Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment - Rotational Kinematics
Assignment - Rotational Kinematics
Uploaded by
arqam SaadCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 8 I - ObjectivesDocument3 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 8 I - ObjectivesIRIS100% (7)
- Reading: Wiesel Chapter 4: Problem Set 5Document3 pagesReading: Wiesel Chapter 4: Problem Set 5danielNo ratings yet
- Rotational MotionDocument19 pagesRotational MotionRamkumar SundaramNo ratings yet
- Caps 6Document7 pagesCaps 6Siddhant SinghNo ratings yet
- Physics: System of Particles & Rotational Dynamics, Rolling MotionDocument3 pagesPhysics: System of Particles & Rotational Dynamics, Rolling MotionShashi Shekhar TripathiNo ratings yet
- Revision Assignment (Adv Level) - 1Document7 pagesRevision Assignment (Adv Level) - 1Gandharv BhoiteNo ratings yet
- A2 Notes Till Mids Sir Usman Ali PhysicsDocument295 pagesA2 Notes Till Mids Sir Usman Ali Physicszainabshafqat9603No ratings yet
- Motion in A CircleDocument28 pagesMotion in A CircleM.K 1013No ratings yet
- DPP (70-72) 11th Physics - Eng - WADocument6 pagesDPP (70-72) 11th Physics - Eng - WAshalini kumariNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Rotational MotionDocument3 pagesDPP - 01 - Rotational Motionaayush bhatiNo ratings yet
- RM 5Document46 pagesRM 5soumengoswami10No ratings yet
- Rotational Motion (Practice Questions)Document46 pagesRotational Motion (Practice Questions)SakshamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Planar Kinematics of Rigid BodiesDocument29 pagesChapter 5. Planar Kinematics of Rigid BodiesDivnesh Lingam100% (1)
- Assignment P-11-09: Problem 7. Problem 8. Problem 9Document4 pagesAssignment P-11-09: Problem 7. Problem 8. Problem 9Jijo SagaiNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion (Practice Questions PDFDocument46 pagesRotational Motion (Practice Questions PDFSakshamNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion JEE Advanced Important QuestionsDocument19 pagesCircular Motion JEE Advanced Important QuestionsRavindra KumarNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument21 pagesPhysicskartikmahtole.8eNo ratings yet
- 2019 JC1 H2 Math (Promotion Exam) St. Andrew's Junior CollegeDocument5 pages2019 JC1 H2 Math (Promotion Exam) St. Andrew's Junior CollegeTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- RBD Bansal Classes Class TestDocument4 pagesRBD Bansal Classes Class TestShivendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion (Question Paper)Document6 pagesCircular Motion (Question Paper)anchlia12345No ratings yet
- 2023 - JEE-Main-7 - Paper (Gen 4A 4B 4C 4D 4E 6A and 6B)Document13 pages2023 - JEE-Main-7 - Paper (Gen 4A 4B 4C 4D 4E 6A and 6B)Archana SharmaNo ratings yet
- ELP-01 To 06 - Rotational MotionDocument16 pagesELP-01 To 06 - Rotational Motionnavy.aulakh11No ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Circular MotionDocument4 pagesDPP - 01 - Circular Motionshivansh mishra roll no. 30No ratings yet
- Assignment-35: Section-I Single Correct Answer Type 5 Q. (3 M (-1) ) 1Document6 pagesAssignment-35: Section-I Single Correct Answer Type 5 Q. (3 M (-1) ) 1ankitrajaj8083No ratings yet
- Class:XII Time: 40 Min. M.M.: 36 DPP. NO.-48: Discussion: 27-28/07/2015Document6 pagesClass:XII Time: 40 Min. M.M.: 36 DPP. NO.-48: Discussion: 27-28/07/2015RahulNo ratings yet
- Class XI Physics DPP Set (23) - Previous Chaps + Rotational MotionDocument21 pagesClass XI Physics DPP Set (23) - Previous Chaps + Rotational MotionNilabha DasNo ratings yet
- 1 Z 3 VIa G2 F Na LSNPQ9 TSVDocument70 pages1 Z 3 VIa G2 F Na LSNPQ9 TSVStandardNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 RevisionDocument4 pagesUnit 13 Revisionl wanningNo ratings yet
- 1.kinematics of RDDocument4 pages1.kinematics of RDAnmolNo ratings yet
- 4 Motion in A Plane-PYQDocument3 pages4 Motion in A Plane-PYQKEVIN P SNo ratings yet
- A2 Assignment 3 M1 Term 2 2022 Due: Monday 30th MAYDocument7 pagesA2 Assignment 3 M1 Term 2 2022 Due: Monday 30th MAYTheLuckS; ラッキー矢印No ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Question Bank Level - 1, 2, 3Document16 pagesMiscellaneous Question Bank Level - 1, 2, 3Jee AspirantNo ratings yet
- W ID8 OL0 EEp 7 Ejg 08 A8 GJDocument3 pagesW ID8 OL0 EEp 7 Ejg 08 A8 GJROHIT ARYANo ratings yet
- 01 Assign # 01 (Circular Motion) - JEE - NURTURE-SCDocument11 pages01 Assign # 01 (Circular Motion) - JEE - NURTURE-SCPiyush PandaNo ratings yet
- 2018-06-05Document27 pages2018-06-05XxyyzzNo ratings yet
- Transformations Work SheetDocument12 pagesTransformations Work SheetPrithvi Viraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- SECTION-I (Single Choice Questions)Document6 pagesSECTION-I (Single Choice Questions)Bhawna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics+Exercise 5 (A)Document5 pagesElectrostatics+Exercise 5 (A)Sumit RajNo ratings yet
- Physics Rotational Motion MCQDocument7 pagesPhysics Rotational Motion MCQAyan Ghosh100% (1)
- Section A Answer Two Questions From This SectionDocument6 pagesSection A Answer Two Questions From This SectionFranklyn kipkuruiNo ratings yet
- Physics Rotational Motion MCQDocument7 pagesPhysics Rotational Motion MCQrkjha70867% (3)
- Assignment On Rigid Body KinematicsDocument4 pagesAssignment On Rigid Body KinematicsKaveesh KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document48 pagesChapter 6Hafizszul FeyzulNo ratings yet
- Uniform Circular Motion Practice Qs With AnswersDocument17 pagesUniform Circular Motion Practice Qs With AnswersLawrence Lim Ah KowNo ratings yet
- Circle Motion, Center of MassDocument6 pagesCircle Motion, Center of MassYUKTESH YuBoNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee JEE (Mains) : Important InstructionsDocument15 pagesFiitjee JEE (Mains) : Important InstructionsYuvi BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Coordinate System TransformationDocument18 pagesCoordinate System TransformationVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesNo ratings yet
- Use of Calculators Is Not Allowed (G 10Nkg) : V S S SDocument9 pagesUse of Calculators Is Not Allowed (G 10Nkg) : V S S SadikaviNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Analysis of LinkagesDocument38 pagesAcceleration Analysis of LinkagesHaile SimachewNo ratings yet
- Race 1 1686742220Document3 pagesRace 1 1686742220xenonverd321No ratings yet
- Motion in Two and Three Dimension IIDocument14 pagesMotion in Two and Three Dimension IISuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Circular MotionDocument6 pagesPhysics Circular MotionNethra SasikumarNo ratings yet
- All India Test Series: FiitjeeDocument19 pagesAll India Test Series: FiitjeeVarri Demudu BabuNo ratings yet
- @bohring Bot × @JEE Tests 06 GR Rolling Dynamics, Angular MomentumDocument8 pages@bohring Bot × @JEE Tests 06 GR Rolling Dynamics, Angular Momentumrandomwork013No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Circular Motion - EQDocument2 pagesChapter 7 Circular Motion - EQelty TanNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 QuizDocument8 pagesTopic 6 Quizlim18187No ratings yet
- Watch and Clock Escapements A Complete Study in Theory and Practice of the Lever, Cylinder and Chronometer Escapements, Together with a Brief Account of the Origin and Evolution of the Escapement in HorologyFrom EverandWatch and Clock Escapements A Complete Study in Theory and Practice of the Lever, Cylinder and Chronometer Escapements, Together with a Brief Account of the Origin and Evolution of the Escapement in HorologyNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of the Rigid Solid with General Constraints by a Multibody ApproachFrom EverandDynamics of the Rigid Solid with General Constraints by a Multibody ApproachNo ratings yet
- Multilinear Functions Of Direction And Their Uses In Differential GeometryFrom EverandMultilinear Functions Of Direction And Their Uses In Differential GeometryNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Differential Geometry and Saddle Synthesis of LinkagesFrom EverandKinematic Differential Geometry and Saddle Synthesis of LinkagesNo ratings yet
- CsprojDocument19 pagesCsprojarqam SaadNo ratings yet
- ManagementsysDocument19 pagesManagementsysarqam SaadNo ratings yet
- Vectors 5Document110 pagesVectors 5arqam SaadNo ratings yet
- Lorentz ForceDocument2 pagesLorentz Forcearqam SaadNo ratings yet
- 0910 SQ AnswersDocument7 pages0910 SQ AnswersPaul BurgessNo ratings yet
- Angeles J Shaoping Bai Kinematics of Mechanical Systems FundDocument342 pagesAngeles J Shaoping Bai Kinematics of Mechanical Systems FundStrahinja DonicNo ratings yet
- Missile 6DOF EquationDocument2 pagesMissile 6DOF EquationyhyogaswaraNo ratings yet
- Inersia and Free FallDocument16 pagesInersia and Free Fallharirie 07No ratings yet
- Final Exam Mec420 Jan 2018 - s1 - AnswerDocument14 pagesFinal Exam Mec420 Jan 2018 - s1 - AnswerIrfan SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Ap Physics C Exam Review 1Document3 pagesAp Physics C Exam Review 1sudhakaralla1100% (1)
- Chapter 6 AnswDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Answsalama alkaabiNo ratings yet
- Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Lect-10Document32 pagesCh-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Lect-10Kishan KumarNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument21 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumTerry Gabriel SignoNo ratings yet
- Theme: Newtonian Mechanics Chapter 3: GravitationDocument11 pagesTheme: Newtonian Mechanics Chapter 3: GravitationvelavanNo ratings yet
- A Tutorial To Inertial Navigation: Yuanxin WuDocument68 pagesA Tutorial To Inertial Navigation: Yuanxin WuNicoli LourençoNo ratings yet
- Science PDF (Module 1)Document19 pagesScience PDF (Module 1)Jean PernitoNo ratings yet
- Math Modelling of Missile For Control TheoryDocument8 pagesMath Modelling of Missile For Control TheoryD.ViswanathNo ratings yet
- 3.7 - Forces Movement Shape and Momentum 2p - Edexcel Igcse Physics QPDocument12 pages3.7 - Forces Movement Shape and Momentum 2p - Edexcel Igcse Physics QPKate BlossomNo ratings yet
- Ultra-Precise Optical CMM: Micro-And Nanometre Resolution For Manufacturing and R&DDocument8 pagesUltra-Precise Optical CMM: Micro-And Nanometre Resolution For Manufacturing and R&Dyarzar17No ratings yet
- Amusement ParkDocument10 pagesAmusement ParkTomasLiefferingNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Prashanna YadavNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Unit - 6Document15 pagesFluid Mechanics Unit - 6Prem T RajuNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Golf RangeDocument6 pagesStudent Exploration: Golf RangeNicholas chinNo ratings yet
- 50 Marks Class Xi Question PaperDocument8 pages50 Marks Class Xi Question PaperTapas Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 PDFDocument12 pagesLecture1 PDFFredrick AwuduNo ratings yet
- Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das Luo Solution ManualDocument40 pagesPrinciples of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das Luo Solution Manualalfred100% (31)
- Cornell Notes For Types of WavesDocument11 pagesCornell Notes For Types of Wavesapi-313808182No ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument5 pagesPHYSICSDaniel GtsadkanNo ratings yet
- Bell 1980Document12 pagesBell 1980Jose Laginha PalmaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank All Units With VTU Old Questions With Front PageDocument11 pagesQuestion Bank All Units With VTU Old Questions With Front PageHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (2) : Dr. Ali Mahmoud Ali Attia ME 413Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics (2) : Dr. Ali Mahmoud Ali Attia ME 413محمد عليNo ratings yet
- The Thorny Way of Truth Part6 MarinovDocument332 pagesThe Thorny Way of Truth Part6 MarinovEvaldas StankeviciusNo ratings yet
Assignment - Rotational Kinematics
Assignment - Rotational Kinematics
Uploaded by
arqam SaadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment - Rotational Kinematics
Assignment - Rotational Kinematics
Uploaded by
arqam SaadCopyright:
Available Formats
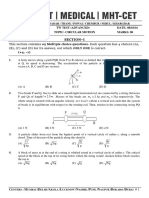
PHYSICS TUTORIAL
ROTATIONAL KINEMATICS
[1] A rod AB of length L is rotating about a fixed axis. Velocities of the two ends are v 1 and v2 directed perpendicular to the
rod as shown in the figure 34 1 . Find the distance of axis of rotation from the end B and the angular velocity of the rod
about the axis of rotation.
[2] Prove that rotation of a body about a fixed axis with angular velocity may be considered
as superposition of pure
translation and pure rotation about an axis parallel to the former with angular velocity .
[3] A rotating disc moves in the positive direction of x axis as shown in the figure 34 2 Find the equation y(x) describing
the position of instantaneous axis of rotation, if at the initial moment the axis C of the disc was located at the point O after
which it moved
(a) with a constant velocity v, while the disc started rotating counterclockwise with a constant angular acceleration
( the initial angular velocity is equal to zero.)
(b) with a constant acceleration w ( zero initial velocity),while the disc rotates counter clockwise with a constant
angular velocity .
[4] A bobbin with thread wound around it lies on a horizontal floor and can roll along it without sliding. With what velocity will
the centre of the bobbin move if the block starts to descend with constant velocity v as shown in the figure 34 3 ? The
inner radius of the bobbin is r and external one R.
figure 34 1 figure 34 2 figure 34 3 figure 34 4 figure 34 5
[5] A point A is located on the rim of a wheel of radius R which rolls without slipping along a horizontal surface with constant
velocity v as shown in the figure 34 4 . Find:
(a) the modulus and the direction of the acceleration vector of the point A ;
(b) the total distance s traversed by the point A between the two successive moments at which it touches the
surface.
[6] A disc rolls without slipping over a horizontal plane. The radius of disc is equal to r. Find the radius of curvature of the
trajectery traced out by a point lying on the circumference of the disc in terms of its angular displacement taking from
the moment when it was point of contact.
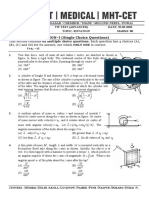
[7] A ball of radius R rolls without slipping on a horizontal plane so that its centre moves with constant acceleration w, t time
after the beginning of motion its position corresponds to that shown in figure 34 5 . Find :
(a) the velocities of the points A , B and O.
(b) the accelerations of these points.
[8] Wheels of a cart rolls without slipping on a rough horizontal floor. Cart moves with constant velocity. Mud particles fly off
top of the rear wheel and fall onto the top of the front wheel. Find the velocity of the cart. Radius of rear wheel is a, radius
of the front wheel is b and distance between the axle of the two wheels is c.
ANSWERS
v 2L v v2
1] x , 1
v1 v 2 L [7] [a] 2 w t, 2 w t, 0
[b] wA 4w2 (w2 t2 / R)2 wB w2 (w w2 t2 / R)2 wO w 2 t2 / R
v2 2wx
[3] [a] y [b] y
x
1/2
g{c2 (a b)2 }
[8] v
4(a b)
Rv
[4]
R r
[5] [a] v 2 / R directed towards the centre. [b] 8R
[6] R 4 r sin ( / 2)
PHYSICS TUTORIAL, Gauri Shankar Nagar, North Office Para, Ranchi-2, Jharkhand, Mob. No. : 9431108812
You might also like
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 8 I - ObjectivesDocument3 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 8 I - ObjectivesIRIS100% (7)
- Reading: Wiesel Chapter 4: Problem Set 5Document3 pagesReading: Wiesel Chapter 4: Problem Set 5danielNo ratings yet
- Rotational MotionDocument19 pagesRotational MotionRamkumar SundaramNo ratings yet
- Caps 6Document7 pagesCaps 6Siddhant SinghNo ratings yet
- Physics: System of Particles & Rotational Dynamics, Rolling MotionDocument3 pagesPhysics: System of Particles & Rotational Dynamics, Rolling MotionShashi Shekhar TripathiNo ratings yet
- Revision Assignment (Adv Level) - 1Document7 pagesRevision Assignment (Adv Level) - 1Gandharv BhoiteNo ratings yet
- A2 Notes Till Mids Sir Usman Ali PhysicsDocument295 pagesA2 Notes Till Mids Sir Usman Ali Physicszainabshafqat9603No ratings yet
- Motion in A CircleDocument28 pagesMotion in A CircleM.K 1013No ratings yet
- DPP (70-72) 11th Physics - Eng - WADocument6 pagesDPP (70-72) 11th Physics - Eng - WAshalini kumariNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Rotational MotionDocument3 pagesDPP - 01 - Rotational Motionaayush bhatiNo ratings yet
- RM 5Document46 pagesRM 5soumengoswami10No ratings yet
- Rotational Motion (Practice Questions)Document46 pagesRotational Motion (Practice Questions)SakshamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Planar Kinematics of Rigid BodiesDocument29 pagesChapter 5. Planar Kinematics of Rigid BodiesDivnesh Lingam100% (1)
- Assignment P-11-09: Problem 7. Problem 8. Problem 9Document4 pagesAssignment P-11-09: Problem 7. Problem 8. Problem 9Jijo SagaiNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion (Practice Questions PDFDocument46 pagesRotational Motion (Practice Questions PDFSakshamNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion JEE Advanced Important QuestionsDocument19 pagesCircular Motion JEE Advanced Important QuestionsRavindra KumarNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument21 pagesPhysicskartikmahtole.8eNo ratings yet
- 2019 JC1 H2 Math (Promotion Exam) St. Andrew's Junior CollegeDocument5 pages2019 JC1 H2 Math (Promotion Exam) St. Andrew's Junior CollegeTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- RBD Bansal Classes Class TestDocument4 pagesRBD Bansal Classes Class TestShivendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion (Question Paper)Document6 pagesCircular Motion (Question Paper)anchlia12345No ratings yet
- 2023 - JEE-Main-7 - Paper (Gen 4A 4B 4C 4D 4E 6A and 6B)Document13 pages2023 - JEE-Main-7 - Paper (Gen 4A 4B 4C 4D 4E 6A and 6B)Archana SharmaNo ratings yet
- ELP-01 To 06 - Rotational MotionDocument16 pagesELP-01 To 06 - Rotational Motionnavy.aulakh11No ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Circular MotionDocument4 pagesDPP - 01 - Circular Motionshivansh mishra roll no. 30No ratings yet
- Assignment-35: Section-I Single Correct Answer Type 5 Q. (3 M (-1) ) 1Document6 pagesAssignment-35: Section-I Single Correct Answer Type 5 Q. (3 M (-1) ) 1ankitrajaj8083No ratings yet
- Class:XII Time: 40 Min. M.M.: 36 DPP. NO.-48: Discussion: 27-28/07/2015Document6 pagesClass:XII Time: 40 Min. M.M.: 36 DPP. NO.-48: Discussion: 27-28/07/2015RahulNo ratings yet
- Class XI Physics DPP Set (23) - Previous Chaps + Rotational MotionDocument21 pagesClass XI Physics DPP Set (23) - Previous Chaps + Rotational MotionNilabha DasNo ratings yet
- 1 Z 3 VIa G2 F Na LSNPQ9 TSVDocument70 pages1 Z 3 VIa G2 F Na LSNPQ9 TSVStandardNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 RevisionDocument4 pagesUnit 13 Revisionl wanningNo ratings yet
- 1.kinematics of RDDocument4 pages1.kinematics of RDAnmolNo ratings yet
- 4 Motion in A Plane-PYQDocument3 pages4 Motion in A Plane-PYQKEVIN P SNo ratings yet
- A2 Assignment 3 M1 Term 2 2022 Due: Monday 30th MAYDocument7 pagesA2 Assignment 3 M1 Term 2 2022 Due: Monday 30th MAYTheLuckS; ラッキー矢印No ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Question Bank Level - 1, 2, 3Document16 pagesMiscellaneous Question Bank Level - 1, 2, 3Jee AspirantNo ratings yet
- W ID8 OL0 EEp 7 Ejg 08 A8 GJDocument3 pagesW ID8 OL0 EEp 7 Ejg 08 A8 GJROHIT ARYANo ratings yet
- 01 Assign # 01 (Circular Motion) - JEE - NURTURE-SCDocument11 pages01 Assign # 01 (Circular Motion) - JEE - NURTURE-SCPiyush PandaNo ratings yet
- 2018-06-05Document27 pages2018-06-05XxyyzzNo ratings yet
- Transformations Work SheetDocument12 pagesTransformations Work SheetPrithvi Viraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- SECTION-I (Single Choice Questions)Document6 pagesSECTION-I (Single Choice Questions)Bhawna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics+Exercise 5 (A)Document5 pagesElectrostatics+Exercise 5 (A)Sumit RajNo ratings yet
- Physics Rotational Motion MCQDocument7 pagesPhysics Rotational Motion MCQAyan Ghosh100% (1)
- Section A Answer Two Questions From This SectionDocument6 pagesSection A Answer Two Questions From This SectionFranklyn kipkuruiNo ratings yet
- Physics Rotational Motion MCQDocument7 pagesPhysics Rotational Motion MCQrkjha70867% (3)
- Assignment On Rigid Body KinematicsDocument4 pagesAssignment On Rigid Body KinematicsKaveesh KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document48 pagesChapter 6Hafizszul FeyzulNo ratings yet
- Uniform Circular Motion Practice Qs With AnswersDocument17 pagesUniform Circular Motion Practice Qs With AnswersLawrence Lim Ah KowNo ratings yet
- Circle Motion, Center of MassDocument6 pagesCircle Motion, Center of MassYUKTESH YuBoNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee JEE (Mains) : Important InstructionsDocument15 pagesFiitjee JEE (Mains) : Important InstructionsYuvi BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Coordinate System TransformationDocument18 pagesCoordinate System TransformationVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesNo ratings yet
- Use of Calculators Is Not Allowed (G 10Nkg) : V S S SDocument9 pagesUse of Calculators Is Not Allowed (G 10Nkg) : V S S SadikaviNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Analysis of LinkagesDocument38 pagesAcceleration Analysis of LinkagesHaile SimachewNo ratings yet
- Race 1 1686742220Document3 pagesRace 1 1686742220xenonverd321No ratings yet
- Motion in Two and Three Dimension IIDocument14 pagesMotion in Two and Three Dimension IISuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Circular MotionDocument6 pagesPhysics Circular MotionNethra SasikumarNo ratings yet
- All India Test Series: FiitjeeDocument19 pagesAll India Test Series: FiitjeeVarri Demudu BabuNo ratings yet
- @bohring Bot × @JEE Tests 06 GR Rolling Dynamics, Angular MomentumDocument8 pages@bohring Bot × @JEE Tests 06 GR Rolling Dynamics, Angular Momentumrandomwork013No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Circular Motion - EQDocument2 pagesChapter 7 Circular Motion - EQelty TanNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 QuizDocument8 pagesTopic 6 Quizlim18187No ratings yet
- Watch and Clock Escapements A Complete Study in Theory and Practice of the Lever, Cylinder and Chronometer Escapements, Together with a Brief Account of the Origin and Evolution of the Escapement in HorologyFrom EverandWatch and Clock Escapements A Complete Study in Theory and Practice of the Lever, Cylinder and Chronometer Escapements, Together with a Brief Account of the Origin and Evolution of the Escapement in HorologyNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of the Rigid Solid with General Constraints by a Multibody ApproachFrom EverandDynamics of the Rigid Solid with General Constraints by a Multibody ApproachNo ratings yet
- Multilinear Functions Of Direction And Their Uses In Differential GeometryFrom EverandMultilinear Functions Of Direction And Their Uses In Differential GeometryNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Differential Geometry and Saddle Synthesis of LinkagesFrom EverandKinematic Differential Geometry and Saddle Synthesis of LinkagesNo ratings yet
- CsprojDocument19 pagesCsprojarqam SaadNo ratings yet
- ManagementsysDocument19 pagesManagementsysarqam SaadNo ratings yet
- Vectors 5Document110 pagesVectors 5arqam SaadNo ratings yet
- Lorentz ForceDocument2 pagesLorentz Forcearqam SaadNo ratings yet
- 0910 SQ AnswersDocument7 pages0910 SQ AnswersPaul BurgessNo ratings yet
- Angeles J Shaoping Bai Kinematics of Mechanical Systems FundDocument342 pagesAngeles J Shaoping Bai Kinematics of Mechanical Systems FundStrahinja DonicNo ratings yet
- Missile 6DOF EquationDocument2 pagesMissile 6DOF EquationyhyogaswaraNo ratings yet
- Inersia and Free FallDocument16 pagesInersia and Free Fallharirie 07No ratings yet
- Final Exam Mec420 Jan 2018 - s1 - AnswerDocument14 pagesFinal Exam Mec420 Jan 2018 - s1 - AnswerIrfan SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Ap Physics C Exam Review 1Document3 pagesAp Physics C Exam Review 1sudhakaralla1100% (1)
- Chapter 6 AnswDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Answsalama alkaabiNo ratings yet
- Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Lect-10Document32 pagesCh-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Lect-10Kishan KumarNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument21 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumTerry Gabriel SignoNo ratings yet
- Theme: Newtonian Mechanics Chapter 3: GravitationDocument11 pagesTheme: Newtonian Mechanics Chapter 3: GravitationvelavanNo ratings yet
- A Tutorial To Inertial Navigation: Yuanxin WuDocument68 pagesA Tutorial To Inertial Navigation: Yuanxin WuNicoli LourençoNo ratings yet
- Science PDF (Module 1)Document19 pagesScience PDF (Module 1)Jean PernitoNo ratings yet
- Math Modelling of Missile For Control TheoryDocument8 pagesMath Modelling of Missile For Control TheoryD.ViswanathNo ratings yet
- 3.7 - Forces Movement Shape and Momentum 2p - Edexcel Igcse Physics QPDocument12 pages3.7 - Forces Movement Shape and Momentum 2p - Edexcel Igcse Physics QPKate BlossomNo ratings yet
- Ultra-Precise Optical CMM: Micro-And Nanometre Resolution For Manufacturing and R&DDocument8 pagesUltra-Precise Optical CMM: Micro-And Nanometre Resolution For Manufacturing and R&Dyarzar17No ratings yet
- Amusement ParkDocument10 pagesAmusement ParkTomasLiefferingNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Prashanna YadavNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Unit - 6Document15 pagesFluid Mechanics Unit - 6Prem T RajuNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Golf RangeDocument6 pagesStudent Exploration: Golf RangeNicholas chinNo ratings yet
- 50 Marks Class Xi Question PaperDocument8 pages50 Marks Class Xi Question PaperTapas Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 PDFDocument12 pagesLecture1 PDFFredrick AwuduNo ratings yet
- Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das Luo Solution ManualDocument40 pagesPrinciples of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das Luo Solution Manualalfred100% (31)
- Cornell Notes For Types of WavesDocument11 pagesCornell Notes For Types of Wavesapi-313808182No ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument5 pagesPHYSICSDaniel GtsadkanNo ratings yet
- Bell 1980Document12 pagesBell 1980Jose Laginha PalmaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank All Units With VTU Old Questions With Front PageDocument11 pagesQuestion Bank All Units With VTU Old Questions With Front PageHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (2) : Dr. Ali Mahmoud Ali Attia ME 413Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics (2) : Dr. Ali Mahmoud Ali Attia ME 413محمد عليNo ratings yet
- The Thorny Way of Truth Part6 MarinovDocument332 pagesThe Thorny Way of Truth Part6 MarinovEvaldas StankeviciusNo ratings yet