Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Describe AC DC
Describe AC DC
Uploaded by
Nancy NursiamCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Alternating Current and Direct CurrentDocument7 pagesAlternating Current and Direct CurrentEllen Jane Cantuba GuardianNo ratings yet
- Ac DCDocument12 pagesAc DCCatherineNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Ac and DC CurrentsDocument32 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Ac and DC CurrentsMohit TyagiNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current (A.C.)Document6 pagesAlternating Current (A.C.)Jonathan ThomasNo ratings yet
- Alternative Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)Document4 pagesAlternative Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)MonirNo ratings yet
- InvertersDocument18 pagesInvertersSolar - Marketing/CELNo ratings yet
- DC SYSTEM by Oli Ullah KhanDocument67 pagesDC SYSTEM by Oli Ullah KhanOliullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2 D.C & A.CDocument3 pagesLesson Plan 2 D.C & A.CHaider RasheedNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Alternating CurrentDocument23 pagesDifference Between Alternating Currentabhi_akNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument3 pagesRectifierTina ErinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 1.0 Fundamental of AC TheoryDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 2 1.0 Fundamental of AC TheoryMUHAMMAD ALIFF DANIAL RAZMINo ratings yet
- Ac Vs DCDocument2 pagesAc Vs DCapi-296499245No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 1.0 Fundamental of AC TheoryDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 2 1.0 Fundamental of AC TheoryfahmiNo ratings yet
- Ac DCDocument3 pagesAc DCSachin NowalNo ratings yet
- Ac DCDocument28 pagesAc DCPreet BassiNo ratings yet
- Unit-II Beee Ac-I NewDocument19 pagesUnit-II Beee Ac-I NewParikshit SinghNo ratings yet
- AC vs. DC (Alternating Current vs. Direct Current) : Comparison ChartDocument2 pagesAC vs. DC (Alternating Current vs. Direct Current) : Comparison Chartmohamed jamaNo ratings yet
- Phy3 Chapter1Document26 pagesPhy3 Chapter1kokoh20No ratings yet
- Alternating Current and Direct Current PDFDocument5 pagesAlternating Current and Direct Current PDFHafiz HamzaNo ratings yet
- Direct Current and Alternating CurrentDocument4 pagesDirect Current and Alternating CurrentYuva RajNo ratings yet
- Chap 31 PDFDocument11 pagesChap 31 PDFJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 DC Circuits Electrical Engineering Is The Field of Engineering That Generally Deals With The StudyDocument60 pagesUnit 1 DC Circuits Electrical Engineering Is The Field of Engineering That Generally Deals With The StudyAayush SinghNo ratings yet
- What Is Alternating CurrentDocument49 pagesWhat Is Alternating CurrentRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 DC Circuits Electrical Engineering Is The Field of Engineering That Generally Deals With The StudyDocument60 pagesUnit 1 DC Circuits Electrical Engineering Is The Field of Engineering That Generally Deals With The StudyAtharv BhedaNo ratings yet
- Comparision of Ac & DCDocument11 pagesComparision of Ac & DCdevshakya885No ratings yet
- Direct Current Only Flows in One Direction. Alternating Current Changes Direction PeriodicallyDocument1 pageDirect Current Only Flows in One Direction. Alternating Current Changes Direction PeriodicallyCarl Justine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document17 pagesChapter 9abcunaNo ratings yet
- AC Vs DCDocument3 pagesAC Vs DCKhushi YadavNo ratings yet
- 12 Chapter 10 Alternating CurrentDocument39 pages12 Chapter 10 Alternating CurrentAhmad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Circuits Review P1Document103 pagesCircuits Review P1José CastilloNo ratings yet
- AC-Circuits Stud PDFDocument22 pagesAC-Circuits Stud PDFPrince PersiaNo ratings yet
- Activity4 Ac&Dc Gacosta NicoleDocument8 pagesActivity4 Ac&Dc Gacosta NicolenicsNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة 2022-11-23 في 9.08.03 ص PDFDocument99 pagesلقطة شاشة 2022-11-23 في 9.08.03 ص PDFsajjad aakulNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument16 pagesBasic ElectronicsMøhamed Abdel FattahNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2-Electricity and MagnesiumDocument24 pagesUNIT 2-Electricity and MagnesiumAar PeeNo ratings yet
- 14 - Current - Electricity - Revision - Notes - by Neet Topper.Document93 pages14 - Current - Electricity - Revision - Notes - by Neet Topper.Parnad BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- 1 - IntroductionDocument74 pages1 - IntroductionNikhil PatelNo ratings yet
- Ac & DC Current Used in PhysiotherapyDocument11 pagesAc & DC Current Used in PhysiotherapyAniket67% (3)
- Ac & DC CurrentDocument11 pagesAc & DC CurrentAniketNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current - Definition, Working Principle, AC GeneratorDocument22 pagesAlternating Current - Definition, Working Principle, AC GeneratorJatin VermaNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Current StudyDocument6 pagesVoltage and Current Studyshyam ubaleNo ratings yet
- L3-Principle of ElectricDocument66 pagesL3-Principle of ElectricIzzah AfiqahNo ratings yet
- AC-and-DC Grade 9 1st QuarterDocument46 pagesAC-and-DC Grade 9 1st QuarterXian DorojaNo ratings yet
- Direct CurrentDocument1 pageDirect CurrentShra 1537No ratings yet
- Direct CurrentDocument1 pageDirect CurrentShehzadi KhanNo ratings yet
- NIKHILDocument3 pagesNIKHILshwetayadav9323No ratings yet
- Comparision of Ac & DCDocument11 pagesComparision of Ac & DCdevshakya885No ratings yet
- Principle of ElectricDocument66 pagesPrinciple of ElectricSyahmi FadziNo ratings yet
- Electricity 4Document17 pagesElectricity 4AdelheidAlNo ratings yet
- ICP AssignmentDocument7 pagesICP Assignmentmeesamali163No ratings yet
- Ac Vs DCDocument8 pagesAc Vs DCapi-295907196No ratings yet
- Complete DC Circuit NotesDocument59 pagesComplete DC Circuit NotesIsha chandravanshiNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuestionsEngr Muhammad Faisal YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Direct Current Alternating Current Battery ElectronicDocument1 pageDirect Current Alternating Current Battery ElectronicJitendra PandeyNo ratings yet
- Why DC Current Is Not Used in HomesDocument6 pagesWhy DC Current Is Not Used in HomesalokNo ratings yet
- Circuit Variables and Elements: A. S. M. BadrudduzaDocument45 pagesCircuit Variables and Elements: A. S. M. BadrudduzaDr-Eng Amir ElsafraweyNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsDocument14 pagesAC CircuitsShiva Sankar BeharaNo ratings yet
- DC AnalysisDocument9 pagesDC Analysisunotjarikandetu32No ratings yet
- Wa0013.Document8 pagesWa0013.Roshan rajNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of 5-AMINOTETRAZOLE - PrepChemcomDocument3 pagesSynthesis of 5-AMINOTETRAZOLE - PrepChemcomxcvNo ratings yet
- Gaurav Singh - Equilibrium of Parallel Forces and MomentsDocument13 pagesGaurav Singh - Equilibrium of Parallel Forces and Momentsgaurav singhNo ratings yet
- CANcaseXL Manual enDocument38 pagesCANcaseXL Manual enHemanth RasineniNo ratings yet
- 1.6.1 Packet Tracer - Implement A Small NetworkDocument6 pages1.6.1 Packet Tracer - Implement A Small NetworkCecilia SánchezNo ratings yet
- Din 2458Document0 pagesDin 2458student_blNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall CalculationDocument1 pageRetaining Wall CalculationNurmuliana Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Ukmt 2009 Junior Math OlympiadDocument4 pagesUkmt 2009 Junior Math OlympiadSadi SnmzNo ratings yet
- Name - Aryan Gupta Reg. No. 199301088 Section - B: Ans.1) A. Rabin Karp String Matching Algorithm CodeDocument7 pagesName - Aryan Gupta Reg. No. 199301088 Section - B: Ans.1) A. Rabin Karp String Matching Algorithm CodebruhNo ratings yet
- Iso 15809Document15 pagesIso 15809Manoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Xc22B Preset Counter Operating Instructions: Terminal Connections SpecificationsDocument1 pageXc22B Preset Counter Operating Instructions: Terminal Connections SpecificationsPasindu PriyankaraNo ratings yet
- 2017 2018 PROJECT AN AND 4fs FormsDocument3 pages2017 2018 PROJECT AN AND 4fs FormsDaaarls100% (1)
- Big English 2 - Video Activity - UNIT 1Document3 pagesBig English 2 - Video Activity - UNIT 1zelindaaNo ratings yet
- NG300 ESales Spec SheetDocument2 pagesNG300 ESales Spec SheetSamrandNo ratings yet
- Innovations in Derivatives MarketsDocument446 pagesInnovations in Derivatives Marketsshrikantmsd100% (1)
- Jmo 2004Document2 pagesJmo 2004Dr Shyam Sundar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- HDTVandFiberProductsCatalog 2013Document9 pagesHDTVandFiberProductsCatalog 2013vitoriacunha70% (1)
- What Is Optical Power BudgetDocument6 pagesWhat Is Optical Power BudgetAmir SalahNo ratings yet
- OIR Test Part 1Document25 pagesOIR Test Part 1Avanindra Nayak100% (1)
- DKK1413 - Chapter 04-1Document37 pagesDKK1413 - Chapter 04-1Salini ShaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Analysis of Vacuum Evacuation in Viscous Flow and Its ApplicationsDocument7 pagesTheoretical Analysis of Vacuum Evacuation in Viscous Flow and Its ApplicationsMansi Shah ShroffNo ratings yet
- History of MathematicsDocument139 pagesHistory of MathematicsMarinella TipoNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration Element BuilderDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration Element BuilderFelix ZununNo ratings yet
- AD8561Document11 pagesAD8561ΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- 5g Filter Saw-BawDocument13 pages5g Filter Saw-BawWilliamNo ratings yet
- 2020 JPJC H2 Chem Prelim Paper 4 QP - Final PDFDocument19 pages2020 JPJC H2 Chem Prelim Paper 4 QP - Final PDFchuasioklengNo ratings yet
- Centrifuge Modeling of Laterally Loaded Pile Groups in Improved Soft ClayDocument13 pagesCentrifuge Modeling of Laterally Loaded Pile Groups in Improved Soft ClayRizky SanadiNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Three Typical Cantilever Scaffold Supporting SystemsDocument18 pagesComparative Analysis of Three Typical Cantilever Scaffold Supporting SystemsEbrahimAbuZaidNo ratings yet
- Measuring and Monitoring The Efficiency of Central Chiller PlantsDocument14 pagesMeasuring and Monitoring The Efficiency of Central Chiller PlantsAqilaAndiNo ratings yet
- Screw-Jack - Mechanical Engineering AssignmentDocument25 pagesScrew-Jack - Mechanical Engineering AssignmentMorteza ShakerienNo ratings yet
Describe AC DC
Describe AC DC
Uploaded by
Nancy NursiamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Describe AC DC
Describe AC DC
Uploaded by
Nancy NursiamCopyright:
Available Formats
Name : Hadrian Anwar
NIM : 221321010
Class : 1A-TLI
Describe about Alternating Current and Direct Current and explain the differences?
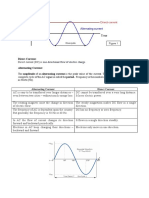
Alternating Current
Alternating Current is the type of electric current whose magnitude changes continuously and direction
changes periodically is known as alternating current or AC. In practice, the alternating current is produced by
alternating voltage source such as alternator or AC generator, etc.
The waveform of alternating current (AC) is shown in Figure, In case of AC, the total amount of time
taken by a waveform of alternating current to itself is known as time period of the AC waveform. The rate at
which the waveform repeats itself, i.e. the number of cycle complete in one second, is known as frequency of
the AC waveform.
Direct Current
Direct Current is the type of electric current whose magnitude does not change with the time and flows
only in one direction (i.e. has unidirectional flow) is known as direct current or DC. Therefore, DC has a
constant magnitude and direction. Consequently, the frequency of DC is zero.
he waveform of the DC is shown in Figure. The DC is widely used in electronic device such as
computers, mobiles, laptops, toys, etc. The DC is obtained from battery, cell, DC generators and rectifiers (by
converting AC into DC).
Difference between AC and DC
Parameter Alternating Current Direct Current
Definition The type of electric current The types of electric current
in whose magnitude changes whose magnitude and
continuously and direction direction does not change
with time is known as direct
changes periodically is
current (DC).
known as alternating current
(AC).
Direction of flow of charge In case of alternating In case of direct current,
(electrons) current, the flow of electrons flow of electrons takes place
is bidirectional, i.e. electrons in only forward direction.
flow in both forward and Thus, the flow of electrons
backward direction. is unidirectiona
Types Alternating current may be Generally, the direct current
of various types based on is of two types: constant DC
the waveform such as and pulsating DC.
sinusoidal, triangular,
square, trapezoidal, etc.
Frequency AC has a specific frequency. The frequency of DC is
In practice, the frequency of zero.
AC is 50 Hz or 60 Hz.
Magnitude The magnitude of The direct current has a
alternating current changes constant magnitude, i.e. it
continuously. does not change with time.
Direct of current & polarity The alternating current The direct current always
flows in both directions flows from positive to
(forward and reverse), thus negative. Hence, polarity
polarity cannot be marking is possible in case
mentioned in the circuit. of DC.
Types of loads For alternating current, there DC load includes only
are three types of loads, i.e. resistive load.
resistive load, inductive load
and capacitive load.
Opposition to current The opposition to flow of For DC, the opposition
flow alternating current offered offered by the circuit is
by the circuit is called termed as resistance.
impedance.
Source AC is obtained from AC The sources of DC are DC
generators or alternators. generators, battery, solar
cell, etc.
Transmission AC can be transmitted over The transmission of DC is
long distances with a few more efficient than AC and
losses. it can be transmitted over
long distances with
negligible losses.
Use of Transformer With AC, a transformer can With DC, transformer does
be used for increasing and not work.
decreasing the voltage
levels.
Power factor Power factor of a circuit The power factor of circuit
with AC lies between 0 and with DC always remains
1. unity, i.e. 1.
Applications AC is used to operate DC is used in laptops,
domestic & commercial mobiles, electronics devices,
appliances like fan, light, toys, industrial processes
fridge, etc. and industrial like electrolysis, etc.
loads like induction motors,
etc.
You might also like
- Alternating Current and Direct CurrentDocument7 pagesAlternating Current and Direct CurrentEllen Jane Cantuba GuardianNo ratings yet
- Ac DCDocument12 pagesAc DCCatherineNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Ac and DC CurrentsDocument32 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Ac and DC CurrentsMohit TyagiNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current (A.C.)Document6 pagesAlternating Current (A.C.)Jonathan ThomasNo ratings yet
- Alternative Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)Document4 pagesAlternative Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)MonirNo ratings yet
- InvertersDocument18 pagesInvertersSolar - Marketing/CELNo ratings yet
- DC SYSTEM by Oli Ullah KhanDocument67 pagesDC SYSTEM by Oli Ullah KhanOliullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2 D.C & A.CDocument3 pagesLesson Plan 2 D.C & A.CHaider RasheedNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Alternating CurrentDocument23 pagesDifference Between Alternating Currentabhi_akNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument3 pagesRectifierTina ErinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 1.0 Fundamental of AC TheoryDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 2 1.0 Fundamental of AC TheoryMUHAMMAD ALIFF DANIAL RAZMINo ratings yet
- Ac Vs DCDocument2 pagesAc Vs DCapi-296499245No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 1.0 Fundamental of AC TheoryDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 2 1.0 Fundamental of AC TheoryfahmiNo ratings yet
- Ac DCDocument3 pagesAc DCSachin NowalNo ratings yet
- Ac DCDocument28 pagesAc DCPreet BassiNo ratings yet
- Unit-II Beee Ac-I NewDocument19 pagesUnit-II Beee Ac-I NewParikshit SinghNo ratings yet
- AC vs. DC (Alternating Current vs. Direct Current) : Comparison ChartDocument2 pagesAC vs. DC (Alternating Current vs. Direct Current) : Comparison Chartmohamed jamaNo ratings yet
- Phy3 Chapter1Document26 pagesPhy3 Chapter1kokoh20No ratings yet
- Alternating Current and Direct Current PDFDocument5 pagesAlternating Current and Direct Current PDFHafiz HamzaNo ratings yet
- Direct Current and Alternating CurrentDocument4 pagesDirect Current and Alternating CurrentYuva RajNo ratings yet
- Chap 31 PDFDocument11 pagesChap 31 PDFJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 DC Circuits Electrical Engineering Is The Field of Engineering That Generally Deals With The StudyDocument60 pagesUnit 1 DC Circuits Electrical Engineering Is The Field of Engineering That Generally Deals With The StudyAayush SinghNo ratings yet
- What Is Alternating CurrentDocument49 pagesWhat Is Alternating CurrentRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 DC Circuits Electrical Engineering Is The Field of Engineering That Generally Deals With The StudyDocument60 pagesUnit 1 DC Circuits Electrical Engineering Is The Field of Engineering That Generally Deals With The StudyAtharv BhedaNo ratings yet
- Comparision of Ac & DCDocument11 pagesComparision of Ac & DCdevshakya885No ratings yet
- Direct Current Only Flows in One Direction. Alternating Current Changes Direction PeriodicallyDocument1 pageDirect Current Only Flows in One Direction. Alternating Current Changes Direction PeriodicallyCarl Justine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document17 pagesChapter 9abcunaNo ratings yet
- AC Vs DCDocument3 pagesAC Vs DCKhushi YadavNo ratings yet
- 12 Chapter 10 Alternating CurrentDocument39 pages12 Chapter 10 Alternating CurrentAhmad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Circuits Review P1Document103 pagesCircuits Review P1José CastilloNo ratings yet
- AC-Circuits Stud PDFDocument22 pagesAC-Circuits Stud PDFPrince PersiaNo ratings yet
- Activity4 Ac&Dc Gacosta NicoleDocument8 pagesActivity4 Ac&Dc Gacosta NicolenicsNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة 2022-11-23 في 9.08.03 ص PDFDocument99 pagesلقطة شاشة 2022-11-23 في 9.08.03 ص PDFsajjad aakulNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument16 pagesBasic ElectronicsMøhamed Abdel FattahNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2-Electricity and MagnesiumDocument24 pagesUNIT 2-Electricity and MagnesiumAar PeeNo ratings yet
- 14 - Current - Electricity - Revision - Notes - by Neet Topper.Document93 pages14 - Current - Electricity - Revision - Notes - by Neet Topper.Parnad BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- 1 - IntroductionDocument74 pages1 - IntroductionNikhil PatelNo ratings yet
- Ac & DC Current Used in PhysiotherapyDocument11 pagesAc & DC Current Used in PhysiotherapyAniket67% (3)
- Ac & DC CurrentDocument11 pagesAc & DC CurrentAniketNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current - Definition, Working Principle, AC GeneratorDocument22 pagesAlternating Current - Definition, Working Principle, AC GeneratorJatin VermaNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Current StudyDocument6 pagesVoltage and Current Studyshyam ubaleNo ratings yet
- L3-Principle of ElectricDocument66 pagesL3-Principle of ElectricIzzah AfiqahNo ratings yet
- AC-and-DC Grade 9 1st QuarterDocument46 pagesAC-and-DC Grade 9 1st QuarterXian DorojaNo ratings yet
- Direct CurrentDocument1 pageDirect CurrentShra 1537No ratings yet
- Direct CurrentDocument1 pageDirect CurrentShehzadi KhanNo ratings yet
- NIKHILDocument3 pagesNIKHILshwetayadav9323No ratings yet
- Comparision of Ac & DCDocument11 pagesComparision of Ac & DCdevshakya885No ratings yet
- Principle of ElectricDocument66 pagesPrinciple of ElectricSyahmi FadziNo ratings yet
- Electricity 4Document17 pagesElectricity 4AdelheidAlNo ratings yet
- ICP AssignmentDocument7 pagesICP Assignmentmeesamali163No ratings yet
- Ac Vs DCDocument8 pagesAc Vs DCapi-295907196No ratings yet
- Complete DC Circuit NotesDocument59 pagesComplete DC Circuit NotesIsha chandravanshiNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuestionsEngr Muhammad Faisal YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Direct Current Alternating Current Battery ElectronicDocument1 pageDirect Current Alternating Current Battery ElectronicJitendra PandeyNo ratings yet
- Why DC Current Is Not Used in HomesDocument6 pagesWhy DC Current Is Not Used in HomesalokNo ratings yet
- Circuit Variables and Elements: A. S. M. BadrudduzaDocument45 pagesCircuit Variables and Elements: A. S. M. BadrudduzaDr-Eng Amir ElsafraweyNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsDocument14 pagesAC CircuitsShiva Sankar BeharaNo ratings yet
- DC AnalysisDocument9 pagesDC Analysisunotjarikandetu32No ratings yet
- Wa0013.Document8 pagesWa0013.Roshan rajNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of 5-AMINOTETRAZOLE - PrepChemcomDocument3 pagesSynthesis of 5-AMINOTETRAZOLE - PrepChemcomxcvNo ratings yet
- Gaurav Singh - Equilibrium of Parallel Forces and MomentsDocument13 pagesGaurav Singh - Equilibrium of Parallel Forces and Momentsgaurav singhNo ratings yet
- CANcaseXL Manual enDocument38 pagesCANcaseXL Manual enHemanth RasineniNo ratings yet
- 1.6.1 Packet Tracer - Implement A Small NetworkDocument6 pages1.6.1 Packet Tracer - Implement A Small NetworkCecilia SánchezNo ratings yet
- Din 2458Document0 pagesDin 2458student_blNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall CalculationDocument1 pageRetaining Wall CalculationNurmuliana Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Ukmt 2009 Junior Math OlympiadDocument4 pagesUkmt 2009 Junior Math OlympiadSadi SnmzNo ratings yet
- Name - Aryan Gupta Reg. No. 199301088 Section - B: Ans.1) A. Rabin Karp String Matching Algorithm CodeDocument7 pagesName - Aryan Gupta Reg. No. 199301088 Section - B: Ans.1) A. Rabin Karp String Matching Algorithm CodebruhNo ratings yet
- Iso 15809Document15 pagesIso 15809Manoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Xc22B Preset Counter Operating Instructions: Terminal Connections SpecificationsDocument1 pageXc22B Preset Counter Operating Instructions: Terminal Connections SpecificationsPasindu PriyankaraNo ratings yet
- 2017 2018 PROJECT AN AND 4fs FormsDocument3 pages2017 2018 PROJECT AN AND 4fs FormsDaaarls100% (1)
- Big English 2 - Video Activity - UNIT 1Document3 pagesBig English 2 - Video Activity - UNIT 1zelindaaNo ratings yet
- NG300 ESales Spec SheetDocument2 pagesNG300 ESales Spec SheetSamrandNo ratings yet
- Innovations in Derivatives MarketsDocument446 pagesInnovations in Derivatives Marketsshrikantmsd100% (1)
- Jmo 2004Document2 pagesJmo 2004Dr Shyam Sundar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- HDTVandFiberProductsCatalog 2013Document9 pagesHDTVandFiberProductsCatalog 2013vitoriacunha70% (1)
- What Is Optical Power BudgetDocument6 pagesWhat Is Optical Power BudgetAmir SalahNo ratings yet
- OIR Test Part 1Document25 pagesOIR Test Part 1Avanindra Nayak100% (1)
- DKK1413 - Chapter 04-1Document37 pagesDKK1413 - Chapter 04-1Salini ShaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Analysis of Vacuum Evacuation in Viscous Flow and Its ApplicationsDocument7 pagesTheoretical Analysis of Vacuum Evacuation in Viscous Flow and Its ApplicationsMansi Shah ShroffNo ratings yet
- History of MathematicsDocument139 pagesHistory of MathematicsMarinella TipoNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration Element BuilderDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration Element BuilderFelix ZununNo ratings yet
- AD8561Document11 pagesAD8561ΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- 5g Filter Saw-BawDocument13 pages5g Filter Saw-BawWilliamNo ratings yet
- 2020 JPJC H2 Chem Prelim Paper 4 QP - Final PDFDocument19 pages2020 JPJC H2 Chem Prelim Paper 4 QP - Final PDFchuasioklengNo ratings yet
- Centrifuge Modeling of Laterally Loaded Pile Groups in Improved Soft ClayDocument13 pagesCentrifuge Modeling of Laterally Loaded Pile Groups in Improved Soft ClayRizky SanadiNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Three Typical Cantilever Scaffold Supporting SystemsDocument18 pagesComparative Analysis of Three Typical Cantilever Scaffold Supporting SystemsEbrahimAbuZaidNo ratings yet
- Measuring and Monitoring The Efficiency of Central Chiller PlantsDocument14 pagesMeasuring and Monitoring The Efficiency of Central Chiller PlantsAqilaAndiNo ratings yet
- Screw-Jack - Mechanical Engineering AssignmentDocument25 pagesScrew-Jack - Mechanical Engineering AssignmentMorteza ShakerienNo ratings yet