Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology Pneumonia
Pathophysiology Pneumonia
Uploaded by
Maythresha GonzalesCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Concept Mapping: Hodgskin'S Disease ComplicationDocument4 pagesConcept Mapping: Hodgskin'S Disease ComplicationAsterlyn ConiendoNo ratings yet
- Ergot and Ergotism PDFDocument2 pagesErgot and Ergotism PDFLukeNo ratings yet
- Bhat 2016Document29 pagesBhat 2016LekshmiNo ratings yet
- Specific EditedDocument12 pagesSpecific EditedLarabelle Avila CoralesNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Abscess Concept MapDocument1 pagePelvic Abscess Concept Mapaijiel talisikNo ratings yet
- IX. Nursing Care Plan: November 10, 2020Document6 pagesIX. Nursing Care Plan: November 10, 2020LNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesNeonatal Pneumonia PathophysiologyRoderick EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis: PathogenesisDocument1 pageGastrointestinal Tuberculosis: Pathogenesis알파No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Patient B's Age: 28 Years OldDocument7 pagesPathophysiology: Patient B's Age: 28 Years Oldkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of TBDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of TBEddie Lou GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDanica Fave AndiamNo ratings yet
- Plant Virus Transmission BT InsectsDocument12 pagesPlant Virus Transmission BT InsectsakshayaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map CovidDocument7 pagesConcept Map CovidMaieca Demecillo100% (3)
- Feb DTRDocument3 pagesFeb DTRFeb NamiaNo ratings yet
- Arboviruses and Other Zoonotic VirusesDocument16 pagesArboviruses and Other Zoonotic VirusesRahmiati LaoNo ratings yet
- Name of Patient: E.J.P Ward/Room/Bed #: Pedia Ward/G.I./Bed 1 Age & Sex: 2 Y.o/ Female Diagnosis: Urinary Tract InfectionDocument1 pageName of Patient: E.J.P Ward/Room/Bed #: Pedia Ward/G.I./Bed 1 Age & Sex: 2 Y.o/ Female Diagnosis: Urinary Tract InfectionSALMA M. TUANONo ratings yet
- Properties: Myxo-TypeDocument4 pagesProperties: Myxo-Typeحسين محمد مطرود كاظمNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesNeonatal Pneumonia PathophysiologyRoderick EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of OxytocinDocument4 pagesDrug Study of OxytocinNichole DancelNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument2 pagesDownloadPaola Judith Torres DonesNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Pneumonia Pathophysiology - FINALDocument5 pagesNeonatal Pneumonia Pathophysiology - FINALRoderick EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyDannielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Henrickson 1972Document6 pagesHenrickson 1972Kmii TspNo ratings yet
- Concept Mapping For COVID-19: BioethicsDocument5 pagesConcept Mapping For COVID-19: BioethicsHelen Fairodz AmoraNo ratings yet
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP - Risk For InfectionJet Bautista100% (1)
- Serological and Molecular DiagnosisDocument9 pagesSerological and Molecular DiagnosisPAIRAT, Ella Joy M.No ratings yet
- Herpes ManuscriptDocument9 pagesHerpes ManuscriptALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONo ratings yet
- Wunner 2014Document19 pagesWunner 2014César VidezNo ratings yet
- Pharma - Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument6 pagesPharma - Chemotherapeutic AgentsSae YanNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendDocument3 pagesPredisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Objective: Short Term Objectives: Diagnostic: Sto: Fully Met, TheDocument3 pagesObjective: Short Term Objectives: Diagnostic: Sto: Fully Met, TheWayne LoriaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Neonatal PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Neonatal Pneumoniaderic93% (42)
- Reitmayer Et Al 2023 Mimicking Superinfection Exclusion Disrupts Alphavirus Infection and Transmission in The YellowDocument8 pagesReitmayer Et Al 2023 Mimicking Superinfection Exclusion Disrupts Alphavirus Infection and Transmission in The YellowvaldirbrazsNo ratings yet
- Herpes Simplex - PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHerpes Simplex - PathophysiologyRainny CommsNo ratings yet
- Can Existing Live Vaccines Prevent COVID-19?Document3 pagesCan Existing Live Vaccines Prevent COVID-19?lejuan0No ratings yet
- Risk of Infection NCPDocument5 pagesRisk of Infection NCPLloyd Adrian GaffudNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Female Reproductive System - Leah NechamkinDocument1 pagePathogens of The Female Reproductive System - Leah NechamkinMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable Factors: Cellular Destruction of Infected Cells Attracts Nearby Immune Cells (NK Cells)Document2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factors Modifiable Factors: Cellular Destruction of Infected Cells Attracts Nearby Immune Cells (NK Cells)Venice Joy CelociaNo ratings yet
- Togaviruses: FindingsDocument4 pagesTogaviruses: Findingsحسين محمد مطرود كاظمNo ratings yet
- Poster Biomedical EngDocument1 pagePoster Biomedical Engalamryzhra62No ratings yet
- Drug-Study Immunizations-And-Chemotherapy Jairah 4Document10 pagesDrug-Study Immunizations-And-Chemotherapy Jairah 4Yasmien MarieNo ratings yet
- Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsDocument3 pagesPrecipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsKEVIN PAUL JUGANASNo ratings yet
- Family Common Name Characteristics Virus Transmission Disease Detection Treatment Prevention Site of LatencyDocument3 pagesFamily Common Name Characteristics Virus Transmission Disease Detection Treatment Prevention Site of LatencyJessa MongcalNo ratings yet
- UTI PathophysiologyDocument1 pageUTI PathophysiologyNathaniel SupanNo ratings yet
- The Novel Insight of Sars-Cov-2 Molecular Biology and Pathogenesis and Therapeutic OptionsDocument13 pagesThe Novel Insight of Sars-Cov-2 Molecular Biology and Pathogenesis and Therapeutic OptionsREYNALDO JESUS HERNANDEZ RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument34 pagesMicrobiologyAli TARARNo ratings yet
- Final Final Patho No NotesDocument1 pageFinal Final Patho No NotesVanessa IbekweNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Drug/Classification Dose/Route Mechanism of Action Common Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Drug/Classification Dose/Route Mechanism of Action Common Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesLiiza G-GsprNo ratings yet
- 1 Ceftizidime - EDHDocument3 pages1 Ceftizidime - EDH1adie1907No ratings yet
- Bacterial Vaginosis A Practical Review.3Document7 pagesBacterial Vaginosis A Practical Review.3Catalina OchoaNo ratings yet
- SchemaDocument3 pagesSchemaLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- PP - Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocument1 pagePP - Community-Acquired Pneumonialpetallo100% (2)
- Nonviral Vectors for Gene TherapyFrom EverandNonviral Vectors for Gene TherapyMien-Chie HungNo ratings yet
- Herpes Simplex Varicella and Zoster: Clinical Manifestations and TreatmentFrom EverandHerpes Simplex Varicella and Zoster: Clinical Manifestations and TreatmentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (19)
- Pediatrics Study ScheduleDocument2 pagesPediatrics Study ScheduleNatnaelNo ratings yet
- L37 Medical Entomology L1Document19 pagesL37 Medical Entomology L1Soon SheedNo ratings yet
- PSM PYP II (1) (1)-CopyDocument93 pagesPSM PYP II (1) (1)-Copyksaurabh027No ratings yet
- Biochem II Mid Sem 2 MCQs Answered SamiDocument339 pagesBiochem II Mid Sem 2 MCQs Answered Samicarolinegatwiri08No ratings yet
- National Polio Eradication ProgramDocument36 pagesNational Polio Eradication Programayushi rainaNo ratings yet
- Collecting Plant Disease and Insect Pest Samples For Problem DiagnosisDocument10 pagesCollecting Plant Disease and Insect Pest Samples For Problem DiagnosisFadhilah SurotoNo ratings yet
- Evidence of ScrapieDocument10 pagesEvidence of ScrapieLaura Tatiana CarreroNo ratings yet
- Types of Wounds 101Document17 pagesTypes of Wounds 101Grey Tapes100% (1)
- STD Awareness ProgramDocument12 pagesSTD Awareness ProgramKevin DamasoNo ratings yet
- The Use of Mathematical Models in Epidemiological Study of Infectious Diseases and in The Design of Mass Immunization ProgrammesDocument21 pagesThe Use of Mathematical Models in Epidemiological Study of Infectious Diseases and in The Design of Mass Immunization ProgrammesAhmed EshebliNo ratings yet
- DraculaDocument5 pagesDraculaWillie ScottNo ratings yet
- Understanding PleomorphismDocument20 pagesUnderstanding PleomorphismDavid100% (2)
- 2020 Lymphatic SystemDocument84 pages2020 Lymphatic Systemsyafi zulNo ratings yet
- K15 - Infeksi Sistem Saraf PusatDocument65 pagesK15 - Infeksi Sistem Saraf PusatZikri Putra Lan LubisNo ratings yet
- Doxycyclin Alkaloid 100mg Capsules - ZIDocument12 pagesDoxycyclin Alkaloid 100mg Capsules - ZIMaja TrajanovikjNo ratings yet
- CDN Post Test Answer KeyDocument5 pagesCDN Post Test Answer KeyCharme Jean Raygon100% (1)
- National Tuberculosis Program MOPDocument192 pagesNational Tuberculosis Program MOPlpanatalioNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNADocument20 pagesRecombinant DNAUmme rubabNo ratings yet
- HSS2121 Week 9 Student SlidesDocument63 pagesHSS2121 Week 9 Student SlidesChiheb DzNo ratings yet
- 9700 w16 QP 23Document16 pages9700 w16 QP 23DevalNo ratings yet
- Virology Lecture 4 BacteriophagesDocument8 pagesVirology Lecture 4 Bacteriophagesao868598No ratings yet
- Health Hazard Manual - Wastewater Treatment Plant and Sewer WorkersDocument54 pagesHealth Hazard Manual - Wastewater Treatment Plant and Sewer WorkersMustafa Cuneyt GezenNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Post TestDocument7 pagesCommunicable Disease Post TestJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Review Lecture SourceDocument18 pagesParasitology Review Lecture SourcePatrickNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument2 pagesLiterature ReviewImran Azizi Zulkifli86% (7)
- Bartonellosis - Clinics in Dermatology 2009 PDFDocument10 pagesBartonellosis - Clinics in Dermatology 2009 PDFMarita Castillo EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Scabies - NarraDocument2 pagesScabies - NarraBryan De HopeNo ratings yet
- Communicating in Public Health Emergencies EnglishDocument32 pagesCommunicating in Public Health Emergencies EnglishGail HoadNo ratings yet
- Abstracts 2018Document363 pagesAbstracts 2018Osa RafshodiaNo ratings yet
Pathophysiology Pneumonia
Pathophysiology Pneumonia
Uploaded by
Maythresha GonzalesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pathophysiology Pneumonia
Pathophysiology Pneumonia
Uploaded by
Maythresha GonzalesCopyright:
Available Formats
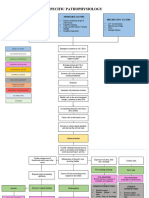
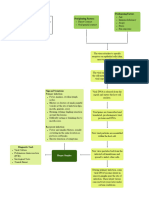
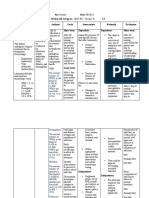
Predisposing Factors:
Non-modifiable: Precipitating Factors:
young Age (21 years old) Bacteria (Streptococcus
female infection)
Weak Immune system Virus (adenovirus,
rhinovirus, influenza,
Modifiable: coronavirus, and
germ exposure respiratory syncytial
Lifestyle virus)
Exposure to a pathogen
NCP #2 Imbalanced nutrition less than NCP #3 Disturbed sleep pattern
body requirements related to related to nonrestorative sleep
susceptible host and
insufficient dietary intake as pattern as evidenced by feeling
virulent pathogen
evidenced by a BMI of 16.6 kg/m2 unrested
presence of a viral
pathogen
pathogen colonizes the pathogen colonizes
nasopharynx oropharynx
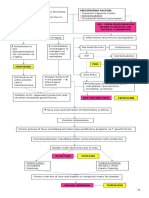
LEGEND:
Precipitating and
Predisposing Factors
WBC: 11.66
Pathophysiology white blood cell (WBC) x10^3/mm³(H)
activation Neutrophil; 80%
inflammatory cytokine
(H)
release
Manifestations
WBCs infiltrate site of
Nursing Diagnosis infection
increased inadvertent systemic
Laboratory results
vascular cellular injury inflammatory
permeability and hemolysis cytokines WBCs kill (B-
Medical Diagnosis disrupt cells) pathogen
hypothalamic
Sequential regulation
leakage of tonsillar
accumulation and
protein and petechiae and
deposition of
fluid into erythema
cellular debris and
surrounding fever
products of
tissue inflammatory
response
swelling and increased lymph
irritation drainage to tonsillar exudate
regional nodes
tonsillar
nasal tissue
tissue
enlarged
anterior
cervical nodes
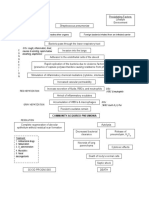
NCP #1 Acute pain related to
infection of the tonsils as evidenced tonsillar nasal
by dysphagia and facial grimace while edema congestion
swallowing and a pain scale of 7/10
nasal
discharge
irritates back
of throat
cough
ACUTE EXUDATIVE
TONSILLOPHARYNGITIS
You might also like
- Concept Mapping: Hodgskin'S Disease ComplicationDocument4 pagesConcept Mapping: Hodgskin'S Disease ComplicationAsterlyn ConiendoNo ratings yet
- Ergot and Ergotism PDFDocument2 pagesErgot and Ergotism PDFLukeNo ratings yet
- Bhat 2016Document29 pagesBhat 2016LekshmiNo ratings yet
- Specific EditedDocument12 pagesSpecific EditedLarabelle Avila CoralesNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Abscess Concept MapDocument1 pagePelvic Abscess Concept Mapaijiel talisikNo ratings yet
- IX. Nursing Care Plan: November 10, 2020Document6 pagesIX. Nursing Care Plan: November 10, 2020LNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesNeonatal Pneumonia PathophysiologyRoderick EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis: PathogenesisDocument1 pageGastrointestinal Tuberculosis: Pathogenesis알파No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Patient B's Age: 28 Years OldDocument7 pagesPathophysiology: Patient B's Age: 28 Years Oldkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of TBDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of TBEddie Lou GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDanica Fave AndiamNo ratings yet
- Plant Virus Transmission BT InsectsDocument12 pagesPlant Virus Transmission BT InsectsakshayaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map CovidDocument7 pagesConcept Map CovidMaieca Demecillo100% (3)
- Feb DTRDocument3 pagesFeb DTRFeb NamiaNo ratings yet
- Arboviruses and Other Zoonotic VirusesDocument16 pagesArboviruses and Other Zoonotic VirusesRahmiati LaoNo ratings yet
- Name of Patient: E.J.P Ward/Room/Bed #: Pedia Ward/G.I./Bed 1 Age & Sex: 2 Y.o/ Female Diagnosis: Urinary Tract InfectionDocument1 pageName of Patient: E.J.P Ward/Room/Bed #: Pedia Ward/G.I./Bed 1 Age & Sex: 2 Y.o/ Female Diagnosis: Urinary Tract InfectionSALMA M. TUANONo ratings yet
- Properties: Myxo-TypeDocument4 pagesProperties: Myxo-Typeحسين محمد مطرود كاظمNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesNeonatal Pneumonia PathophysiologyRoderick EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of OxytocinDocument4 pagesDrug Study of OxytocinNichole DancelNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument2 pagesDownloadPaola Judith Torres DonesNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Pneumonia Pathophysiology - FINALDocument5 pagesNeonatal Pneumonia Pathophysiology - FINALRoderick EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyDannielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Henrickson 1972Document6 pagesHenrickson 1972Kmii TspNo ratings yet
- Concept Mapping For COVID-19: BioethicsDocument5 pagesConcept Mapping For COVID-19: BioethicsHelen Fairodz AmoraNo ratings yet
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP - Risk For InfectionJet Bautista100% (1)
- Serological and Molecular DiagnosisDocument9 pagesSerological and Molecular DiagnosisPAIRAT, Ella Joy M.No ratings yet
- Herpes ManuscriptDocument9 pagesHerpes ManuscriptALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONo ratings yet
- Wunner 2014Document19 pagesWunner 2014César VidezNo ratings yet
- Pharma - Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument6 pagesPharma - Chemotherapeutic AgentsSae YanNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendDocument3 pagesPredisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Objective: Short Term Objectives: Diagnostic: Sto: Fully Met, TheDocument3 pagesObjective: Short Term Objectives: Diagnostic: Sto: Fully Met, TheWayne LoriaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Neonatal PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Neonatal Pneumoniaderic93% (42)
- Reitmayer Et Al 2023 Mimicking Superinfection Exclusion Disrupts Alphavirus Infection and Transmission in The YellowDocument8 pagesReitmayer Et Al 2023 Mimicking Superinfection Exclusion Disrupts Alphavirus Infection and Transmission in The YellowvaldirbrazsNo ratings yet
- Herpes Simplex - PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHerpes Simplex - PathophysiologyRainny CommsNo ratings yet
- Can Existing Live Vaccines Prevent COVID-19?Document3 pagesCan Existing Live Vaccines Prevent COVID-19?lejuan0No ratings yet
- Risk of Infection NCPDocument5 pagesRisk of Infection NCPLloyd Adrian GaffudNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Female Reproductive System - Leah NechamkinDocument1 pagePathogens of The Female Reproductive System - Leah NechamkinMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable Factors: Cellular Destruction of Infected Cells Attracts Nearby Immune Cells (NK Cells)Document2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factors Modifiable Factors: Cellular Destruction of Infected Cells Attracts Nearby Immune Cells (NK Cells)Venice Joy CelociaNo ratings yet
- Togaviruses: FindingsDocument4 pagesTogaviruses: Findingsحسين محمد مطرود كاظمNo ratings yet
- Poster Biomedical EngDocument1 pagePoster Biomedical Engalamryzhra62No ratings yet
- Drug-Study Immunizations-And-Chemotherapy Jairah 4Document10 pagesDrug-Study Immunizations-And-Chemotherapy Jairah 4Yasmien MarieNo ratings yet
- Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsDocument3 pagesPrecipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsKEVIN PAUL JUGANASNo ratings yet
- Family Common Name Characteristics Virus Transmission Disease Detection Treatment Prevention Site of LatencyDocument3 pagesFamily Common Name Characteristics Virus Transmission Disease Detection Treatment Prevention Site of LatencyJessa MongcalNo ratings yet
- UTI PathophysiologyDocument1 pageUTI PathophysiologyNathaniel SupanNo ratings yet
- The Novel Insight of Sars-Cov-2 Molecular Biology and Pathogenesis and Therapeutic OptionsDocument13 pagesThe Novel Insight of Sars-Cov-2 Molecular Biology and Pathogenesis and Therapeutic OptionsREYNALDO JESUS HERNANDEZ RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument34 pagesMicrobiologyAli TARARNo ratings yet
- Final Final Patho No NotesDocument1 pageFinal Final Patho No NotesVanessa IbekweNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Drug/Classification Dose/Route Mechanism of Action Common Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Drug/Classification Dose/Route Mechanism of Action Common Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesLiiza G-GsprNo ratings yet
- 1 Ceftizidime - EDHDocument3 pages1 Ceftizidime - EDH1adie1907No ratings yet
- Bacterial Vaginosis A Practical Review.3Document7 pagesBacterial Vaginosis A Practical Review.3Catalina OchoaNo ratings yet
- SchemaDocument3 pagesSchemaLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- PP - Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocument1 pagePP - Community-Acquired Pneumonialpetallo100% (2)
- Nonviral Vectors for Gene TherapyFrom EverandNonviral Vectors for Gene TherapyMien-Chie HungNo ratings yet
- Herpes Simplex Varicella and Zoster: Clinical Manifestations and TreatmentFrom EverandHerpes Simplex Varicella and Zoster: Clinical Manifestations and TreatmentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (19)
- Pediatrics Study ScheduleDocument2 pagesPediatrics Study ScheduleNatnaelNo ratings yet
- L37 Medical Entomology L1Document19 pagesL37 Medical Entomology L1Soon SheedNo ratings yet
- PSM PYP II (1) (1)-CopyDocument93 pagesPSM PYP II (1) (1)-Copyksaurabh027No ratings yet
- Biochem II Mid Sem 2 MCQs Answered SamiDocument339 pagesBiochem II Mid Sem 2 MCQs Answered Samicarolinegatwiri08No ratings yet
- National Polio Eradication ProgramDocument36 pagesNational Polio Eradication Programayushi rainaNo ratings yet
- Collecting Plant Disease and Insect Pest Samples For Problem DiagnosisDocument10 pagesCollecting Plant Disease and Insect Pest Samples For Problem DiagnosisFadhilah SurotoNo ratings yet
- Evidence of ScrapieDocument10 pagesEvidence of ScrapieLaura Tatiana CarreroNo ratings yet
- Types of Wounds 101Document17 pagesTypes of Wounds 101Grey Tapes100% (1)
- STD Awareness ProgramDocument12 pagesSTD Awareness ProgramKevin DamasoNo ratings yet
- The Use of Mathematical Models in Epidemiological Study of Infectious Diseases and in The Design of Mass Immunization ProgrammesDocument21 pagesThe Use of Mathematical Models in Epidemiological Study of Infectious Diseases and in The Design of Mass Immunization ProgrammesAhmed EshebliNo ratings yet
- DraculaDocument5 pagesDraculaWillie ScottNo ratings yet
- Understanding PleomorphismDocument20 pagesUnderstanding PleomorphismDavid100% (2)
- 2020 Lymphatic SystemDocument84 pages2020 Lymphatic Systemsyafi zulNo ratings yet
- K15 - Infeksi Sistem Saraf PusatDocument65 pagesK15 - Infeksi Sistem Saraf PusatZikri Putra Lan LubisNo ratings yet
- Doxycyclin Alkaloid 100mg Capsules - ZIDocument12 pagesDoxycyclin Alkaloid 100mg Capsules - ZIMaja TrajanovikjNo ratings yet
- CDN Post Test Answer KeyDocument5 pagesCDN Post Test Answer KeyCharme Jean Raygon100% (1)
- National Tuberculosis Program MOPDocument192 pagesNational Tuberculosis Program MOPlpanatalioNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNADocument20 pagesRecombinant DNAUmme rubabNo ratings yet
- HSS2121 Week 9 Student SlidesDocument63 pagesHSS2121 Week 9 Student SlidesChiheb DzNo ratings yet
- 9700 w16 QP 23Document16 pages9700 w16 QP 23DevalNo ratings yet
- Virology Lecture 4 BacteriophagesDocument8 pagesVirology Lecture 4 Bacteriophagesao868598No ratings yet
- Health Hazard Manual - Wastewater Treatment Plant and Sewer WorkersDocument54 pagesHealth Hazard Manual - Wastewater Treatment Plant and Sewer WorkersMustafa Cuneyt GezenNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Post TestDocument7 pagesCommunicable Disease Post TestJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Review Lecture SourceDocument18 pagesParasitology Review Lecture SourcePatrickNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument2 pagesLiterature ReviewImran Azizi Zulkifli86% (7)
- Bartonellosis - Clinics in Dermatology 2009 PDFDocument10 pagesBartonellosis - Clinics in Dermatology 2009 PDFMarita Castillo EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Scabies - NarraDocument2 pagesScabies - NarraBryan De HopeNo ratings yet
- Communicating in Public Health Emergencies EnglishDocument32 pagesCommunicating in Public Health Emergencies EnglishGail HoadNo ratings yet
- Abstracts 2018Document363 pagesAbstracts 2018Osa RafshodiaNo ratings yet