Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 14 and 15
Chapter 14 and 15
Uploaded by
rohanjacksons2Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Recruiting and Selecting Leaders For InnovationDocument7 pagesRecruiting and Selecting Leaders For InnovationPattyNo ratings yet
- PovertyDocument5 pagesPovertyYeta TakNo ratings yet
- Neo LoDocument6 pagesNeo Lothanyani.mosimane567No ratings yet
- UNIT-1 OF ISSUES OF INDIAN ECONOMYDocument15 pagesUNIT-1 OF ISSUES OF INDIAN ECONOMYPiyush SinghNo ratings yet
- poverty in indiaDocument3 pagespoverty in indiaakashNo ratings yet
- Doc1 1Document2 pagesDoc1 1berhanuoromanNo ratings yet
- Poverty in PeruDocument2 pagesPoverty in PeruAndres MendezNo ratings yet
- Epi Unit 2Document7 pagesEpi Unit 2aksharma765499No ratings yet
- Education Turnd Into Economic DevelopmentsDocument4 pagesEducation Turnd Into Economic DevelopmentsUsman ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Social Science PDFDocument21 pagesSocial Science PDFshahhazm553No ratings yet
- WRT Task 2Document1 pageWRT Task 2buitrannhubaoNo ratings yet
- 26 Economic Development & 4.2 Measuring DevelopmentDocument95 pages26 Economic Development & 4.2 Measuring DevelopmentDarryn FlettNo ratings yet
- Education Health Government Role On EconomyDocument3 pagesEducation Health Government Role On Economywattooawais065No ratings yet
- Causes of PovertyDocument3 pagesCauses of PovertyMagabiro MaerereNo ratings yet
- New Text Document (2) 4Document2 pagesNew Text Document (2) 4zainkazmi2005No ratings yet
- Education and Economic SystemsDocument9 pagesEducation and Economic Systemslemayian.steveNo ratings yet
- Micro Finance ProjectDocument38 pagesMicro Finance ProjectmanojrengarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Financing EducationDocument8 pagesChapter Six Financing EducationKaren May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- Bcog 172 2Document1 pageBcog 172 2ACS DersNo ratings yet
- Social ScienceDocument19 pagesSocial Scienceshahhazm553No ratings yet
- EmploymentDocument3 pagesEmploymentχριστινα παπNo ratings yet
- Social Infrastructural Facilities Are The Nerves of The Process of Development of A Developing Economy Like IndiaDocument8 pagesSocial Infrastructural Facilities Are The Nerves of The Process of Development of A Developing Economy Like IndiaLeki WangpoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Financing EducationDocument8 pagesChapter Six Financing EducationKaren May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- The Provision and Politics of AidsDocument7 pagesThe Provision and Politics of Aidsswager.army600220060000No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 DEDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 DEbakhtawarNo ratings yet
- Income InequalityDocument5 pagesIncome Inequalityxhxmpx4pc5No ratings yet
- Cost of Living and Standard of LivingDocument23 pagesCost of Living and Standard of LivingsafwanaliibroNo ratings yet
- Seremeta Unemployment ResearchDocument7 pagesSeremeta Unemployment Researchumaruedirisa60No ratings yet
- Ways To Overcome Unemployment in PakistanDocument20 pagesWays To Overcome Unemployment in PakistanNouman AliNo ratings yet
- Reflection PaperDocument1 pageReflection Paperfvxvfg9wrxNo ratings yet
- Impact of Unemployment in India: Group MembersDocument17 pagesImpact of Unemployment in India: Group Membersrajesh8811No ratings yet
- I-Reflect! - Dela CruzDocument1 pageI-Reflect! - Dela CruzJOHN JUSTIN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Session 1&2 AnswersDocument12 pagesSession 1&2 AnswersParvathaneni KarishmaNo ratings yet
- Economic Exclussion ClassDocument3 pagesEconomic Exclussion ClassVanshika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 2 ECO 214Document3 pagesClass 2 ECO 214Peter DundeeNo ratings yet
- Dev'Tal Economics L & LL OwnDocument11 pagesDev'Tal Economics L & LL OwnTeddy DerNo ratings yet
- Effect of National Saving On Economic Growth of EthiopiaDocument8 pagesEffect of National Saving On Economic Growth of EthiopiaLema AsnakewNo ratings yet
- Population Problems Faced by Developing and Developed CountriesDocument3 pagesPopulation Problems Faced by Developing and Developed CountriesSalvador ValdizonNo ratings yet
- PovertyDocument6 pagesPovertyJunaid DahriNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Tugas 3Document1 pageJawaban Tugas 3Geva Tri AgungNo ratings yet
- Tugas 3 Bahasa Inggris NiagaDocument2 pagesTugas 3 Bahasa Inggris Niagaevip874No ratings yet
- External Influences On EDDocument18 pagesExternal Influences On EDand1sailorNo ratings yet
- Causes / Reasons of PovertyDocument4 pagesCauses / Reasons of PovertyGhalib HussainNo ratings yet
- Problems Facing Indian EconomyDocument10 pagesProblems Facing Indian EconomyAshananda RoyNo ratings yet
- AsvDocument12 pagesAsvkuldip choudhuryNo ratings yet
- The Fallacy of Collective Terms, AlDocument5 pagesThe Fallacy of Collective Terms, AlEda YildezNo ratings yet
- UnemploymentDocument3 pagesUnemploymentvipin kpNo ratings yet
- INEQUALITYDocument6 pagesINEQUALITYjacquelyn.salvador001No ratings yet
- Exploring Income InequalityDocument3 pagesExploring Income InequalityMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- MONEY AND FINANCE-DỊCHDocument2 pagesMONEY AND FINANCE-DỊCHGiuongNguyenNo ratings yet
- PovertyDocument8 pagesPovertysmaryguinevereNo ratings yet
- IBM Assignment 1 (Haris, Uzair)Document6 pagesIBM Assignment 1 (Haris, Uzair)Frosty's Life With Your EyesNo ratings yet
- DfidDocument26 pagesDfidVijay Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Aadhith-12-General Studies ProjectDocument22 pagesAadhith-12-General Studies ProjectAnusanth RNo ratings yet
- Eco ProjctDocument8 pagesEco Projctneha shaikhNo ratings yet
- 08 Task Performance - Barrion PunzalanDocument5 pages08 Task Performance - Barrion PunzalanquenerypaulchristopherNo ratings yet
- Exposé UnemploymentDocument5 pagesExposé Unemploymentouedraogomike99No ratings yet
- Sociology SeminarDocument28 pagesSociology SeminarjanagankalpanaNo ratings yet
- SwabhimaanDocument30 pagesSwabhimaanswati kartikayNo ratings yet
- The Economics of Inequality: A Call to Action for PoliticiansFrom EverandThe Economics of Inequality: A Call to Action for PoliticiansNo ratings yet
- Basic Economic ProblemsDocument4 pagesBasic Economic ProblemsSarah Nicole BrionesNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 3 - Prepared by Baroda Academy, AHMEDABAD - Print - Quizizz-1Document26 pagesQUIZ 3 - Prepared by Baroda Academy, AHMEDABAD - Print - Quizizz-1Shilpa Jha100% (1)
- Course Primer - PSE CSSCDocument9 pagesCourse Primer - PSE CSSCRon CatalanNo ratings yet
- CH 13Document80 pagesCH 13ddNo ratings yet
- Crams - 1Document28 pagesCrams - 1Janam AroraNo ratings yet
- Far160 (CT XXX 2022) QuestionDocument4 pagesFar160 (CT XXX 2022) QuestionFarah HusnaNo ratings yet
- AS-Solved Past Paper Business 9609 P1 2023-2022Document51 pagesAS-Solved Past Paper Business 9609 P1 2023-2022TheOfficialTitaniumNo ratings yet
- Transfer Taxes and Basic SuccessionDocument59 pagesTransfer Taxes and Basic SuccessionARC SVIORNo ratings yet
- Plant AssetsDocument41 pagesPlant AssetsShawon RahmanNo ratings yet
- 9410 - Job Order CostingDocument7 pages9410 - Job Order CostingMarshmallowNo ratings yet
- R.T. Leuchtkafer's BibliographyDocument23 pagesR.T. Leuchtkafer's BibliographysmallakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Income From House PropertyDocument15 pagesChapter 2 - Income From House PropertyPuran GuptaNo ratings yet
- General Partnership AgrrementDocument7 pagesGeneral Partnership AgrrementAbhinav BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior - Leadership in The Digital AgeDocument8 pagesOrganizational Behavior - Leadership in The Digital AgeVincent StuhlenNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Stock MarketDocument5 pagesDeterminants of Stock MarketvikaorlovaNo ratings yet
- Comps 1 1531 Stewart STDocument2 pagesComps 1 1531 Stewart STCharlie HarrisNo ratings yet
- Industrial-Tour-report in Bangladesh ChittagongDocument16 pagesIndustrial-Tour-report in Bangladesh ChittagongSubrata BakshiNo ratings yet
- Business Process Reengineering: Chapter# 01 The Crisis That Will Not Go AwayDocument47 pagesBusiness Process Reengineering: Chapter# 01 The Crisis That Will Not Go AwayShaique SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Operations and Supply Chain Strategy: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument12 pagesOperations and Supply Chain Strategy: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinVanessa Aulia PutriNo ratings yet
- Corporate Presentation (Company Update)Document39 pagesCorporate Presentation (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- MBA630 Price-Barret Minor Project 1Document21 pagesMBA630 Price-Barret Minor Project 1sylvia priceNo ratings yet
- Sales Quotation: Salesman Sign: Customer SignDocument1 pageSales Quotation: Salesman Sign: Customer SignjacobNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Affin Hwang World Series - China Allocation Opportunity FundDocument1 pageFact Sheet Affin Hwang World Series - China Allocation Opportunity FundHenry So E DiarkoNo ratings yet
- Operating CostingDocument15 pagesOperating CostingBishnuNo ratings yet
- NWRB Tariff Users Manual - 2018-Oct-20Document65 pagesNWRB Tariff Users Manual - 2018-Oct-20Leo PastorNo ratings yet
- Modul Implementasi StrategiDocument44 pagesModul Implementasi StrategiPutri VioNo ratings yet
- ABSOLUTE ADVANTAGE THEORY PresentationDocument8 pagesABSOLUTE ADVANTAGE THEORY PresentationAjmal RoshanNo ratings yet
- Trainig and Development of SupervisiorsDocument20 pagesTrainig and Development of Supervisiorskarthiba jeganNo ratings yet
- Strategic Supply Chain Management-The Case of Toyota UAEDocument23 pagesStrategic Supply Chain Management-The Case of Toyota UAEurbanus matiluNo ratings yet
Chapter 14 and 15
Chapter 14 and 15
Uploaded by
rohanjacksons2Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 14 and 15
Chapter 14 and 15
Uploaded by
rohanjacksons2Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 14 and 15
Why does inequality of income act as barrier for economic growth m?
High income inequality can hinder economic growth for several reasons. It often leads to unequal
access to education and healthcare, limiting the development of human capital. Additionally,
when a significant portion of the population has limited purchasing power, it can dampen overall
demand for goods and services, affecting economic expansion. Furthermore, unequal
distribution of resources may result in social and political unrest, creating an unstable
environment that is unfavorable for sustained economic growth.
Why poor infrastructures cause inequality of income
Poor infrastructure can contribute to income inequality in various ways. Insufficient
infrastructure, such as inadequate transportation, limited access to education, and poor
healthcare facilities, can hinder economic opportunities for individuals with lower incomes.
1. **Limited Job Opportunities:** In regions with poor infrastructure, there may be fewer job
opportunities or limited access to markets, making it challenging for people to find well-paying
employment.
2. **Reduced Access to Education:** Inadequate infrastructure, like a lack of schools or
transportation, can restrict access to education. This limits the skill development and job
prospects for individuals, perpetuating income disparities.
3. **Healthcare Disparities:** Poor healthcare infrastructure can lead to health issues that affect
productivity and income-earning potential. Without access to proper medical facilities,
individuals may face challenges in maintaining good health.
4. **Barriers to Entrepreneurship:** Weak infrastructure can impede the growth of businesses,
making it difficult for entrepreneurs to establish and expand their enterprises. This
disproportionately affects those with fewer resources to overcome these challenges.
Addressing infrastructure deficiencies is crucial for promoting economic equality, as it creates an
environment where individuals can access education, healthcare, and job opportunities more
equitably.
Why lack if formal employment opportunities cause inequality
The lack of formal employment opportunities can contribute to income inequality for several
reasons:
1. **Informal Sector Vulnerability:** People who engage in informal employment often face
unstable income, lack of job security, and limited access to social benefits. This vulnerability can
perpetuate poverty and widen the income gap.
2. **Limited Income and Benefits:** Informal jobs typically offer lower wages and fewer, if any,
benefits compared to formal employment. This disparity in compensation contributes to unequal
income distribution.
3. **Lack of Legal Protections:** Informal workers often lack legal protections that formal
employees enjoy, such as minimum wage regulations, overtime pay, and workplace safety
standards. This absence of safeguards can lead to exploitation and lower income levels.
4. **Reduced Skill Development:** Informal jobs may not provide opportunities for skill
development or career advancement. This limitation can hinder individuals from acquiring the
skills needed for higher-paying formal employment.
5. **Exclusion from Social Security Nets:** Informal workers may not have access to social
security nets, including healthcare, retirement benefits, and unemployment insurance. This
exclusion further deepens economic disparities.
Addressing the lack of formal employment opportunities is crucial for reducing income inequality.
Policies that promote the formalization of jobs, improve labor market conditions, and provide
social protections can help create a more equitable economic landscape.
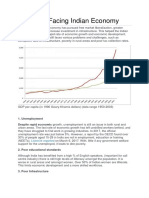
How low rate of savings hold back public sector investment
A low rate of savings can constrain public sector investment in several ways:
1. **Limited Fiscal Space:** When the government has a low savings rate, it has limited fiscal
space to allocate funds for public investments. Insufficient savings may restrict the
government's ability to finance large-scale infrastructure projects, education, healthcare, and
other critical sectors.
2. **Higher Borrowing Costs:** A low savings rate can lead to increased reliance on borrowing to
fund public investments. This heightened demand for borrowing may drive up interest rates,
making it more expensive for the government to finance projects, and potentially leading to a
higher debt burden.
3. **Risk of Fiscal Imbalances:** Depending heavily on borrowing without a corresponding
increase in savings can lead to fiscal imbalances. High levels of debt without adequate savings
or revenue streams can jeopardize a country's fiscal stability and limit its capacity for sustained
public sector investment.
4. **Reduced Investment in Human Capital:** Inadequate savings may limit the government's
ability to invest in education and healthcare, impacting human capital development. This, in turn,
can hinder long-term economic growth and productivity.
5. **Vulnerability to External Shocks:** Countries with low savings rates may be more vulnerable
to external economic shocks. In the absence of substantial savings, governments may struggle
to respond effectively to economic downturns or crises.
Increasing the rate of savings can provide governments with more financial resources to invest in
crucial public projects and services, fostering economic development and stability. It is an
essential element for sustaining public sector investment over the long term.
You might also like
- Recruiting and Selecting Leaders For InnovationDocument7 pagesRecruiting and Selecting Leaders For InnovationPattyNo ratings yet
- PovertyDocument5 pagesPovertyYeta TakNo ratings yet
- Neo LoDocument6 pagesNeo Lothanyani.mosimane567No ratings yet
- UNIT-1 OF ISSUES OF INDIAN ECONOMYDocument15 pagesUNIT-1 OF ISSUES OF INDIAN ECONOMYPiyush SinghNo ratings yet
- poverty in indiaDocument3 pagespoverty in indiaakashNo ratings yet
- Doc1 1Document2 pagesDoc1 1berhanuoromanNo ratings yet
- Poverty in PeruDocument2 pagesPoverty in PeruAndres MendezNo ratings yet
- Epi Unit 2Document7 pagesEpi Unit 2aksharma765499No ratings yet
- Education Turnd Into Economic DevelopmentsDocument4 pagesEducation Turnd Into Economic DevelopmentsUsman ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Social Science PDFDocument21 pagesSocial Science PDFshahhazm553No ratings yet
- WRT Task 2Document1 pageWRT Task 2buitrannhubaoNo ratings yet
- 26 Economic Development & 4.2 Measuring DevelopmentDocument95 pages26 Economic Development & 4.2 Measuring DevelopmentDarryn FlettNo ratings yet
- Education Health Government Role On EconomyDocument3 pagesEducation Health Government Role On Economywattooawais065No ratings yet
- Causes of PovertyDocument3 pagesCauses of PovertyMagabiro MaerereNo ratings yet
- New Text Document (2) 4Document2 pagesNew Text Document (2) 4zainkazmi2005No ratings yet
- Education and Economic SystemsDocument9 pagesEducation and Economic Systemslemayian.steveNo ratings yet
- Micro Finance ProjectDocument38 pagesMicro Finance ProjectmanojrengarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Financing EducationDocument8 pagesChapter Six Financing EducationKaren May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- Bcog 172 2Document1 pageBcog 172 2ACS DersNo ratings yet
- Social ScienceDocument19 pagesSocial Scienceshahhazm553No ratings yet
- EmploymentDocument3 pagesEmploymentχριστινα παπNo ratings yet
- Social Infrastructural Facilities Are The Nerves of The Process of Development of A Developing Economy Like IndiaDocument8 pagesSocial Infrastructural Facilities Are The Nerves of The Process of Development of A Developing Economy Like IndiaLeki WangpoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Financing EducationDocument8 pagesChapter Six Financing EducationKaren May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- The Provision and Politics of AidsDocument7 pagesThe Provision and Politics of Aidsswager.army600220060000No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 DEDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 DEbakhtawarNo ratings yet
- Income InequalityDocument5 pagesIncome Inequalityxhxmpx4pc5No ratings yet
- Cost of Living and Standard of LivingDocument23 pagesCost of Living and Standard of LivingsafwanaliibroNo ratings yet
- Seremeta Unemployment ResearchDocument7 pagesSeremeta Unemployment Researchumaruedirisa60No ratings yet
- Ways To Overcome Unemployment in PakistanDocument20 pagesWays To Overcome Unemployment in PakistanNouman AliNo ratings yet
- Reflection PaperDocument1 pageReflection Paperfvxvfg9wrxNo ratings yet
- Impact of Unemployment in India: Group MembersDocument17 pagesImpact of Unemployment in India: Group Membersrajesh8811No ratings yet
- I-Reflect! - Dela CruzDocument1 pageI-Reflect! - Dela CruzJOHN JUSTIN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Session 1&2 AnswersDocument12 pagesSession 1&2 AnswersParvathaneni KarishmaNo ratings yet
- Economic Exclussion ClassDocument3 pagesEconomic Exclussion ClassVanshika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 2 ECO 214Document3 pagesClass 2 ECO 214Peter DundeeNo ratings yet
- Dev'Tal Economics L & LL OwnDocument11 pagesDev'Tal Economics L & LL OwnTeddy DerNo ratings yet
- Effect of National Saving On Economic Growth of EthiopiaDocument8 pagesEffect of National Saving On Economic Growth of EthiopiaLema AsnakewNo ratings yet
- Population Problems Faced by Developing and Developed CountriesDocument3 pagesPopulation Problems Faced by Developing and Developed CountriesSalvador ValdizonNo ratings yet
- PovertyDocument6 pagesPovertyJunaid DahriNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Tugas 3Document1 pageJawaban Tugas 3Geva Tri AgungNo ratings yet
- Tugas 3 Bahasa Inggris NiagaDocument2 pagesTugas 3 Bahasa Inggris Niagaevip874No ratings yet
- External Influences On EDDocument18 pagesExternal Influences On EDand1sailorNo ratings yet
- Causes / Reasons of PovertyDocument4 pagesCauses / Reasons of PovertyGhalib HussainNo ratings yet
- Problems Facing Indian EconomyDocument10 pagesProblems Facing Indian EconomyAshananda RoyNo ratings yet
- AsvDocument12 pagesAsvkuldip choudhuryNo ratings yet
- The Fallacy of Collective Terms, AlDocument5 pagesThe Fallacy of Collective Terms, AlEda YildezNo ratings yet
- UnemploymentDocument3 pagesUnemploymentvipin kpNo ratings yet
- INEQUALITYDocument6 pagesINEQUALITYjacquelyn.salvador001No ratings yet
- Exploring Income InequalityDocument3 pagesExploring Income InequalityMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- MONEY AND FINANCE-DỊCHDocument2 pagesMONEY AND FINANCE-DỊCHGiuongNguyenNo ratings yet
- PovertyDocument8 pagesPovertysmaryguinevereNo ratings yet
- IBM Assignment 1 (Haris, Uzair)Document6 pagesIBM Assignment 1 (Haris, Uzair)Frosty's Life With Your EyesNo ratings yet
- DfidDocument26 pagesDfidVijay Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Aadhith-12-General Studies ProjectDocument22 pagesAadhith-12-General Studies ProjectAnusanth RNo ratings yet
- Eco ProjctDocument8 pagesEco Projctneha shaikhNo ratings yet
- 08 Task Performance - Barrion PunzalanDocument5 pages08 Task Performance - Barrion PunzalanquenerypaulchristopherNo ratings yet
- Exposé UnemploymentDocument5 pagesExposé Unemploymentouedraogomike99No ratings yet
- Sociology SeminarDocument28 pagesSociology SeminarjanagankalpanaNo ratings yet
- SwabhimaanDocument30 pagesSwabhimaanswati kartikayNo ratings yet
- The Economics of Inequality: A Call to Action for PoliticiansFrom EverandThe Economics of Inequality: A Call to Action for PoliticiansNo ratings yet
- Basic Economic ProblemsDocument4 pagesBasic Economic ProblemsSarah Nicole BrionesNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 3 - Prepared by Baroda Academy, AHMEDABAD - Print - Quizizz-1Document26 pagesQUIZ 3 - Prepared by Baroda Academy, AHMEDABAD - Print - Quizizz-1Shilpa Jha100% (1)
- Course Primer - PSE CSSCDocument9 pagesCourse Primer - PSE CSSCRon CatalanNo ratings yet
- CH 13Document80 pagesCH 13ddNo ratings yet
- Crams - 1Document28 pagesCrams - 1Janam AroraNo ratings yet
- Far160 (CT XXX 2022) QuestionDocument4 pagesFar160 (CT XXX 2022) QuestionFarah HusnaNo ratings yet
- AS-Solved Past Paper Business 9609 P1 2023-2022Document51 pagesAS-Solved Past Paper Business 9609 P1 2023-2022TheOfficialTitaniumNo ratings yet
- Transfer Taxes and Basic SuccessionDocument59 pagesTransfer Taxes and Basic SuccessionARC SVIORNo ratings yet
- Plant AssetsDocument41 pagesPlant AssetsShawon RahmanNo ratings yet
- 9410 - Job Order CostingDocument7 pages9410 - Job Order CostingMarshmallowNo ratings yet
- R.T. Leuchtkafer's BibliographyDocument23 pagesR.T. Leuchtkafer's BibliographysmallakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Income From House PropertyDocument15 pagesChapter 2 - Income From House PropertyPuran GuptaNo ratings yet
- General Partnership AgrrementDocument7 pagesGeneral Partnership AgrrementAbhinav BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior - Leadership in The Digital AgeDocument8 pagesOrganizational Behavior - Leadership in The Digital AgeVincent StuhlenNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Stock MarketDocument5 pagesDeterminants of Stock MarketvikaorlovaNo ratings yet
- Comps 1 1531 Stewart STDocument2 pagesComps 1 1531 Stewart STCharlie HarrisNo ratings yet
- Industrial-Tour-report in Bangladesh ChittagongDocument16 pagesIndustrial-Tour-report in Bangladesh ChittagongSubrata BakshiNo ratings yet
- Business Process Reengineering: Chapter# 01 The Crisis That Will Not Go AwayDocument47 pagesBusiness Process Reengineering: Chapter# 01 The Crisis That Will Not Go AwayShaique SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Operations and Supply Chain Strategy: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument12 pagesOperations and Supply Chain Strategy: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinVanessa Aulia PutriNo ratings yet
- Corporate Presentation (Company Update)Document39 pagesCorporate Presentation (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- MBA630 Price-Barret Minor Project 1Document21 pagesMBA630 Price-Barret Minor Project 1sylvia priceNo ratings yet
- Sales Quotation: Salesman Sign: Customer SignDocument1 pageSales Quotation: Salesman Sign: Customer SignjacobNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Affin Hwang World Series - China Allocation Opportunity FundDocument1 pageFact Sheet Affin Hwang World Series - China Allocation Opportunity FundHenry So E DiarkoNo ratings yet
- Operating CostingDocument15 pagesOperating CostingBishnuNo ratings yet
- NWRB Tariff Users Manual - 2018-Oct-20Document65 pagesNWRB Tariff Users Manual - 2018-Oct-20Leo PastorNo ratings yet
- Modul Implementasi StrategiDocument44 pagesModul Implementasi StrategiPutri VioNo ratings yet
- ABSOLUTE ADVANTAGE THEORY PresentationDocument8 pagesABSOLUTE ADVANTAGE THEORY PresentationAjmal RoshanNo ratings yet
- Trainig and Development of SupervisiorsDocument20 pagesTrainig and Development of Supervisiorskarthiba jeganNo ratings yet
- Strategic Supply Chain Management-The Case of Toyota UAEDocument23 pagesStrategic Supply Chain Management-The Case of Toyota UAEurbanus matiluNo ratings yet