Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2023-2023 - As.1 - Lesson Outline
2023-2023 - As.1 - Lesson Outline
Uploaded by
salamat panjaitanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2023-2023 - As.1 - Lesson Outline
2023-2023 - As.1 - Lesson Outline
Uploaded by
salamat panjaitanCopyright:
Available Formats
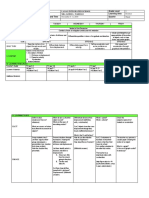
PHYSICS ADVANCE SECONDARY 1 LESSON OUTLINE
1st Semester
Link Date
CHAPTER UNIT SUB-UNIT LEARNING OUTCOMES MEETING Activity Duration
Files As 1-2 As 1-3 As 1-4
define and use distance, displacement, speed, velocity and acceleration
use graphical methods to represent distance, displacement, speed, velocity and acceleration
determine displacement from the area under a velocity–time graph
1 explanation using PPT 24-Jul-23
determine velocity using the gradient of a displacement–time graph
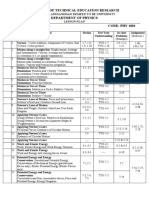
CHAPTER 2
2.1 Equations of motion determine acceleration using the gradient of a velocity–time graph
5 X 80
2. Kinematics derive, from the definitions of velocity and acceleration, equations that represent uniformly accelerated motion in a straight line
MINUTES
solve problems using equations that represent uniformly accelerated motion in a straight line, including the motion of bodies falling in a
uniform gravitational field without air resistance 2 27-Jul-23
describe an experiment to determine the acceleration of free fall using a falling object explanation using PPT
describe and explain motion due to a uniform velocity in one direction and a uniform acceleration in a perpendicular direction 3 31-Jul-23
LATIHAN SOAL WORKSHEET UNTUK EXAM 4 3 August 2023
EXAM 5 7-Aug-23
understand that mass is the property of an object that resists change in motion
recall F = ma and solve problems using it, understanding that acceleration and resultant force are always in the same direction
3.1 Newton’s laws of motion 6 explanation using PPT 10-Aug-23
state and apply each of Newton’s laws of motion
describe and use the concept of weight as the effect of a gravitational field on a mass and recall that the weight of an object is equal to the
product of its mass and the acceleration of free fall
show a qualitative understanding of frictional forces and viscous/drag forces including air resistance (no treatment of the coefficients of
CHAPTER 3
friction and viscosity is required, and a simple model of drag force increasing as speed increases is sufficient)
3.2 Non-uniform motion describe and explain qualitatively the motion of objects in a uniform gravitational field with air resistance
3. Dynamics 4x 80 minutes
understand that objects moving against a resistive force may reach a terminal (constant) velocity
recall the following SI base quantities and their units: mass (kg), length (m), time (s), current (A), temperature (K) 7 explanation using PPT 14-Aug-23
express derived units as products or quotients of the SI base units and use the derived units for quantities listed in this syllabus as
3.1 SI units appropriate
use SI base units to check the homogeneity of physical equations
recall and use the following prefixes and their symbols to indicate decimal submultiples or multiples of both base and derived units: pico (p),
nano (n), micro (μ), milli (m), centi (c), deci (d), kilo (k), mega (M), giga (G), tera (T)
WORKSHEET 8 21-Aug-23
4.1 Combining Forces add two or more coplanar forces 9 8/24/2023
CHAPTER 4
4.3 Centre of Gravity represent the weight of the body as acting at a single point known as its centre of gravity
4. Forces, vectors explanation using PPT
apply the principle of moments 3x 80 minutes
and Moments 4.4 the Turning Effect of Force 10 28-Aug-23
state the conditions for a body to be in equilibrium
4.5 The torque Of the Coouple define and apply the moment of a force and the torque of a couple
DAILY PROJECT 11 activities in physics lab 31-August-2023
understand the concept of work, and recall and use work done = force × displacement in the direction of the force
recall and apply the principle of conservation of energy
recall and understand that the efficiency of a system is the ratio of useful energy output from the system to the total energy input
4 x 80 minutes
5.1 Energy conservation use the concept of efficiency to solve problems 12 explanation using PPT 4-SEPT-2023
define power as work done per unit time
CHAPTER 5
solve problems using P = W/t
5. Work, Energy And
derive P = Fv and use it to solve problem
Power
derive, using W = Fs, the formula ∆EP = mg∆h for gravitational potential energy changes in a uniform gravitational field
5.2 Gravitational potential energy and recall and use the formula ∆EP = mg∆h for gravitational potential energy changes in a uniform gravitational field
kinetic energy
13 explanation using PPT 7-SEPT-2023
derive, using the equations of motion, the formula for kinetic energy EK = 1/2mv2
recall and use EK = 1/2mv2
LATIHAN SOAL UNTUK QUIZ 14 11-SEPT-2023
QUIZ 15 14-SEPT-2023
6.1 The Idea Of Momentum define linear momentum
16 18-SEPT-2023
CHAPTER 6
state and apply the principle of conservation of momentum to collisions in one and two dimensions explanation using PPT
6. Momentum 4x 80 minutes
6.2 Modelling Collision relate force to the rate of change of momentum
17 21-sept-2023
discuss energy changes in perfectly elastic and inelastic collisions
WORKSHEET 18 25-sept-2023
understand that deformation is caused by tensile or compressive forces (forces and deformations will be assumed to be in one dimension
only)
understand and use the terms load, extension, compression and limit of proportionality
recall and use Hooke’s law
7.1 Stress and strain 19 explanation using PPT 2-Oct-23
recall and use the formula for the spring constant k = F / x
define and use the terms stress, strain and the Young modulus
CHAPTER 7
7. Matters and describe an experiment to determine the Young modulus of a metal in the form of a wire
4 x 80 minutes
Materials understand and use the terms elastic deformation, plastic deformation and elastic limit
understand that the area under the force–extension graph represents the work done
Elastic and plastic behaviour 20 explanation using PPT 5-Oct-2023
determine the elastic potential energy of a material deformed within its limit of proportionality from the area under the force–extension graph
recall and use EP = 1/2 Fx = 1/2 kx2 for a material deformed within its limit of proportionality
LATIHAN SOAL UNTUK QUIZ 21 9-Oct-23
QUIZ 22 12-Oct-2023
recall Kirchhoff’s first law and understand that it is a consequence of conservation of charge
8.1 Kirchhof's laws recall Kirchhoff’s second law and understand that it is a consequence of conservation of energy 23 explanation using PPT 16-Oct-23
derive, using Kirchhoff’s laws, a formula for the combined resistance of two or more resistors in series
CHAPTER 9
use the formula for the combined resistance of two or more resistors in series
9.1 Kirchhoff's Law 4 x 80 minutes
derive, using Kirchhoff’s laws, a formula for the combined resistance of two or more resistors in parallel
9.2 Resistor Combinations 24 explanation using PPT 20-Oct-23
use the formula for the combined resistance of two or more resistors in parallel
use Kirchhoff’s laws to solve simple circuit problems
EXAM 25 23-Oct-23
define resistance
10.1 Metallic Conductor sketch the I–V characteristics of a metallic conductor at constant temperature, a semiconductor diode and a filament lamp
explain that the resistance of a filament lamp increases as current increases because its temperature increases 26 explanation using PPT 30-Oct-2023
CHAPTER 10
recall and use V = IR
10. Resistance and 10.2 Ohm's Law
state Ohm’s law 4 x 80 minutes
Resistivity
understand that the resistance of a light-dependent resistor (LDR) decreases as the light intensity increases
10.3 Resistance and Temperature
understand that the resistance of a thermistor decreases as the temperature increases (it will be assumed that thermistors have a negative 27 explanation using PPT 2-Nov-23
temperature coefficient)
10.4 Resisitivity recall and use R = ρL /A
WORKSHEET 28 6-Nov-23
11.1 Internal Resistance understand the principle of a potential divider circuit
29 explanation using PPT 9-Nov-23
CHAPTER 11
11.2 Potential Deviders recall and use the principle of the potentiometer as a means of comparing potential differences
11. Practical Circuit explain the use of thermistors and light-dependent resistors in potential dividers to provide a potential difference that is dependent on 3 x80 minutes
11.3 sensors
temperature and light intensit
30 explanation using PPT 13-Nov-23
11.4 Potentiometer Cricuit understand the use of a galvanometer in null methods
FINAL PROJECT 31 16-Nov-23
You might also like
- AP Physics C Mechanics Course at A GlanceDocument3 pagesAP Physics C Mechanics Course at A GlanceTarun AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Explicit Dynamic Analysis - AbaqusDocument19 pagesExplicit Dynamic Analysis - AbaqusDavid RivadeneiraNo ratings yet
- DHIS Monthly Reporting Form (PHC Facilities)Document4 pagesDHIS Monthly Reporting Form (PHC Facilities)Usman89% (9)
- Mechanism and Mechanical Vibration (Lab Work) Teaching PlanDocument8 pagesMechanism and Mechanical Vibration (Lab Work) Teaching PlanBelia NomeNo ratings yet
- Grade 7, Quarter 3 PDFDocument44 pagesGrade 7, Quarter 3 PDFJulius Salas76% (17)
- 2023-2024 - As.2 - Lesson Outline.Document1 page2023-2024 - As.2 - Lesson Outline.salamat panjaitanNo ratings yet
- Science 3rd QuarterDocument22 pagesScience 3rd Quartermae missionNo ratings yet
- 'Physics Class 9 AY 2022-23Document11 pages'Physics Class 9 AY 2022-23Anusha TalrejaNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide General Physics 1Document8 pagesLearning Guide General Physics 1lj BoniolNo ratings yet
- Class Plan Dynamics Winter 2023Document1 pageClass Plan Dynamics Winter 2023Trushank PatelNo ratings yet
- Module1.coverpage - Units PhysicsDocument27 pagesModule1.coverpage - Units PhysicsMariecor MaghanoyNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - Syllabus 2023-24 (Medical)Document41 pagesClass 9 - Syllabus 2023-24 (Medical)Learn Online With JaveriaNo ratings yet
- Class 9-Syllabus2023-24 1st TermDocument20 pagesClass 9-Syllabus2023-24 1st TermLearn Online With JaveriaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Physics SyllabusDocument9 pagesCambridge Physics SyllabusEeshaal FarooqNo ratings yet
- Grade 7, Quarter 3Document46 pagesGrade 7, Quarter 3Ariel Josue DaparNo ratings yet
- Control of Evidence TSM 2023Document3 pagesControl of Evidence TSM 2023Jennifer PradoNo ratings yet
- 5th+grade+ +week+4Document7 pages5th+grade+ +week+4steffany camachoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Quarter 3Document46 pagesGrade 7 Quarter 3Bonachita YamNo ratings yet
- Gp2 7th Week DLL 4thDocument7 pagesGp2 7th Week DLL 4thmaryann santosNo ratings yet
- Grade 7, Quarter 3Document44 pagesGrade 7, Quarter 3James Lacuesta TabioloNo ratings yet
- MAT391 Course OutlineDocument4 pagesMAT391 Course OutlinePHENYONo ratings yet
- CM 9igcseDocument33 pagesCM 9igcsevishnus22No ratings yet
- PHYSICS Alevel AQA 7407 Unit 4 Mechanics and MaterialsDocument41 pagesPHYSICS Alevel AQA 7407 Unit 4 Mechanics and MaterialsValentina R. RusevaNo ratings yet
- Notice-Minor Test 3 - Nurture-Phase 1 (Tallentpro, Evening, Weekend) - IIT JEEDocument1 pageNotice-Minor Test 3 - Nurture-Phase 1 (Tallentpro, Evening, Weekend) - IIT JEEAryan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Grade: 11 Semester: First Semester: Culminating Performance StandardDocument4 pagesGrade: 11 Semester: First Semester: Culminating Performance Standardnorielle oberioNo ratings yet
- Grade IX Syllabus (Physics) AY 2023 - 24Document13 pagesGrade IX Syllabus (Physics) AY 2023 - 24Tahera AkterNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - One Dimensional MotionDocument2 pagesUnit 2 - One Dimensional MotionJeah Asilum DalogdogNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Log: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofJay MellizaNo ratings yet
- Saturated Soil in ABAQUSDocument8 pagesSaturated Soil in ABAQUSAhmed ArafaNo ratings yet
- Physics CriteriaDocument4 pagesPhysics CriteriaaatifNo ratings yet
- PHYS Module 1 OnScreenDocument21 pagesPHYS Module 1 OnScreenadiNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips - Revised Gce As A Level Scheme of Work PhysicsDocument59 pagesSilo - Tips - Revised Gce As A Level Scheme of Work PhysicsNathaniell Dongo KasekeNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Quarter 3 Daily Lesson LogDocument45 pagesGrade 7 Quarter 3 Daily Lesson LogmicujulieannNo ratings yet
- DLL - OGARTE - Grade 7, Quarter 3 - Week 1Document9 pagesDLL - OGARTE - Grade 7, Quarter 3 - Week 1Charmalou Pampilo OgarteNo ratings yet
- Physics For Engineers IM3Document17 pagesPhysics For Engineers IM3Rexie Magastino100% (1)
- Universiti Malaysia Perlis Institut Matematik Kejuruteraan Course Schedule For Engineering Statistics / EQT 271 (Academic Session I, 2013/2014)Document3 pagesUniversiti Malaysia Perlis Institut Matematik Kejuruteraan Course Schedule For Engineering Statistics / EQT 271 (Academic Session I, 2013/2014)Mohanarajan Mohan KumarNo ratings yet
- 4th Week-2Document16 pages4th Week-2BACUAL Gemzsar E.100% (1)
- Revised Gce As A Level Scheme of Work PhysicsDocument59 pagesRevised Gce As A Level Scheme of Work PhysicsNathaniell Dongo KasekeNo ratings yet
- Parameter IdentificationDocument24 pagesParameter IdentificationRex LebanonNo ratings yet
- Development of Motion Learning Media and Energy Conservation Law Through Coaster Tracks Based On Logger Pro AnalysisDocument5 pagesDevelopment of Motion Learning Media and Energy Conservation Law Through Coaster Tracks Based On Logger Pro AnalysisfapriliaNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter (Physics)Document21 pages4th Quarter (Physics)Evelyn A. Uy100% (1)
- V2-Assignment Brief Form Project Fall - 23 - 24Document9 pagesV2-Assignment Brief Form Project Fall - 23 - 24ramayasser381No ratings yet
- Instructor:: Aleahy@knox - EduDocument4 pagesInstructor:: Aleahy@knox - EduUyên HiếuNo ratings yet
- Developments in Response Spectrum - Based Stochastic Response of Structural SystemsDocument19 pagesDevelopments in Response Spectrum - Based Stochastic Response of Structural SystemsVinay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - UPM 2022-23 - Upto Ch-7Document1 pageLesson Plan - UPM 2022-23 - Upto Ch-7Aryan AnsNo ratings yet
- Grade 7, Quarter 3 File.Document139 pagesGrade 7, Quarter 3 File.Shaynie Mhe Amar AntonioNo ratings yet
- Week003 Vectors and Two Dimensional MotionDocument3 pagesWeek003 Vectors and Two Dimensional MotionBleep BloopNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Birla Institute of Technology and Science, PilaniDocument4 pagesBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Birla Institute of Technology and Science, PilaniPiyush hurkatNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena 1Document8 pagesTransport Phenomena 1Al- DhaheriNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Response Analysis Using ABAQUS PDFDocument20 pagesDynamic Response Analysis Using ABAQUS PDFKekek QatarNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Lesson PlanDocument22 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Lesson PlanKazuya Sensei100% (1)
- General Physics 1 MOTION ALONG STRAIGHT LINEDocument28 pagesGeneral Physics 1 MOTION ALONG STRAIGHT LINEWarren SilvaNo ratings yet
- Array-Representation Integration Factor Method ForDocument16 pagesArray-Representation Integration Factor Method ForTezera ChubaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dynamics FundamentalsDocument4 pagesFluid Dynamics FundamentalsNicholas NicholasNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Outline - Yr12 MathDocument5 pagesCurriculum Outline - Yr12 MathagrbovicNo ratings yet
- Week 9 AristotleDocument2 pagesWeek 9 AristotleChristian nebreNo ratings yet
- Boore Filtered Strong Motion DataDocument10 pagesBoore Filtered Strong Motion DataVicente VeraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Extension 2 Year 12 Topic Guide MechanicsDocument14 pagesMathematics Extension 2 Year 12 Topic Guide MechanicsTony TranNo ratings yet
- Sos Mdcat Test Session - 2020Document10 pagesSos Mdcat Test Session - 2020Hamza Ihsan100% (1)
- 5.1. Contoh Silabus Navigasi ElektronikDocument7 pages5.1. Contoh Silabus Navigasi ElektronikGus Misb AkhNo ratings yet
- The Partial Regularity Theory of Caffarelli, Kohn, and Nirenberg and its SharpnessFrom EverandThe Partial Regularity Theory of Caffarelli, Kohn, and Nirenberg and its SharpnessNo ratings yet
- Quiz US 2020Document4 pagesQuiz US 2020salamat panjaitanNo ratings yet
- Collet 2016 in Tan Shafi NazDocument8 pagesCollet 2016 in Tan Shafi NazTech vixenNo ratings yet
- Sport Sport Sport Sport ART: Daftar Pemaikaian Peralatan Dan Ruangan Daftar Pemaikaian Peralatan Dan RuanganDocument3 pagesSport Sport Sport Sport ART: Daftar Pemaikaian Peralatan Dan Ruangan Daftar Pemaikaian Peralatan Dan Ruangansalamat panjaitanNo ratings yet
- CH 13 WavesDocument15 pagesCH 13 Wavessalamat panjaitanNo ratings yet
- X-Rays USG CT Scan MRI: Medical ImagingDocument7 pagesX-Rays USG CT Scan MRI: Medical Imagingsalamat panjaitanNo ratings yet
- Linear AlgebraDocument395 pagesLinear AlgebraRehan Javed100% (2)
- List of Coolers and HeatersDocument2 pagesList of Coolers and HeatersadityasahayNo ratings yet
- Construction Method (PICC)Document2 pagesConstruction Method (PICC)rheymar diwaNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 SolutionDocument5 pagesHomework 2 SolutiongretabunciNo ratings yet
- 03 Problem On Steam Turbine - RevisedDocument16 pages03 Problem On Steam Turbine - RevisedKonstantina AsimakopoulouNo ratings yet
- LDPDocument46 pagesLDPSoundradevi ArumugamNo ratings yet
- LNG Easy Pvt. LTD: Pioneers of Small Scale LNG Distribution Through Virtual PipelineDocument49 pagesLNG Easy Pvt. LTD: Pioneers of Small Scale LNG Distribution Through Virtual PipelineAMIRNo ratings yet
- PaintsDocument20 pagesPaintsPashmi Shah100% (1)
- Test Bank For Chemistry 9th Edition Zumdahl Isbn 10 1133611095 Isbn 13 9781133611097Document17 pagesTest Bank For Chemistry 9th Edition Zumdahl Isbn 10 1133611095 Isbn 13 9781133611097Lynn Higgins100% (38)
- FINAL Ulster Combined Report From STONE 12-15Document104 pagesFINAL Ulster Combined Report From STONE 12-15Watershed PostNo ratings yet
- Msds UreaDocument5 pagesMsds UreaHunterlan Register FilanNo ratings yet
- 6 - DNV - Composites Repair JIP - New Approach To Repair of FPSO's Without Hot Work Using Glueing PolymersDocument31 pages6 - DNV - Composites Repair JIP - New Approach To Repair of FPSO's Without Hot Work Using Glueing PolymersAnonymous 19QCaJNo ratings yet
- NE2R757GT-P6: Specifications For Red LedDocument19 pagesNE2R757GT-P6: Specifications For Red LedYiannis PapadopoulosNo ratings yet
- Life On MarsDocument3 pagesLife On MarsSahar SmNo ratings yet
- The Bird CageDocument1 pageThe Bird CageNick BlueNo ratings yet
- SECTEC AI WIFI YCC365 PLUS Camera Pricelist201906Document5 pagesSECTEC AI WIFI YCC365 PLUS Camera Pricelist201906Glenn JattanNo ratings yet
- BD707/709/711 BD708/712: Complementary Silicon Power TransistorsDocument7 pagesBD707/709/711 BD708/712: Complementary Silicon Power TransistorsGheorghe DanielNo ratings yet
- Hotpoint Washing Machine Wmf740Document16 pagesHotpoint Washing Machine Wmf740furheavensakeNo ratings yet
- 03051Document2 pages03051JojolasNo ratings yet
- Valve SelectionDocument5 pagesValve SelectionmansurNo ratings yet
- A2QVP2 TrainingDocument9 pagesA2QVP2 Trainingdanny wangNo ratings yet
- Soft Computing Module IDocument161 pagesSoft Computing Module INatarajanSubramanyamNo ratings yet
- Fortran CF DDocument160 pagesFortran CF DLahcen AkerkouchNo ratings yet
- Yaesu FT-1802 Operating ManualDocument88 pagesYaesu FT-1802 Operating ManualYayok S. AnggoroNo ratings yet
- Cement Grout AAADocument4 pagesCement Grout AAAabualamalNo ratings yet
- Circut Diagram For GlucometerDocument22 pagesCircut Diagram For GlucometerSaranyaNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Electronic Control of Linear-To-circular Polarization Conversion Using A Reconfigurable MetasurfaceDocument6 pages2017 - Electronic Control of Linear-To-circular Polarization Conversion Using A Reconfigurable Metasurfaceab4azizNo ratings yet
- Wifi Smart: Thank You For Choosing Our Product. For Proper Operation, Please Read and Keep This Manual CarefullyDocument24 pagesWifi Smart: Thank You For Choosing Our Product. For Proper Operation, Please Read and Keep This Manual Carefullykari.junttilaNo ratings yet
- Asahi Carbon Black (For Rubber) Physical Chemistry Properties of Main Products - Products - Products and Technology - ASAHI CARBON CO., LTDDocument1 pageAsahi Carbon Black (For Rubber) Physical Chemistry Properties of Main Products - Products - Products and Technology - ASAHI CARBON CO., LTDSUDARSHAN dAWNo ratings yet