Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 6
Assignment 6
Uploaded by
tokaselim780 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesThe document discusses the relationship between price elasticity of demand and total revenue through examples and graphs. It defines price elasticity of supply as the percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price. It also explains that when a gas tax is implemented, consumers bear most of the burden as the retail price increases, while suppliers receive a small fraction, because demand for gas is relatively price inelastic, whereas supply is relatively price elastic.
Original Description:
,dcvdddfvbbcsdbbccvn
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the relationship between price elasticity of demand and total revenue through examples and graphs. It defines price elasticity of supply as the percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price. It also explains that when a gas tax is implemented, consumers bear most of the burden as the retail price increases, while suppliers receive a small fraction, because demand for gas is relatively price inelastic, whereas supply is relatively price elastic.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesAssignment 6
Assignment 6
Uploaded by
tokaselim78The document discusses the relationship between price elasticity of demand and total revenue through examples and graphs. It defines price elasticity of supply as the percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price. It also explains that when a gas tax is implemented, consumers bear most of the burden as the retail price increases, while suppliers receive a small fraction, because demand for gas is relatively price inelastic, whereas supply is relatively price elastic.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Assignment 6
Dalia Mohamed sayed
Group 1
Q1: Explain with graph the relationship between price elasticity of demand and revenue?
1- When demand is price-inelastic, a price decrease reduces total revenue.
2- When demand is price-elastic, a price decrease increases total revenue.
3- in the case of unit-elastic demand, a price decrease leads to no change in total revenue.
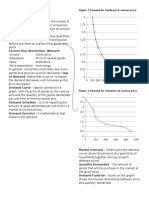
Total revenue is the product of price times quantity, P*Q. further, the area of a rectangle is
always equal to the product of its base times its height. Therefore, total revenue at any point on a
demand curve can be found by examining the area of the rectangle determined by the P and Q at
that point
• The relationship between elasticity and revenue for the unit-elastic case in Figure 4-2(b). Note
that the shaded revenue region (P*Q) is $1000 million for both point A and B. The shaded areas
representing total revenue are the same because of offsetting changes in the Q base and the P
height.
• that Figure 4-2(a) corresponds to elastic demand. In this figure, the revenue rectangle expands
from $1000 million to $1500 million when price is halved. Since total revenue goes up when price
is cut, demand is elastic.
• In Figure 4-2(c ) the revenue rectangle falls from $40 million to $30 million when price is
halved, so demand is inelastic.
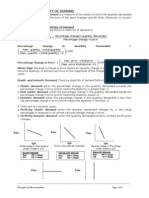
Q2: define the price elasticity of supply?
• The Price Elasticity of Supply is the percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the
percentage change in price.
• The exact definition of the Price Elasticity of Supply , is as follows:
ES = Percentage change in quantitySupplied
Percentage change inPrice
Q3: Who pays the Tax? (Use the Gasoline example)
• The demand curve does not shift because the quantity demanded at each retail price is
unchanged by the gasoline-tax increase. Note that the demand curve for gasoline is relatively
inelastic.
• the oil industry pays a small fraction, for it receives only $1.80 rather than $2. But the
consumer bears most of the burden, with the retail price rising $1.80, because supply is relatively
price-elastic whereas demand is relatively price-inelastic
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Microeconomics 5th Edition by David BesankoDocument26 pagesSolution Manual For Microeconomics 5th Edition by David BesankomohsinwazirNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6-1Document3 pagesAssignment 6-1tokaselim78No ratings yet
- Mikroekonomi Untuk Kebijakan - Permintaan Dan PenawaranDocument28 pagesMikroekonomi Untuk Kebijakan - Permintaan Dan PenawaranCyntia DelfianNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics CompleteDocument18 pagesManagerial Economics CompleteAmlan BhowmikNo ratings yet
- 1 - Basic Supply DemandDocument28 pages1 - Basic Supply DemandYohanes AnggoroNo ratings yet
- Problems PDFDocument92 pagesProblems PDFghalia0% (1)
- HomeworkDocument3 pagesHomeworkXanalarmaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity and ApplicationsDocument8 pagesElasticity and ApplicationsshubhamNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and Supply Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesElasticity of Demand and Supply Lecture NotesNastya CurcubetNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignmentAmara JavaidNo ratings yet
- Applying The Supply-and-Demand Model: Answers To Textbook QuestionsDocument7 pagesApplying The Supply-and-Demand Model: Answers To Textbook Questions蔡杰翰No ratings yet
- Economics Grade 11 Revision Term 2 - 2024Document11 pagesEconomics Grade 11 Revision Term 2 - 2024nombusoz608No ratings yet
- Lecture 09 Engineering Economics MN 30-Jan-2024Document25 pagesLecture 09 Engineering Economics MN 30-Jan-2024Sai PriyaNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument14 pagesElasticitysidlbsimNo ratings yet
- Chapter5-Supply and Demand in Individual MarketDocument56 pagesChapter5-Supply and Demand in Individual MarketTony MontaanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Demand & Supply PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment 2 Demand & Supply PDFhemantNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Topic 5Document65 pagesManagerial Economics Topic 5Anish Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Chap 04 Supply and Demand Elasticity and ApplicationsDocument25 pagesChap 04 Supply and Demand Elasticity and ApplicationsZain MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Micro Tutorial Seminar 2 Answer GuideDocument3 pagesMicro Tutorial Seminar 2 Answer GuideHashma KhanNo ratings yet
- Exercises ElasticityDocument4 pagesExercises ElasticityAA BB MMNo ratings yet
- Ch03 - Demand and Supply - Part 2Document35 pagesCh03 - Demand and Supply - Part 2Robert AxelssonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document29 pagesChapter 8Tafirenyika SundeNo ratings yet
- AssignmentNO2 (Fa22 Rba 001)Document9 pagesAssignmentNO2 (Fa22 Rba 001)Taskeen ZafarNo ratings yet
- WKSHTDocument8 pagesWKSHTjohnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Topics in Demand and Supply Analysis - HandoutsDocument15 pagesModule 1 - Topics in Demand and Supply Analysis - HandoutsAyman Al HakimNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Topic 3 Elasticity of DemandDocument65 pagesManagerial Economics Topic 3 Elasticity of Demandyaminis.0223No ratings yet
- Assignment ECON 260Document13 pagesAssignment ECON 260Mohammed AwadNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Elasticity and Its Application - FR - 2023Document54 pagesWeek 3 - Elasticity and Its Application - FR - 2023A.A FajriNo ratings yet
- Econ 24 CH1 To CH3Document18 pagesEcon 24 CH1 To CH3Muyano, Mira Joy M.No ratings yet
- The Demand Curve: That Consumers Are Willing To Buy and The Price of The GoodDocument49 pagesThe Demand Curve: That Consumers Are Willing To Buy and The Price of The GoodBiz E-ComNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand PDFDocument35 pagesElasticity of Demand PDFSona Chalasani100% (2)
- Elasticity of DemandDocument34 pagesElasticity of DemandAGRAWAL UTKARSHNo ratings yet
- Me 4pptDocument55 pagesMe 4pptarchana_anuragiNo ratings yet
- UNIT-II BEFA Notes.Document13 pagesUNIT-II BEFA Notes.N. RAMANA REDDYNo ratings yet
- Chap 011 NotesDocument10 pagesChap 011 Notesfree50No ratings yet
- Worked Solutions 3Document7 pagesWorked Solutions 3Zahied MukaddamNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Elasticity of Demand: Elasticity of Demand Can Be Defined As The Degree of Responsiveness of QuantityDocument6 pagesUNIT-2 Elasticity of Demand: Elasticity of Demand Can Be Defined As The Degree of Responsiveness of Quantityarzun666No ratings yet
- Figure 1 Demand For Pandesal at Various PriceDocument7 pagesFigure 1 Demand For Pandesal at Various PriceCaptain BleueNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand: Perfect Elasticity or Infinite ElasticityDocument10 pagesElasticity of Demand: Perfect Elasticity or Infinite ElasticitySeakh Mohammad ShihabNo ratings yet
- Ome Merged PDFDocument311 pagesOme Merged PDFNavya MohankaNo ratings yet
- OME - 01 - Introduction To MarketDocument30 pagesOME - 01 - Introduction To MarketAkshay PNo ratings yet
- Elasticity and Its ApplicationsDocument52 pagesElasticity and Its ApplicationsNikita SarangpuriyaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument25 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplyPrabin KhanalNo ratings yet
- DIHE - Notes.elasticiy of DemandDocument5 pagesDIHE - Notes.elasticiy of DemandjavedhanifNo ratings yet
- Basic Microeconomics: Chapter 3: Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument12 pagesBasic Microeconomics: Chapter 3: Elasticity of Demand and SupplyJane Gonzaga100% (1)
- Tutorial 03 Solution 05-03-2024Document59 pagesTutorial 03 Solution 05-03-2024Aziz AyadiNo ratings yet
- ELASTICITYDocument5 pagesELASTICITYRaymark Raymundo MejiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: (Elasticity and Its Application) Section ADocument7 pagesChapter 5: (Elasticity and Its Application) Section APhạm Huy100% (1)
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument9 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplyAlex HongoNo ratings yet
- Income Elasticity of Demand: InterpretationDocument10 pagesIncome Elasticity of Demand: Interpretationabhijeet9981No ratings yet
- Producer's Equilibrium: Total Revenue & Total Cost ApproachDocument12 pagesProducer's Equilibrium: Total Revenue & Total Cost ApproachSarim KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - AD-AS - DiplomaDocument52 pagesChapter 3 - AD-AS - DiplomaBenny TanNo ratings yet
- ECO WORKSHEETS (Stats - 8 QS) : Q1) Distinguish BTW Short Run and Long RunDocument8 pagesECO WORKSHEETS (Stats - 8 QS) : Q1) Distinguish BTW Short Run and Long RunmickeyNo ratings yet
- CH. 3 Applications of Supply and DemandDocument26 pagesCH. 3 Applications of Supply and Demandsamah.fathi3No ratings yet
- Ch03 ElasticityDocument6 pagesCh03 Elasticitycarlhoorn91No ratings yet
- B 7006 Part 1 - Intro & Demand & SupplyDocument70 pagesB 7006 Part 1 - Intro & Demand & SupplySanjay DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Lec-4 (Elasticity)Document44 pagesLec-4 (Elasticity)MD Shamim HOSSAINNo ratings yet
- Economics: Chapter 2 .Managerial Economics & Business StrategyDocument20 pagesEconomics: Chapter 2 .Managerial Economics & Business StrategySwathy SidharthanNo ratings yet
- Econ 2003 Chapter 5Document24 pagesEcon 2003 Chapter 5ali meselelliNo ratings yet