Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transes - Assessing Abdomen
Transes - Assessing Abdomen
Uploaded by
camatoviancaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Toltec Body Healing EbookDocument204 pagesToltec Body Healing EbookDanielle Grace100% (3)
- The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument31 pagesThe Gastrointestinal SystemEen AliNo ratings yet
- Os 206: Pe of The Abdomen - ©spcabellera, Upcm Class 2021Document4 pagesOs 206: Pe of The Abdomen - ©spcabellera, Upcm Class 2021Ronneil BilbaoNo ratings yet
- BIOL 103 - Final Exam Guide - Comprehensive Notes For The Exam (258 Pages Long!) - 2Document258 pagesBIOL 103 - Final Exam Guide - Comprehensive Notes For The Exam (258 Pages Long!) - 2Edwin Lee0% (1)
- Transes - AbdomenDocument8 pagesTranses - AbdomencamatoviancaNo ratings yet
- HA Notes Whole Term 2Document21 pagesHA Notes Whole Term 2kpv454yk7mNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 Health Assessment AbdomenDocument30 pagesNCM 101 Health Assessment AbdomenSherinne Jane CariazoNo ratings yet
- The GastroDocument25 pagesThe Gastroangel_maui100% (7)
- DIGESTIVE SYSTEM (Handout)Document2 pagesDIGESTIVE SYSTEM (Handout)Bea Isabel CabalNo ratings yet
- GIT Part 1Document10 pagesGIT Part 1Unli MoviesNo ratings yet
- DIGESTIVEANDRESPIRATORYDocument9 pagesDIGESTIVEANDRESPIRATORYAlyssa keith JarillaNo ratings yet
- 2 Nutritional Metabolic PatternDocument22 pages2 Nutritional Metabolic PatternMyles Zen Dieta EaNo ratings yet
- Digestive 24Document7 pagesDigestive 24Angel Ann Gertos Inojales INo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Human Anatomy & Physiology University of WashingtonDocument41 pagesDigestive System: Human Anatomy & Physiology University of WashingtonSyed Waqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Zoology Finals ReviewerDocument18 pagesZoology Finals ReviewerZian Lei MienNo ratings yet
- Althea Report - The Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesAlthea Report - The Digestive SystemHarold Kent MendozaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesDigestive SystemMJMadlangbayanNo ratings yet
- Updated - CHAPTER 3 Nutrition and DigestionDocument40 pagesUpdated - CHAPTER 3 Nutrition and Digestiondeela decemberNo ratings yet
- Internal System of The FrogDocument1 pageInternal System of The FrogYumi GarciaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function: AbdomenDocument6 pagesStructure and Function: Abdomendiana borromeoNo ratings yet
- BIOL 546 DigestionDocument71 pagesBIOL 546 DigestiontNo ratings yet
- System, Consists of A Digestive Tube Called GI Tract or Alimentary Canal and Several Accessory Organs (LiverDocument5 pagesSystem, Consists of A Digestive Tube Called GI Tract or Alimentary Canal and Several Accessory Organs (LiverJm AshiiNo ratings yet
- 3.5. Digestion and AbsorptionDocument15 pages3.5. Digestion and AbsorptionWondwosenGetachewNo ratings yet
- AP14 DigestiveDocument7 pagesAP14 DigestiveAmore BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument33 pagesDigestive SystemBassel AmrNo ratings yet
- Function of Git System:: Pepsinogen, Increases Gastric Blood Flow, Stimulates Gastric Smooth Muscle ContractionDocument9 pagesFunction of Git System:: Pepsinogen, Increases Gastric Blood Flow, Stimulates Gastric Smooth Muscle ContractionRovefrances ErpeluaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesDigestive Systemshane.surigaoNo ratings yet
- Student Notes For Medication Administration and Oxygenation With Fill-InsDocument45 pagesStudent Notes For Medication Administration and Oxygenation With Fill-InsTabitha EaglehouseNo ratings yet
- III - Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesIII - Digestive SystemGael QuingNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDigestive Systemshanelhello1No ratings yet
- Unit D - Digestive System and Digestive System ProblemsDocument33 pagesUnit D - Digestive System and Digestive System Problemsqptolentino2No ratings yet
- Abdomen, Neuro, Musculoskeletal, Male and Female Genitalia, and RectumDocument29 pagesAbdomen, Neuro, Musculoskeletal, Male and Female Genitalia, and Rectums2020106372No ratings yet
- The Digestive System and Body MetabolismDocument12 pagesThe Digestive System and Body Metabolismtriciap.maltoNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesThe Human Digestive SystemDanielSenpai69No ratings yet
- Bahan Pemicu 3 Gastrointestinal Ivan BuntaraDocument109 pagesBahan Pemicu 3 Gastrointestinal Ivan BuntaraMarco GunawanNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesDigestive SystemKathleenNicole De Castro EnfectanaNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Digestive System: StructuresDocument18 pagesCH 8 Digestive System: StructuresBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Acute GastritisDocument107 pagesAcute GastritisfitrahNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 1Document37 pagesBiochemistry 1Odongo TonnyNo ratings yet
- The Liver, Gall-Bladder and PancreasDocument13 pagesThe Liver, Gall-Bladder and PancreasJoseph A MwitupaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in HumansDocument82 pagesNutrition in HumansSyed Burhan UddinNo ratings yet
- Medterm DigestiveDocument14 pagesMedterm DigestiveVince BalloriNo ratings yet
- Norbe GastroDocument23 pagesNorbe GastroMarlo Dañez NorbeNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesDigestive Systemkirsten merielleNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument19 pagesDigestive Systemlindsay tanNo ratings yet
- 3 - Physiology of The Stomach and Regulation of Gastric SecretionsDocument31 pages3 - Physiology of The Stomach and Regulation of Gastric SecretionsMaleeha YasminNo ratings yet
- DSystemDocument17 pagesDSystemJelly beansNo ratings yet
- Ana DigesDocument2 pagesAna DigesSTEM-G.04 Kiarrah Katrina BotinNo ratings yet
- Digestive System (2015 - 06 - 09 20 - 43 - 48 Utc)Document90 pagesDigestive System (2015 - 06 - 09 20 - 43 - 48 Utc)DiazNo ratings yet
- Ms GastroDocument19 pagesMs GastrohanonkomatsuuNo ratings yet
- Thursday, April 09, 2009 4:45 PMDocument266 pagesThursday, April 09, 2009 4:45 PMkcs2012No ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument38 pagesThe Digestive SystemrabiaNo ratings yet
- The Huma N Ig e S Tive S Ys Te MDocument21 pagesThe Huma N Ig e S Tive S Ys Te MJoshua RuntuweneNo ratings yet
- 13 DigestionDocument21 pages13 DigestionElmerNo ratings yet
- AnP 22Document64 pagesAnP 22Dee HNo ratings yet
- Can Hold 4l of Food (Maximum)Document4 pagesCan Hold 4l of Food (Maximum)Sofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: SphinctersDocument33 pagesThe Digestive System: SphinctersJerome EkohNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Stomach & DuodenumDocument24 pagesDiseases of Stomach & DuodenumPlày GameNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Digestive SystemDocument10 pagesLesson 4 Digestive SystemJulio De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument45 pagesDigestive SystemvturnerNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal TractDocument63 pagesGastrointestinal TractLalajimNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument19 pagesDigestive SystemIbsa AbdelaNo ratings yet
- Innate Immunity (DrWahyuni)Document42 pagesInnate Immunity (DrWahyuni)Nurfadilah Zahratul WahidahNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 - 机能解剖学(Chapter 1 - Functional anatomy) 笔记Document7 pagesSem 1 - 机能解剖学(Chapter 1 - Functional anatomy) 笔记Cah YeeNo ratings yet
- Imhm321 Laboratory RH Typing With Test For Weak DDocument11 pagesImhm321 Laboratory RH Typing With Test For Weak DprnfbmsdqnNo ratings yet
- Embryology - The First WeekDocument51 pagesEmbryology - The First WeekLugembe MasolaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy at A GlanceDocument327 pagesAnatomy at A GlanceANo ratings yet
- Caps HTMLDocument152 pagesCaps HTMLUchy Luph'milimiLy0% (1)
- Musculoskeletal Module First Professional Year MBBS 8 WeeksDocument41 pagesMusculoskeletal Module First Professional Year MBBS 8 WeeksEdward XiamNo ratings yet
- Spine Structure and FunctionDocument19 pagesSpine Structure and Functionakhil dattaNo ratings yet
- Immunofluorescence (IF) Assay: Learning Objectives by The End of This Chapter The Reader Should Be Able ToDocument8 pagesImmunofluorescence (IF) Assay: Learning Objectives by The End of This Chapter The Reader Should Be Able ToAlex de la TorreNo ratings yet
- 10 Biology 1 - 16 - 07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDocument32 pages10 Biology 1 - 16 - 07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsErivieNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH BiokimiaDocument19 pagesMAKALAH BiokimiaGitha YaniNo ratings yet
- HydronephrosisDocument11 pagesHydronephrosis黃昱睿No ratings yet
- CELL-THE UNIT OF LIFE-Ribosomes, CytoskeletonDocument19 pagesCELL-THE UNIT OF LIFE-Ribosomes, CytoskeletonHridyanshu Singh RoyNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology Chapter 1 Practice QuestionsDocument30 pagesMedical Terminology Chapter 1 Practice Questionshtb495No ratings yet
- Human Nutrition - 90 QPDocument16 pagesHuman Nutrition - 90 QPStephen AreriNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 MCQDocument5 pagesFundamental Unit of Life Class 9 MCQEnter NameNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System 2020Document91 pagesIntegumentary System 2020Danielle AvelynNo ratings yet
- JOSE - M1 L3-Check-in ActivityDocument3 pagesJOSE - M1 L3-Check-in ActivityPrince Kier JoseNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2015 Sh-1Document41 pagesAnatomy 2015 Sh-1Dania ZaidNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 LE 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesBio 11 LE 2 ReviewerLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Forehead and Brow Lift: Gregory S. Keller, M.D., F.A.C.S., and Grigoriy Mashkevich, M.DDocument12 pagesEndoscopic Forehead and Brow Lift: Gregory S. Keller, M.D., F.A.C.S., and Grigoriy Mashkevich, M.DVivekanand ChandrashekarNo ratings yet
- Histo-Anatomical Aspects of The Ajuga Genevensis L. and AjugaDocument8 pagesHisto-Anatomical Aspects of The Ajuga Genevensis L. and AjugaAlina LambaNo ratings yet
- Physiology Practical For 1st Year Institute Pharmacy StudentsDocument14 pagesPhysiology Practical For 1st Year Institute Pharmacy StudentsSnipper HunterNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Leukostasis Mimicking Pulmonary Embolism: Case of The MonthDocument4 pagesPulmonary Leukostasis Mimicking Pulmonary Embolism: Case of The MonthkaremiaNo ratings yet
- Water Vascular System - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument3 pagesWater Vascular System - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDebarunAcharyaNo ratings yet
- Library of Teachings - Preparatory Exercises For Lungs Magnetic Field and Deep Meditation - ©the-Teachings-Of-Yogi-BhajanDocument7 pagesLibrary of Teachings - Preparatory Exercises For Lungs Magnetic Field and Deep Meditation - ©the-Teachings-Of-Yogi-BhajanValentinaZoccaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Workshop For Kids by SlidesgoDocument16 pagesDigestive System Workshop For Kids by Slidesgoapi-649419165No ratings yet
Transes - Assessing Abdomen
Transes - Assessing Abdomen
Uploaded by
camatoviancaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transes - Assessing Abdomen
Transes - Assessing Abdomen
Uploaded by
camatoviancaCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessing Abdomen
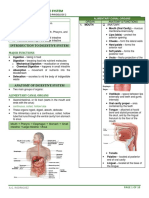
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION • INTERNAL ANATOMY
• ABDOMINAL QUADRANTS o Peritoneum Lines
o Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ) - Thin, shiny, serous membrane
o Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ) - Provides a protective covering for most
o Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ) internal abdominal organs.
o Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ)
Within the abdominal cavity are structures of
several body systems: gastrointestinal,
reproductive (female), lymphatic, and urinary.
These structures are typically referred to as the
abdominal viscera and can be divided into two
types: Solid Viscera and Hollow Viscera.
SOLID VISCERA
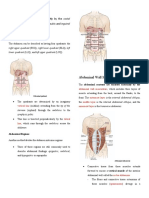
• ABDOMINAL WALL MUSCLES • Liver
o External Abdominal Oblique - Largest solid organ in the body.
- Outermost layer - Located below the diaphragm in the
right upper quadrant of the abdomen.
o Internal Abdominal Oblique
- It is composed of four lobes that fill
- Middle layer most of the right upper quadrant and
o Transverse Abdominis extend to the left midclavicular line.
- Innermost layer • Pancreas
o Rectus Abdominis - Located mostly behind the stomach
- Connective tissue from these muscles deep in the upper abdomen.
extends forward to encase a vertical - Normally not palpable.
- The pancreas has two functions: it is an
muscle of the anterior abdominal wall.
endocrine gland and an accessory organ
o Linea Alba of digestion.
- a tendinous, fibrous raphe that runs - Approximately 7 cm wide
vertically down the midline of the - In some healthy clients, the lower tip
abdomen. It extends between the can be felt below the left costal margin.
inferior limit of the sternum and the • Spleen
pubis, separating the rectus abdominis - Functions primarily to filter the blood of
cellular debris, to digest
muscles.
microorganisms, and to return the
o Abdominal Wall Muscles breakdown products to the liver.
- Muscles protect the internal organs • Kidneys
- Allow normal compression during - Glandular, bean-shaped organs
functional activities such as coughing, - Approximately 10 x 5 x 2.5 cm
sneezing, urination, defecation, and - The tops of both kidneys are protected
childbirth. by the posterior rib cage.
- Primary function: filtration and
elimination of metabolic waste
products.
ako gumawa neto – ibyangca adrianca
- Also plays a role in blood pressure • Urinary Bladder
control and maintenance of water, salt, - A distensible muscular sac located
and electrolyte balances. behind the pubic bone in the midline of
- They also function as endocrine glands
the abdomen.
by secreting hormones.
- Function: acts a temporary receptable
• Right Kidney for urine.
- Positioned slightly lower because of the NURSING PROCESS
position of the liver.
• Pregnant Uterus ASSESSMENT
- May be palpated above the level of the • Abdominal Pain
symphysis pubis in the midline.
- COLDSPA (Character, Onset, Location,
• Ovaries
- Located in the right lower quadrant and Duration, Severity, Pattern, Associated
left lower quadrant Factors)
- Normally palpated only during by a - Indigestion
bimanual examination of the internal - Nausea and Vomiting
genitalia. - Appetite
- Bowel Elimination
HOLLOW VISCERA
- Personal Health History
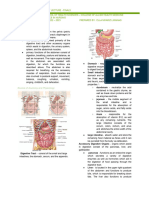
• Stomach
- Family History
- Not usually palpable.
- Lifestyle and Health Practices
- Main function: store, churn, and digest
food. TYPES OF PAIN
• Gallbladder
TYPES OF PAIN
- Muscular sac approx. 10 cm long
• Visceral Pain
- Functions: to concentrate and store the
- Occurs when hollow abdominal organs
bile needed to digest fat.
─ such as the intestines ─ become
- Not normally palpated.
distended or contract forcefully, or
• Small Intestine
when the capsules of the organs such as
- The longest portion of the digestive
the liver and spleen are stretched.
tract
- Poorly defined or localized and
- Two major functions: digestion and
intermittently timed, this type of pain is
absorption of nutrients.
often characterized as dull, aching,
• Colon/Large Intestine
burning, cramping, or colicky.
- Composed of three major sections:
• Parietal Pain
ascending transverse, and descending.
- Occurs when parietal peritoneum
- Functions: secrete large amounts of
becomes inflamed, as in appendicitis or
alkaline mucus to lubricate the intestine
peritonitis.
and neutralize acids formed by the
- This type of pain tends to localize more
intestinal bacteria.
to the source and is characterized as
- Water is also absorbed in the large
more severe and steady pain.
intestine, leaving waste products to be
eliminated in a stool.
ako gumawa neto – ibyangca adrianca
• Referred Pain • Feces
- Occurs at distant sites that are - Hard stools in the colon appear as
innervated at approximately the same localized distention. Percussion over the
levels as the disrupted abdominal area discloses dullness.
organ. • Fibroids and other Masses
- This type of pain travels, or refers, from - A large ovarian cyst or fibroid tumor
the primary site and becomes highly appears as generalized distention in the
localized at the distant site. lower abdomen. The mass displaces
bowel, thus the percussion tone over
Equipment: the distended area is dullness with
o Small pillow or rolled blanket tympany at the periphery. The
o Centimeter Ruler umbilicus may be everted.
o Stethoscope (Warm the diaphragm and • Flatus
the bell) - The abdomen distended with gas may
o Marking Pen appear as a generalized protuberance
or it may appear more localized.
PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT
PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT - Tympany is the percussion tone over the
Common Abnormal findings include: area.
o Abdominal Edema, or swelling, signifying • Ascitic Fluid
ascites - Fluid in the abdomen causes
o Abdominal masses, signifying abnormal generalized protuberance, bulging
growths or constipation flanks.
o Unusual pulsations such as those seen - Percussion reveals dullness over fluid
with an aneurysm of the abdominal and tympany over the intestines.
aorta • Umbilical Hernia
o Pain associated with appendicitis - Results from bowel protruding through
a weakness in the umbilical ring.
ABNORMAL FINDINGS - This condition occurs more frequently in
infants but occurs in adults.
ABDOMINAL DISTENTION • Epigastric Hernia
• Pregnancy - Occurs when the bowel protrudes
- it causes a generalized protuberant through a weakness in the linea alba.
abdomen, protuberant umbilicus, a The small bulge appears midline
fetal heartbeat that can be heard on between the xiphoid process and the
auscultation, percussible tympany over umbilicus. It may be discovered only on
the intestines, and dullness over the palpation.
uterus. • Incisional Hernia
• Fat - Occurs when the bowel protrudes
- Obesity accounts for most uniformly through a defect or weakness resulting
protuberant abdomens. The abdominal from a surgical incision. It appears as a
wall is thick, and tympany is the bulge near a surgical scar on the
percussion tone is elicited. The abdomen.
umbilicus usually appears sunken.
ako gumawa neto – ibyangca adrianca
You might also like
- Toltec Body Healing EbookDocument204 pagesToltec Body Healing EbookDanielle Grace100% (3)
- The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument31 pagesThe Gastrointestinal SystemEen AliNo ratings yet
- Os 206: Pe of The Abdomen - ©spcabellera, Upcm Class 2021Document4 pagesOs 206: Pe of The Abdomen - ©spcabellera, Upcm Class 2021Ronneil BilbaoNo ratings yet
- BIOL 103 - Final Exam Guide - Comprehensive Notes For The Exam (258 Pages Long!) - 2Document258 pagesBIOL 103 - Final Exam Guide - Comprehensive Notes For The Exam (258 Pages Long!) - 2Edwin Lee0% (1)
- Transes - AbdomenDocument8 pagesTranses - AbdomencamatoviancaNo ratings yet
- HA Notes Whole Term 2Document21 pagesHA Notes Whole Term 2kpv454yk7mNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 Health Assessment AbdomenDocument30 pagesNCM 101 Health Assessment AbdomenSherinne Jane CariazoNo ratings yet
- The GastroDocument25 pagesThe Gastroangel_maui100% (7)
- DIGESTIVE SYSTEM (Handout)Document2 pagesDIGESTIVE SYSTEM (Handout)Bea Isabel CabalNo ratings yet
- GIT Part 1Document10 pagesGIT Part 1Unli MoviesNo ratings yet
- DIGESTIVEANDRESPIRATORYDocument9 pagesDIGESTIVEANDRESPIRATORYAlyssa keith JarillaNo ratings yet
- 2 Nutritional Metabolic PatternDocument22 pages2 Nutritional Metabolic PatternMyles Zen Dieta EaNo ratings yet
- Digestive 24Document7 pagesDigestive 24Angel Ann Gertos Inojales INo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Human Anatomy & Physiology University of WashingtonDocument41 pagesDigestive System: Human Anatomy & Physiology University of WashingtonSyed Waqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Zoology Finals ReviewerDocument18 pagesZoology Finals ReviewerZian Lei MienNo ratings yet
- Althea Report - The Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesAlthea Report - The Digestive SystemHarold Kent MendozaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesDigestive SystemMJMadlangbayanNo ratings yet
- Updated - CHAPTER 3 Nutrition and DigestionDocument40 pagesUpdated - CHAPTER 3 Nutrition and Digestiondeela decemberNo ratings yet
- Internal System of The FrogDocument1 pageInternal System of The FrogYumi GarciaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function: AbdomenDocument6 pagesStructure and Function: Abdomendiana borromeoNo ratings yet
- BIOL 546 DigestionDocument71 pagesBIOL 546 DigestiontNo ratings yet
- System, Consists of A Digestive Tube Called GI Tract or Alimentary Canal and Several Accessory Organs (LiverDocument5 pagesSystem, Consists of A Digestive Tube Called GI Tract or Alimentary Canal and Several Accessory Organs (LiverJm AshiiNo ratings yet
- 3.5. Digestion and AbsorptionDocument15 pages3.5. Digestion and AbsorptionWondwosenGetachewNo ratings yet
- AP14 DigestiveDocument7 pagesAP14 DigestiveAmore BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument33 pagesDigestive SystemBassel AmrNo ratings yet
- Function of Git System:: Pepsinogen, Increases Gastric Blood Flow, Stimulates Gastric Smooth Muscle ContractionDocument9 pagesFunction of Git System:: Pepsinogen, Increases Gastric Blood Flow, Stimulates Gastric Smooth Muscle ContractionRovefrances ErpeluaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesDigestive Systemshane.surigaoNo ratings yet
- Student Notes For Medication Administration and Oxygenation With Fill-InsDocument45 pagesStudent Notes For Medication Administration and Oxygenation With Fill-InsTabitha EaglehouseNo ratings yet
- III - Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesIII - Digestive SystemGael QuingNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDigestive Systemshanelhello1No ratings yet
- Unit D - Digestive System and Digestive System ProblemsDocument33 pagesUnit D - Digestive System and Digestive System Problemsqptolentino2No ratings yet
- Abdomen, Neuro, Musculoskeletal, Male and Female Genitalia, and RectumDocument29 pagesAbdomen, Neuro, Musculoskeletal, Male and Female Genitalia, and Rectums2020106372No ratings yet
- The Digestive System and Body MetabolismDocument12 pagesThe Digestive System and Body Metabolismtriciap.maltoNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesThe Human Digestive SystemDanielSenpai69No ratings yet
- Bahan Pemicu 3 Gastrointestinal Ivan BuntaraDocument109 pagesBahan Pemicu 3 Gastrointestinal Ivan BuntaraMarco GunawanNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesDigestive SystemKathleenNicole De Castro EnfectanaNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Digestive System: StructuresDocument18 pagesCH 8 Digestive System: StructuresBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Acute GastritisDocument107 pagesAcute GastritisfitrahNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 1Document37 pagesBiochemistry 1Odongo TonnyNo ratings yet
- The Liver, Gall-Bladder and PancreasDocument13 pagesThe Liver, Gall-Bladder and PancreasJoseph A MwitupaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in HumansDocument82 pagesNutrition in HumansSyed Burhan UddinNo ratings yet
- Medterm DigestiveDocument14 pagesMedterm DigestiveVince BalloriNo ratings yet
- Norbe GastroDocument23 pagesNorbe GastroMarlo Dañez NorbeNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesDigestive Systemkirsten merielleNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument19 pagesDigestive Systemlindsay tanNo ratings yet
- 3 - Physiology of The Stomach and Regulation of Gastric SecretionsDocument31 pages3 - Physiology of The Stomach and Regulation of Gastric SecretionsMaleeha YasminNo ratings yet
- DSystemDocument17 pagesDSystemJelly beansNo ratings yet
- Ana DigesDocument2 pagesAna DigesSTEM-G.04 Kiarrah Katrina BotinNo ratings yet
- Digestive System (2015 - 06 - 09 20 - 43 - 48 Utc)Document90 pagesDigestive System (2015 - 06 - 09 20 - 43 - 48 Utc)DiazNo ratings yet
- Ms GastroDocument19 pagesMs GastrohanonkomatsuuNo ratings yet
- Thursday, April 09, 2009 4:45 PMDocument266 pagesThursday, April 09, 2009 4:45 PMkcs2012No ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument38 pagesThe Digestive SystemrabiaNo ratings yet
- The Huma N Ig e S Tive S Ys Te MDocument21 pagesThe Huma N Ig e S Tive S Ys Te MJoshua RuntuweneNo ratings yet
- 13 DigestionDocument21 pages13 DigestionElmerNo ratings yet
- AnP 22Document64 pagesAnP 22Dee HNo ratings yet
- Can Hold 4l of Food (Maximum)Document4 pagesCan Hold 4l of Food (Maximum)Sofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: SphinctersDocument33 pagesThe Digestive System: SphinctersJerome EkohNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Stomach & DuodenumDocument24 pagesDiseases of Stomach & DuodenumPlày GameNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Digestive SystemDocument10 pagesLesson 4 Digestive SystemJulio De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument45 pagesDigestive SystemvturnerNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal TractDocument63 pagesGastrointestinal TractLalajimNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument19 pagesDigestive SystemIbsa AbdelaNo ratings yet
- Innate Immunity (DrWahyuni)Document42 pagesInnate Immunity (DrWahyuni)Nurfadilah Zahratul WahidahNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 - 机能解剖学(Chapter 1 - Functional anatomy) 笔记Document7 pagesSem 1 - 机能解剖学(Chapter 1 - Functional anatomy) 笔记Cah YeeNo ratings yet
- Imhm321 Laboratory RH Typing With Test For Weak DDocument11 pagesImhm321 Laboratory RH Typing With Test For Weak DprnfbmsdqnNo ratings yet
- Embryology - The First WeekDocument51 pagesEmbryology - The First WeekLugembe MasolaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy at A GlanceDocument327 pagesAnatomy at A GlanceANo ratings yet
- Caps HTMLDocument152 pagesCaps HTMLUchy Luph'milimiLy0% (1)
- Musculoskeletal Module First Professional Year MBBS 8 WeeksDocument41 pagesMusculoskeletal Module First Professional Year MBBS 8 WeeksEdward XiamNo ratings yet
- Spine Structure and FunctionDocument19 pagesSpine Structure and Functionakhil dattaNo ratings yet
- Immunofluorescence (IF) Assay: Learning Objectives by The End of This Chapter The Reader Should Be Able ToDocument8 pagesImmunofluorescence (IF) Assay: Learning Objectives by The End of This Chapter The Reader Should Be Able ToAlex de la TorreNo ratings yet
- 10 Biology 1 - 16 - 07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDocument32 pages10 Biology 1 - 16 - 07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsErivieNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH BiokimiaDocument19 pagesMAKALAH BiokimiaGitha YaniNo ratings yet
- HydronephrosisDocument11 pagesHydronephrosis黃昱睿No ratings yet
- CELL-THE UNIT OF LIFE-Ribosomes, CytoskeletonDocument19 pagesCELL-THE UNIT OF LIFE-Ribosomes, CytoskeletonHridyanshu Singh RoyNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology Chapter 1 Practice QuestionsDocument30 pagesMedical Terminology Chapter 1 Practice Questionshtb495No ratings yet
- Human Nutrition - 90 QPDocument16 pagesHuman Nutrition - 90 QPStephen AreriNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 MCQDocument5 pagesFundamental Unit of Life Class 9 MCQEnter NameNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System 2020Document91 pagesIntegumentary System 2020Danielle AvelynNo ratings yet
- JOSE - M1 L3-Check-in ActivityDocument3 pagesJOSE - M1 L3-Check-in ActivityPrince Kier JoseNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2015 Sh-1Document41 pagesAnatomy 2015 Sh-1Dania ZaidNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 LE 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesBio 11 LE 2 ReviewerLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Forehead and Brow Lift: Gregory S. Keller, M.D., F.A.C.S., and Grigoriy Mashkevich, M.DDocument12 pagesEndoscopic Forehead and Brow Lift: Gregory S. Keller, M.D., F.A.C.S., and Grigoriy Mashkevich, M.DVivekanand ChandrashekarNo ratings yet
- Histo-Anatomical Aspects of The Ajuga Genevensis L. and AjugaDocument8 pagesHisto-Anatomical Aspects of The Ajuga Genevensis L. and AjugaAlina LambaNo ratings yet
- Physiology Practical For 1st Year Institute Pharmacy StudentsDocument14 pagesPhysiology Practical For 1st Year Institute Pharmacy StudentsSnipper HunterNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Leukostasis Mimicking Pulmonary Embolism: Case of The MonthDocument4 pagesPulmonary Leukostasis Mimicking Pulmonary Embolism: Case of The MonthkaremiaNo ratings yet
- Water Vascular System - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument3 pagesWater Vascular System - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDebarunAcharyaNo ratings yet
- Library of Teachings - Preparatory Exercises For Lungs Magnetic Field and Deep Meditation - ©the-Teachings-Of-Yogi-BhajanDocument7 pagesLibrary of Teachings - Preparatory Exercises For Lungs Magnetic Field and Deep Meditation - ©the-Teachings-Of-Yogi-BhajanValentinaZoccaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Workshop For Kids by SlidesgoDocument16 pagesDigestive System Workshop For Kids by Slidesgoapi-649419165No ratings yet