Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phychem Lab Assignment - R104 R105
Phychem Lab Assignment - R104 R105
Uploaded by
vegamaharajfaith02Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Phychem Lab Assignment - R104 R105
Phychem Lab Assignment - R104 R105
Uploaded by
vegamaharajfaith02Copyright:
Available Formats
CHEM 150.
1 (LAB)
ASSIGNMENT
Name: ___________________________ Score: _____________
Date: _______________
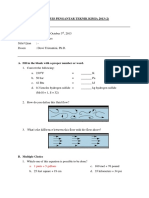
I. Definition of terms. Describe briefly. (3 pts/item)
1. What is calorimetry? Show equations that are involve in this process?
2. What is partition coefficient or the Nernst distribution law? Show an equation.
3. What is Gibb’s phase rule?
4. What are the colligative properties? Give examples and show the equations involve.
II. Calculations: Show your complete solution on a separate sheet of bond paper. Box your final answer. (3 pts/item)
1. 2.00 g R was shaken with a mixture of 100 mL hexane and 50 mL water. At equilibrium the water layer was found
to contain 0.400 g R. Calculate the partition coefficient of R between hexane and water. 2.00
2. A solution of P in water was shaken with some benzene, and the concentrations of P in both solvents were
measured. The concentration of P in water was 0.00100 mol/mL and its concentration in benzene was found to be
0.0200 mol/mL. Calculate the partition coefficient for P between benzene and water. 20.0
3. A mixture of gases contains 4.46 moles of neon (Ne), 0.74 mole of argon (Ar), and 2.15 moles of xenon (Xe).
Calculate the partial pressures of the gases if the total pressure is 2.00 atm at a certain temperature.
P(Ne) = 1.21 atm, P(Ar) = 0.20 atm, P(Xe) = 0.586 atm
4. Consider the three gas containers shown here. All of them have the same volume and are at the same temperature.
(a) Which container has the smallest mole fraction of gas A (blue sphere)? (b) Which container has the highest
partial pressure of gas B (green sphere)? A (iii), B (iii)
5. Calculate the vapor pressure of a solution made by dissolving 218 g of glucose (molar mass = 180.2 g/mol) in 460
mL of water at 30°C. What is the vapor-pressure lowering? The vapor pressure of pure water at 30°C is 31.82 mmHg.
Assume the density of the solution is 1.00 g/mL. P (glucose) = 30.4 mmHg; lowering = 1.4 mmHg
6. Ethylene glycol (EG), CH2(OH)CH2(OH), is a common automobile antifreeze. It is water soluble and fairly nonvolatile.
Calculate the freezing point and boiling point of a solution containing 651 g of this substance in 2505 g of water.
The molar mass of ethylene glycol is 62.01 g/mol. (Kf (water) = 1.86°C/m; Kb (water) = 0.52°C/m)
-7.79°C
102.2°C
You might also like
- Kinsley David R Tantric Visions of The Divine Feminine 330p PDFDocument330 pagesKinsley David R Tantric Visions of The Divine Feminine 330p PDFvoiddoor94% (18)
- Problem 1.1ADocument23 pagesProblem 1.1AJohnathan Ortega MenesesNo ratings yet
- Clamped, Square Isotropic Plate With A Uniform Pressure LoadDocument3 pagesClamped, Square Isotropic Plate With A Uniform Pressure LoadLucas MartinsNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document2 pagesQuiz 2JNo ratings yet
- Determination of Molar Mass by Boiling Point Elevetion BA Jan - 1Document5 pagesDetermination of Molar Mass by Boiling Point Elevetion BA Jan - 1Melvin Cubilla100% (1)
- Class 12 (Solution Chapter) HSC PYQsDocument2 pagesClass 12 (Solution Chapter) HSC PYQspriyanka deshmukhNo ratings yet
- ANALYTICAL CHEM LEC 3 - Unit 2, Chapter 2 (Sample Problems)Document3 pagesANALYTICAL CHEM LEC 3 - Unit 2, Chapter 2 (Sample Problems)ARRIANE CYREL CAMACHONo ratings yet
- 48 Practice Problems For CH 17Document9 pages48 Practice Problems For CH 17Hasantha PereraNo ratings yet
- Himmeblau Chp1 (WWW - Myuet.net - TC)Document23 pagesHimmeblau Chp1 (WWW - Myuet.net - TC)redj288No ratings yet
- 練習單3 1Document11 pages練習單3 1Lin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Solutions Class 12th Practice Paper 1Document6 pagesSolutions Class 12th Practice Paper 1Liyutsa ZirangeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document5 pagesChapter 7Earl averzosaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bab Campuran SederhanaDocument2 pagesTugas Bab Campuran SederhanaMichael Lesa0% (2)
- Experiment 2 (Freezing Point Depression)Document10 pagesExperiment 2 (Freezing Point Depression)dewirizhNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual CHM213 - 2022Document20 pagesLab Manual CHM213 - 2022NUR SABRINA MOHD SHAHNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Chemical Measurements: Topic OutlineDocument20 pagesUnit 2: Chemical Measurements: Topic OutlineJherby TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Chemistry I Final Exam Study GuideDocument12 pagesChemistry I Final Exam Study Guidejeek ekekNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document12 pagesLecture 3Supriya KadamNo ratings yet
- Experiment 17 Colligative PropertiesDocument4 pagesExperiment 17 Colligative PropertiesLILYNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 Phase EquilibriumDocument3 pagesTutorial 5 Phase EquilibriumezanaNo ratings yet
- Chap 12-13Document5 pagesChap 12-13noviNo ratings yet
- Previous HSE Questions From The Chapter "SOLUTIONS": A B TotalDocument2 pagesPrevious HSE Questions From The Chapter "SOLUTIONS": A B TotalChemistry MESNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Review On Basic Principles Applied in Analytical ChemistryDocument14 pagesUnit 4 - Review On Basic Principles Applied in Analytical Chemistryariel egonNo ratings yet
- Principal CH 1.3Document11 pagesPrincipal CH 1.3Zyxw VutNo ratings yet
- Soal Kuis Pengantar Teknik Kimia 2013Document4 pagesSoal Kuis Pengantar Teknik Kimia 2013shawn iceNo ratings yet
- CHE121 Lec8 SP120Document52 pagesCHE121 Lec8 SP120djpsychoscientzNo ratings yet
- Solution Solved QuestionsDocument7 pagesSolution Solved QuestionsAnanya ThatyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 2Document4 pagesChemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 2maxime namaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Q1 Week 7-8Document15 pagesGeneral Chemistry Q1 Week 7-8ljbenares19No ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-04 Class - 12 Chemistry (Solutions) : Decrease in PressureDocument5 pagesCbse Test Paper-04 Class - 12 Chemistry (Solutions) : Decrease in PressurePiyasa MandalNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document2 pagesHW 5msoccerdude291No ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Processand Calculation NotesDocument18 pagesChemical Engineering Processand Calculation Notesbhushansoni1No ratings yet
- CHM271 - Tutorial 6 - Phase EquilibriumDocument5 pagesCHM271 - Tutorial 6 - Phase Equilibriumfiefy zmrNo ratings yet
- Exam 4 Study GuideDocument2 pagesExam 4 Study GuideCeline KameraNo ratings yet
- Ncertsolutions. d03 May 2024Document34 pagesNcertsolutions. d03 May 2024Roll no 15No ratings yet
- Quiz 8Document5 pagesQuiz 8cikgu_aminNo ratings yet
- OtDocument12 pagesOtJoash SalamancaNo ratings yet
- Bomb CalorimeterDocument5 pagesBomb CalorimeterTahiraNo ratings yet
- (Q1) MODULE 10 - Gas Stoichiometry PDFDocument18 pages(Q1) MODULE 10 - Gas Stoichiometry PDFJewel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Quantities of Reactants and Products Involved in A Chemical Reaction. It Is Based On TheDocument5 pagesQuantities of Reactants and Products Involved in A Chemical Reaction. It Is Based On TheArdia Regita HirayantiNo ratings yet
- Class 12th For Board ExamDocument5 pagesClass 12th For Board Examakashsadoriya5477No ratings yet
- CalculationsDocument7 pagesCalculationsAlimjan AblaNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Review 2013Document14 pagesCH 13 Review 2013FariaFaruqChoaNo ratings yet
- Solution: Chapter 9: Chemical Equilibrium Review QuestionsDocument47 pagesSolution: Chapter 9: Chemical Equilibrium Review QuestionsSanjhi JainNo ratings yet
- Chap1-6,9 QB 12th STDDocument7 pagesChap1-6,9 QB 12th STDnikhil2002yadav17No ratings yet
- GAAN Lab Procedure Final-2010Document4 pagesGAAN Lab Procedure Final-2010subramaniyam.ek28210% (1)
- Hsslive-XII-Chemistry-QB-ch-2. Solutions-SignedDocument3 pagesHsslive-XII-Chemistry-QB-ch-2. Solutions-SignedkdramabiasNo ratings yet
- LQ1 Checal Pet EngDocument1 pageLQ1 Checal Pet EngRugi Vicente RubiNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XII Chem QN Bank 2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesHsslive XII Chem QN Bank 2 SolutionsZaibunisa MehaboobNo ratings yet
- CHM 471 Tutorial 3 Phase DiagramDocument4 pagesCHM 471 Tutorial 3 Phase DiagramCharlesRolendNo ratings yet
- AP Chapter 11 - SolutionsDocument6 pagesAP Chapter 11 - SolutionspearlynpuayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document4 pagesChapter 13Poonam CheemaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 GAS STOICHIOMETRYDocument4 pagesModule 7 GAS STOICHIOMETRYAnn DayritNo ratings yet
- Learning Material 5: General Chemistry 2 PLM For April 5-9,2021Document6 pagesLearning Material 5: General Chemistry 2 PLM For April 5-9,2021Justeny TabbayNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry Questions CorrectedDocument2 pagesCalorimetry Questions CorrectedMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- Physic Pharmacy Module 2 - PrelimDocument7 pagesPhysic Pharmacy Module 2 - PrelimRegine PeñarandaNo ratings yet
- 8.1HW Colligative Properties-SolDocument5 pages8.1HW Colligative Properties-SolabcdNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Review On Basic Principles Applied in Analytical ChemistryDocument12 pagesUnit 4 - Review On Basic Principles Applied in Analytical ChemistryJayson PolinarNo ratings yet
- A. Multiple ChoiceDocument8 pagesA. Multiple ChoicenerosituNo ratings yet
- Selected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionFrom EverandSelected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionNo ratings yet
- Live Pig MarketsDocument25 pagesLive Pig MarketsKoffee FarmerNo ratings yet
- Stopping and Positioning Modules For Automation Technology: Product Overview - 2018 /19Document19 pagesStopping and Positioning Modules For Automation Technology: Product Overview - 2018 /19Siddiqui SarfarazNo ratings yet
- 22 - Relative Permeability Effects On The Miscible CO2 WAG Injection SchemesDocument9 pages22 - Relative Permeability Effects On The Miscible CO2 WAG Injection SchemesheviNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument4 pagesGestational Trophoblastic DiseasePrincess PlateroNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument23 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectManikandan s100% (1)
- Cambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International EducationDocument7 pagesCambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International Educationigloo79No ratings yet
- Contoh Praktis Menggunakan EVIEWSDocument46 pagesContoh Praktis Menggunakan EVIEWSDidi JunaediNo ratings yet
- AP II Assignment 1Document2 pagesAP II Assignment 1manan khndlwlNo ratings yet
- Pioneer WoodlandsDocument38 pagesPioneer Woodlandsapi-249262419No ratings yet
- Introduction To Histology: Preparation of Tissue For Histology Dr. OkoloDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Histology: Preparation of Tissue For Histology Dr. OkoloAbiola NerdNo ratings yet
- Good and Evil of Moby Dick and Captain AhabDocument4 pagesGood and Evil of Moby Dick and Captain AhabCismaru ElenaNo ratings yet
- Probability and Measurement UncertaintyDocument99 pagesProbability and Measurement UncertaintypticicaaaNo ratings yet
- Buyers Guide For MDUDocument18 pagesBuyers Guide For MDUjatinrastogi28No ratings yet
- DP086LA: Doosan Infracore Generator EngineDocument4 pagesDP086LA: Doosan Infracore Generator EnginehirararaNo ratings yet
- Kings Meadows Public ToiletDocument16 pagesKings Meadows Public ToiletThe ExaminerNo ratings yet
- Smart System For Potholes Detection Using Computer Vision With Transfer LearningDocument9 pagesSmart System For Potholes Detection Using Computer Vision With Transfer LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Resource Pack - Science - Year 1 - Human Body and SensesDocument19 pagesResource Pack - Science - Year 1 - Human Body and Sensesnur fazlynaNo ratings yet
- BSC 116 SyllabusDocument8 pagesBSC 116 SyllabussahanchemNo ratings yet
- 86 Iron and Steel Industry Final Report 29may12 VFDocument212 pages86 Iron and Steel Industry Final Report 29may12 VFAnonymous jLZ2f5tB100% (2)
- Get Art Sex Music Cosey Fanni Tutti pdf full chapterDocument24 pagesGet Art Sex Music Cosey Fanni Tutti pdf full chapterrajaifrenk100% (5)
- Mock Test 1 (Q.e.)Document3 pagesMock Test 1 (Q.e.)Mehul PatilNo ratings yet
- Stem 2c-Music On Plant Growth FinalDocument91 pagesStem 2c-Music On Plant Growth FinalYonaNo ratings yet
- Net Ionic Equations-ProblemsDocument3 pagesNet Ionic Equations-ProblemsChikuta ShingaliliNo ratings yet
- Half Value Layer CalculationsDocument52 pagesHalf Value Layer Calculationsshabbir62675% (4)
- StepanFormulation196 PDFDocument1 pageStepanFormulation196 PDFdedeteNo ratings yet
- QUINTA DE PACOS PresentationDocument2 pagesQUINTA DE PACOS PresentationBeatrice ŞtefaniaNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology Statistics Summary Test Formula Use Degrees of Freedom Accept/reject Null Hypothesis Extra InformationDocument12 pagesA Level Biology Statistics Summary Test Formula Use Degrees of Freedom Accept/reject Null Hypothesis Extra InformationmohammedNo ratings yet