Professional Documents
Culture Documents
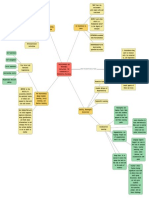
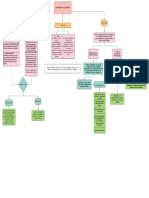
ATTITUDE Learned Tendency To Evaluate Things in A Certain Way This Can Include Positivenegative Evaluations of People Issues Objects or Events
ATTITUDE Learned Tendency To Evaluate Things in A Certain Way This Can Include Positivenegative Evaluations of People Issues Objects or Events
Uploaded by
Attila VáradiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ATTITUDE Learned Tendency To Evaluate Things in A Certain Way This Can Include Positivenegative Evaluations of People Issues Objects or Events
ATTITUDE Learned Tendency To Evaluate Things in A Certain Way This Can Include Positivenegative Evaluations of People Issues Objects or Events
Uploaded by
Attila VáradiCopyright:
Available Formats
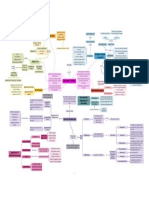
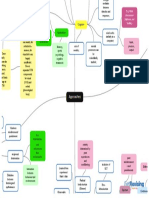
Affective
expressions,feelings towards the subject
3 COMPONENT MODEL Behavioural
apparent actions influencing behaviour
beliefs, thoughts about the subject
Cognitive
Observational learning Bandura Bobo Doll
tendency for person to reproduce action attitudes & emotional
responses exhibited by someone else
FACTORS INFLUENCING ORIGIN OF
ATTITUDES; Formation part of Socialisation Mere Exposure Effect; repeated exposure results in greater
people think carefully about any available information when Systematic processing process attraction to object personal experience, direct observation
forming an opinion to determine whether the information is increases how much we like/dislike subject
accurate or valid
learning a new behaviour through process of association exposure most impactful when lacking info
Heuristic processing ; rule of thumb Heuristic-Systematic model
people usually only have limited time and ability to think
carefully,attitudes on simpler manner Associative learning repetitive association cause neutral stimulus able to evoke a
Classical conditioning
reaction which is previously evoked by another stimulus
Reinforcement; any event that strengthens or increases the Positive situations that reflect positive reinforcement, a response or
behavior it follows behavior is strengthened by the addition of something, such as
praise or a direct reward
a person (P) tries maintaining consistency in attitudes to &
Balance Theory: people prefer attitudes that are consistent Operant conditioning removal of an unfavorable events or outcomes after the display
relationships with other people (O) and environmental elements
(X)
with each other than not of a behavior
Negative
absence of info, people agree to like what others like Positive
spanking for misbehavior is an example of punishment by
Restore balance in a manner requiring least effort (choose easier application
options) ATTITUDE; learned tendency to evaluate Punishment; presentation of an adverse event or outcome that punishment by removal, occurs when a favorable event or
CHANGING ATTITUDES causes a decrease in the behavior it follows outcome is removed after a behavior occurs
things in a certain way. This can include Negative
people motivated to change contradictory beliefs to set harmony
Cognitive Dissonance (positive/negative) evaluations of people, inferring attitude to own behaviour
issues, objects, or events Self-Perception Theory
Knowledge Satisfy psychological needs
permanent change in our attitude Central route need for order, structure or meaning-need is presents when
motivated and able to pay attention, we take a logical, conscious person in ambiguous situation or with a new product
thinking, to decision-making Utilitarian
rapid evaluative judgments of targets, which facilitate approach
Ego-defensive or avoidance (positive/negative)
temporary change protect our self-esteem or that justify actions that make us feel
Elaboration-Likelihood model; persuasion dual process guilty
use little effort, quick change to attitude theory Value expressive
help communicate who we are & may make us feel good
Peripheral route
because we have asserted our identity (self-concept)
Cognitive theories;Cognitive consistency: people try to
maintain internal consistency and order among various
cognitions COGNITIVE DISSONANCE THEORY
an inner drive to hold all our attitudes and beliefs in harmony and
avoid disharmony (or dissonance)
Predicting behaviour, understanding why and how of a
behaviour
cognitive and affective components of attitudes are not FUNCTIONS OF ATTITUDE
necessarily expressed in behavior.
people responded more to appearance and self-confidence REASONS TO MEASURE ATTITUDE
Likert scale : principle of measuring attitudes by asking people to
rather than race respond to a series of statements about a topic, in terms of the Disadv: individuals may lie to put themselves in a positive light.
LaPiere's study(investigating relationship between attitudes
extent to which they agree with them
and behavior)
Subjective norm Adv: allow for degrees of opinion, and even no opinion at all
what the individual perceives to be others' beliefs
Attitude towards behaviour
individual's beliefs about target behaviour and how they are Self-report measures Implicit association test: to detect the strength of a person's
Processes of belief,intention and action
evaluated automatic association(hidden bias) between mental
representations of objects (concepts) in memory
internal declaration to act Theory of Reasoned Action; model that links attitude and
Behavioural intention behaviour, best prediction is to ask whether the person
Physiological measures
action performed; when person's attitude & social norm intends to do it
pupil dilation, heart rate, lie detector
favourable
Behaviour MEASURING ATTITUDES
frequency of behaviour, non-verbal behaviour
Overt behaviour measures
extension of basic model to emphasise role of volition(willpower)
Theory of Planned Behaviour; suggests that behaviour
prediction from an attitude measure is improved if people
depends on past experience, present obstacles believe they control over that behaviour
perceived behavioural control is extent in which person believes
it is easy or difficult to perform an act
moral values
habits
Improvements; by adding variables
anticipated regret
You might also like
- McWilliams' Defensive Functioning - Table by BeierDocument3 pagesMcWilliams' Defensive Functioning - Table by BeierMatthiasBeier91% (11)
- Members' Directory 2023 ICSB FinalDocument228 pagesMembers' Directory 2023 ICSB FinalJoynul Abedin100% (1)
- Mte511 - v2 - Theorists - Worksheet 2Document5 pagesMte511 - v2 - Theorists - Worksheet 2connie thomeczek100% (1)
- Understanding Voltage Regulators - Smart Grid Solutions - SiemensDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Voltage Regulators - Smart Grid Solutions - SiemenstusarNo ratings yet
- This Poster at WWW - Yourbias.isDocument1 pageThis Poster at WWW - Yourbias.isAstekMadden100% (1)
- Gotopage Dario OsoriowebsiteDocument21 pagesGotopage Dario Osoriowebsiteapi-663957612No ratings yet
- Mindmap 1Document1 pageMindmap 1api-584042936No ratings yet
- Estructura Estandar AIPM Professional Competency Standards For Project Management, Australian Instit...Document1 pageEstructura Estandar AIPM Professional Competency Standards For Project Management, Australian Instit...Maleja SanabriaNo ratings yet
- Ch.13 Social PsychologyDocument10 pagesCh.13 Social PsychologyRishendri -No ratings yet
- A4 Psychometric Book RecoveredDocument69 pagesA4 Psychometric Book RecoveredGoodluckleo De Great100% (1)
- Adlerian TheoryDocument1 pageAdlerian TheorycandybyunNo ratings yet
- Psychology - ApproachesDocument1 pagePsychology - ApproachesJul 480weshNo ratings yet
- Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development: EquilibrationDocument2 pagesPiaget's Stages of Cognitive Development: EquilibrationJohn Harold CastroNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument5 pagesLeadershipJulrey Angelo SedenoNo ratings yet
- This Poster at WWW - Yourbias.isDocument1 pageThis Poster at WWW - Yourbias.isAlfonso Molina RNo ratings yet
- 3.2: Defense MechanismsDocument3 pages3.2: Defense MechanismsGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEANo ratings yet
- Behavioral Cognitive Developmental Social-Cognitive ConstructivistDocument5 pagesBehavioral Cognitive Developmental Social-Cognitive ConstructivistAira Guerrero100% (2)
- Exploring IConference March 2009Document2 pagesExploring IConference March 2009Floortime RepositoryNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence Salovey2013Document6 pagesEmotional Intelligence Salovey2013inesterrinhaNo ratings yet
- Increasing Parenting Skills and Parenting E Cacy: Parent-Training Program Based Seamless Learning To Promoting Assessment Child DevelopmentDocument1 pageIncreasing Parenting Skills and Parenting E Cacy: Parent-Training Program Based Seamless Learning To Promoting Assessment Child Developmentkerja malamNo ratings yet
- The Science of Emotional IntelligenceDocument6 pagesThe Science of Emotional IntelligencePrachi DokaniaNo ratings yet
- Psychological Bias: Spotlight EffectDocument1 pagePsychological Bias: Spotlight Effectapi-534389058No ratings yet
- EDUC5410 Unit 2 WrittenDocument9 pagesEDUC5410 Unit 2 Writtenus nNo ratings yet
- EDUC5410 Unit 2 Written 1Document9 pagesEDUC5410 Unit 2 Written 1us nNo ratings yet
- Eq MindsetsDocument1 pageEq MindsetsNamjaa EnkhbatNo ratings yet
- PEDM2L3Document3 pagesPEDM2L3rere sincoNo ratings yet
- Design Research - Hussein Chalayan - Reversible ClothingDocument95 pagesDesign Research - Hussein Chalayan - Reversible ClothingPrachiNo ratings yet
- Bandura 1977Document2 pagesBandura 1977Dithya Malar SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER5 - Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorDocument1 pageCHAPTER5 - Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorVy TườngNo ratings yet
- Doing Philosophy Modified True or False And: Highest Thinking Skill To Assess Teaching Strategies RBTDocument8 pagesDoing Philosophy Modified True or False And: Highest Thinking Skill To Assess Teaching Strategies RBTRoss OsorabNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Attitudes & Social CognitionDocument1 pageCH 6 Attitudes & Social CognitionlorenlouisbernardNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Attitudes & Social CognitionDocument1 pageCH 6 Attitudes & Social CognitionMudita DaniNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Attitudes & Social CognitionDocument1 pageCH 6 Attitudes & Social CognitionKshitij DasariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Grade 11Document8 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Grade 11danteNo ratings yet
- Workplace Emotions, Attitudes, and Stress: Mcshane/Von Glinow M:Ob 3EDocument24 pagesWorkplace Emotions, Attitudes, and Stress: Mcshane/Von Glinow M:Ob 3EMuraliNo ratings yet
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument1 pageThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective Peopleminaymin85No ratings yet
- IJNBS-02-00004 (With I) - CopiarDocument5 pagesIJNBS-02-00004 (With I) - Copiarf gNo ratings yet
- We Don'T See Things As They Are, We See Things As We Are.Document42 pagesWe Don'T See Things As They Are, We See Things As We Are.RiyaNo ratings yet
- Contruction: Pretend Play AestheticsDocument1 pageContruction: Pretend Play AestheticsRuri OctavianiNo ratings yet
- TriangulationDocument2 pagesTriangulationSouvik SenNo ratings yet
- Santos Judy Ann A. Activity 1 Beed2a.....Document3 pagesSantos Judy Ann A. Activity 1 Beed2a.....Rosanna TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Section CDocument5 pagesSection CAllyssa Mae De LeonNo ratings yet
- PerceptionDocument25 pagesPerceptionadidas14388% (16)
- Curriculum Map - PhiloDocument7 pagesCurriculum Map - PhilodannaNo ratings yet
- The Interplay of Affect and Cognition in Attitude Formation and Change PDFDocument15 pagesThe Interplay of Affect and Cognition in Attitude Formation and Change PDFVicente RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Ped5 FinalsDocument1 pagePed5 FinalsAlvarez, Ara Bea JoyNo ratings yet
- EducativaDocument1 pageEducativaKata'ou ColombiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document8 pagesChapter 7tranm21410caNo ratings yet
- Which Are The Signs That Indicate That A Child Is AutisticDocument3 pagesWhich Are The Signs That Indicate That A Child Is AutisticIfigeneia VouzaNo ratings yet
- Lauridsen What Is Learning Styles New enDocument9 pagesLauridsen What Is Learning Styles New enJennalyn GomezNo ratings yet
- Krathwohl's Taxonomy of Affective Domain (1964) : ReceivingDocument2 pagesKrathwohl's Taxonomy of Affective Domain (1964) : ReceivingMary Joy CanalanNo ratings yet
- Part One The Nature of Approaches and MethodsDocument1 pagePart One The Nature of Approaches and Methodsbertaniamine7No ratings yet
- 7558 Neuroscience Infographic FINAL Tcm18 24930Document2 pages7558 Neuroscience Infographic FINAL Tcm18 24930Michael LouisNo ratings yet
- Evabel (Mita Sari Halawa, 17029035)Document8 pagesEvabel (Mita Sari Halawa, 17029035)Mita Sari HalawaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Others Through Perspective-Taking: Lesson TitleDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Others Through Perspective-Taking: Lesson TitleMary-Jane SighsNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Level: 1. Striated Muscle AbilityDocument7 pagesKnowledge Level: 1. Striated Muscle AbilityMita Sari HalawaNo ratings yet
- AIESEC Global Competency Model 2010Document1 pageAIESEC Global Competency Model 2010amilyn_No ratings yet
- NeuroSuccess: Your Brain Retraining Guide to Wealth and AccomplishmentFrom EverandNeuroSuccess: Your Brain Retraining Guide to Wealth and AccomplishmentNo ratings yet
- Situated Artificial Intelligence: Fundamentals and Applications for Integrating Intelligence With ActionFrom EverandSituated Artificial Intelligence: Fundamentals and Applications for Integrating Intelligence With ActionNo ratings yet
- Discovering Computers Enhanced Edition ©2017: Introducing Today's TechnologiesDocument37 pagesDiscovering Computers Enhanced Edition ©2017: Introducing Today's TechnologiesKent PerezNo ratings yet
- Theory of ArchitectureDocument3 pagesTheory of ArchitectureHarita Salvi50% (2)
- PAS 28 - Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures-1Document12 pagesPAS 28 - Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures-1Krizzia DizonNo ratings yet
- Big Data Insurance Case Study PDFDocument2 pagesBig Data Insurance Case Study PDFVivek SaahilNo ratings yet
- A Histeria - Teoria e Clínica PsicanalíticaDocument653 pagesA Histeria - Teoria e Clínica PsicanalíticaDaniel BraunaNo ratings yet
- Resume Li Cui JhuDocument1 pageResume Li Cui Jhuapi-340127718No ratings yet
- Research in Organizational Behavior: Sabine SonnentagDocument17 pagesResearch in Organizational Behavior: Sabine SonnentagBobby DNo ratings yet
- Roger Bacon Resume Nov2020Document1 pageRoger Bacon Resume Nov2020api-232293986No ratings yet
- Effect of IBA and NAA With or Without GA Treatment On Rooting Attributes of Hard Wood Stem Cuttings of Pomegranate (Punica Granatum L.)Document5 pagesEffect of IBA and NAA With or Without GA Treatment On Rooting Attributes of Hard Wood Stem Cuttings of Pomegranate (Punica Granatum L.)warlord_ckNo ratings yet
- SSB Tanitim CatalogDocument201 pagesSSB Tanitim CatalogAmir Cahyadi100% (1)
- Ch04 Case and FairDocument24 pagesCh04 Case and FairrazialamNo ratings yet
- Pamagat NG Isang Thesis Sa FilipinoDocument6 pagesPamagat NG Isang Thesis Sa Filipinocdayxnzcf100% (2)
- 1.5 Introducing Petty Cash Books: Suggested ActivitiesDocument2 pages1.5 Introducing Petty Cash Books: Suggested ActivitiesDonatien Oulaii100% (2)
- Aerodur Finish HF A 130: ® Akzonobel Aerospace CoatingsDocument3 pagesAerodur Finish HF A 130: ® Akzonobel Aerospace CoatingsАндрей МошкинNo ratings yet
- Rambabu Singh Thakur v. Sunil Arora & Ors. (2020 3 SCC 733)Document4 pagesRambabu Singh Thakur v. Sunil Arora & Ors. (2020 3 SCC 733)JahnaviSinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Practical Research 2 Teaching Date Quarter Teaching Time No. of DaysDocument9 pagesLesson Exemplar School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Practical Research 2 Teaching Date Quarter Teaching Time No. of DaysJovie Bitas DaeloNo ratings yet
- Carroll JungDocument27 pagesCarroll JungNico GarcíaNo ratings yet
- The Eqv: Effective From May 2021 ProductionDocument40 pagesThe Eqv: Effective From May 2021 ProductionariNo ratings yet
- Statics 2e Solns Ch01Document36 pagesStatics 2e Solns Ch01Samuel Montalvo100% (5)
- College of Engineering Course Syllabus Information Technology ProgramDocument5 pagesCollege of Engineering Course Syllabus Information Technology ProgramKhaled Al WahhabiNo ratings yet
- Summary of VivekachudamaniDocument3 pagesSummary of VivekachudamaniBr SarthakNo ratings yet
- Dan Webb Concealment GradeDocument2 pagesDan Webb Concealment Gradeapi-565691734No ratings yet
- DAO 34 & 35 RonaldDocument33 pagesDAO 34 & 35 Ronaldcris guzonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology-Threatened MiscarriageDocument1 pagePathophysiology-Threatened MiscarriageMoses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- Leon Battista Alberti - Sebastino Serlio - Giacomo Barozzi Da Vignola - Andrea Palladio - Philibert de L'ormeDocument32 pagesLeon Battista Alberti - Sebastino Serlio - Giacomo Barozzi Da Vignola - Andrea Palladio - Philibert de L'ormeYsabelle Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Ariston As 600 V DryerDocument40 pagesAriston As 600 V DryermmvdlpNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Isaac B 1Document17 pagesPortfolio Isaac B 1api-690889230No ratings yet
- Horn Persistence Natural HornDocument4 pagesHorn Persistence Natural Hornapi-478106051No ratings yet