Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 viewsCH7 The Termination of Contracts
CH7 The Termination of Contracts
Uploaded by
missalali3Contracts can terminate in several ways:
1. By performance or agreement of the parties when both sides fulfill their obligations.
2. By mutual agreement of the parties to end it early through rescission, novation, or accord and satisfaction.
3. Through operation of law if an unforeseen event makes performance impossible, or if one party goes bankrupt or the statute of limitations expires.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Discharge of A Contract Dr. KiworyDocument26 pagesDischarge of A Contract Dr. KiworyRwaki Donatus100% (1)
- Hermet E'zine - Issue No1Document39 pagesHermet E'zine - Issue No1Rubaphilos Salfluere100% (3)
- HARP Character Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesHARP Character Sheet PDFBarbarianYNo ratings yet
- GERDDocument11 pagesGERDJenadi BinartoNo ratings yet
- Part 4unit1Document2 pagesPart 4unit1tshering chodenNo ratings yet
- Termination of ContractDocument7 pagesTermination of ContractManikant SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Discharge of Contract FINALDocument6 pagesDischarge of Contract FINALRavikant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Contract Law By: Syed Aun Abbas Advocate LL.B, LL.M Discharge of ContractDocument4 pagesContract Law By: Syed Aun Abbas Advocate LL.B, LL.M Discharge of ContractAun NaqviNo ratings yet
- Discharge of Contract Unit 3Document5 pagesDischarge of Contract Unit 3Shubham Jain ModiNo ratings yet
- Blaw PPT 9Document25 pagesBlaw PPT 9kiran gosuNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument8 pagesDischarge of Contractareal alphaNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument7 pagesDischarge of ContractJyotsna AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Week 05Document48 pagesWeek 05Muhammad Taha SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Business Law Week 7 (Discharge of Contract)Document22 pagesBusiness Law Week 7 (Discharge of Contract)Saed MirasNo ratings yet
- C6 Discharge and Remedies of ContractDocument3 pagesC6 Discharge and Remedies of ContractShashwat JhaNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractsDocument14 pagesDischarge of ContractsAditya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Termination of ContractDocument28 pagesTermination of ContractsteNo ratings yet
- Div A - Roll No. 31Document5 pagesDiv A - Roll No. 31Krish JainNo ratings yet
- Discharge of Contracts and Remedies For Breach of Contract Discharge of Contracts - Meaning and DefinitionDocument12 pagesDischarge of Contracts and Remedies For Breach of Contract Discharge of Contracts - Meaning and DefinitionTitus ClementNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document12 pagesUnit 2tanakamuzira20No ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument63 pagesDischarge of ContractEldard KafulaNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument15 pagesDischarge of ContractVikram DevilNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument13 pagesDischarge of ContractVaibhav BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Business Regulations Notes: Elements of A ContractDocument19 pagesBusiness Regulations Notes: Elements of A ContractFa DreamsNo ratings yet
- Introduce A Valid Contract With The Modes of Termination and Possible Legal Remedies To ItDocument7 pagesIntroduce A Valid Contract With The Modes of Termination and Possible Legal Remedies To ItsagunNo ratings yet
- Contract Law in PakistanDocument7 pagesContract Law in PakistanSyeda Sana AliNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Ways in Which A Contract Can Be Discharged? Describe These Ways in Details.Document3 pagesWhat Are The Different Ways in Which A Contract Can Be Discharged? Describe These Ways in Details.sunnykapoor757% (7)
- Legal Aspects of Business Notes 5 SemDocument17 pagesLegal Aspects of Business Notes 5 SemOm RathNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument4 pagesDischarge of Contractgoon baboonNo ratings yet
- The Law of Contracts Forms A Substantial Part of Our Various Relationships That Can Have Some Sort of Influence Over Us On An Almost Daily BasisDocument4 pagesThe Law of Contracts Forms A Substantial Part of Our Various Relationships That Can Have Some Sort of Influence Over Us On An Almost Daily BasisNarmatha Mani MaranNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument12 pagesDischarge of ContractlakshamuNo ratings yet
- Business Law Chapter-3Document3 pagesBusiness Law Chapter-3Gita KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- Construction Contract Law - Discharge of Contract and RemediesDocument37 pagesConstruction Contract Law - Discharge of Contract and RemediesWilliam TongNo ratings yet
- 2.contract LawDocument28 pages2.contract LawShafiq ShajaNo ratings yet
- Business Law AssignmentDocument3 pagesBusiness Law AssignmentShaikh IrzamNo ratings yet
- FinaDocument10 pagesFinaAnena AlbrightNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Performance and Discharge of ContractDocument17 pagesChapter 9 Performance and Discharge of ContractSahil PatekarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Performance and Discharge of ContractDocument17 pagesChapter 9 Performance and Discharge of Contract0412Payal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Modes of Discharge of ContractDocument5 pagesModes of Discharge of ContractAhsan butt100% (1)
- Lahore Garrison UniversityDocument6 pagesLahore Garrison UniversityAnonymous vVUSLoGKygNo ratings yet
- Example: A Is Indebted To B and B To C. by Mutual Agreement B'C Debt To C and A's Debt To B Is Cancelled and C Accepts A As His DebtorDocument4 pagesExample: A Is Indebted To B and B To C. by Mutual Agreement B'C Debt To C and A's Debt To B Is Cancelled and C Accepts A As His DebtorMd Rifat MotalebNo ratings yet
- DISCHARGE OF CONTRACT-notesDocument7 pagesDISCHARGE OF CONTRACT-notesPremalatha JNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Discharge and BreachDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - Discharge and Breachdeepika vettikuntlaNo ratings yet
- Lecture2022 Lecture14A - Termination - of - ObligationsDocument17 pagesLecture2022 Lecture14A - Termination - of - ObligationsJacksonVanHerdenAlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument14 pagesDischarge of ContractUmar Shabir BaigNo ratings yet
- FinlTypes of ContractsDocument27 pagesFinlTypes of ContractsYatin MundejaNo ratings yet
- Business Law - Unit1Document13 pagesBusiness Law - Unit1DrKhushboo KumarNo ratings yet
- Discharge of A ContractDocument34 pagesDischarge of A ContractApm MabulaNo ratings yet
- Presentation ON: Discharge of ContractDocument15 pagesPresentation ON: Discharge of ContractnimmyjoeNo ratings yet
- Assignment Set 1 Mb0035 Legal Aspects of Business 1. ExplainDocument17 pagesAssignment Set 1 Mb0035 Legal Aspects of Business 1. Explainnsmu83860% (5)
- Discharge of Contracts: Discharge by Performance (Section 39-55)Document24 pagesDischarge of Contracts: Discharge by Performance (Section 39-55)LegionalbladeNo ratings yet
- Various Modes of Discharging of A Contract Various Modes of Discharging of A ContractDocument5 pagesVarious Modes of Discharging of A Contract Various Modes of Discharging of A ContractIranzi Fabrice100% (7)
- Termination or Discharge of ContractsDocument3 pagesTermination or Discharge of ContractsKawsar HossainNo ratings yet
- Discharge of Contract FullDocument14 pagesDischarge of Contract FullNavneet ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Business Law Sp21 Bba 011Document5 pagesBusiness Law Sp21 Bba 011Ali ChampNo ratings yet
- CP-302 Additional Lessons - 21012019Document111 pagesCP-302 Additional Lessons - 21012019mohammad areebNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument18 pagesChapter TwoDemsew AdelahuNo ratings yet
- Business Law Final AssignmentDocument9 pagesBusiness Law Final AssignmentSyed Sheraz AliNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Slides (Upsa)Document31 pagesWeek 6 Slides (Upsa)BISMARK ANKUNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument10 pagesDischarge of Contractpradep100% (4)
- DetailDocument4 pagesDetail2023000130.mohammadNo ratings yet
- Dischargeofcontract NewDocument29 pagesDischargeofcontract NewSyeda Ayesha TabassumNo ratings yet
- Seci ModelDocument2 pagesSeci Modelmissalali3No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Knowledge ManagementDocument2 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To Knowledge Managementmissalali3No ratings yet
- CH5 CapacityDocument1 pageCH5 Capacitymissalali3No ratings yet
- CH3 AgreementDocument2 pagesCH3 Agreementmissalali3No ratings yet
- CH4 ConsiderationDocument1 pageCH4 Considerationmissalali3No ratings yet
- CH2 ContractDocument1 pageCH2 Contractmissalali3No ratings yet
- My Sexual Autobiography Vol 1Document218 pagesMy Sexual Autobiography Vol 1megan fisher50% (2)
- Iot Standardisation: Challenges, Perspectives and Solution: June 2018Document10 pagesIot Standardisation: Challenges, Perspectives and Solution: June 2018Iman MagzoubNo ratings yet
- A Case With Pancytopenia The Role of CytomorphologyDocument2 pagesA Case With Pancytopenia The Role of CytomorphologyFile TuyulNo ratings yet
- Synfocity 632 PDFDocument2 pagesSynfocity 632 PDFMizoram Presbyterian Church SynodNo ratings yet
- Customs of The TagalogsDocument14 pagesCustoms of The TagalogsACIO, STEPHANY G.No ratings yet
- Booking Report 11-18-2020Document2 pagesBooking Report 11-18-2020WCTV Digital Team0% (2)
- (Board Review Series) BRS Pathology-Lippincott Williams - Wilkins (2013)Document12 pages(Board Review Series) BRS Pathology-Lippincott Williams - Wilkins (2013)g.rainer2001No ratings yet
- Review of Mcpherson Strut Suspension (Courtesy of Science Direct)Document4 pagesReview of Mcpherson Strut Suspension (Courtesy of Science Direct)Srikar ChinmayaNo ratings yet
- Pilot Testing, Monitoring and Evaluating The Implementation of The CurriculumDocument34 pagesPilot Testing, Monitoring and Evaluating The Implementation of The CurriculumJoshua Dela Cruz Rogador100% (2)
- Customer Experience Director: Job DetailsDocument3 pagesCustomer Experience Director: Job DetailsEng. Mohammed MoazinNo ratings yet
- 2014 - Design Thinking Research - Building Innovation Eco-Systems PDFDocument254 pages2014 - Design Thinking Research - Building Innovation Eco-Systems PDFABDIEL ADRIAZOLA MURIELNo ratings yet
- Masters ThesisDocument61 pagesMasters ThesissampathdtNo ratings yet
- Alchemy Air Element Theoricus and The JoDocument41 pagesAlchemy Air Element Theoricus and The JoElena ENo ratings yet
- The Edict of MilanDocument7 pagesThe Edict of MilanDoha MansourNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan & ObjectivesDocument6 pagesLesson Plan & Objectivesapi-284227922No ratings yet
- JCR 2019 PDFDocument385 pagesJCR 2019 PDFpervezkanjuNo ratings yet
- The Neuroscience Joyful Education Judy Willis MDDocument6 pagesThe Neuroscience Joyful Education Judy Willis MDcecilitusNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab ManualDocument11 pagesBiochemistry Lab ManualShela MalubagNo ratings yet
- RS 1803 HFS BP Enterprise Artificial Intelligence (AI) Services 2018Document70 pagesRS 1803 HFS BP Enterprise Artificial Intelligence (AI) Services 2018pantmukulNo ratings yet
- Definition of Good GovernanceDocument3 pagesDefinition of Good GovernanceHaziq KhanNo ratings yet
- LOUIS PASTEUR & First Year at HarrowDocument4 pagesLOUIS PASTEUR & First Year at HarrowSaif UllahNo ratings yet
- Referat Mata KeratititsDocument28 pagesReferat Mata Keratititswidya melianitaNo ratings yet
- Process Control, Network Systems, and SCADADocument13 pagesProcess Control, Network Systems, and SCADASTNo ratings yet
- EDU Development of Malaysian EducationDocument47 pagesEDU Development of Malaysian EducationNabilFikriChumiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: AnswerDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: AnswerJoel DufaleNo ratings yet
- Online Bike Parts Store and Rental SystemDocument4 pagesOnline Bike Parts Store and Rental SystemriysNo ratings yet
- 4987-2007 Network of RaingaugeDocument7 pages4987-2007 Network of RaingaugeIshwari TiwariNo ratings yet
CH7 The Termination of Contracts
CH7 The Termination of Contracts
Uploaded by
missalali30 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageContracts can terminate in several ways:
1. By performance or agreement of the parties when both sides fulfill their obligations.
2. By mutual agreement of the parties to end it early through rescission, novation, or accord and satisfaction.
3. Through operation of law if an unforeseen event makes performance impossible, or if one party goes bankrupt or the statute of limitations expires.
Original Description:
Original Title
CH7 The Termination of contracts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentContracts can terminate in several ways:
1. By performance or agreement of the parties when both sides fulfill their obligations.
2. By mutual agreement of the parties to end it early through rescission, novation, or accord and satisfaction.
3. Through operation of law if an unforeseen event makes performance impossible, or if one party goes bankrupt or the statute of limitations expires.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageCH7 The Termination of Contracts
CH7 The Termination of Contracts
Uploaded by
missalali3Contracts can terminate in several ways:
1. By performance or agreement of the parties when both sides fulfill their obligations.
2. By mutual agreement of the parties to end it early through rescission, novation, or accord and satisfaction.
3. Through operation of law if an unforeseen event makes performance impossible, or if one party goes bankrupt or the statute of limitations expires.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
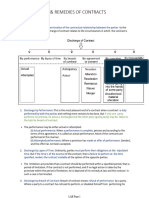
CH7 The Termination of contracts: Discharge
- Contracts end when:
one or both parties are discharged from any further obligation under the contract
one of the parties breached the contract
- Contract discharge:-
1. Discharge by performance
A. Degree of performance:
o If parties have fulfilled their duties under the terms of the contract as promised.
o Tender of performance: offer to perform the obligations of a contract
o Full performance: when both parties do all they agreed to do under a contract
o Substantial (essential) performance: performance in good faith of all the terms of
the contract except the small details of it.
B. Performance to personal satisfaction of another
o If the other person is satisfied with the performance
2. Agreement of parties
o By mutual agreement on the specified date the agreement ends in
o By a new agreement that will discharge or modify the obligations of one or both
parties under the original agreement. [rescission/novation/accord and satisfaction]
A. Rescission: The parties may mutually agree to call off the contract before either party
has performed and revert back to the position they were in prior to forming their
agreement. This is called legally rescind of the contract.
Rescind: to cancel a contract and return parties to the position that existed prior to
the making of the contract.
A. Novation(substitution of obligation): after entering into a contract the parties may agree
to release one party form the obligation to perform. A new third party would be
substituted who would then assume this obligation by means of a novation. The original
contract is actually terminated and a new contract formed between the remaining party
of the original contract and the new party.
A. Accord and satisfaction:
Accord: An agreement to accept performance different from that performance in
original contract.
Satisfaction: performance of the terms of a new agreement resulting from an accord.
3. Operation of law
A. Impossibility: an unforeseen event that prevents a party from performing a contract
as promised
destruction of the subject matter of the contract
death, serious illness or other incapacity in a personal services contract.
change in law.
B. Bankruptcy: A person who is hopelessly in debt
C. Statute of limitation: law fixing a time limit within which lawsuits must be started.
D. Material alteration of a written contract : An alteration is a material change in a
contract’s terms(rights or duties) by one party without the consent of the other
party.
4. Breach of contract
o Anticipatory
o Material
You might also like
- Discharge of A Contract Dr. KiworyDocument26 pagesDischarge of A Contract Dr. KiworyRwaki Donatus100% (1)
- Hermet E'zine - Issue No1Document39 pagesHermet E'zine - Issue No1Rubaphilos Salfluere100% (3)
- HARP Character Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesHARP Character Sheet PDFBarbarianYNo ratings yet
- GERDDocument11 pagesGERDJenadi BinartoNo ratings yet
- Part 4unit1Document2 pagesPart 4unit1tshering chodenNo ratings yet
- Termination of ContractDocument7 pagesTermination of ContractManikant SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Discharge of Contract FINALDocument6 pagesDischarge of Contract FINALRavikant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Contract Law By: Syed Aun Abbas Advocate LL.B, LL.M Discharge of ContractDocument4 pagesContract Law By: Syed Aun Abbas Advocate LL.B, LL.M Discharge of ContractAun NaqviNo ratings yet
- Discharge of Contract Unit 3Document5 pagesDischarge of Contract Unit 3Shubham Jain ModiNo ratings yet
- Blaw PPT 9Document25 pagesBlaw PPT 9kiran gosuNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument8 pagesDischarge of Contractareal alphaNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument7 pagesDischarge of ContractJyotsna AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Week 05Document48 pagesWeek 05Muhammad Taha SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Business Law Week 7 (Discharge of Contract)Document22 pagesBusiness Law Week 7 (Discharge of Contract)Saed MirasNo ratings yet
- C6 Discharge and Remedies of ContractDocument3 pagesC6 Discharge and Remedies of ContractShashwat JhaNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractsDocument14 pagesDischarge of ContractsAditya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Termination of ContractDocument28 pagesTermination of ContractsteNo ratings yet
- Div A - Roll No. 31Document5 pagesDiv A - Roll No. 31Krish JainNo ratings yet
- Discharge of Contracts and Remedies For Breach of Contract Discharge of Contracts - Meaning and DefinitionDocument12 pagesDischarge of Contracts and Remedies For Breach of Contract Discharge of Contracts - Meaning and DefinitionTitus ClementNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document12 pagesUnit 2tanakamuzira20No ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument63 pagesDischarge of ContractEldard KafulaNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument15 pagesDischarge of ContractVikram DevilNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument13 pagesDischarge of ContractVaibhav BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Business Regulations Notes: Elements of A ContractDocument19 pagesBusiness Regulations Notes: Elements of A ContractFa DreamsNo ratings yet
- Introduce A Valid Contract With The Modes of Termination and Possible Legal Remedies To ItDocument7 pagesIntroduce A Valid Contract With The Modes of Termination and Possible Legal Remedies To ItsagunNo ratings yet
- Contract Law in PakistanDocument7 pagesContract Law in PakistanSyeda Sana AliNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Ways in Which A Contract Can Be Discharged? Describe These Ways in Details.Document3 pagesWhat Are The Different Ways in Which A Contract Can Be Discharged? Describe These Ways in Details.sunnykapoor757% (7)
- Legal Aspects of Business Notes 5 SemDocument17 pagesLegal Aspects of Business Notes 5 SemOm RathNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument4 pagesDischarge of Contractgoon baboonNo ratings yet
- The Law of Contracts Forms A Substantial Part of Our Various Relationships That Can Have Some Sort of Influence Over Us On An Almost Daily BasisDocument4 pagesThe Law of Contracts Forms A Substantial Part of Our Various Relationships That Can Have Some Sort of Influence Over Us On An Almost Daily BasisNarmatha Mani MaranNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument12 pagesDischarge of ContractlakshamuNo ratings yet
- Business Law Chapter-3Document3 pagesBusiness Law Chapter-3Gita KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- Construction Contract Law - Discharge of Contract and RemediesDocument37 pagesConstruction Contract Law - Discharge of Contract and RemediesWilliam TongNo ratings yet
- 2.contract LawDocument28 pages2.contract LawShafiq ShajaNo ratings yet
- Business Law AssignmentDocument3 pagesBusiness Law AssignmentShaikh IrzamNo ratings yet
- FinaDocument10 pagesFinaAnena AlbrightNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Performance and Discharge of ContractDocument17 pagesChapter 9 Performance and Discharge of ContractSahil PatekarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Performance and Discharge of ContractDocument17 pagesChapter 9 Performance and Discharge of Contract0412Payal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Modes of Discharge of ContractDocument5 pagesModes of Discharge of ContractAhsan butt100% (1)
- Lahore Garrison UniversityDocument6 pagesLahore Garrison UniversityAnonymous vVUSLoGKygNo ratings yet
- Example: A Is Indebted To B and B To C. by Mutual Agreement B'C Debt To C and A's Debt To B Is Cancelled and C Accepts A As His DebtorDocument4 pagesExample: A Is Indebted To B and B To C. by Mutual Agreement B'C Debt To C and A's Debt To B Is Cancelled and C Accepts A As His DebtorMd Rifat MotalebNo ratings yet
- DISCHARGE OF CONTRACT-notesDocument7 pagesDISCHARGE OF CONTRACT-notesPremalatha JNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Discharge and BreachDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - Discharge and Breachdeepika vettikuntlaNo ratings yet
- Lecture2022 Lecture14A - Termination - of - ObligationsDocument17 pagesLecture2022 Lecture14A - Termination - of - ObligationsJacksonVanHerdenAlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument14 pagesDischarge of ContractUmar Shabir BaigNo ratings yet
- FinlTypes of ContractsDocument27 pagesFinlTypes of ContractsYatin MundejaNo ratings yet
- Business Law - Unit1Document13 pagesBusiness Law - Unit1DrKhushboo KumarNo ratings yet
- Discharge of A ContractDocument34 pagesDischarge of A ContractApm MabulaNo ratings yet
- Presentation ON: Discharge of ContractDocument15 pagesPresentation ON: Discharge of ContractnimmyjoeNo ratings yet
- Assignment Set 1 Mb0035 Legal Aspects of Business 1. ExplainDocument17 pagesAssignment Set 1 Mb0035 Legal Aspects of Business 1. Explainnsmu83860% (5)
- Discharge of Contracts: Discharge by Performance (Section 39-55)Document24 pagesDischarge of Contracts: Discharge by Performance (Section 39-55)LegionalbladeNo ratings yet
- Various Modes of Discharging of A Contract Various Modes of Discharging of A ContractDocument5 pagesVarious Modes of Discharging of A Contract Various Modes of Discharging of A ContractIranzi Fabrice100% (7)
- Termination or Discharge of ContractsDocument3 pagesTermination or Discharge of ContractsKawsar HossainNo ratings yet
- Discharge of Contract FullDocument14 pagesDischarge of Contract FullNavneet ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Business Law Sp21 Bba 011Document5 pagesBusiness Law Sp21 Bba 011Ali ChampNo ratings yet
- CP-302 Additional Lessons - 21012019Document111 pagesCP-302 Additional Lessons - 21012019mohammad areebNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument18 pagesChapter TwoDemsew AdelahuNo ratings yet
- Business Law Final AssignmentDocument9 pagesBusiness Law Final AssignmentSyed Sheraz AliNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Slides (Upsa)Document31 pagesWeek 6 Slides (Upsa)BISMARK ANKUNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument10 pagesDischarge of Contractpradep100% (4)
- DetailDocument4 pagesDetail2023000130.mohammadNo ratings yet
- Dischargeofcontract NewDocument29 pagesDischargeofcontract NewSyeda Ayesha TabassumNo ratings yet
- Seci ModelDocument2 pagesSeci Modelmissalali3No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Knowledge ManagementDocument2 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To Knowledge Managementmissalali3No ratings yet
- CH5 CapacityDocument1 pageCH5 Capacitymissalali3No ratings yet
- CH3 AgreementDocument2 pagesCH3 Agreementmissalali3No ratings yet
- CH4 ConsiderationDocument1 pageCH4 Considerationmissalali3No ratings yet
- CH2 ContractDocument1 pageCH2 Contractmissalali3No ratings yet
- My Sexual Autobiography Vol 1Document218 pagesMy Sexual Autobiography Vol 1megan fisher50% (2)
- Iot Standardisation: Challenges, Perspectives and Solution: June 2018Document10 pagesIot Standardisation: Challenges, Perspectives and Solution: June 2018Iman MagzoubNo ratings yet
- A Case With Pancytopenia The Role of CytomorphologyDocument2 pagesA Case With Pancytopenia The Role of CytomorphologyFile TuyulNo ratings yet
- Synfocity 632 PDFDocument2 pagesSynfocity 632 PDFMizoram Presbyterian Church SynodNo ratings yet
- Customs of The TagalogsDocument14 pagesCustoms of The TagalogsACIO, STEPHANY G.No ratings yet
- Booking Report 11-18-2020Document2 pagesBooking Report 11-18-2020WCTV Digital Team0% (2)
- (Board Review Series) BRS Pathology-Lippincott Williams - Wilkins (2013)Document12 pages(Board Review Series) BRS Pathology-Lippincott Williams - Wilkins (2013)g.rainer2001No ratings yet
- Review of Mcpherson Strut Suspension (Courtesy of Science Direct)Document4 pagesReview of Mcpherson Strut Suspension (Courtesy of Science Direct)Srikar ChinmayaNo ratings yet
- Pilot Testing, Monitoring and Evaluating The Implementation of The CurriculumDocument34 pagesPilot Testing, Monitoring and Evaluating The Implementation of The CurriculumJoshua Dela Cruz Rogador100% (2)
- Customer Experience Director: Job DetailsDocument3 pagesCustomer Experience Director: Job DetailsEng. Mohammed MoazinNo ratings yet
- 2014 - Design Thinking Research - Building Innovation Eco-Systems PDFDocument254 pages2014 - Design Thinking Research - Building Innovation Eco-Systems PDFABDIEL ADRIAZOLA MURIELNo ratings yet
- Masters ThesisDocument61 pagesMasters ThesissampathdtNo ratings yet
- Alchemy Air Element Theoricus and The JoDocument41 pagesAlchemy Air Element Theoricus and The JoElena ENo ratings yet
- The Edict of MilanDocument7 pagesThe Edict of MilanDoha MansourNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan & ObjectivesDocument6 pagesLesson Plan & Objectivesapi-284227922No ratings yet
- JCR 2019 PDFDocument385 pagesJCR 2019 PDFpervezkanjuNo ratings yet
- The Neuroscience Joyful Education Judy Willis MDDocument6 pagesThe Neuroscience Joyful Education Judy Willis MDcecilitusNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab ManualDocument11 pagesBiochemistry Lab ManualShela MalubagNo ratings yet
- RS 1803 HFS BP Enterprise Artificial Intelligence (AI) Services 2018Document70 pagesRS 1803 HFS BP Enterprise Artificial Intelligence (AI) Services 2018pantmukulNo ratings yet
- Definition of Good GovernanceDocument3 pagesDefinition of Good GovernanceHaziq KhanNo ratings yet
- LOUIS PASTEUR & First Year at HarrowDocument4 pagesLOUIS PASTEUR & First Year at HarrowSaif UllahNo ratings yet
- Referat Mata KeratititsDocument28 pagesReferat Mata Keratititswidya melianitaNo ratings yet
- Process Control, Network Systems, and SCADADocument13 pagesProcess Control, Network Systems, and SCADASTNo ratings yet
- EDU Development of Malaysian EducationDocument47 pagesEDU Development of Malaysian EducationNabilFikriChumiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: AnswerDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: AnswerJoel DufaleNo ratings yet
- Online Bike Parts Store and Rental SystemDocument4 pagesOnline Bike Parts Store and Rental SystemriysNo ratings yet
- 4987-2007 Network of RaingaugeDocument7 pages4987-2007 Network of RaingaugeIshwari TiwariNo ratings yet