content in the food is also
associated with kidney diseases.
• Starch or complex sugar is used in fast food
to enhance flavour and texture. The body
will break down starch into sugars in the
form of glucose during digestion. The
excessive intake of sugar may cause serious
health issues and is associated with
increased risk of getting diabetes, heart
diseases and obesity. Excessive sugar is
also associated with depression.
• Chemicals are added to fast and frozen
foods to make it last longer and tastier. On
the other hand, the high chemical content
can be toxic to the body. For example,
monosodium glutamate (MSG) is
associated with headaches, nausea, chest
pain, lethargy and breathing difficulties.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
1
FORMATIVE PRACTICES F4 3. How does the phagocyte destroy pathogens
C11: Immunity in Humans that have penetrated the first line of
defence?
Phagocytes carry out phagocytosis by
List the physical and chemical defences found surrounding, trapping and digesting pathogens.
in the first line of defence.
4. Differentiate between antigens and
antibodies.
• Antigen is a foreign substance that enters
the body.
• Antigen is usually a protein molecule found
on the wall or external membrane of a
pathogen.
• Antibody is a protein produced by
lymphocytes that functions to destroy the
antigen
The Ministry of Health (MOH) recommends
that babies aged 2 to 3 months be immunised
against diseases such as diphtheria, pertussis,
tetanus, poliomyelitis and meningitis.
Why are only female pupils given the HPV
FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 11.1 vaccination (Human papillomavirus)?
1. What is the meaning of immunity?
Immunity is the body’s ability to fight against
disease infections caused by pathogens or
foreign substances, by specifically fighting the
particular pathogen
2. Name two characteristics of the skin that
allows the skin to react as an effective first
line of defence.
FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 11.2
• The skin is a physical defence that
prevents the entry of pathogens. 1. What are the types of immunity that
• The pH of the skin which ranges from 3 to decrease according to time? Explain why.
5 provides an acidic environment which is
unfit for microbial growth. Artificial passive immunity. The body does not
produce its own antibody; therefore, the
immunity does not last long and only provides
a temporary protection.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
2
2. Explain how HIV infection can cause
2. Propose immediate treatment that can be someone to suffer from AIDS.
given to someone who has been bitten by a
poisonous snake. • The HIV virus attacks and disables the
immune system of the individual infected by
• An antiserum injection against snake the virus.
venom provides immediate protection but • The HIV virus attacks and destroys
only for a short term. lymphocytes that function to destroy
• The immunity is acquired immediately after pathogenic microorganisms.
the injection. • This may result in the individual contracting
AIDS or acquired immunodeficiency
3. State one difference between artificial syndrome.
passive immunity and artificial active • The immune system of the patient becomes
immunity. so weak that his/her body is unable to fight
against diseases that would normally not
The period of immunity for artificial passive infect individuals with healthy immune
immunity is shorter than that of artificial active systems
immunity.
3. Why is a person who is infected with HIV,
4. In your opinion, why must we follow and may not necessarily suffer from AIDS?
complete the immunisation plan in
Malaysia? • A person who is infected with HIV can be a
carrier without showing any symptoms for a
• Immunisation helps to boost the immune period longer than 10 years.
system by stimulating the body’s defence • This individual will only develop AIDS if
cells which then protect us from any his/her immune system becomes weak and
possibility of life-threatening less resistant to diseases that are usually not
complications. harmful.
• Therefore, we are advised to comply with • example of a disease that can prove fatal to
and complete the immunisation plan as an AIDS patient is pneumonia.
early as possible according to the • Thus, someone who is infected by the HIV
recommended schedule virus does not necessarily contract AIDS, as
long as his/her immune system stays strong
and is not crippled by the HIV virus.
HIV is able to mutate and change the cell
structure when it spreads. This gives the virus 4. How can AIDS be prevented?
a high resistance to drug therapy.
• AIDS can be prevented by avoiding risky
activities such as
FORMAT IVE PRACT ICE 11.3 o unprotected sex with infected
individuals,
o sharing contaminated needles used for
1. What is the meaning of AIDS? drug abuse or tattooing,
o or receiving transfusion of HIV-
AIDS is Acquired Immunodeficiency infected blood.
Syndrome
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
3
SUMMAT IVE PRACT ICE 11
1. Suggest an immediate treatment to an
individual bitten by a very poisonous snake.
The individual must be given a serum injection
containing antibodies that can fight the toxin
found in the snake venom.
2. Explain how a mother who has HIV can
infect a foetus in her womb.
Through the mother’s placenta to the foetus in (a) (i) What type of immunity did
the womb, or breastfeeding individuals X and Y acquire?
3. (a) State the type of immunity a foetus X: Artificial passive immunity
receives from its mother. Y: Artificial active immunity
Natural passive immunity (ii) State the substance injected in
individuals X and Y.
(b) Explain how the placenta helps in the
immune system of the foetus. X: Antiserum Y: Vaccine
• Through the placenta, antibodies are able to (iii) Explain the differences in the content of
diffuse from the mother to the foetus. the substances you mentioned in (a)(ii).
• When antibodies enter the foetus, they will
act on the pathogen. • Antiserum is blood plasma that contains
• This provides immunity to the foetus and antibodies or antitoxins for a particular
prevents disease infection. disease.
• Vaccine is dead or weakened antigens
4. Figure 1 illustrates the changes in the antibody which are injected into a person’s body to
levels in the blood of individuals X and Y for induce his/her immune system to produce
a specific period of time. the required immunity
(b) (i) On the graph curves of individuals X
and Y, mark with an arrow, the time of the
second injection is given.
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
4
• In individual X, lymphocytes are stimulated
to produce antibodies that destroy antigens.
Memory cells remain in the body.
• Individual X acquires natural active
immunity and is able to fight against the
disease in the future.
(b) individual Y
• The suspension that is injected into
individual Y is a vaccine. Vaccine is
weakened pathogens used to induce
lymphocytes to produce antibodies.
(ii) Why do individuals X and Y need a
second injection? • Individual Y acquires artificial active
immunity and obtains immunity against
measles
• Individual X: The second injection is
required to increase the quantity of
6. (a) A newborn baby needs to receive
antibodies beyond the immunity level
immunisation based on the Immunisation Plan
because the quantity of the antibodies drops
recommended by the World Health
below the immunity level after a period of
Organisation (WHO). Explain why the
time
immunisation programme is required.
• Individual Y: The second injection is needed
to induce more antibodies beyond the
• A newborn needs to acquire immunisation
immunity level because the first dose is
based on the Immunisation Plan because, the
insufficient for the individual to achieve the
baby does not acquire immunity against
required immunity level
certain diseases from the mother (natural
passive immunity) during the foetal stage.
(iii) Based on the graph curves for
individuals X and Y, state two differences in • Also, after the baby reaches the age of 6
the immunity achieved by individuals X months, his/her natural passive immunity
and Y. will recede.
• Furthermore, the baby maybe exposed to
• The immunity acquired by individual X is various infectious diseases, for example
immediate while the immunity acquired by measles. Babies are unable to fight
individual Y is slow. infections because they do not have the
immunity against the disease.
• The period of immunity for individual X
after reaching immunity level is temporary • Therefore, babies must be given
but for individual Y, it is permanent. immunisation for him/her to acquire
immunity against diseases
ESSAY QUEST IONS b) (i) Some vaccine injections require only
one dose throughout the lifetime of an
5. Two individuals acquired immunity against individual. Explain why.
chickenpox in different situations. Individual
X recovered from chickenpox. Individual Y • One dose is sufficient to induce the body’s
was injected with a type of suspension and immune system to produce an antibody
received immunity against chickenpox after a concentration that exceeds the immunity
few months. Explain the immunity acquired level and permanent throughout life to
by prevent infections
(a) individual X
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
5
(ii) Sinti’s mother forgot to bring Sinti to the • This is because the HIV virus attacks and
clinic for the third dosage of the hepatitis destroys cells that carry the CD4 molecule
vaccination. Explain the effects on Sinti’s on their surface, for example, T lymphocyte.
immunity. The function of the T lymphocyte is to
destroy pathogenic microorganisms. In an
Sinti may contract hepatitis B if she is exposed infection, the T lymphocyte becomes a host
to the hepatitis B virus because the antibody for the HIV virus. The HIV virus will attach
level in her body has not reached the required itself to the plasma membrane of the T
concentration to offer complete protection lymphocyte and start building its DNA’s
from the disease. genetic materials.
• The viral DNA then enters the nucleus of the
(iii) Aziman accidentally stepped on a rusty T lymphocyte, combines with and becomes
nail during a mountain climbing a part of the T lymphocyte’s DNA
expedition. Describe the type of injection • In the T lymphocyte, the HIV virus can
that is suitable to be administered by the replicate to produce new HIV populations
doctor. Explain your answer. that will attack other T lymphocytes. In this
way, the HIV virus will cripple the immune
• For an immediate treatment, Aziman needs system of the infected individual.
to be given an antitetanus injection.
Antitetanus contains antibodies that will act ENRICHMENT
against tetanus. The rusty nail stepped on by
Aziman may contain Clostridium tetani that 7. Sometimes doctors prescribe antibiotics to
can cause tetanus (lockjaw). treat some infectious diseases. Doctors will
• As the antibodies for tetanus is already advise taking all the antibiotics prescribed
available in the antitetanus, the antibodies for the recommended period. Explain why
can act immediately against the bacteria. it is important to follow this step.
• The body immune system does not need to
be stimulated to produce antibodies against
• If the antibiotic prescribed is not taken
the disease.
completely, the undestroyed bacteria will
• Thus the immunity acquired by Aziman is
become immune towards the antibiotic
known as artificial passive immunity.
• This will produce a bacterial strain which is
• The antiserum injection can save Aziman
immune to the antibiotic
immediately compared to immunisation that
will take a long time to stimulate the body’s • This strain of bacteria will grow rapidly and
immune system to produce the required the existing antibiotic would not be able to
quantity of antibodies. destroy it anymore
• Thus once infected, treatment with the
(c) Explain how HIV can paralyse the available antibiotic will not be effective and
immune system of a person infected by the the immune system may not be able to fight
virus. against the new bacteria strain.
• The HIV virus attacks and cripples the
immune system (lymphocytes), rendering
the body incapable of fighting diseases.
• Bacteria, yeasts, parasites and viruses that
normally do not cause any serious diseases
in individuals with healthy immune systems
can now endanger and become fatal to those
with AIDS
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
6
8. You visited a sick friend in a hospital. MRSA
(methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
is a strain of bacteria that is usually found in
hospitals. This bacterial strain is immune to
many types of antibiotics due to the numerous
types of antibiotics used to treat patients in the
hospital. Suggest steps that you can take to
prevent the infection of MRSA.
• Wash your hands using antiseptics after
visiting.
• Cover your mouth with a mask when
talking to patients.
• Avoid touching any hospital equipment
Biology Unit Mrsm Johor Bahru
Formative Practice 14.1
Formative Practice 14.3
1. Why do organisms need to maintain their body 1. In your opinion, why do birds have hollow
shapes? bones?
Body shape is important for movement and Hollow bones are light which facilitates
support, and enables organs in the body to flying.
function properly.
2. Explain how the forearm is moved upwards.
2. State two functions of the skeletal system to When biceps contracts, the tendon transmits
humans. a pulling force produced by the contracting
-To protect the internal organs in vertebrates (for muscles to the arm. At the same time,
example, the skull protects the human brain) triceps relaxes. As a result, the elbow bends
-To produce red blood cells (in the bone marrow) and the arm moves up.
3. For animals that move on then ground, what is the
3. Explain the locomotion mechanism in fish.
advantage of having legs below the body (for The vertebral column of fish is flexible and
example, rats) compared to having legs at the side of moves from side to side through the
the body (for example, crocodile)? contraction and relaxation of myotome, W-
Animals with legs below the body (for example, shaped muscle segments. When the right
mice) lift their body mass above the ground to myotome contracts, the left relaxes and the
reduce friction while moving. tail is whipped to the right. On the other
Formative Practice 14.2 hand, when the left myotome contracts,
the right relaxes and the tail is whipped to
1. Name the bones that form the axial skeleton of the the left.Waves of alternate contractions and
human body. relaxations along the myotome causes the
The skull, vertebral column, rib cage and sternum. body parts to move from side to side,
pushing water backwards and sideways, thus
2. State the function of cartilage and synovial fluid in moving the body forward.
the joint.
The cartilage acts as cushion to joints, absorbs 4. Describe how a grasshopper performs a
shock and reduces friction between the ends jump/leap.
of bones. Synovial fluid acts as a lubricant that Grasshoppers have long hind legs that can
reduces friction between the ends of bones. be folded into a Z-shape, and in this position,
it functions as a jumping spring. When the
3. State the differences between the structure and hind legs are in the Z-position, the extensor
function of tendon and ligament. and flexor muscles are undergoing
• Tendon is not elastic but ligament is. contraction. When the extensor muscles of
• Tendon connects muscle to bone. Ligament the hind legs contract and straighten rapidly
connects bone to bone. backwards and downwards to the ground, it
provides the grasshopper a lifting force that
4. Explain the differences between the ball-and-socket pushes it up and forward into the air.
joint and hinge joint.
Ball-and-socket joints allow rotational movement
in all directions whereas hinge joints only allow the
movement of bones in one plane.
Formative Practice 14.4 1. Why is it important for an organism to
maintain its shape?
1. Suggest two ways to care for the musculoskeletal
Body shape is important for movement and
system.
support, and enables body organs to function
Practice a balanced diet intake and correct body
properly.
posture.
2. Describe the meaning of good posture. Why
2. As a doctor, explain ways to help scoliosis patients
must we always practise good posture while
go through normal daily life.
doing any activity?
• In the case of a minor scoliosis, doctors will carry
• Good posture refers to the correct way of
out routine observation until the maturity level of
sitting,standing, kneeling and carrying out
the bone is almost completed.
other body movements.
• Special equipment to support the backbone
• We need to practise good posture because
(bracing)
good posture provides perfect support to the
• Surgery
musculoskeletal system, eases blood flow,
reduces injury to skeletal muscles and
3. Define osteoporosis and explain the measures that
relieves pressure to the vertebral muscles and
should be adopted at a young age to prevent
column.
osteoporosis at old age.
Osteoporosis is a disease whereby the bones
3. Explain why muscle contractions require
become thin, porous and break easily. Osteoporosis
adequate blood supply.
can be prevented by taking calcium, phosphorus
• Muscle contraction needs a lot of ATP
and vitamin D.
energy
produced during cellular respiration.
4. Explain three practices that can help maintain a
• A large amount of blood is needed to
healthy musculoskeletal system.
transport and supply oxygen and glucose to
To maintain a healthy musculoskeletal system, we
the muscle cells.
must wear proper attire, exercise and practice
• At the same time, blood transports waste
correct body postures.
products such as carbon dioxide and lactic
Summative practice 14 acid out of the muscle cells.
5. State the differences between cervical and thoracic
4. Figure 2 shows two types of vertebrae,
vertebrae.
X and Y in the human vertebral column.
The cervical vertebra possesses a short spinous
process, a small centrum, wide transverse
processes and a pair of transverse foramens. The
thoracic vertebra has a long spinous process, short
but bigger and thicker centrum. The transverse
processes are longer but no transverse foramen is
present.
6. Explain the muscle action in segments T and S that
enables the earthworm to move in the direction (a) Name vertebrae X and Y.
shown. X: Lumbar vertebra
Segment T: Circular muscles contract Y: Cervical vertebra
Segment S: Longitudinal muscles contract (b) Explain the role of vertebrae during body
movement.
The vertebrae provide a surface for muscle
attachment. The vertebral column consists of
many vertebrae which are connected to each
other and enables the backbone to bend.
(c) If tissue X is torn due to an accident, what
(c) Relate the thoracic vertebrae to the
problems will the victim face?
breathing mechanism.
Movement cannot take place at the joints.
• The thoracic vertebrae possess a
Biceps is not attached to radius.
long
spinous process and transverse
(d) Suggest a suitable food for a person with
process for
fractured bone Y. In your opinion, explain why this
muscle and ligament attachment.
particular food is presumed suitable for the
• The thoracic vertebrae have a two-
individual.
face joint on the transverse process
Milk, because it contains calcium for bone
forming a joint with the ribs. This
formation and growth.
allows the ribs to move up and down.
The joints between the thoracic
(e) Explain how all the parts labelled in Figure 3 react
vertebrae and ribs enable the ribs to
in the condition shown.
move up and down when the
When biceps contracts, the pulling force is
intercostal muscles contract and
transferred to the bone through the tendon.
relax.
This action causes the radius to be pulled up
and the arm bends. At the same time, triceps
relaxes.
Essay questions
7. Figure 4 shows a human movement.
8. Figure 3 shows muscles P and Q, bone Based on Figure 4, describe how muscles, bones,
Y and tissue X that are involved in the tendons, ligaments and joints enable the above
forearm movement. movement to happen.
(a) Name muscle P and Q, bone Y and The big and long femur adds strength to support
tissue X. body weight.
Muscle P: biceps • Tendon connects muscles to bones.
Muscle Q: triceps • Tendon is tough and inelastic.
Tissue X: tendon • Ligament supports joints for movement.
Bone Y: humerus • The hinge joint at the knee, and the ball-
and-socket joint at the pelvic girdle produce
(b) State two characteristics of tissue X movements.
that enable it to • The quadriceps femoris and the biceps femoris are
function. antagonistic muscles.
Inelastic and can be bent • When the quadriceps femoris or the extensor
muscle contracts and the biceps femoris relaxes, the
leg is straightened.
• When the biceps femoris contracts and the
quadriceps relaxes, the leg is bent.
• When the calf muscle contracts, the heel is lifted.
• At the same time, the foot pushes downwards and
backwards.
• The repetitive contraction and relaxation
produces movements. (b) (i) Explain the measures that can be practised
to maintain a healthy musculoskeletal system.
9. Describe how the earthworm and fish • The intake of balanced nutrition, for
skeletal systems are adapted for example, taking calcium supplement,
locomotion in their respective habitats. phosphate, vitamin A, C and D. Vitamin
Locomotion of an earthworm D aids in calcium absorption and vitamin
C increases bone mass.
• Earthworms have a hydrostatic skeleton. • Wear comfortable and loose attire.
• Earthworms move with the aid of • Avoid wearing high-heeled shoes.
hydrostatic pressure changes in the body. • Exercise and participate in sports
• The circular muscles contract and the regularly.
longitudinal muscles relax • Practise correct and safe exercise
antagonistically. techniques to prevent injury to the
• This causes the hydrostatic pressure to musculoskeletal system
be • Always adopt good posture in all daily
transferred from the anterior to the activities.
posterior.
(ii) Describe the factors that may put an individual
Locomotion of a fish at a high risk of developing
osteoporosis.
• Possesses endoskeleton • Age factor: as a person ages, the
• The fish bone provides surface for density of the bone decreases
muscle and subsequently, the bone mass
attachment. decreases.
• The left myotome contracts and the • Lack of oestrogen: osteoporosis is
right more common in menopausal women
myotome relaxes antagonistically. because the oestrogen level drops after
• The tail moves to the left and right menopause. Oestrogen is involved in
producing a push forward. calcium metabolism; helps the body
absorb calcium and reduce its loss.
10. (a) Explain the property of muscles • Lack of exercise: exercise stimulates
involved in human movement. calcium sedimentation
• The muscles involved in movement is • Lack of calcium intake in the diet
skeletal muscles. Skeletal muscles produce
a voluntary response because they are (c) Describe how muscles work together with the
controlled by the nervous system and can ligament and tendon to move the forearm.
be stimulated under conscious control. Bending the arm
• Skeletal muscles provide the force that • At the shoulder, the tendon from one end of
is the biceps is attached to the scapula (fixed
needed to move bones at the joints. bone) while at the elbows, the tendon at the
• Skeletal muscles are unable to push or other end of the biceps is attached to the
stretch but can contract and relax. radius (free-moving bone).
• Contraction shortens the skeletal • The tendon from one end of the triceps is
muscle. attached to the end of the scapula while the
• Relaxation returns the muscle to its tendon on the other end is attached to the
original shape and size. ulna.
.
•When bending the arm, the pulling force
produced is transmitted to the bone
through the tendon. The contraction of the
13. The latest research in treating bone
biceps causes the radius to be pulled
fracture includes the use of materials
upwards and the arm is bent.
such as carbon nanotube that serves as a
•At the same time, the triceps relaxes.
scaffolding for bone tissue growth. If you
are a scientist looking for new material to
Straightening the arm
treat damaged bones, what are the
•The triceps contracts causing the ulna to
characteristics that the material should
be pulled down and the arm is
have in order to replace broken bones?
straightened.
• The new material must be very light
•At the same time, the biceps relaxes.
but strong enough to support body
weight.
•The material must also be inexpensive
Enrichment
and the patient’s body must not reject it.
•The material used must be
11. The long bones in mammals are not
biodegradable after the actual bone
compact but hollow. Explain the advantages
regrows.
of hollow bones.
Hollow bones reduce body weight. They
Brainstorm!!!
also require less building material such as
What are theadvantages and
calcium and phosphorus. The force that
disadvantages if humans have
can break a long hollow bone is
exoskeletons like insects?
concentrated at the edges of the bone.
Therefore, bones that are hollow in the
middle are just as strong as compact
bones.
12. Birds fly using wings. The wing movement
allows birds to exert an upthrust. However,
the ability of birds to fly not only depends
on its wings but also its support system.
Explain how the support system helps birds
to fly.
The bone marrow of birds is porous and
not compact. Apart from that, the
arrangement of bone cells is also not
compact. Therefore, a flying bird’s bones
are lighter. This reduces the bird’s weight
and helps it to fly.
wallet in your back pocket
(c) Carrying a heavy bag
STEM Bulletin (d) Incorrect body posture when using smartphones
and computers
Electroactive plastic polymer is used to produce
synthetic muscle. The plastic is used in the
production of human-like robots and enables the Millennial Career
robots to walk. The synthetic muscle contracts in
response to electric current. It is also used to help Orthopaedics is a specialised medical field that
those with missing limbs. focuses on the diagnosis, care and treatment of the
musculoskeletal system. Doctors who specialise in this
field are called orthopaedic surgeons.
Brain storm!!!
What would happen if
(a) you only have the quadriceps femoris?
(b) the muscle is attached directly to the bone?
Activity zone
Work in a group and gather information on
osteoporosis, osteomalacia, rickets, arthritis and
scoliosis. Conduct a scientific study on treatments
that may help individuals with health issues
related to the skeletal muscle.
Activity zone
Build a walking aid for an individual with issues of
muscle injury and joint pain.
Activity zone
Discuss the effects of the following practices on the
musculoskeletal system:
(a) Wearing high-heeled shoes
(b) Sitting with your
You might also like
- Bio Module 2 PhotoMasterDocument23 pagesBio Module 2 PhotoMasterh33% (3)
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-FunctionsDocument23 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-FunctionsEmer Perez50% (2)
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanElizer100% (9)
- Model Answers: Chapter 2 Cell Biology and OrganizationDocument4 pagesModel Answers: Chapter 2 Cell Biology and Organizationsyed ali100% (1)
- Handout 2: Amity International School, Noida Class Ix Biology Chapter: The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesHandout 2: Amity International School, Noida Class Ix Biology Chapter: The Fundamental Unit of LifeayaanNo ratings yet
- Cells Activity QuestionsDocument2 pagesCells Activity QuestionsMusab AlbarbariNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: Name: - Class: - DateDocument7 pagesWorksheet: Name: - Class: - DateKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument8 pagesBIOENERGETICSSarah CalventasNo ratings yet
- Module 5 EALSDocument9 pagesModule 5 EALSKleffer YnanNo ratings yet
- BIO KPM Textbook ExercisesDocument33 pagesBIO KPM Textbook ExercisesJs TeoNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological OrganizationsDocument23 pagesLevels of Biological OrganizationsYuu KieNo ratings yet
- Student Booklet 8 Sci Student Activiry BookletDocument14 pagesStudent Booklet 8 Sci Student Activiry Bookletthe.efroNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4Document9 pagesBiology Form 4Ashlyn OoiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesRahul ManhasNo ratings yet
- Sallim Herniza P. Week 1 General Biology 1 SW1Document8 pagesSallim Herniza P. Week 1 General Biology 1 SW1Nurhaliza KuhutanNo ratings yet
- Biology Y10 Ch2Document7 pagesBiology Y10 Ch2zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- G9 - NCERT - The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument7 pagesG9 - NCERT - The Fundamental Unit of LifeYour mother Is fatNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument15 pagesBiologyChit su su zawNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument6 pagesCell Organelles WorksheetAndi ImanNo ratings yet
- Bio1 Lesson 1 NotesDocument7 pagesBio1 Lesson 1 Notesykanemoto81No ratings yet
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Document21 pagesAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.No ratings yet
- m2 DraftDocument4 pagesm2 DraftMae lea AndoloyNo ratings yet
- g11 Els OrganellesDocument3 pagesg11 Els OrganellesJarod PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Document17 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Dette Dominic Ballano67% (3)
- Short Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFDocument6 pagesShort Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFTanUeiHorngNo ratings yet
- M3 - Exercise 4. Plant and Animal CellDocument10 pagesM3 - Exercise 4. Plant and Animal CellVanessa RafaelNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Activity in Chapter 2. Exploring The CellDocument4 pagesAssessment and Activity in Chapter 2. Exploring The CellArmie Rose FaldasNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and FunstionsDocument4 pagesEukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and FunstionsCiara PanenNo ratings yet
- B.S 8.1 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesB.S 8.1 Lesson PlanNiranjan UniqueNo ratings yet
- General Biology Cells1Document6 pagesGeneral Biology Cells1Kristine CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Chapter IvDocument20 pagesChapter IvLaila Abdullah AmparoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure CH 1 CH 2 Ver 2Document22 pagesCell Structure CH 1 CH 2 Ver 2FaizNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Differences Between Light and Electron MicroscopeDocument14 pagesCell Structure: Differences Between Light and Electron Microscopeshen doweNo ratings yet
- Ch2. Notes - CellsDocument7 pagesCh2. Notes - Cellsmelodyau.seNo ratings yet
- Ex 3 Anaphysio PDFDocument6 pagesEx 3 Anaphysio PDFJayren Ramos TanghalNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument2 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Lifegamingayush4608No ratings yet
- 9th Unit 1Document17 pages9th Unit 1[36] IX-B P.Vishnu Vardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cell Growth and ReproductionDocument5 pagesCell Growth and ReproductionIsrael EsmileNo ratings yet
- Cell PortfolioDocument7 pagesCell PortfolioChhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cl6001 Module 1Document11 pagesCl6001 Module 1reshalyavikaumadi19No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Cell Structure and OrganizationDocument32 pagesChapter 2: Cell Structure and Organizationaida maroNo ratings yet
- Types of Cell PDFDocument20 pagesTypes of Cell PDFDave Billona100% (1)
- Science 7 Animals and Plant Cells 3Document33 pagesScience 7 Animals and Plant Cells 3Welfredo Jr YuNo ratings yet
- Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesCell: The Basic Unit of LifePradyun DSNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesDelhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionSaket TNo ratings yet
- CH 6 BioDocument5 pagesCH 6 BioedwarddameNo ratings yet
- CH - 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Text Book ExercisesDocument6 pagesCH - 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Text Book ExercisesUnkown HumanNo ratings yet
- Act 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportDocument7 pagesAct 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportAmy BalicagNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure AND Cell OrganisationDocument54 pagesCell Structure AND Cell OrganisationAngel Cascayan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 CellDocument109 pagesChapter 8 CellhafsaNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio Quiz 1Document3 pagesCell Bio Quiz 1raphaelNo ratings yet
- Cells Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCells Revision NotesmarzybarNo ratings yet
- Life Science 1Document5 pagesLife Science 1api-381391951No ratings yet
- O Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsDocument10 pagesO Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsTakudzwa ZvidzaNo ratings yet
- The Science of Cytology Cell Theory: The Principle Core of BiologyDocument6 pagesThe Science of Cytology Cell Theory: The Principle Core of Biologyhendrix obciana100% (1)
- CELLDocument17 pagesCELLdina ahmedNo ratings yet
- Rganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument26 pagesRganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationGasterNo ratings yet
- VPHYS 3 200 General Physiology 1 Sem 2021-2022 Laboratory Exercise Written ReportDocument4 pagesVPHYS 3 200 General Physiology 1 Sem 2021-2022 Laboratory Exercise Written ReportRated SPGNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Topic 1 Past Paper QuestionsDocument9 pagesBIOLOGY Topic 1 Past Paper QuestionsLoraine NNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Nutrient Losses Throughout The Blood FlowDocument2 pagesNutrient Losses Throughout The Blood FlowGwenethVineEscalanteNo ratings yet
- Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 2005 PDFDocument773 pagesAnnual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 2005 PDFditabokNo ratings yet
- Electrical Steel - PoscoDocument193 pagesElectrical Steel - PoscoJesus Verduzco100% (2)
- Physical Science Lesson 1Document2 pagesPhysical Science Lesson 1Mary Ann TolibaoNo ratings yet
- References For Human Hair PDFDocument2 pagesReferences For Human Hair PDFAbdelkader ZerroukNo ratings yet
- Past Year CHM510Document5 pagesPast Year CHM510May LeeNo ratings yet
- True Final Oral Presentation ScriptDocument2 pagesTrue Final Oral Presentation ScriptPich'y C. YiengveerachonNo ratings yet
- Design of S El Superstructure ElementsDocument75 pagesDesign of S El Superstructure Elementsyilkal kassahunNo ratings yet
- Marcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabDocument5 pagesMarcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabShiyas Basheer100% (1)
- Inventory StatusDocument19 pagesInventory StatusMuhaiminul IslamNo ratings yet
- Ansi 61Document3 pagesAnsi 61emperor_vamsiNo ratings yet
- VSD Program Guide v2Document43 pagesVSD Program Guide v2David BEN HAIMNo ratings yet
- 220 - Válvula de GloboDocument1 page220 - Válvula de GloboRafael SalazarNo ratings yet
- Batch No: Wurth SR No: 1 Date: 2/1/2018 Tested For: PAHARPUR Test Type: Tensile - Rod/Tube Basic Load/Displacement GraphDocument7 pagesBatch No: Wurth SR No: 1 Date: 2/1/2018 Tested For: PAHARPUR Test Type: Tensile - Rod/Tube Basic Load/Displacement GraphkasvikrajNo ratings yet
- MSDS Blasocut: Blaser Swisslube IncDocument4 pagesMSDS Blasocut: Blaser Swisslube InczaqNo ratings yet
- Halogen Boiling Point 10.1.1.510.8630Document6 pagesHalogen Boiling Point 10.1.1.510.8630NITIN P SHAHNo ratings yet
- Cells and Microscopes. Ms CooperDocument33 pagesCells and Microscopes. Ms CooperzeeNo ratings yet
- Distillation Technology and Need of Simultaneous Design and Control A ReviewDocument24 pagesDistillation Technology and Need of Simultaneous Design and Control A ReviewHesam AhmadianNo ratings yet
- Design of A Cryogenic Grinding System For SpicesDocument10 pagesDesign of A Cryogenic Grinding System For Spicesdeepakkumar2626No ratings yet
- Pet Fiber Spinning MethodDocument15 pagesPet Fiber Spinning Methodsuresh shobanatNo ratings yet
- BM1 ProcessDocument55 pagesBM1 Processeduardo_umNo ratings yet
- I SEM Backlog 12-11-2021Document46 pagesI SEM Backlog 12-11-2021Îdíøt Bøy SâtyäNo ratings yet
- Chol 440 - 576 XL-1000 - Xsys0009 - 70 - GDocument4 pagesChol 440 - 576 XL-1000 - Xsys0009 - 70 - GMatibar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Teknik Eksplorasi-Eksplorasi GeokimiaDocument27 pagesTeknik Eksplorasi-Eksplorasi GeokimiaAndry FerdianNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical ReactionsDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Chemical ReactionsHema lathaNo ratings yet
- A Citizen's Guide To BioremediationDocument2 pagesA Citizen's Guide To BioremediationRenatoNo ratings yet
- WinWave Power Point PresentationDocument34 pagesWinWave Power Point PresentationpatrizziamarieNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Di Deionised WaterDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Di Deionised Watercgjp120391No ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument5 pagesPhysical Sciencecatherine aleluyaNo ratings yet
- PolymerDocument30 pagesPolymerBarang TeknikNo ratings yet