Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsActin Cytoskeleton Alterations in Podocytes
Actin Cytoskeleton Alterations in Podocytes
Uploaded by
Calvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaThis document summarizes recent research on targeting the actin cytoskeleton via dynamin as a potential therapy for chronic kidney disease (CKD). The research found that dynamin regulates podocyte structure and function by binding actin filaments and influencing actin dynamics. A small molecule called Bis-T-23 was found to promote actin-dependent dynamin oligomerization, which induced actin polymerization and improved podocyte injury in mouse and zebrafish models of CKD. Administration of Bis-T-23 reduced proteinuria and protected against CKD in multiple animal models, demonstrating that dynamin oligomerization is a druggable target that could be a novel therapeutic approach for CKD. However, B
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- A Practical Approach To Cardiac Anesthesia-Lippincot - Wolters Kluwer (2012)Document1,677 pagesA Practical Approach To Cardiac Anesthesia-Lippincot - Wolters Kluwer (2012)ElenaCondratscribdNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial AgentsDocument31 pagesAntibacterial AgentsdragajojicNo ratings yet
- Skeletal MuscleDocument72 pagesSkeletal Musclekiedd_0475% (4)
- Cell Bio Exam 2 Lecure QuizzesDocument42 pagesCell Bio Exam 2 Lecure QuizzesHafiza Dia Islam100% (4)
- Handbook of Meat ProcessingDocument584 pagesHandbook of Meat ProcessingNguyễn Quang93% (15)
- CisplatinDocument15 pagesCisplatinBrantas Pra AzariNo ratings yet
- Use of CisplatinDocument14 pagesUse of CisplatinsmijatovicibissNo ratings yet
- 5 Azacytidine Treatment Reorganizes Genomic Histone Modification PatternsDocument13 pages5 Azacytidine Treatment Reorganizes Genomic Histone Modification PatternsTiago TorresNo ratings yet
- Cisplatin Cause NephrotoxicityDocument11 pagesCisplatin Cause NephrotoxicityZiRong TsengNo ratings yet
- Vitiligo MetaloproteinasesDocument7 pagesVitiligo MetaloproteinasesJose Rodrigues JuniorNo ratings yet
- Intl Journal of Cancer - 2020 - Wang - The Roles of PAD2 and PAD4 Mediated Protein Citrullination Catalysis in CancersDocument10 pagesIntl Journal of Cancer - 2020 - Wang - The Roles of PAD2 and PAD4 Mediated Protein Citrullination Catalysis in CancersPrakash JhaNo ratings yet
- Epigenetics in Cancer: Review ArticleDocument12 pagesEpigenetics in Cancer: Review ArticleItzel MercadoNo ratings yet
- Vivarelli 2019Document4 pagesVivarelli 2019chloe1411No ratings yet
- Fang Dietary Polyphenols Comt 2007Document6 pagesFang Dietary Polyphenols Comt 2007Nufitbell NufitbellNo ratings yet
- Annsurg00068 0081Document9 pagesAnnsurg00068 0081alexanderniles2987No ratings yet
- Biochemical and Molecular Analysis in A Patient With The Severe Form of Hunter Syndrome After Bone Marrow TransplantationDocument5 pagesBiochemical and Molecular Analysis in A Patient With The Severe Form of Hunter Syndrome After Bone Marrow TransplantationmgNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa 2304194Document13 pagesNejmoa 2304194franck tolfoNo ratings yet
- Aguennouz Et Al 2016Document9 pagesAguennouz Et Al 2016Dário Talita SantanaNo ratings yet
- Suppression of Microtubule Dynamics by LY290181: Dulal Panda, Jai Pal Singh, and Leslie WilsonDocument7 pagesSuppression of Microtubule Dynamics by LY290181: Dulal Panda, Jai Pal Singh, and Leslie Wilsonapi-3806049No ratings yet
- Pathogenic Mechanisms in Lupus NephritisDocument10 pagesPathogenic Mechanisms in Lupus NephritisAndreea AdaNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Amyloidosis Lecture Slides - 2022-23Document42 pages1.4 Amyloidosis Lecture Slides - 2022-23dlee021129No ratings yet
- Cisplatin-Membrane Interactions and Their InfluencDocument15 pagesCisplatin-Membrane Interactions and Their InfluencTanysha PetrasheuskayaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Collagen IV On Neuroblastoma Cell Matrix-Related FunctionsDocument9 pagesEffects of Collagen IV On Neuroblastoma Cell Matrix-Related FunctionsdjackapNo ratings yet
- Truong Et Al-2017-Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part ADocument9 pagesTruong Et Al-2017-Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part ARoberto FernandesNo ratings yet
- Ferrara 2003Document8 pagesFerrara 2003Chaima DjabouNo ratings yet
- TriogenDocument30 pagesTriogenblain mathewNo ratings yet
- Chronic Stress InmmunityDocument9 pagesChronic Stress InmmunityAntonio CeverinoNo ratings yet
- Zebrafish Model of Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic MemoryDocument7 pagesZebrafish Model of Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic MemoryGabiich AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences: Haocheng Ao, Haichun Li, Xiujuan Zhao, Bingqian Liu, Lin LuDocument15 pagesLife Sciences: Haocheng Ao, Haichun Li, Xiujuan Zhao, Bingqian Liu, Lin LuPaoloMafaldoNo ratings yet
- Journal Neuro 6Document4 pagesJournal Neuro 6Arfiani Ika KusumawatiNo ratings yet
- tmp24F6 TMPDocument20 pagestmp24F6 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- FEBS Letters - 2013 - Joshi - High Glucose Modulates IL 6 Mediated Immune Homeostasis Through Impeding NeutrophilDocument6 pagesFEBS Letters - 2013 - Joshi - High Glucose Modulates IL 6 Mediated Immune Homeostasis Through Impeding NeutrophilFlávia PampolhaNo ratings yet
- Cisplatin in Anticancer DrugsDocument22 pagesCisplatin in Anticancer DrugswatiNo ratings yet
- Epigenetics and MicroRNAs.5Document6 pagesEpigenetics and MicroRNAs.5Saurabh GayaliNo ratings yet
- Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity PDFDocument10 pagesCisplatin Nephrotoxicity PDFChaa CiieCuiitt AfrNo ratings yet
- Piperlongumine Attenuates Il1induced Inflammatory Response in ChondrocytesDocument6 pagesPiperlongumine Attenuates Il1induced Inflammatory Response in ChondrocytesRiya CassendraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0945053X08005088 MainDocument1 page1 s2.0 S0945053X08005088 MainG. S.No ratings yet
- Surinder M. Singh, Swati Bandi, Dinen D. Shah, Geoffrey Armstrong, Krishna M. G. MallelaDocument9 pagesSurinder M. Singh, Swati Bandi, Dinen D. Shah, Geoffrey Armstrong, Krishna M. G. MallelaJon RumbleyNo ratings yet
- Steiner TDocument7 pagesSteiner TBabu MolinaNo ratings yet
- A Novel Modified Curcumin 2.24 Resolves Inflammation by Promoting M2 Macrophage PolarizationDocument14 pagesA Novel Modified Curcumin 2.24 Resolves Inflammation by Promoting M2 Macrophage PolarizationYeti MaretaNo ratings yet
- Shen 2018Document6 pagesShen 2018Arturo JiménezNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Phenotypic Variability in Niemann Pick Disease Type C (NPC) A Need For Precision MedicineDocument13 pagesUnderstanding The Phenotypic Variability in Niemann Pick Disease Type C (NPC) A Need For Precision MedicineLINA MARIA TRIANA MARINNo ratings yet
- 2000-Drug Development ResearchDocument10 pages2000-Drug Development ResearchEmerson CasaliNo ratings yet
- Arzuman 2014 BDocument14 pagesArzuman 2014 BMonikaNo ratings yet
- Balancing The Effect of Leukotrienes in Asthma: Clinical Implications of Basic ResearchDocument4 pagesBalancing The Effect of Leukotrienes in Asthma: Clinical Implications of Basic ResearchMauricio MerancioNo ratings yet
- Abeloff Clinical Oncology (Part 2)Document35 pagesAbeloff Clinical Oncology (Part 2)Emiliana LarionesiNo ratings yet
- Vaccines 06 00044 PDFDocument11 pagesVaccines 06 00044 PDFDrMohamed AssadawyNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumours: Origin and Molecular OncologyDocument14 pagesGastrointestinal Stromal Tumours: Origin and Molecular OncologywulanNo ratings yet
- Semiquantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis of Syndecan-1 and - 4 Messages in Cartilage and Cultured Chondrocytes From Osteoarthritic JointsDocument10 pagesSemiquantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis of Syndecan-1 and - 4 Messages in Cartilage and Cultured Chondrocytes From Osteoarthritic Jointsinvestbiz optionstarNo ratings yet
- IMM 265 - Galley Proof - 5may21 - VelikkakamDocument13 pagesIMM 265 - Galley Proof - 5may21 - VelikkakamSoraya Torres GazeNo ratings yet
- 2004 AngiogenesisDocument7 pages2004 AngiogenesisAnonymous n2DPWfNuNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin II Induces Calcium-Mediated Autophagy in Podocytes Through Enhancing Reactive Oxygen Species LevelsDocument9 pagesAngiotensin II Induces Calcium-Mediated Autophagy in Podocytes Through Enhancing Reactive Oxygen Species LevelsSatriyo Dwi SuryantoroNo ratings yet
- Nej M 200104053441404Document5 pagesNej M 200104053441404bennyrolandnababanNo ratings yet
- PIIS0085253817308104Document3 pagesPIIS0085253817308104Freddy Shanner Chávez VásquezNo ratings yet
- Inhibición de La Angiogénesis Tumoral Por CannabinoidesDocument16 pagesInhibición de La Angiogénesis Tumoral Por CannabinoidesjessicaNo ratings yet
- Gao 2015Document17 pagesGao 2015saherrodriguezNo ratings yet
- Huang Et Al 2010Document11 pagesHuang Et Al 2010tcardosodelgadoNo ratings yet
- Ijms 22 05654Document22 pagesIjms 22 05654Alber AvendañoNo ratings yet
- Communication: Nephrogenic Diabetes InsipidusDocument4 pagesCommunication: Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipiduslinda aprilNo ratings yet
- D-Penicillamine-induced Pemphigus Vulgaris in A Patient With Scleroderma-Rheumatoid Arthritis Overlap SyndromeDocument2 pagesD-Penicillamine-induced Pemphigus Vulgaris in A Patient With Scleroderma-Rheumatoid Arthritis Overlap SyndromeNiken Tri HapsariNo ratings yet
- Centrin Gene Disruption Impairs Stage-Specific Basal Body Duplication and Cell Cycle Progression in LeishmaniaDocument9 pagesCentrin Gene Disruption Impairs Stage-Specific Basal Body Duplication and Cell Cycle Progression in LeishmaniamclimacoNo ratings yet
- JASN2017Document16 pagesJASN2017Yuli KiaNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam AnswersDocument21 pagesPractice Exam AnswersGeraldine LeeNo ratings yet
- Administration of Fasudil, A ROCK Inhibitor, Attenuates Disease in Stirzaker2012Document6 pagesAdministration of Fasudil, A ROCK Inhibitor, Attenuates Disease in Stirzaker2012Calvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- An Open-Label Pilot Study of Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone in The Treatment of IgA Nephropathy at High Risk of Progression Zand2019Document8 pagesAn Open-Label Pilot Study of Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone in The Treatment of IgA Nephropathy at High Risk of Progression Zand2019Calvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Abatacept in B7-1-Positive Proteinuric Kidney DiseaseDocument10 pagesAbatacept in B7-1-Positive Proteinuric Kidney DiseaseCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Bab 3Document18 pagesBab 3Calvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- E-Poster Vit D FinalDocument1 pageE-Poster Vit D FinalCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Anestesi Pada Penyakit GinjalDocument16 pagesAnestesi Pada Penyakit GinjalCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Toksikologi Dan ToxindromeDocument29 pagesPengantar Toksikologi Dan ToxindromeCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Neuroscience: Basic and Clinical: Jose-Alberto Palma, Lucy Norcli Ffe-Kaufmann, Horacio KaufmannDocument11 pagesAutonomic Neuroscience: Basic and Clinical: Jose-Alberto Palma, Lucy Norcli Ffe-Kaufmann, Horacio KaufmannCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Transfer Patient Covid PDFDocument29 pagesTransfer Patient Covid PDFCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
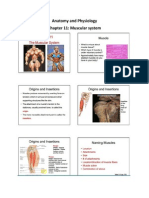
- Chapter Six The Muscular SystemDocument30 pagesChapter Six The Muscular SystemabiyotNo ratings yet
- CYTOSKELETON The Discovery of The Prokaryotic CytoskeletonDocument2 pagesCYTOSKELETON The Discovery of The Prokaryotic CytoskeletonYunn ZhangNo ratings yet
- Burger SteakDocument14 pagesBurger SteakMaureenValdezSeguiNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Practice 2Document15 pagesCell Biology Practice 2NgMinhHaiNo ratings yet
- Muscle MCQs Answer PDFDocument41 pagesMuscle MCQs Answer PDFHarun Mohamed50% (2)
- Lecture 4-Cell PolarityDocument52 pagesLecture 4-Cell PolarityFarrelita Nayla GhaniNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 S 13Document10 pagesExam 1 S 13Asad Javed MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Patho FEU PGI BCA Exit Exam May 2020Document34 pagesPatho FEU PGI BCA Exit Exam May 2020Sheryl Layne LaoNo ratings yet
- Cell Mechanics and Cellular EngineeringDocument570 pagesCell Mechanics and Cellular Engineeringlifejuice100% (1)
- Active Gel Physics: J. Prost, F. Jülicher and J-F. JoannyDocument7 pagesActive Gel Physics: J. Prost, F. Jülicher and J-F. JoannyokafoieahovanNo ratings yet
- NeurulationDocument6 pagesNeurulationnumannazir3276No ratings yet
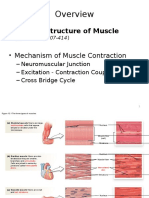
- Cellular Structure of Muscle: - Neuromuscular Junction - Excitation - Contraction Coupling - Cross Bridge CycleDocument44 pagesCellular Structure of Muscle: - Neuromuscular Junction - Excitation - Contraction Coupling - Cross Bridge CycleJon SteinerNo ratings yet
- Acta Cryst Sec F - 2013Document5 pagesActa Cryst Sec F - 2013Ajay RanaNo ratings yet
- BM 1 1 CytoskeletonDocument24 pagesBM 1 1 CytoskeletonSanthoshi Sadhanaa SankarNo ratings yet
- Robbins 10th Edition Chapter 1 McqsDocument6 pagesRobbins 10th Edition Chapter 1 McqsMaruf Raza DarubagiNo ratings yet
- The Sliding Filament TheoryDocument4 pagesThe Sliding Filament TheoryJinno VeldadNo ratings yet
- Ch. 10 and 6Document25 pagesCh. 10 and 6Bammary88909No ratings yet
- B21a7e87 1Document136 pagesB21a7e87 1Bogdan ZorilaNo ratings yet
- Thecytoskeleton PPTDocument11 pagesThecytoskeleton PPTseenu mohapatra100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Notes For Exam 3Document58 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Notes For Exam 3mike921gold100% (2)
- Physiology of Labor PDFDocument68 pagesPhysiology of Labor PDFAJ MendozaNo ratings yet
- NESDB2018 Program With PostersDocument8 pagesNESDB2018 Program With PostersJennifer Wong-DeyrupNo ratings yet
- Modulation of Skeletal Muscle Contraction by Myosin PhosphorylationDocument42 pagesModulation of Skeletal Muscle Contraction by Myosin PhosphorylationSanti Sanchez ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue SummaryDocument2 pagesMuscle Tissue SummaryLindenScholesNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Physiology: Susan V. Brooks Herzog Department of Physiology University of MichiganDocument32 pagesSkeletal Muscle Physiology: Susan V. Brooks Herzog Department of Physiology University of Michiganmanish1007No ratings yet
- Locomation and MovementDocument11 pagesLocomation and MovementsuryababaNo ratings yet
Actin Cytoskeleton Alterations in Podocytes
Actin Cytoskeleton Alterations in Podocytes
Uploaded by
Calvin Tanuwijaya Stick Bola0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThis document summarizes recent research on targeting the actin cytoskeleton via dynamin as a potential therapy for chronic kidney disease (CKD). The research found that dynamin regulates podocyte structure and function by binding actin filaments and influencing actin dynamics. A small molecule called Bis-T-23 was found to promote actin-dependent dynamin oligomerization, which induced actin polymerization and improved podocyte injury in mouse and zebrafish models of CKD. Administration of Bis-T-23 reduced proteinuria and protected against CKD in multiple animal models, demonstrating that dynamin oligomerization is a druggable target that could be a novel therapeutic approach for CKD. However, B
Original Description:
Original Title
Actin cytoskeleton alterations in podocytes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes recent research on targeting the actin cytoskeleton via dynamin as a potential therapy for chronic kidney disease (CKD). The research found that dynamin regulates podocyte structure and function by binding actin filaments and influencing actin dynamics. A small molecule called Bis-T-23 was found to promote actin-dependent dynamin oligomerization, which induced actin polymerization and improved podocyte injury in mouse and zebrafish models of CKD. Administration of Bis-T-23 reduced proteinuria and protected against CKD in multiple animal models, demonstrating that dynamin oligomerization is a druggable target that could be a novel therapeutic approach for CKD. However, B
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageActin Cytoskeleton Alterations in Podocytes
Actin Cytoskeleton Alterations in Podocytes
Uploaded by
Calvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaThis document summarizes recent research on targeting the actin cytoskeleton via dynamin as a potential therapy for chronic kidney disease (CKD). The research found that dynamin regulates podocyte structure and function by binding actin filaments and influencing actin dynamics. A small molecule called Bis-T-23 was found to promote actin-dependent dynamin oligomerization, which induced actin polymerization and improved podocyte injury in mouse and zebrafish models of CKD. Administration of Bis-T-23 reduced proteinuria and protected against CKD in multiple animal models, demonstrating that dynamin oligomerization is a druggable target that could be a novel therapeutic approach for CKD. However, B
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS
Nature Reviews Nephrology 11, 385 (2015); published online 12 May 2015; doi:10.1038/nrneph.2015.79
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
Actin cytoskeleton alterations in podocytes:
a therapeutic target for chronic kidney disease
Dysregulation of the actin cytoskeleton Control DMSO Bis-T-23
following podocyte injury underlies foot-
process effacement and progression of renal
injury in various forms of chronic kidney
disease (CKD). New research demonstrates
the therapeutic potential of repairing
actin cytoskeleton dynamics by targeting
dynamin oligomerization. “The fact that
dysregulation of the actin cytoskeleton is
Administration of Bis-T-23 but not DMSO improved glomerular histology in mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetic
a common downstream effect that occurs nephropathy. Permission obtained from Nature Publishing Group © Schiffer, M. et al. Nat. Med. doi:10.1038/nm.3843.
regardless of the original podocyte injury is
well established, and the potential benefit of in zebrafish and diverse rodent models In mice, intraperitoneal administration
targeting actin cytoskeleton dynamics has of podocyte injury. In line with previous of Bis-T-23 reduced lipopolysaccharide
occurred to us as well as to others,” explains studies, depletion of the zebrafish dynamin (LPS)-induced proteinuria. Similarly,
researcher Sanja Sever. “The finding that it homologue, Dyn2, resulted in gross administration of Bis-T-23 to cultured
is possible to target the actin cytoskeleton in morphological changes and reduced mouse podocytes reversed the LPS-
a specific manner by targeting dynamin in zebrafish lifespan. Foot-process effacement induced loss of stress fibers and focal
the whole organism is highly unexpected, was also observed, together with a decrease adhesions. To further investigate whether
and strongly suggests that pharmacological in circulating levels of green fluorescent dynamin oligomerization protects against
targets of dynamin have potential as novel protein-tagged vitamin D-binding protein podocyte injury, Sever and colleagues
therapeutics in CKD.” (eGFP–DBP), indicative of dysregulated generated mice expressing an inducible
The GTPase dynamin is best known for glomerular filtration. dynamin transgene with enhanced
its role in regulating clathrin-mediated Schiffer’s group then performed cross- propensity to oligomerize. These mice were
endocytosis, but more recently has been species rescue experiments using wild type protected from LPS-induced nephropathy.
recognized for its essential role in regulating and mutated dynamin isoforms to assess In addition, Bis-T-23 provided renal
podocyte structure and function by binding whether the zebrafish kidney phenotypes protection in various genetic models of
actin filaments and influencing actin were caused by loss of dynamin. “A cross- CKD and in mice with streptozotocin-
cytoskeleton dynamics. “We discovered an species rescue is a powerful tool to test the induced diabetes. “The fact that dynamin
unexpected and highly unusual property functional relevance of protein mutations oligomerization directly regulates the actin
of dynamin,” says Sever. “Not only could in vivo,” says Schiffer. Wild type rat and cytoskeleton and is a druggable target in
it directly interact with actin filaments human dynamin, and a mutant human the whole organism is a concept that most
but, when oligomerized into higher order dynamin with increased actin-dependent people will find hard to reconcile with their
structures, dynamin could induce de novo oligomerization, recovered levels of current view of dynamin’s role in the cell,”
actin polymerization, independent of any circulating eGFP–DBP. By contrast, notes Sever.
additional downstream effectors.” These expression of a mutant with decreased The researchers hope to eventually
findings led her to hypothesize that a small actin-dependent oligomerization translate their findings to patients with
molecule that could specifically promote (Dyn1K/E) or an oligomerization- CKD. “As Bis-T-23 is not suitable for use in
dynamin oligomerization might have a incompetent mutant (Dyn1I690K) did not humans, we are actively screening libraries
beneficial effect on injured podocytes have this effect, demonstrating that actin- to identify a compound with the same
via the ability of dynamin to promote dependent dynamin oligomerization is biochemical and biological properties that
actin polymerization. essential for proper glomerular filtration. can be used in patients,” says Sever.
To examine whether targeting the actin Administration of Bis-T-23 promoted
cytoskeleton via dynamin can ameliorate oligomerization of Dyn2 and restored Susan J. Allison
proteinuria and podocyte injury, Sever circulating eGFP–DBP levels in zebrafish
and Mario Schiffer collaborated to study expressing Dyn1K/E or Dyn1I690K, but only Original article Schiffer, M. et al. Pharmacological targeting
the effects of genetic manipulation and the in the presence of endogenous Dyn2, of actin-dependent dynamin oligomerization ameliorates
small molecule Bis-T-23, which promotes demonstrating that Bis-T-23 directly chronic kidney disease in diverse animal models. Nat. Med.
doi:10.1038/nm.3843
actin-dependent dynamin oligomerization, targets dynamin.
NATURE REVIEWS | NEPHROLOGY VOLUME 11 | JULY 2015
© 2015 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
You might also like
- A Practical Approach To Cardiac Anesthesia-Lippincot - Wolters Kluwer (2012)Document1,677 pagesA Practical Approach To Cardiac Anesthesia-Lippincot - Wolters Kluwer (2012)ElenaCondratscribdNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial AgentsDocument31 pagesAntibacterial AgentsdragajojicNo ratings yet
- Skeletal MuscleDocument72 pagesSkeletal Musclekiedd_0475% (4)
- Cell Bio Exam 2 Lecure QuizzesDocument42 pagesCell Bio Exam 2 Lecure QuizzesHafiza Dia Islam100% (4)
- Handbook of Meat ProcessingDocument584 pagesHandbook of Meat ProcessingNguyễn Quang93% (15)
- CisplatinDocument15 pagesCisplatinBrantas Pra AzariNo ratings yet
- Use of CisplatinDocument14 pagesUse of CisplatinsmijatovicibissNo ratings yet
- 5 Azacytidine Treatment Reorganizes Genomic Histone Modification PatternsDocument13 pages5 Azacytidine Treatment Reorganizes Genomic Histone Modification PatternsTiago TorresNo ratings yet
- Cisplatin Cause NephrotoxicityDocument11 pagesCisplatin Cause NephrotoxicityZiRong TsengNo ratings yet
- Vitiligo MetaloproteinasesDocument7 pagesVitiligo MetaloproteinasesJose Rodrigues JuniorNo ratings yet
- Intl Journal of Cancer - 2020 - Wang - The Roles of PAD2 and PAD4 Mediated Protein Citrullination Catalysis in CancersDocument10 pagesIntl Journal of Cancer - 2020 - Wang - The Roles of PAD2 and PAD4 Mediated Protein Citrullination Catalysis in CancersPrakash JhaNo ratings yet
- Epigenetics in Cancer: Review ArticleDocument12 pagesEpigenetics in Cancer: Review ArticleItzel MercadoNo ratings yet
- Vivarelli 2019Document4 pagesVivarelli 2019chloe1411No ratings yet
- Fang Dietary Polyphenols Comt 2007Document6 pagesFang Dietary Polyphenols Comt 2007Nufitbell NufitbellNo ratings yet
- Annsurg00068 0081Document9 pagesAnnsurg00068 0081alexanderniles2987No ratings yet
- Biochemical and Molecular Analysis in A Patient With The Severe Form of Hunter Syndrome After Bone Marrow TransplantationDocument5 pagesBiochemical and Molecular Analysis in A Patient With The Severe Form of Hunter Syndrome After Bone Marrow TransplantationmgNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa 2304194Document13 pagesNejmoa 2304194franck tolfoNo ratings yet
- Aguennouz Et Al 2016Document9 pagesAguennouz Et Al 2016Dário Talita SantanaNo ratings yet
- Suppression of Microtubule Dynamics by LY290181: Dulal Panda, Jai Pal Singh, and Leslie WilsonDocument7 pagesSuppression of Microtubule Dynamics by LY290181: Dulal Panda, Jai Pal Singh, and Leslie Wilsonapi-3806049No ratings yet
- Pathogenic Mechanisms in Lupus NephritisDocument10 pagesPathogenic Mechanisms in Lupus NephritisAndreea AdaNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Amyloidosis Lecture Slides - 2022-23Document42 pages1.4 Amyloidosis Lecture Slides - 2022-23dlee021129No ratings yet
- Cisplatin-Membrane Interactions and Their InfluencDocument15 pagesCisplatin-Membrane Interactions and Their InfluencTanysha PetrasheuskayaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Collagen IV On Neuroblastoma Cell Matrix-Related FunctionsDocument9 pagesEffects of Collagen IV On Neuroblastoma Cell Matrix-Related FunctionsdjackapNo ratings yet
- Truong Et Al-2017-Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part ADocument9 pagesTruong Et Al-2017-Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part ARoberto FernandesNo ratings yet
- Ferrara 2003Document8 pagesFerrara 2003Chaima DjabouNo ratings yet
- TriogenDocument30 pagesTriogenblain mathewNo ratings yet
- Chronic Stress InmmunityDocument9 pagesChronic Stress InmmunityAntonio CeverinoNo ratings yet
- Zebrafish Model of Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic MemoryDocument7 pagesZebrafish Model of Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic MemoryGabiich AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences: Haocheng Ao, Haichun Li, Xiujuan Zhao, Bingqian Liu, Lin LuDocument15 pagesLife Sciences: Haocheng Ao, Haichun Li, Xiujuan Zhao, Bingqian Liu, Lin LuPaoloMafaldoNo ratings yet
- Journal Neuro 6Document4 pagesJournal Neuro 6Arfiani Ika KusumawatiNo ratings yet
- tmp24F6 TMPDocument20 pagestmp24F6 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- FEBS Letters - 2013 - Joshi - High Glucose Modulates IL 6 Mediated Immune Homeostasis Through Impeding NeutrophilDocument6 pagesFEBS Letters - 2013 - Joshi - High Glucose Modulates IL 6 Mediated Immune Homeostasis Through Impeding NeutrophilFlávia PampolhaNo ratings yet
- Cisplatin in Anticancer DrugsDocument22 pagesCisplatin in Anticancer DrugswatiNo ratings yet
- Epigenetics and MicroRNAs.5Document6 pagesEpigenetics and MicroRNAs.5Saurabh GayaliNo ratings yet
- Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity PDFDocument10 pagesCisplatin Nephrotoxicity PDFChaa CiieCuiitt AfrNo ratings yet
- Piperlongumine Attenuates Il1induced Inflammatory Response in ChondrocytesDocument6 pagesPiperlongumine Attenuates Il1induced Inflammatory Response in ChondrocytesRiya CassendraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0945053X08005088 MainDocument1 page1 s2.0 S0945053X08005088 MainG. S.No ratings yet
- Surinder M. Singh, Swati Bandi, Dinen D. Shah, Geoffrey Armstrong, Krishna M. G. MallelaDocument9 pagesSurinder M. Singh, Swati Bandi, Dinen D. Shah, Geoffrey Armstrong, Krishna M. G. MallelaJon RumbleyNo ratings yet
- Steiner TDocument7 pagesSteiner TBabu MolinaNo ratings yet
- A Novel Modified Curcumin 2.24 Resolves Inflammation by Promoting M2 Macrophage PolarizationDocument14 pagesA Novel Modified Curcumin 2.24 Resolves Inflammation by Promoting M2 Macrophage PolarizationYeti MaretaNo ratings yet
- Shen 2018Document6 pagesShen 2018Arturo JiménezNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Phenotypic Variability in Niemann Pick Disease Type C (NPC) A Need For Precision MedicineDocument13 pagesUnderstanding The Phenotypic Variability in Niemann Pick Disease Type C (NPC) A Need For Precision MedicineLINA MARIA TRIANA MARINNo ratings yet
- 2000-Drug Development ResearchDocument10 pages2000-Drug Development ResearchEmerson CasaliNo ratings yet
- Arzuman 2014 BDocument14 pagesArzuman 2014 BMonikaNo ratings yet
- Balancing The Effect of Leukotrienes in Asthma: Clinical Implications of Basic ResearchDocument4 pagesBalancing The Effect of Leukotrienes in Asthma: Clinical Implications of Basic ResearchMauricio MerancioNo ratings yet
- Abeloff Clinical Oncology (Part 2)Document35 pagesAbeloff Clinical Oncology (Part 2)Emiliana LarionesiNo ratings yet
- Vaccines 06 00044 PDFDocument11 pagesVaccines 06 00044 PDFDrMohamed AssadawyNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumours: Origin and Molecular OncologyDocument14 pagesGastrointestinal Stromal Tumours: Origin and Molecular OncologywulanNo ratings yet
- Semiquantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis of Syndecan-1 and - 4 Messages in Cartilage and Cultured Chondrocytes From Osteoarthritic JointsDocument10 pagesSemiquantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis of Syndecan-1 and - 4 Messages in Cartilage and Cultured Chondrocytes From Osteoarthritic Jointsinvestbiz optionstarNo ratings yet
- IMM 265 - Galley Proof - 5may21 - VelikkakamDocument13 pagesIMM 265 - Galley Proof - 5may21 - VelikkakamSoraya Torres GazeNo ratings yet
- 2004 AngiogenesisDocument7 pages2004 AngiogenesisAnonymous n2DPWfNuNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin II Induces Calcium-Mediated Autophagy in Podocytes Through Enhancing Reactive Oxygen Species LevelsDocument9 pagesAngiotensin II Induces Calcium-Mediated Autophagy in Podocytes Through Enhancing Reactive Oxygen Species LevelsSatriyo Dwi SuryantoroNo ratings yet
- Nej M 200104053441404Document5 pagesNej M 200104053441404bennyrolandnababanNo ratings yet
- PIIS0085253817308104Document3 pagesPIIS0085253817308104Freddy Shanner Chávez VásquezNo ratings yet
- Inhibición de La Angiogénesis Tumoral Por CannabinoidesDocument16 pagesInhibición de La Angiogénesis Tumoral Por CannabinoidesjessicaNo ratings yet
- Gao 2015Document17 pagesGao 2015saherrodriguezNo ratings yet
- Huang Et Al 2010Document11 pagesHuang Et Al 2010tcardosodelgadoNo ratings yet
- Ijms 22 05654Document22 pagesIjms 22 05654Alber AvendañoNo ratings yet
- Communication: Nephrogenic Diabetes InsipidusDocument4 pagesCommunication: Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipiduslinda aprilNo ratings yet
- D-Penicillamine-induced Pemphigus Vulgaris in A Patient With Scleroderma-Rheumatoid Arthritis Overlap SyndromeDocument2 pagesD-Penicillamine-induced Pemphigus Vulgaris in A Patient With Scleroderma-Rheumatoid Arthritis Overlap SyndromeNiken Tri HapsariNo ratings yet
- Centrin Gene Disruption Impairs Stage-Specific Basal Body Duplication and Cell Cycle Progression in LeishmaniaDocument9 pagesCentrin Gene Disruption Impairs Stage-Specific Basal Body Duplication and Cell Cycle Progression in LeishmaniamclimacoNo ratings yet
- JASN2017Document16 pagesJASN2017Yuli KiaNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam AnswersDocument21 pagesPractice Exam AnswersGeraldine LeeNo ratings yet
- Administration of Fasudil, A ROCK Inhibitor, Attenuates Disease in Stirzaker2012Document6 pagesAdministration of Fasudil, A ROCK Inhibitor, Attenuates Disease in Stirzaker2012Calvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- An Open-Label Pilot Study of Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone in The Treatment of IgA Nephropathy at High Risk of Progression Zand2019Document8 pagesAn Open-Label Pilot Study of Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone in The Treatment of IgA Nephropathy at High Risk of Progression Zand2019Calvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Abatacept in B7-1-Positive Proteinuric Kidney DiseaseDocument10 pagesAbatacept in B7-1-Positive Proteinuric Kidney DiseaseCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Bab 3Document18 pagesBab 3Calvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- E-Poster Vit D FinalDocument1 pageE-Poster Vit D FinalCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Anestesi Pada Penyakit GinjalDocument16 pagesAnestesi Pada Penyakit GinjalCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Toksikologi Dan ToxindromeDocument29 pagesPengantar Toksikologi Dan ToxindromeCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Neuroscience: Basic and Clinical: Jose-Alberto Palma, Lucy Norcli Ffe-Kaufmann, Horacio KaufmannDocument11 pagesAutonomic Neuroscience: Basic and Clinical: Jose-Alberto Palma, Lucy Norcli Ffe-Kaufmann, Horacio KaufmannCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Transfer Patient Covid PDFDocument29 pagesTransfer Patient Covid PDFCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six The Muscular SystemDocument30 pagesChapter Six The Muscular SystemabiyotNo ratings yet
- CYTOSKELETON The Discovery of The Prokaryotic CytoskeletonDocument2 pagesCYTOSKELETON The Discovery of The Prokaryotic CytoskeletonYunn ZhangNo ratings yet
- Burger SteakDocument14 pagesBurger SteakMaureenValdezSeguiNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Practice 2Document15 pagesCell Biology Practice 2NgMinhHaiNo ratings yet
- Muscle MCQs Answer PDFDocument41 pagesMuscle MCQs Answer PDFHarun Mohamed50% (2)
- Lecture 4-Cell PolarityDocument52 pagesLecture 4-Cell PolarityFarrelita Nayla GhaniNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 S 13Document10 pagesExam 1 S 13Asad Javed MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Patho FEU PGI BCA Exit Exam May 2020Document34 pagesPatho FEU PGI BCA Exit Exam May 2020Sheryl Layne LaoNo ratings yet
- Cell Mechanics and Cellular EngineeringDocument570 pagesCell Mechanics and Cellular Engineeringlifejuice100% (1)
- Active Gel Physics: J. Prost, F. Jülicher and J-F. JoannyDocument7 pagesActive Gel Physics: J. Prost, F. Jülicher and J-F. JoannyokafoieahovanNo ratings yet
- NeurulationDocument6 pagesNeurulationnumannazir3276No ratings yet
- Cellular Structure of Muscle: - Neuromuscular Junction - Excitation - Contraction Coupling - Cross Bridge CycleDocument44 pagesCellular Structure of Muscle: - Neuromuscular Junction - Excitation - Contraction Coupling - Cross Bridge CycleJon SteinerNo ratings yet
- Acta Cryst Sec F - 2013Document5 pagesActa Cryst Sec F - 2013Ajay RanaNo ratings yet
- BM 1 1 CytoskeletonDocument24 pagesBM 1 1 CytoskeletonSanthoshi Sadhanaa SankarNo ratings yet
- Robbins 10th Edition Chapter 1 McqsDocument6 pagesRobbins 10th Edition Chapter 1 McqsMaruf Raza DarubagiNo ratings yet
- The Sliding Filament TheoryDocument4 pagesThe Sliding Filament TheoryJinno VeldadNo ratings yet
- Ch. 10 and 6Document25 pagesCh. 10 and 6Bammary88909No ratings yet
- B21a7e87 1Document136 pagesB21a7e87 1Bogdan ZorilaNo ratings yet
- Thecytoskeleton PPTDocument11 pagesThecytoskeleton PPTseenu mohapatra100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Notes For Exam 3Document58 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Notes For Exam 3mike921gold100% (2)
- Physiology of Labor PDFDocument68 pagesPhysiology of Labor PDFAJ MendozaNo ratings yet
- NESDB2018 Program With PostersDocument8 pagesNESDB2018 Program With PostersJennifer Wong-DeyrupNo ratings yet
- Modulation of Skeletal Muscle Contraction by Myosin PhosphorylationDocument42 pagesModulation of Skeletal Muscle Contraction by Myosin PhosphorylationSanti Sanchez ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue SummaryDocument2 pagesMuscle Tissue SummaryLindenScholesNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Physiology: Susan V. Brooks Herzog Department of Physiology University of MichiganDocument32 pagesSkeletal Muscle Physiology: Susan V. Brooks Herzog Department of Physiology University of Michiganmanish1007No ratings yet
- Locomation and MovementDocument11 pagesLocomation and MovementsuryababaNo ratings yet