Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Polymers Notes
Chemistry Polymers Notes
Uploaded by
kainaattufail1110 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesPolymers are formed through addition polymerization or condensation polymerization. Addition polymerization requires one monomer and produces only polymer, while condensation polymerization requires two monomers and produces water as a byproduct. Both polymerization reactions require an initiator to start the reaction. Common natural polymers include DNA, RNA, wool, fibers and starch. The six most important synthetic polymers are polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene, polytetrafluoroethylene, polyethylene terephthalate, and nylon 6,6. Each has different monomer units, properties and common uses.
Original Description:
Original Title
CHEMISTRY POLYMERS NOTES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPolymers are formed through addition polymerization or condensation polymerization. Addition polymerization requires one monomer and produces only polymer, while condensation polymerization requires two monomers and produces water as a byproduct. Both polymerization reactions require an initiator to start the reaction. Common natural polymers include DNA, RNA, wool, fibers and starch. The six most important synthetic polymers are polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene, polytetrafluoroethylene, polyethylene terephthalate, and nylon 6,6. Each has different monomer units, properties and common uses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesChemistry Polymers Notes
Chemistry Polymers Notes
Uploaded by
kainaattufail111Polymers are formed through addition polymerization or condensation polymerization. Addition polymerization requires one monomer and produces only polymer, while condensation polymerization requires two monomers and produces water as a byproduct. Both polymerization reactions require an initiator to start the reaction. Common natural polymers include DNA, RNA, wool, fibers and starch. The six most important synthetic polymers are polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene, polytetrafluoroethylene, polyethylene terephthalate, and nylon 6,6. Each has different monomer units, properties and common uses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
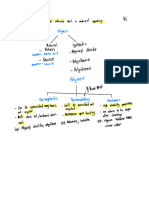
Polymers – the big 6 required for the HSC
Addition polymerisation results in no other product other
than the addition polymer and requires only one monomer.
Condensation polymerisation requires two monomers and
also produces water.
Both require a radical initiator to start the reaction.
Chemical or thermal cracking is used to create monomers.
Natural polymers include: DNA, RNA, wool, fibres and
starch.
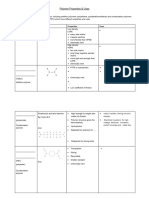
Monomer Polymer Common names Systematic names Properties Uses
Ethylene Ethene Flexible LDPE:
Polyethylene Polyethene Hydrophobic Plastic
Soft bags
Thermoplastic Water
Inert bottles
HDPE:
Buckets
Cutting
boards
Vinyl Chloride Chloroethene Thermoplastic Piping
Polyvinylchloride Polychloroethene Very hard Gutters
Rigid Credit
Brittle cards
Flame Raincoats
retardant Electrical
Resistant to insulation
chemical
corrosion
Styrene Ethylbenzene Higher Plastic
polystyrene Polyethylbenezene softening wine
point of 94 glasses
degrees Flotation
Stiff devices
Brittle Shock
Transparent absorbent
Can be packaging
expanded to Coffee
form cups
styrofoam
Tetraflouroethylene Tetraflouroethene Hard Non-stick
Polytetraflouroethylene Polytetraflouroethene Rigid coating for
High melting pans
point Anti
High corrosion
chemical container,
resistance pipe and
Low medical
coefficient of equipment
friction coatings
Ethylene glycol and Ethane-1,2-diol and Thermoplastic Fabric for
terephthalic acid benzene-1,4- High strength clothes,
dicarboxylic acid Stiff carpets,
Semi-rigid to furniture
Polyethylene
rigid and
terephthalate Poly(ethyl benezene- Resistant to blankets
1,4-dicarboxylic impact
acid) Lightweight Recyclable
drink
bottles and
food
packaging.
1,6-diaminohexane and Hexane-1,6-diaamine Thermoplastic Seat belts
adipic acid and hexanoic Acid High melting Rope
point Fishing
Strong line
Nylon 6,6 Poly(imino(1,6-
dixohexamethylene) High tensile Mechanical
iminohexamethylene) strength parts.
elastic
You might also like
- Comparison Between Dry Lamination and Extrusion LaminationDocument26 pagesComparison Between Dry Lamination and Extrusion LaminationRicardo PratiwiharjaNo ratings yet
- GM Passlock II SystemDocument14 pagesGM Passlock II Systemalmia tronicsNo ratings yet
- Ergonomic Interventions For Electricians in Fossil-Fueled Power PlantsDocument48 pagesErgonomic Interventions For Electricians in Fossil-Fueled Power PlantsSushayan HunsasukNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture Question BankDocument16 pagesComputer Architecture Question BankGreenkings100% (1)
- Listing of Important CompoundsDocument5 pagesListing of Important CompoundsGLUSITANIO, DIANA YSABELA JOHANA T.No ratings yet
- Materials - PlasticsDocument20 pagesMaterials - PlasticsHafizh PrashantyoNo ratings yet
- SUEZ ANZ Plastics Identification CodeDocument1 pageSUEZ ANZ Plastics Identification Codesurya saputraNo ratings yet
- Common Types of PlasticsDocument8 pagesCommon Types of PlasticsAnis SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Types Plastic Properties ApplicationsDocument1 pagePlastic Types Plastic Properties ApplicationsWaad MajidNo ratings yet
- High Density Polyethylene (Hdpe)Document38 pagesHigh Density Polyethylene (Hdpe)Goutam AbbadNo ratings yet
- Plastics TecnoDocument4 pagesPlastics TecnoJuan Andres NavasNo ratings yet
- PolyethyleneDocument31 pagesPolyethyleneHesham chemecology100% (1)
- Expt. No. 7 Plastics and PolymersDocument8 pagesExpt. No. 7 Plastics and PolymersJan Divrec CaballesNo ratings yet
- Resin Identification CodeDocument21 pagesResin Identification CodepraveenNo ratings yet
- Process Calculations BookDocument3 pagesProcess Calculations BookAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Ficha 1Document1 pageFicha 1pamontes11No ratings yet
- Polymer Mind MapDocument4 pagesPolymer Mind Mapzahida0515No ratings yet
- PolymersDocument3 pagesPolymersGrace leongNo ratings yet
- PlasticsDocument8 pagesPlasticsmogakolodi MotingwaNo ratings yet
- Polymer NoteDocument5 pagesPolymer NoteYen Jie WongNo ratings yet
- Exxonmobil High Density Polyethylene Product Guide: Europe Asia Pacific Middle East Africa AmericasDocument6 pagesExxonmobil High Density Polyethylene Product Guide: Europe Asia Pacific Middle East Africa AmericasvenkithankamNo ratings yet
- Polymers and Properties WorksheetDocument4 pagesPolymers and Properties WorksheetRaghav GanaNo ratings yet
- Polymer Energy System IndiaDocument2 pagesPolymer Energy System IndiaAshok AndresNo ratings yet
- Polyethylene (PE) - Properties, Uses & ApplicationDocument19 pagesPolyethylene (PE) - Properties, Uses & ApplicationMagamba MirandaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Identification Code With Recycled ProductsDocument12 pagesPlastic Identification Code With Recycled ProductsLvlNo ratings yet
- Thermo Softening Plastics and Thermo Setting PlasticsDocument1 pageThermo Softening Plastics and Thermo Setting Plasticsharyati yudiNo ratings yet
- Oil Refinery ProcessesDocument54 pagesOil Refinery ProcessesAndrie MaulanaNo ratings yet
- The Joy of RubberDocument34 pagesThe Joy of Rubbercmmswim67No ratings yet
- Adhesives and SealantsDocument21 pagesAdhesives and SealantsBPrakashNo ratings yet
- Plastic Identification CodesDocument1 pagePlastic Identification CodesMuhammad Adnan HafeezNo ratings yet
- Technological, Environmental and Policy Issues in The Chemical & Petrochemical Industry Sector With Particular Emphasis On SmesDocument84 pagesTechnological, Environmental and Policy Issues in The Chemical & Petrochemical Industry Sector With Particular Emphasis On Smesniraj nairNo ratings yet
- Plastic Properties of High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) : Quote RequestDocument1 pagePlastic Properties of High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) : Quote RequestVENKATESAN JNo ratings yet
- All PlasticsDocument11 pagesAll PlasticsSaNam KhanNo ratings yet
- Polyolefins 170917074212 PDFDocument26 pagesPolyolefins 170917074212 PDFTrinh Đình VũNo ratings yet
- Polymers OEDocument36 pagesPolymers OEBikash MahasethNo ratings yet
- Plastic Polymers CompleteDocument57 pagesPlastic Polymers CompleteMaria OzaoNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument4 pagesPolymersLydiaRHNo ratings yet
- List of Synthetic PolymersDocument7 pagesList of Synthetic PolymersfikaduNo ratings yet
- Polymers Polymer MONOMER (Name & Structure) Uses Addition or Chain Growth PolymerDocument2 pagesPolymers Polymer MONOMER (Name & Structure) Uses Addition or Chain Growth PolymerYash KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastic Polyesters: Polyethyleneterephthalate (PET) and Polybutyleneterephthalate (PBT)Document4 pagesThermoplastic Polyesters: Polyethyleneterephthalate (PET) and Polybutyleneterephthalate (PBT)naninoNo ratings yet
- Polimer Sintetik PlasticsDocument21 pagesPolimer Sintetik PlasticsYu QingNo ratings yet
- Block 3: Technical Use MaterialsDocument24 pagesBlock 3: Technical Use MaterialsFlorenta ManoleNo ratings yet
- Section A - Fact Files - PlasticDocument5 pagesSection A - Fact Files - PlasticSafo NewmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compatibility Guide: First Choice When Quality CountsDocument28 pagesChemical Compatibility Guide: First Choice When Quality CountsYavuz SolmazNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 RecyclingDocument37 pagesLecture 12 RecyclingelmomonsteNo ratings yet
- Science Form 5 Synthetic Materials in IndustryDocument10 pagesScience Form 5 Synthetic Materials in Industrydebbycley100% (11)
- Plastic Polymers CompleteDocument57 pagesPlastic Polymers CompleteMaria Ozao100% (1)
- PolystyreneDocument14 pagesPolystyrenemeysamNo ratings yet
- 1.3 PolymersDocument10 pages1.3 PolymersHady JawadNo ratings yet
- HDPE Product Catalouge - RevisedDocument2 pagesHDPE Product Catalouge - RevisedEfvan Adhe Putra PradanaNo ratings yet
- OWS Oil Water SeparatorDocument61 pagesOWS Oil Water Separatordiazf2004No ratings yet
- Polymer 1Document30 pagesPolymer 1MhelveneNo ratings yet
- Industrial Hose Chemical Resistance GuideDocument32 pagesIndustrial Hose Chemical Resistance Guidemat gaiatoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of PolymersDocument21 pagesChemistry of PolymersSiya SamriddhiNo ratings yet
- Polyethylene TerephthalateDocument7 pagesPolyethylene Terephthalateapi-3828258100% (1)
- PolyethyleneDocument51 pagesPolyethyleneiiphyd2403No ratings yet
- Studies of Some Thermoplastic Resins Note - DR Akinsiku PDFDocument12 pagesStudies of Some Thermoplastic Resins Note - DR Akinsiku PDFGlory Usoro100% (1)
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (Pet) : HistoryDocument3 pagesPolyethylene Terephthalate (Pet) : HistoryMaleha SalimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Wax: Wax Types and PropertiesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Wax: Wax Types and Propertiesسلوى سلمان داود سلمانNo ratings yet
- Line Bending ProcessDocument6 pagesLine Bending ProcessmonamoikoNo ratings yet
- EC Tech Report High Performance Polyurethanes: PDFFrom EverandEC Tech Report High Performance Polyurethanes: PDFVincentz Network GmbH & Co. KGNo ratings yet
- Creative Resin: Easy techniques for contemporary resin artFrom EverandCreative Resin: Easy techniques for contemporary resin artNo ratings yet
- Heavy Duty Outdoor Vitrified TilesDocument68 pagesHeavy Duty Outdoor Vitrified Tilesshaswat vermaNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Combined Operation: 1. OutlineDocument9 pagesGroup 5 Combined Operation: 1. OutlineالمهندسوليدالطويلNo ratings yet
- RE - 5 - Auto-Reclosure Function (AR5Func) : Issued: 10/1997 Version: D Data Subject To Change Without NoticeDocument35 pagesRE - 5 - Auto-Reclosure Function (AR5Func) : Issued: 10/1997 Version: D Data Subject To Change Without NoticerajeshNo ratings yet
- Non-Destructive Ageing State Determination of Solid Rocket Motors Charges423 - TussiwandDocument19 pagesNon-Destructive Ageing State Determination of Solid Rocket Motors Charges423 - Tussiwandg c agnihotriNo ratings yet
- Danish ImportantDocument14 pagesDanish ImportantDanish_Memon_68No ratings yet
- X24C44 256 Bit 16 X 16 Bit: Features DescriptionDocument16 pagesX24C44 256 Bit 16 X 16 Bit: Features DescriptionMarinaBogaoNo ratings yet
- SonophoresisDocument32 pagesSonophoresisHiren J PatelNo ratings yet
- 6-Stage Cascade ImpactorDocument10 pages6-Stage Cascade ImpactornimaaandmNo ratings yet
- Series: Wheel LoadersDocument12 pagesSeries: Wheel LoadersHandoko Dwi raharjoNo ratings yet
- DFTDocument32 pagesDFTjeevithpaul100% (1)
- Noga FlyerDocument12 pagesNoga FlyerJamie SmokieNo ratings yet
- 0819492485Document405 pages0819492485arulmurugu100% (1)
- Configuration Guide For BIG-IP Application Security ManagerDocument461 pagesConfiguration Guide For BIG-IP Application Security ManagerMANNo ratings yet
- Lab Report PTDocument20 pagesLab Report PTCruise CHNo ratings yet
- MEP - MRSA - UkDocument7 pagesMEP - MRSA - UkLuiz HenriqueNo ratings yet
- (Ted M. Knowlton, Chair) Proceedings of InternationalDocument832 pages(Ted M. Knowlton, Chair) Proceedings of InternationalAbshar ParamaNo ratings yet
- CE6015 Tall BuildingsDocument13 pagesCE6015 Tall BuildingsShan Cv0% (1)
- Android: Uni-Stroke Touch Gesture Recognition Using $1 Gesture ReconigizerDocument13 pagesAndroid: Uni-Stroke Touch Gesture Recognition Using $1 Gesture Reconigizerpi194043No ratings yet
- DC ChopperDocument63 pagesDC ChopperMalyaj SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Rockwell Analogue EncoderDocument40 pagesRockwell Analogue EncoderreinaldomdNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Drafting - Freehand Sketching: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Drafting - Freehand Sketching: Objectiveskay chikwandaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Department of Mechanical Engineering PDFDocument7 pagesStrength of Materials - Department of Mechanical Engineering PDFM.Thirunavukkarasu100% (2)
- AME OIE WhitepaperDocument34 pagesAME OIE Whitepaperanishajohins100% (2)
- The ASTM Copper Strip Corrosion Test: Application To Propane With Carbonyl Sulfide and Hydrogen SulfideDocument7 pagesThe ASTM Copper Strip Corrosion Test: Application To Propane With Carbonyl Sulfide and Hydrogen SulfideAJ ManurungNo ratings yet
- Hull Suite by InSilico and SupertrendDocument3 pagesHull Suite by InSilico and SupertrendDeni SuryadiNo ratings yet
- Powertech ™ 6135Sfm85 Diesel Engine: Marine Propulsion Engine SpecificationsDocument2 pagesPowertech ™ 6135Sfm85 Diesel Engine: Marine Propulsion Engine SpecificationspngchanhNo ratings yet