Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 2
Topic 2
Uploaded by
P&l PalCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- James P. Hogan - 2 - The Gentle Giants of Ganymede (1984)Document237 pagesJames P. Hogan - 2 - The Gentle Giants of Ganymede (1984)CiprianNo ratings yet
- Tinkantan (Our Solar System)Document30 pagesTinkantan (Our Solar System)notemusic100% (1)
- Makalah MajuDocument14 pagesMakalah MajuIsnaNurhayatiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AstronomyDocument3 pagesFundamentals of AstronomykirarakiNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument23 pagesScienceJanice RomeroNo ratings yet
- Solar System and Kepler's Law of Planetary MotionDocument4 pagesSolar System and Kepler's Law of Planetary MotionGiorgi KandelakiNo ratings yet
- Navigation 3 Nautical Astronomy and Celestial Navigation (PART 1)Document526 pagesNavigation 3 Nautical Astronomy and Celestial Navigation (PART 1)Cyver Kent DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Moons and PlanetsDocument46 pagesMoons and PlanetsCearra Mae EbronaNo ratings yet
- Section 2b - Positional Astronomy - StudentDocument41 pagesSection 2b - Positional Astronomy - StudentDeon SmithNo ratings yet
- Welcome, Grade 3!Document22 pagesWelcome, Grade 3!Vhia GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Elementary AstronomyDocument7 pagesElementary AstronomyJoseph ManaseNo ratings yet
- Document 17Document8 pagesDocument 17Trishna AryalNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument31 pagesSolar System8 E Shubh BhadauriaNo ratings yet
- The Space Around Us - A Short Book On The Solar Sysem and Many More.Document26 pagesThe Space Around Us - A Short Book On The Solar Sysem and Many More.Chirathi WalpitaNo ratings yet
- Our Solar System: Terrestrial Asteroid Belt Gas Giant Scattered Disc Heliopause Oort CloudDocument4 pagesOur Solar System: Terrestrial Asteroid Belt Gas Giant Scattered Disc Heliopause Oort CloudAshutosh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Stars and The Solar System: CBSE Class 8Document26 pagesStars and The Solar System: CBSE Class 8AbhiNo ratings yet
- Earth and The Solar System 220913 004914Document50 pagesEarth and The Solar System 220913 004914Bobfian WidjajaNo ratings yet
- FST01 Unit 11 To 20Document152 pagesFST01 Unit 11 To 20sumit prajapatiNo ratings yet
- 8 Science Stars&SolarSystemDocument7 pages8 Science Stars&SolarSystemAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Stars: BY: Tejanidhyan, Adithya, Faaz, Faris, Daksh, Eshaan, Isa, Sohail and AhmedDocument36 pagesStars: BY: Tejanidhyan, Adithya, Faaz, Faris, Daksh, Eshaan, Isa, Sohail and AhmedEshaan SanalNo ratings yet
- Solar System:: Mercury: Venus: EarthDocument3 pagesSolar System:: Mercury: Venus: EarthWajiha's WorldNo ratings yet
- Planets and Their MoonsDocument3 pagesPlanets and Their MoonsWajiha's WorldNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 4 - Chapter 13Document9 pagesExp SC 4 - Chapter 13megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Earth and The Solar SystemDocument21 pagesEarth and The Solar SystemRija FatimaNo ratings yet
- Sky MapsDocument2 pagesSky MapsPatrick SchwartzNo ratings yet
- The Evening Sky Map: September 2013Document2 pagesThe Evening Sky Map: September 20133582No ratings yet
- GuideDocument4 pagesGuidereoverosjonathan1No ratings yet
- Skymaps Com 2012 08Document2 pagesSkymaps Com 2012 083582No ratings yet
- Unit 1. Earth and Space: The Solar SystemDocument2 pagesUnit 1. Earth and Space: The Solar Systemtsuki1No ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument15 pagesSolar Systemapi-3731257No ratings yet
- SOLARDocument12 pagesSOLARIrish Jean HocomanNo ratings yet
- Earth and The Solar System Geography Notes For UPSCDocument2 pagesEarth and The Solar System Geography Notes For UPSCpriyanka suklaNo ratings yet
- Skymaps Com 2015 03Document2 pagesSkymaps Com 2015 033582No ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument47 pagesSolar SystemHarvey Villalobos100% (1)
- Navigation III: STCW Table A-II/1Document259 pagesNavigation III: STCW Table A-II/1Karen DavilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - FinalDocument24 pagesChapter 1 - FinalAbhi XNo ratings yet
- Cel. Nav TheoryDocument27 pagesCel. Nav TheoryRahul DevnathNo ratings yet
- Skymaps Com 2014 04Document2 pagesSkymaps Com 2014 043582No ratings yet
- Our Universe Class 8Document10 pagesOur Universe Class 8shihabnittNo ratings yet
- Solar System and Sun - Geography UPSCDocument13 pagesSolar System and Sun - Geography UPSCTeja AbhiNo ratings yet
- The Solar SystemDocument14 pagesThe Solar SystemAman PandeyNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Earth and The Solar System-HandoutDocument4 pages6.1 Earth and The Solar System-HandoutMohammad Wajeeh MohsinNo ratings yet
- Basic AstrologyDocument37 pagesBasic AstrologyT. Manohar Rao100% (3)
- The Earth in The Solar SystemDocument13 pagesThe Earth in The Solar SystemAyush BansalNo ratings yet
- The UniverseDocument14 pagesThe UniverseDrishti GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Earth in The Solar System Class 6 Notes Social Science Geography Chapter 1-Converted1Document6 pagesThe Earth in The Solar System Class 6 Notes Social Science Geography Chapter 1-Converted1SampathkumarNo ratings yet
- Astronomical Phenomena - EditedDocument79 pagesAstronomical Phenomena - EditedRIZALINA BATANNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Geography Notes Chapter 1 - The Earth in The Solar SystemDocument20 pagesCBSE Class 6 Geography Notes Chapter 1 - The Earth in The Solar SystemscedhuNo ratings yet
- Examples of Astronomical PhenominaDocument38 pagesExamples of Astronomical PhenominaMary Rhodelyn Fermin100% (1)
- The Evening Sky Map: JANUARY 2014Document2 pagesThe Evening Sky Map: JANUARY 20143582No ratings yet
- The Earth in The Solar System: Globe: Latitudes and LongitudesDocument10 pagesThe Earth in The Solar System: Globe: Latitudes and LongitudesPranit PrasoonNo ratings yet
- Planet Facts: The PlanetsDocument5 pagesPlanet Facts: The Planetsgerone remultaNo ratings yet
- Geography: Chapter - IDocument25 pagesGeography: Chapter - IDiveshNo ratings yet
- Atienza, Shaidie Rose S. (Beed-2)Document12 pagesAtienza, Shaidie Rose S. (Beed-2)clarkbesenioNo ratings yet
- Our Earth and Solar SystemDocument20 pagesOur Earth and Solar SystemKalai Selvi MohanNo ratings yet
- Phy 208 Lecture Note 2Document14 pagesPhy 208 Lecture Note 2Oluwaferanmi AwosanyaNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Astrology NotesDocument80 pages1st Year Astrology Notesrahul106100% (3)
- Social Note For Form ThreeDocument64 pagesSocial Note For Form ThreeKafui AugustineNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Week 6 Q4 1Document36 pagesScience 5 Week 6 Q4 1Smiley DeSmillingNo ratings yet
- CBR - Ipba - Nur Elisa Rambe - Pipa B 20Document7 pagesCBR - Ipba - Nur Elisa Rambe - Pipa B 20Telleng NurNo ratings yet
- What Do We Know about Uranus? Astronomy for Beginners | Children's Astronomy & Space BooksFrom EverandWhat Do We Know about Uranus? Astronomy for Beginners | Children's Astronomy & Space BooksNo ratings yet
- STARMAP: AN INTRODUCTORY PICTORIAL TOUR OF THE UNIVERSEFrom EverandSTARMAP: AN INTRODUCTORY PICTORIAL TOUR OF THE UNIVERSENo ratings yet
- The Colonization of Tiamat IV Phoenix III Daniel1Document12 pagesThe Colonization of Tiamat IV Phoenix III Daniel1dragutu18100% (1)
- Tech-Startup - PPTX 0Document42 pagesTech-Startup - PPTX 0aarzu qadriNo ratings yet
- EnvPhys CH2 Solar System PDFDocument79 pagesEnvPhys CH2 Solar System PDFSean RNo ratings yet
- French Lesson by SlidesgoDocument44 pagesFrench Lesson by SlidesgoEliza BudeanuNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition Workshop Infographics by SlidesgoDocument33 pagesFood and Nutrition Workshop Infographics by SlidesgoDyandra AhmadyNo ratings yet
- Procurement Software Pitch DeckDocument63 pagesProcurement Software Pitch DeckSelena ThaliaNo ratings yet
- The Second House by Dana GerhardtDocument5 pagesThe Second House by Dana GerhardtSultanademerkadilloNo ratings yet
- Hubble Birthdays Full YearDocument41 pagesHubble Birthdays Full YearlrpontesNo ratings yet
- AA Michael - Ascension Is Near - Aug 1 2009Document198 pagesAA Michael - Ascension Is Near - Aug 1 2009richx7100% (3)
- Heart Failure Clinical Case by SlidesgoDocument61 pagesHeart Failure Clinical Case by SlidesgoQamar HassanNo ratings yet
- General KnowlwdgeDocument115 pagesGeneral KnowlwdgeMUDASSAR IDRIS98% (44)
- Activitysheets6 4Document12 pagesActivitysheets6 4Benmar L. OrterasNo ratings yet
- World Geography MCQ'sDocument14 pagesWorld Geography MCQ'sIfLah ITooNo ratings yet
- Kawaii Interface For MarketingDocument56 pagesKawaii Interface For Marketingayshel thaliaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Space Research CardsDocument7 pagesEarth and Space Research CardsCAASI BERNARDNo ratings yet
- History Subject For High School - Indonesian Independence Day by SlidesgoDocument54 pagesHistory Subject For High School - Indonesian Independence Day by SlidesgoGangNama StailNo ratings yet
- The Moon Problem Attic Test For StudentsDocument30 pagesThe Moon Problem Attic Test For Studentsapi-290509627No ratings yet
- Outer Space Toastmasters MOST UPDATSDocument76 pagesOuter Space Toastmasters MOST UPDATSAbhay ChhabraNo ratings yet
- BioethicsDocument55 pagesBioethicsEzekiel John GarciaNo ratings yet
- Students Guide Learning From Home StickersDocument32 pagesStudents Guide Learning From Home Stickersnur liyana syafiqahNo ratings yet
- IAAC Qualification Round 2019 PDFDocument3 pagesIAAC Qualification Round 2019 PDFMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- StructureDocument23 pagesStructureJefry Gunawan MrgNo ratings yet
- GR 17 E.secretaryDocument50 pagesGR 17 E.secretaryKhairunnisa AndreviiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 8 - Worksheet 1 (The Solar System)Document3 pagesUNIT 8 - Worksheet 1 (The Solar System)sara.demoipekaNo ratings yet
- Direction: Read The Following Statement Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument8 pagesDirection: Read The Following Statement Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerPaul Senen DiduloNo ratings yet
- The Order of The Planets in The Solar SystemDocument2 pagesThe Order of The Planets in The Solar SystemLouis CasianoNo ratings yet
- Science Subject For Middle School-6th Grade - Physics I by SlidesgoDocument45 pagesScience Subject For Middle School-6th Grade - Physics I by SlidesgoTasya Syifa AltanzaniaNo ratings yet
- Aqua Marketing Plan - by SlidesgoDocument42 pagesAqua Marketing Plan - by Slidesgoroxinny jimenezNo ratings yet
Topic 2
Topic 2
Uploaded by
P&l PalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 2
Topic 2
Uploaded by
P&l PalCopyright:
Available Formats
ASTRONOMY RELEVANT TO ASTROLOGY (A R T A)
TOPIC – 2
SOLAR SYSTEM.
Milky way is one of the many Galaxy in the Universe. It is referred as SOURA VYUHA
in our Jyotisha.
The Solar system consists of Stars, Planets and Satellites. (Nakshatra, Graha,
Upagraha)
Stars are Self-Luminous bodies which radiate light and heat. Sun is also a star. A
group of Stars is called constellation.
Planets – Other than the stars, Sun and Moon there are other heavenly bodies which
are visible to the Naked eye and moving around the Sun. As their motion is different
for each planet they are called PLANETS or MOVING STARS. Fixed stars twinkle
while planets shine with steady light. The planets which can be seen by naked eye are
Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Uranus and Neptune can be seen through
Telescopes.
In Jyotisha even Sun and Moon are considered as Planets and thus we have 7 planets
and 2 mathematical points thus making a total of NINE PLANETS.
Satellites - The Heavenly bodies which move around the planets and in turn move
around the Sun along with the planets are termed satellites. They are also called
Moon of the particular planet.
Our Solar system is centered round the Sun and all other planets are moving in
elliptical orbit around the Sun. There are 8 planets – Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars,
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. We are living on Earth. With the Invention of
telescope several other Large and Small planets are seen or identified
The names of the Planets in their order of distance from Sun are
Mercury
Venus INNER PLANETS or INFERIOR PLANETS
(EARTH)
diwakar ASTRONOMY Page 1 of 5
Mars OUTER PLANETS or
Asteroids SUPERIOR PLANETS.
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus (Herschel)
Neptune
The Planets whose orbits are between Sun and the orbit of Earth are called INNER or
INTERIOR PLANETS. - Mercury & Venus.
The Planets whose orbits are outside the orbit of Earth are called OUTER or SUPERIOR
PLANETS - Mars, Asteroids, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus & Neptune.
Mean distance from Sun
Sidereal Mean Mean daily
Period Synodic motion
Astronomical
(Days) Period (d m s) Miles
Unit
Moon 27.3216 29.531 13-10-35 0.00257
Mercury 87.9692 115.878 04-05-32 0.38710 36000000
Venus 224.70080 583.921 01-36-07 0.72333 67200000
Earth 365.25636 ----------- 00-59-08 1.00000 93000000
Mars 686.9798 770.936 00-31-26 1.52369 141600000
(1.9 yrs)
Jupiter 4332.589 398.84 00-04-59 5.20280 483600000
(11.80 yrs)
Saturn 10759.23 378.092 0-02-01 9.53884 886700000
(29.46 yrs)
Rahu 693.470 340.620 ------- ------ -----
(18.60 yrs)
EARTH –
Earth is the 3rd planet in order of the distance from Sun. The orbit of the Earth is not a
perfect circle but an ecliptical one. Sun is at one of its foci.
The Minimum distance - when earth is nearer to the Sun – PERIHELION
Is 91,400.000 miles.
The Maximum distance – when earth is farthest to Sun - APHELION
Is 94.600,000 miles.
Its MASS is about 6 X 10 (21 times). Consists of 77.6 % Nitrogen and 20.70 % Oxygen.
diwakar ASTRONOMY Page 2 of 5
Earth is not a perfect sphere but an oblate spheroid.
Its diameter is 7926 miles at the Equator and 7900 miles across the poles.
Earth completes its one revolution around the Sun in 365 ¼ days.
The Earth is rotating around its axis from West to East and it causes the formation of
day and night. The rotating axis of the Earth is perpendicular to its Equator.
THE MOON
Moon is the Earth’s only satellite. Moon is the most important planet to us after the
Sun. It takes about 27 days 7 hours and 43 minutes i.e., 27.3217 days to complete one
revolution. This is the sidereal period.
The Synodic month is from one Amavasya to another Amavasya and is 29.5305887
solar days. This is because Sun also moves by 1 degree everyday and 1 sign in a
month. Moon has to catch up with the Sun to have the next Amavasya.(conjunction)
The mean distance of the Moon from Earth is 238,000 miles. Due to the elliptic orbit
the PERIGEE will be 221,460 miles and APOGEE will be 252,700 miles.
Moon is the only satellite of Earth. It is the most important Graha (Planet) after Sun.
In PURUSHA SOOKTA a reference is made –
CHANDRAMA MANASO JAATA CHAKSHO SOORYA AJAAYATA.
meaning Moon symbolizes mind and Sun symbolizes eyes.
The Moon’s orbit is inclined to the ecliptic by a maximum of 5 degrees 15 minutes on
either side of the ecliptic. Moon does not rotate on its axis as such the same side
(face) of the Moon is visible to Earth. Moon reflects the light received by Sun, As Moon
revolves around the Earth and Earth revolves around the Sun, thus Moon also revolves
around Sun. Due to this the Moon is viewed in different sizes everyday and this
phenomenon is called as PHASES OF THE MOON.
PHASES OF THE MOON.
As told above Moon has no light of its own and it reflects the light recvied by
Sun. Moon revolves round the Earth and its path is inclined by 5 degrees
approximately to the ecliptic orbit. It is because of this reason that Eclipses do not
occur on every Amavasya (New Moon) or Pournima (Full Moon)
diwakar ASTRONOMY Page 3 of 5
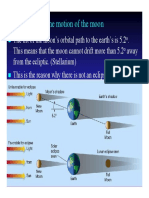
In the figure above Earth is shown in the centre and 8 different positions of the Moon
are shown. The Sun light is coming from the Left hand side which is depicted by many
rays of light (arrows).
diwakar ASTRONOMY Page 4 of 5
At Position-1 Moon is in straight line to Sun and Earth. The illuminated portion of the
Moon is towards Earth, and this portion of the Moon is fully illuminated. As such the
illuminated hemispherical portion of the Moon is seen from Earth. This position is
POURNIMA (FULL MOON)
At positions – 2 & 8 about three-fourths of the disc of the Moon receives Sun light and
the visible portion of the Moon from the earth will be three-fourths.
At positions 3 & 7 only half the hemisphere of the Moon is illuminated by Sun light and
hence only half of the Moon hemisphere is visible from Earth.
At positions 4 & 6 about one-fourth of the disc of the Moon receives Sun light and the
visible portion on the Moon from the earth will be one-fourth.
At position 5 the portion of the Moon which is facing Earth does not receive Sun light
hence Moon is not visible from Earth at this position. This phenomenon is called as
Amavasya (New Moon).
NODES OF THE MOON.
We have seen above that the axis of the Moon is inclined to a maximum extent of 5
degrees with respect to the celestial axis. Due to this the Moon’s axis cuts the
celestial axis at TWO points. The point of intersection at the Northern point is called
the North Node and the point of intersection at the Southern point is called South
Node.
In Vedic Jyotisha North Node is called as RAHU and South Node is called as KETU.
diwakar ASTRONOMY Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- James P. Hogan - 2 - The Gentle Giants of Ganymede (1984)Document237 pagesJames P. Hogan - 2 - The Gentle Giants of Ganymede (1984)CiprianNo ratings yet
- Tinkantan (Our Solar System)Document30 pagesTinkantan (Our Solar System)notemusic100% (1)
- Makalah MajuDocument14 pagesMakalah MajuIsnaNurhayatiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AstronomyDocument3 pagesFundamentals of AstronomykirarakiNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument23 pagesScienceJanice RomeroNo ratings yet
- Solar System and Kepler's Law of Planetary MotionDocument4 pagesSolar System and Kepler's Law of Planetary MotionGiorgi KandelakiNo ratings yet
- Navigation 3 Nautical Astronomy and Celestial Navigation (PART 1)Document526 pagesNavigation 3 Nautical Astronomy and Celestial Navigation (PART 1)Cyver Kent DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Moons and PlanetsDocument46 pagesMoons and PlanetsCearra Mae EbronaNo ratings yet
- Section 2b - Positional Astronomy - StudentDocument41 pagesSection 2b - Positional Astronomy - StudentDeon SmithNo ratings yet
- Welcome, Grade 3!Document22 pagesWelcome, Grade 3!Vhia GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Elementary AstronomyDocument7 pagesElementary AstronomyJoseph ManaseNo ratings yet
- Document 17Document8 pagesDocument 17Trishna AryalNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument31 pagesSolar System8 E Shubh BhadauriaNo ratings yet
- The Space Around Us - A Short Book On The Solar Sysem and Many More.Document26 pagesThe Space Around Us - A Short Book On The Solar Sysem and Many More.Chirathi WalpitaNo ratings yet
- Our Solar System: Terrestrial Asteroid Belt Gas Giant Scattered Disc Heliopause Oort CloudDocument4 pagesOur Solar System: Terrestrial Asteroid Belt Gas Giant Scattered Disc Heliopause Oort CloudAshutosh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Stars and The Solar System: CBSE Class 8Document26 pagesStars and The Solar System: CBSE Class 8AbhiNo ratings yet
- Earth and The Solar System 220913 004914Document50 pagesEarth and The Solar System 220913 004914Bobfian WidjajaNo ratings yet
- FST01 Unit 11 To 20Document152 pagesFST01 Unit 11 To 20sumit prajapatiNo ratings yet
- 8 Science Stars&SolarSystemDocument7 pages8 Science Stars&SolarSystemAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Stars: BY: Tejanidhyan, Adithya, Faaz, Faris, Daksh, Eshaan, Isa, Sohail and AhmedDocument36 pagesStars: BY: Tejanidhyan, Adithya, Faaz, Faris, Daksh, Eshaan, Isa, Sohail and AhmedEshaan SanalNo ratings yet
- Solar System:: Mercury: Venus: EarthDocument3 pagesSolar System:: Mercury: Venus: EarthWajiha's WorldNo ratings yet
- Planets and Their MoonsDocument3 pagesPlanets and Their MoonsWajiha's WorldNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 4 - Chapter 13Document9 pagesExp SC 4 - Chapter 13megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Earth and The Solar SystemDocument21 pagesEarth and The Solar SystemRija FatimaNo ratings yet
- Sky MapsDocument2 pagesSky MapsPatrick SchwartzNo ratings yet
- The Evening Sky Map: September 2013Document2 pagesThe Evening Sky Map: September 20133582No ratings yet
- GuideDocument4 pagesGuidereoverosjonathan1No ratings yet
- Skymaps Com 2012 08Document2 pagesSkymaps Com 2012 083582No ratings yet
- Unit 1. Earth and Space: The Solar SystemDocument2 pagesUnit 1. Earth and Space: The Solar Systemtsuki1No ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument15 pagesSolar Systemapi-3731257No ratings yet
- SOLARDocument12 pagesSOLARIrish Jean HocomanNo ratings yet
- Earth and The Solar System Geography Notes For UPSCDocument2 pagesEarth and The Solar System Geography Notes For UPSCpriyanka suklaNo ratings yet
- Skymaps Com 2015 03Document2 pagesSkymaps Com 2015 033582No ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument47 pagesSolar SystemHarvey Villalobos100% (1)
- Navigation III: STCW Table A-II/1Document259 pagesNavigation III: STCW Table A-II/1Karen DavilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - FinalDocument24 pagesChapter 1 - FinalAbhi XNo ratings yet
- Cel. Nav TheoryDocument27 pagesCel. Nav TheoryRahul DevnathNo ratings yet
- Skymaps Com 2014 04Document2 pagesSkymaps Com 2014 043582No ratings yet
- Our Universe Class 8Document10 pagesOur Universe Class 8shihabnittNo ratings yet
- Solar System and Sun - Geography UPSCDocument13 pagesSolar System and Sun - Geography UPSCTeja AbhiNo ratings yet
- The Solar SystemDocument14 pagesThe Solar SystemAman PandeyNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Earth and The Solar System-HandoutDocument4 pages6.1 Earth and The Solar System-HandoutMohammad Wajeeh MohsinNo ratings yet
- Basic AstrologyDocument37 pagesBasic AstrologyT. Manohar Rao100% (3)
- The Earth in The Solar SystemDocument13 pagesThe Earth in The Solar SystemAyush BansalNo ratings yet
- The UniverseDocument14 pagesThe UniverseDrishti GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Earth in The Solar System Class 6 Notes Social Science Geography Chapter 1-Converted1Document6 pagesThe Earth in The Solar System Class 6 Notes Social Science Geography Chapter 1-Converted1SampathkumarNo ratings yet
- Astronomical Phenomena - EditedDocument79 pagesAstronomical Phenomena - EditedRIZALINA BATANNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Geography Notes Chapter 1 - The Earth in The Solar SystemDocument20 pagesCBSE Class 6 Geography Notes Chapter 1 - The Earth in The Solar SystemscedhuNo ratings yet
- Examples of Astronomical PhenominaDocument38 pagesExamples of Astronomical PhenominaMary Rhodelyn Fermin100% (1)
- The Evening Sky Map: JANUARY 2014Document2 pagesThe Evening Sky Map: JANUARY 20143582No ratings yet
- The Earth in The Solar System: Globe: Latitudes and LongitudesDocument10 pagesThe Earth in The Solar System: Globe: Latitudes and LongitudesPranit PrasoonNo ratings yet
- Planet Facts: The PlanetsDocument5 pagesPlanet Facts: The Planetsgerone remultaNo ratings yet
- Geography: Chapter - IDocument25 pagesGeography: Chapter - IDiveshNo ratings yet
- Atienza, Shaidie Rose S. (Beed-2)Document12 pagesAtienza, Shaidie Rose S. (Beed-2)clarkbesenioNo ratings yet
- Our Earth and Solar SystemDocument20 pagesOur Earth and Solar SystemKalai Selvi MohanNo ratings yet
- Phy 208 Lecture Note 2Document14 pagesPhy 208 Lecture Note 2Oluwaferanmi AwosanyaNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Astrology NotesDocument80 pages1st Year Astrology Notesrahul106100% (3)
- Social Note For Form ThreeDocument64 pagesSocial Note For Form ThreeKafui AugustineNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Week 6 Q4 1Document36 pagesScience 5 Week 6 Q4 1Smiley DeSmillingNo ratings yet
- CBR - Ipba - Nur Elisa Rambe - Pipa B 20Document7 pagesCBR - Ipba - Nur Elisa Rambe - Pipa B 20Telleng NurNo ratings yet
- What Do We Know about Uranus? Astronomy for Beginners | Children's Astronomy & Space BooksFrom EverandWhat Do We Know about Uranus? Astronomy for Beginners | Children's Astronomy & Space BooksNo ratings yet
- STARMAP: AN INTRODUCTORY PICTORIAL TOUR OF THE UNIVERSEFrom EverandSTARMAP: AN INTRODUCTORY PICTORIAL TOUR OF THE UNIVERSENo ratings yet
- The Colonization of Tiamat IV Phoenix III Daniel1Document12 pagesThe Colonization of Tiamat IV Phoenix III Daniel1dragutu18100% (1)
- Tech-Startup - PPTX 0Document42 pagesTech-Startup - PPTX 0aarzu qadriNo ratings yet
- EnvPhys CH2 Solar System PDFDocument79 pagesEnvPhys CH2 Solar System PDFSean RNo ratings yet
- French Lesson by SlidesgoDocument44 pagesFrench Lesson by SlidesgoEliza BudeanuNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition Workshop Infographics by SlidesgoDocument33 pagesFood and Nutrition Workshop Infographics by SlidesgoDyandra AhmadyNo ratings yet
- Procurement Software Pitch DeckDocument63 pagesProcurement Software Pitch DeckSelena ThaliaNo ratings yet
- The Second House by Dana GerhardtDocument5 pagesThe Second House by Dana GerhardtSultanademerkadilloNo ratings yet
- Hubble Birthdays Full YearDocument41 pagesHubble Birthdays Full YearlrpontesNo ratings yet
- AA Michael - Ascension Is Near - Aug 1 2009Document198 pagesAA Michael - Ascension Is Near - Aug 1 2009richx7100% (3)
- Heart Failure Clinical Case by SlidesgoDocument61 pagesHeart Failure Clinical Case by SlidesgoQamar HassanNo ratings yet
- General KnowlwdgeDocument115 pagesGeneral KnowlwdgeMUDASSAR IDRIS98% (44)
- Activitysheets6 4Document12 pagesActivitysheets6 4Benmar L. OrterasNo ratings yet
- World Geography MCQ'sDocument14 pagesWorld Geography MCQ'sIfLah ITooNo ratings yet
- Kawaii Interface For MarketingDocument56 pagesKawaii Interface For Marketingayshel thaliaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Space Research CardsDocument7 pagesEarth and Space Research CardsCAASI BERNARDNo ratings yet
- History Subject For High School - Indonesian Independence Day by SlidesgoDocument54 pagesHistory Subject For High School - Indonesian Independence Day by SlidesgoGangNama StailNo ratings yet
- The Moon Problem Attic Test For StudentsDocument30 pagesThe Moon Problem Attic Test For Studentsapi-290509627No ratings yet
- Outer Space Toastmasters MOST UPDATSDocument76 pagesOuter Space Toastmasters MOST UPDATSAbhay ChhabraNo ratings yet
- BioethicsDocument55 pagesBioethicsEzekiel John GarciaNo ratings yet
- Students Guide Learning From Home StickersDocument32 pagesStudents Guide Learning From Home Stickersnur liyana syafiqahNo ratings yet
- IAAC Qualification Round 2019 PDFDocument3 pagesIAAC Qualification Round 2019 PDFMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- StructureDocument23 pagesStructureJefry Gunawan MrgNo ratings yet
- GR 17 E.secretaryDocument50 pagesGR 17 E.secretaryKhairunnisa AndreviiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 8 - Worksheet 1 (The Solar System)Document3 pagesUNIT 8 - Worksheet 1 (The Solar System)sara.demoipekaNo ratings yet
- Direction: Read The Following Statement Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument8 pagesDirection: Read The Following Statement Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerPaul Senen DiduloNo ratings yet
- The Order of The Planets in The Solar SystemDocument2 pagesThe Order of The Planets in The Solar SystemLouis CasianoNo ratings yet
- Science Subject For Middle School-6th Grade - Physics I by SlidesgoDocument45 pagesScience Subject For Middle School-6th Grade - Physics I by SlidesgoTasya Syifa AltanzaniaNo ratings yet
- Aqua Marketing Plan - by SlidesgoDocument42 pagesAqua Marketing Plan - by Slidesgoroxinny jimenezNo ratings yet