Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BONE Uqs
BONE Uqs
Uploaded by
Aroosha JamshaidCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Principles of Bone GraftingDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Bone GraftingJayanth Perumal100% (2)
- Bone 5Document54 pagesBone 5Parikshit DhayalNo ratings yet
- Histology of Bone 2022Document30 pagesHistology of Bone 2022zahra nabilaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 22 Bone Physiology IDocument26 pagesLecture 22 Bone Physiology Ijurgen klein-WernerNo ratings yet
- BONE Healing Uii 24 April 2014Document38 pagesBONE Healing Uii 24 April 2014Taufiq HidayatNo ratings yet
- BONE (Histology)Document65 pagesBONE (Histology)fhfebriiNo ratings yet
- CH8 Bone: Medullary CavitiesDocument9 pagesCH8 Bone: Medullary Cavitiesdanny olulanaNo ratings yet
- Histology 8Document6 pagesHistology 8amirhsheikhiNo ratings yet
- Tereos - Structure of PresentationDocument72 pagesTereos - Structure of PresentationSumitNo ratings yet
- Bones: Defination: Bone Is Highly Vascular, Living, Constantly ChangingDocument21 pagesBones: Defination: Bone Is Highly Vascular, Living, Constantly ChangingMd Ahsanuzzaman PinkuNo ratings yet
- Alveolar BoneDocument8 pagesAlveolar BoneAsruni Ab GhaniNo ratings yet
- Lec3 TransesDocument7 pagesLec3 Transes4xwqm42hyrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Bones and JointsDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Bones and JointsJade Karen Lingo-lingoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument80 pagesSkeletal SystemElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of BoneDocument32 pagesPhysiology of BoneAnandhu GNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics and Biomaterials in Orthopedic SurgeryDocument11 pagesBiomechanics and Biomaterials in Orthopedic SurgeryManiventhan NachimuthuNo ratings yet
- Bone HistologyDocument56 pagesBone HistologyNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- Fracture Healing and BonegraftingDocument76 pagesFracture Healing and BonegraftingJio AmurNo ratings yet
- Bone Grafts BhanuDocument113 pagesBone Grafts BhanuBhanu Praseedha100% (1)
- BONEDocument4 pagesBONEvallecerajamaicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document3 pagesChapter 8Ella LagramaNo ratings yet
- BIOL3307 - Unit1Mod2 - Bone Growth & Repair1Document16 pagesBIOL3307 - Unit1Mod2 - Bone Growth & Repair1Ren StudyNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument14 pagesSkeletal SystemCharlize PalmaNo ratings yet
- Bone Tissue: OsteocytesDocument11 pagesBone Tissue: OsteocytesA18- Jessa Mae DayagNo ratings yet
- OssificationDocument40 pagesOssificationElena CristinaNo ratings yet
- Bone Histology & Few Notes About Bone BiomechanicsDocument48 pagesBone Histology & Few Notes About Bone BiomechanicsArvind ManikantanNo ratings yet
- Lec Activity6 Skeletal System CastroDocument8 pagesLec Activity6 Skeletal System CastropelielNo ratings yet
- Salter Bab 1-2Document30 pagesSalter Bab 1-2elizabeth angelinaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System (2015 - 06 - 09 20 - 43 - 48 Utc)Document120 pagesSkeletal System (2015 - 06 - 09 20 - 43 - 48 Utc)DiazNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 ANAPHY TransesDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 6 ANAPHY TransesHoly HaeinNo ratings yet
- Tortora Principles of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesTortora Principles of Anatomy and PhysiologybebeNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes On BonesDocument4 pagesAdditional Notes On Bonesmober jonNo ratings yet
- Handout - Bone Anatomy and Healing - Nlogo - HighDocument11 pagesHandout - Bone Anatomy and Healing - Nlogo - HighlevimacoNo ratings yet
- Kalsifikasi, Deposisi Dan Resorpsi TulangDocument40 pagesKalsifikasi, Deposisi Dan Resorpsi TulangrifkaNo ratings yet
- Bone ReviewerDocument7 pagesBone ReviewerClyde BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Bone Formation - Ossification 2 PDFDocument35 pagesBone Formation - Ossification 2 PDFalan100% (1)
- Bones As A Living Dynamic TissueDocument13 pagesBones As A Living Dynamic TissueSanish Basnet100% (1)
- 6 Skeletal SystemDocument8 pages6 Skeletal SystemmargaretNo ratings yet
- Alveolarbone Graftingand Reconstruction Procedurespriorto ImplantplacementDocument10 pagesAlveolarbone Graftingand Reconstruction Procedurespriorto ImplantplacementKranti PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- BONEDocument48 pagesBONEnivethaseshaNo ratings yet
- AN OVERVIEW OF BONE CELLS AND THEIR REGULATING FACTORS OF DIFFERENTIATION, Mohamed 2008Document9 pagesAN OVERVIEW OF BONE CELLS AND THEIR REGULATING FACTORS OF DIFFERENTIATION, Mohamed 2008Faizal Reza PahleviNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument14 pagesSkeletal SystemCharlize PalmaNo ratings yet
- MAXILLA and MANDIBLE (Alveolar Process)Document35 pagesMAXILLA and MANDIBLE (Alveolar Process)ANVI SHARMANo ratings yet
- 2020-2021 AP 1 Lecture 6b Skeletal System 1Document16 pages2020-2021 AP 1 Lecture 6b Skeletal System 1OscarJaiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal 6Document28 pagesSkeletal 6BSN-2F Neutral Axis SiazonNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Midterms-1Document65 pagesAnaphy Midterms-1kiann130405No ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Estimation of Content of Bone AshDocument18 pagesChemistry Project On Estimation of Content of Bone AshKim TaesiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument97 pagesSkeletal SystemFardzli MatjakirNo ratings yet
- Breeland Et Al., 2023Document6 pagesBreeland Et Al., 2023hamdaniamr21cNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Comia, Joshua Cyryll Habacon, Gabrielle AnneDocument56 pagesThe Skeletal System: Comia, Joshua Cyryll Habacon, Gabrielle Annegian habaconNo ratings yet
- Cartlage Bone 2012Document34 pagesCartlage Bone 2012Omar Ali AyoubkhanNo ratings yet
- Alveolar Bone DR DeepakDocument107 pagesAlveolar Bone DR DeepakDeepak Kumar100% (2)
- HO Chapter 6 Pharm 123Document5 pagesHO Chapter 6 Pharm 123malfoymidnight394No ratings yet
- 6 PATHO 3b Part 1 - Musculoskeletal IIA - Dr. Dy-LedesmaDocument12 pages6 PATHO 3b Part 1 - Musculoskeletal IIA - Dr. Dy-LedesmaBanana BananaNo ratings yet
- English 20.05.2020Document100 pagesEnglish 20.05.2020Bernythefly axcNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Bones and Joints Components of The Skeletal System: Long Bone StructuresDocument8 pagesSkeletal System: Bones and Joints Components of The Skeletal System: Long Bone StructurespangetkoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: CartilageDocument20 pagesSkeletal System: CartilageGrace PascualNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument123 pagesSkeletal SystemZekiah MagsayoNo ratings yet
- Histology of Bone DevelopmentDocument11 pagesHistology of Bone DevelopmentLaidy Aizahlyn Indoc AngodNo ratings yet
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionFrom EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionNo ratings yet
- Histology SlidesDocument32 pagesHistology SlidesAroosha JamshaidNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Central IncisorDocument17 pagesMandibular Central IncisorAroosha JamshaidNo ratings yet
- DENTINOGENESISDocument14 pagesDENTINOGENESISAroosha JamshaidNo ratings yet
- Compiled Reading Material For TBL (30-9-22)Document6 pagesCompiled Reading Material For TBL (30-9-22)Aroosha JamshaidNo ratings yet
- DentinDocument5 pagesDentinAroosha JamshaidNo ratings yet
- 4 19003572427424163 PDFDocument4 pages4 19003572427424163 PDFAwadhNo ratings yet
- 4 Classes of Connective TissueDocument4 pages4 Classes of Connective TissueJoanne GodezanoNo ratings yet
- Cap 22Document47 pagesCap 22Andreea AronNo ratings yet
- Hematologic SystemDocument81 pagesHematologic Systemseigelystic100% (23)
- Anticoagulant PresentationDocument29 pagesAnticoagulant Presentationrozha100% (2)
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemMaxwell C Jay KafwaniNo ratings yet
- Muscle: Gerald Dale Giron MD Department of Human Structural BiologyDocument23 pagesMuscle: Gerald Dale Giron MD Department of Human Structural BiologyMarx AsuncionNo ratings yet
- 14-16 Juli 2022, Jayapura I Post Test (Jawaban)Document10 pages14-16 Juli 2022, Jayapura I Post Test (Jawaban)Abdul Charis KonorasNo ratings yet
- Skripsi Fix YaDocument134 pagesSkripsi Fix YaSabrina Putri DewantiNo ratings yet
- Immune Thrombocytopenia Purpura: Clinical PathwayDocument6 pagesImmune Thrombocytopenia Purpura: Clinical PathwayAsterlyn ConiendoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Hematology 2 LectureDocument8 pagesWeek 1 - Hematology 2 LectureRubenne Miles ElagasNo ratings yet
- Trishla Chaturvedi Automated Blood Cell CounterDocument26 pagesTrishla Chaturvedi Automated Blood Cell CounterNidhi Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Bone MarrowDocument6 pagesBone MarrowKIPRUTO DENNISNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of FBC Part 3Document17 pagesInterpretation of FBC Part 3reuel nareshNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissuesDocument9 pagesMuscle Tissuesangelo beldaNo ratings yet
- Mylein SheathDocument5 pagesMylein SheathSwordNo ratings yet
- Measurement Barang DinginDocument39 pagesMeasurement Barang DinginW. HerlambangNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2013 - TissueDocument25 pagesLesson Plan 2013 - Tissuesonyblank100% (1)
- Mechanism of Blood Clotting Extensic Pathway Factors Affecting Blood ClottingDocument18 pagesMechanism of Blood Clotting Extensic Pathway Factors Affecting Blood ClottingRaunak TripathiNo ratings yet
- Cordlife BrochureDocument16 pagesCordlife BrochureMelodie YlaganNo ratings yet
- Hematology Quick Facts Part1 PDFDocument10 pagesHematology Quick Facts Part1 PDFJohn Rhel DenqueNo ratings yet
- Exchange Blood Transfusion 2Document15 pagesExchange Blood Transfusion 2Sarah100% (1)
- Hematology UQU 2022Document94 pagesHematology UQU 2022Elyas MehdarNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument21 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationAbdisalan hassanNo ratings yet
- Article: Pengaruh Terapi Pijat Refleksi Kaki Terhadap Penurunan Tekanan Darah Pada Pasien HipertensiDocument10 pagesArticle: Pengaruh Terapi Pijat Refleksi Kaki Terhadap Penurunan Tekanan Darah Pada Pasien HipertensiTP20AZaidan azharNo ratings yet
- Appendix I - Plant TissuesDocument24 pagesAppendix I - Plant TissuesAmeera ChaitramNo ratings yet
- Infographics III Blood Smear 27 07 2020Document1 pageInfographics III Blood Smear 27 07 2020MARIA AUBREY GOLIATNo ratings yet
- Emergency and Critical Care Procedures in Small AnimalsDocument9 pagesEmergency and Critical Care Procedures in Small AnimalsTessaNo ratings yet
- Isbb FC Part 3Document13 pagesIsbb FC Part 3Lynther Myle Arizo100% (1)
- Isoimmunization and Anemia RH IncompatibilityDocument2 pagesIsoimmunization and Anemia RH IncompatibilityAriaNo ratings yet
BONE Uqs
BONE Uqs
Uploaded by
Aroosha JamshaidOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BONE Uqs
BONE Uqs
Uploaded by
Aroosha JamshaidCopyright:
Available Formats
Bone
Q1). Draw and label organizational components of bone
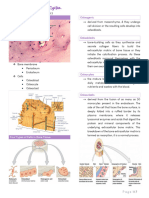
Q2).Draw, Label and explain the role of osteoclast in bone resorption
The osteoclasts are the bone resorption cells . The bone resorption occours through following process
1) Attachement of osteoclasts to mineralized surface of bone.
2) Creation of sealed acidic microenvoirnment through the action of the proton pump ,which
demineralizes bone and exposes the organic matrix
3) Degradation of exposed matrix by action of released enzymes such as acid phosphatase and
cathepsin B
4) Endocytosis at the ruffled border of organic degradation products
5) Translocation of degradation products in transport veshicles and extracellular release along
membrane opposite the ruffled border
What are different processes of bone ossification /What is endochondral & intramembraneous bone
ossification
Intramembranous ossification
At the site where bone formation occour loose mesenchymal
cells that are widely deperated pale stained and stellate
shaped form
Capillaries grown into the mesenchyme and the center of
osteogenisis develop
The mesenchymal cells which are round basophilic with
thick interplasmic processes diffrentiate into osteoblasts
which secrete osteoid.
The osteoblasts are then entrapped in bone matrix and
osteocyte
in the end there is the calcification of the matrix
Endochondal Bone Ossification
The process of ossification which takes place by replacement of cartilage is endochomdral
ossification
Example: extremities of long bones, vertebrae, ribs, articular extremity of mandible, base of skull
Q5. What is bone turnover? What are its different phases.
The process by which the overall size and shape of bone is established is referred to as bone remodeling
Occurs in discrete focal areas involving group of cells called basic multicellular units
Phases:
Activation: osteoclasts get activated by RANK and RANKL interaction
Resoprtion: osteoclasts resorb the bone with the help of ruffled border, proton pump and
enzymes
Reversal: inhibition of osteoclastic activity by OPG and RANK interaction. Osteoblasts also
produce a cement line
Formation: new bone is deposited by osteoblasts
Resting: osteoblasts become quiescent and flattened bone lining cells
Q7.What is diffrences between mature and immature bone
Parameters Mature Bone Immature Bone
Nomenculature Known as Lamellar Bone Known as Woven Bone
Collagen Fiber arrangement Orderly Intertwined
Interfibrillar space Less More
Rate of Formation Slow Fast
Rate of Mineraltion Slow Fast
Mineral Density High Low
Water Content Low High
Removal Process Only a portion can be removed Can be removed completely by
by osteoclasts the osteoclasts
Q6. Differentiate
between compact and
spongy bone
You might also like
- Principles of Bone GraftingDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Bone GraftingJayanth Perumal100% (2)
- Bone 5Document54 pagesBone 5Parikshit DhayalNo ratings yet
- Histology of Bone 2022Document30 pagesHistology of Bone 2022zahra nabilaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 22 Bone Physiology IDocument26 pagesLecture 22 Bone Physiology Ijurgen klein-WernerNo ratings yet
- BONE Healing Uii 24 April 2014Document38 pagesBONE Healing Uii 24 April 2014Taufiq HidayatNo ratings yet
- BONE (Histology)Document65 pagesBONE (Histology)fhfebriiNo ratings yet
- CH8 Bone: Medullary CavitiesDocument9 pagesCH8 Bone: Medullary Cavitiesdanny olulanaNo ratings yet
- Histology 8Document6 pagesHistology 8amirhsheikhiNo ratings yet
- Tereos - Structure of PresentationDocument72 pagesTereos - Structure of PresentationSumitNo ratings yet
- Bones: Defination: Bone Is Highly Vascular, Living, Constantly ChangingDocument21 pagesBones: Defination: Bone Is Highly Vascular, Living, Constantly ChangingMd Ahsanuzzaman PinkuNo ratings yet
- Alveolar BoneDocument8 pagesAlveolar BoneAsruni Ab GhaniNo ratings yet
- Lec3 TransesDocument7 pagesLec3 Transes4xwqm42hyrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Bones and JointsDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Bones and JointsJade Karen Lingo-lingoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument80 pagesSkeletal SystemElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of BoneDocument32 pagesPhysiology of BoneAnandhu GNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics and Biomaterials in Orthopedic SurgeryDocument11 pagesBiomechanics and Biomaterials in Orthopedic SurgeryManiventhan NachimuthuNo ratings yet
- Bone HistologyDocument56 pagesBone HistologyNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- Fracture Healing and BonegraftingDocument76 pagesFracture Healing and BonegraftingJio AmurNo ratings yet
- Bone Grafts BhanuDocument113 pagesBone Grafts BhanuBhanu Praseedha100% (1)
- BONEDocument4 pagesBONEvallecerajamaicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document3 pagesChapter 8Ella LagramaNo ratings yet
- BIOL3307 - Unit1Mod2 - Bone Growth & Repair1Document16 pagesBIOL3307 - Unit1Mod2 - Bone Growth & Repair1Ren StudyNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument14 pagesSkeletal SystemCharlize PalmaNo ratings yet
- Bone Tissue: OsteocytesDocument11 pagesBone Tissue: OsteocytesA18- Jessa Mae DayagNo ratings yet
- OssificationDocument40 pagesOssificationElena CristinaNo ratings yet
- Bone Histology & Few Notes About Bone BiomechanicsDocument48 pagesBone Histology & Few Notes About Bone BiomechanicsArvind ManikantanNo ratings yet
- Lec Activity6 Skeletal System CastroDocument8 pagesLec Activity6 Skeletal System CastropelielNo ratings yet
- Salter Bab 1-2Document30 pagesSalter Bab 1-2elizabeth angelinaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System (2015 - 06 - 09 20 - 43 - 48 Utc)Document120 pagesSkeletal System (2015 - 06 - 09 20 - 43 - 48 Utc)DiazNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 ANAPHY TransesDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 6 ANAPHY TransesHoly HaeinNo ratings yet
- Tortora Principles of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesTortora Principles of Anatomy and PhysiologybebeNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes On BonesDocument4 pagesAdditional Notes On Bonesmober jonNo ratings yet
- Handout - Bone Anatomy and Healing - Nlogo - HighDocument11 pagesHandout - Bone Anatomy and Healing - Nlogo - HighlevimacoNo ratings yet
- Kalsifikasi, Deposisi Dan Resorpsi TulangDocument40 pagesKalsifikasi, Deposisi Dan Resorpsi TulangrifkaNo ratings yet
- Bone ReviewerDocument7 pagesBone ReviewerClyde BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Bone Formation - Ossification 2 PDFDocument35 pagesBone Formation - Ossification 2 PDFalan100% (1)
- Bones As A Living Dynamic TissueDocument13 pagesBones As A Living Dynamic TissueSanish Basnet100% (1)
- 6 Skeletal SystemDocument8 pages6 Skeletal SystemmargaretNo ratings yet
- Alveolarbone Graftingand Reconstruction Procedurespriorto ImplantplacementDocument10 pagesAlveolarbone Graftingand Reconstruction Procedurespriorto ImplantplacementKranti PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- BONEDocument48 pagesBONEnivethaseshaNo ratings yet
- AN OVERVIEW OF BONE CELLS AND THEIR REGULATING FACTORS OF DIFFERENTIATION, Mohamed 2008Document9 pagesAN OVERVIEW OF BONE CELLS AND THEIR REGULATING FACTORS OF DIFFERENTIATION, Mohamed 2008Faizal Reza PahleviNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument14 pagesSkeletal SystemCharlize PalmaNo ratings yet
- MAXILLA and MANDIBLE (Alveolar Process)Document35 pagesMAXILLA and MANDIBLE (Alveolar Process)ANVI SHARMANo ratings yet
- 2020-2021 AP 1 Lecture 6b Skeletal System 1Document16 pages2020-2021 AP 1 Lecture 6b Skeletal System 1OscarJaiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal 6Document28 pagesSkeletal 6BSN-2F Neutral Axis SiazonNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Midterms-1Document65 pagesAnaphy Midterms-1kiann130405No ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Estimation of Content of Bone AshDocument18 pagesChemistry Project On Estimation of Content of Bone AshKim TaesiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument97 pagesSkeletal SystemFardzli MatjakirNo ratings yet
- Breeland Et Al., 2023Document6 pagesBreeland Et Al., 2023hamdaniamr21cNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Comia, Joshua Cyryll Habacon, Gabrielle AnneDocument56 pagesThe Skeletal System: Comia, Joshua Cyryll Habacon, Gabrielle Annegian habaconNo ratings yet
- Cartlage Bone 2012Document34 pagesCartlage Bone 2012Omar Ali AyoubkhanNo ratings yet
- Alveolar Bone DR DeepakDocument107 pagesAlveolar Bone DR DeepakDeepak Kumar100% (2)
- HO Chapter 6 Pharm 123Document5 pagesHO Chapter 6 Pharm 123malfoymidnight394No ratings yet
- 6 PATHO 3b Part 1 - Musculoskeletal IIA - Dr. Dy-LedesmaDocument12 pages6 PATHO 3b Part 1 - Musculoskeletal IIA - Dr. Dy-LedesmaBanana BananaNo ratings yet
- English 20.05.2020Document100 pagesEnglish 20.05.2020Bernythefly axcNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Bones and Joints Components of The Skeletal System: Long Bone StructuresDocument8 pagesSkeletal System: Bones and Joints Components of The Skeletal System: Long Bone StructurespangetkoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: CartilageDocument20 pagesSkeletal System: CartilageGrace PascualNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument123 pagesSkeletal SystemZekiah MagsayoNo ratings yet
- Histology of Bone DevelopmentDocument11 pagesHistology of Bone DevelopmentLaidy Aizahlyn Indoc AngodNo ratings yet
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionFrom EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionNo ratings yet
- Histology SlidesDocument32 pagesHistology SlidesAroosha JamshaidNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Central IncisorDocument17 pagesMandibular Central IncisorAroosha JamshaidNo ratings yet
- DENTINOGENESISDocument14 pagesDENTINOGENESISAroosha JamshaidNo ratings yet
- Compiled Reading Material For TBL (30-9-22)Document6 pagesCompiled Reading Material For TBL (30-9-22)Aroosha JamshaidNo ratings yet
- DentinDocument5 pagesDentinAroosha JamshaidNo ratings yet
- 4 19003572427424163 PDFDocument4 pages4 19003572427424163 PDFAwadhNo ratings yet
- 4 Classes of Connective TissueDocument4 pages4 Classes of Connective TissueJoanne GodezanoNo ratings yet
- Cap 22Document47 pagesCap 22Andreea AronNo ratings yet
- Hematologic SystemDocument81 pagesHematologic Systemseigelystic100% (23)
- Anticoagulant PresentationDocument29 pagesAnticoagulant Presentationrozha100% (2)
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemMaxwell C Jay KafwaniNo ratings yet
- Muscle: Gerald Dale Giron MD Department of Human Structural BiologyDocument23 pagesMuscle: Gerald Dale Giron MD Department of Human Structural BiologyMarx AsuncionNo ratings yet
- 14-16 Juli 2022, Jayapura I Post Test (Jawaban)Document10 pages14-16 Juli 2022, Jayapura I Post Test (Jawaban)Abdul Charis KonorasNo ratings yet
- Skripsi Fix YaDocument134 pagesSkripsi Fix YaSabrina Putri DewantiNo ratings yet
- Immune Thrombocytopenia Purpura: Clinical PathwayDocument6 pagesImmune Thrombocytopenia Purpura: Clinical PathwayAsterlyn ConiendoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Hematology 2 LectureDocument8 pagesWeek 1 - Hematology 2 LectureRubenne Miles ElagasNo ratings yet
- Trishla Chaturvedi Automated Blood Cell CounterDocument26 pagesTrishla Chaturvedi Automated Blood Cell CounterNidhi Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Bone MarrowDocument6 pagesBone MarrowKIPRUTO DENNISNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of FBC Part 3Document17 pagesInterpretation of FBC Part 3reuel nareshNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissuesDocument9 pagesMuscle Tissuesangelo beldaNo ratings yet
- Mylein SheathDocument5 pagesMylein SheathSwordNo ratings yet
- Measurement Barang DinginDocument39 pagesMeasurement Barang DinginW. HerlambangNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2013 - TissueDocument25 pagesLesson Plan 2013 - Tissuesonyblank100% (1)
- Mechanism of Blood Clotting Extensic Pathway Factors Affecting Blood ClottingDocument18 pagesMechanism of Blood Clotting Extensic Pathway Factors Affecting Blood ClottingRaunak TripathiNo ratings yet
- Cordlife BrochureDocument16 pagesCordlife BrochureMelodie YlaganNo ratings yet
- Hematology Quick Facts Part1 PDFDocument10 pagesHematology Quick Facts Part1 PDFJohn Rhel DenqueNo ratings yet
- Exchange Blood Transfusion 2Document15 pagesExchange Blood Transfusion 2Sarah100% (1)
- Hematology UQU 2022Document94 pagesHematology UQU 2022Elyas MehdarNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument21 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationAbdisalan hassanNo ratings yet
- Article: Pengaruh Terapi Pijat Refleksi Kaki Terhadap Penurunan Tekanan Darah Pada Pasien HipertensiDocument10 pagesArticle: Pengaruh Terapi Pijat Refleksi Kaki Terhadap Penurunan Tekanan Darah Pada Pasien HipertensiTP20AZaidan azharNo ratings yet
- Appendix I - Plant TissuesDocument24 pagesAppendix I - Plant TissuesAmeera ChaitramNo ratings yet
- Infographics III Blood Smear 27 07 2020Document1 pageInfographics III Blood Smear 27 07 2020MARIA AUBREY GOLIATNo ratings yet
- Emergency and Critical Care Procedures in Small AnimalsDocument9 pagesEmergency and Critical Care Procedures in Small AnimalsTessaNo ratings yet
- Isbb FC Part 3Document13 pagesIsbb FC Part 3Lynther Myle Arizo100% (1)
- Isoimmunization and Anemia RH IncompatibilityDocument2 pagesIsoimmunization and Anemia RH IncompatibilityAriaNo ratings yet