Professional Documents
Culture Documents
02-2001cja101021230041-Enthuse Act Paper - 1
02-2001cja101021230041-Enthuse Act Paper - 1
Uploaded by
bothravarun39Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CLG418 Operation &maintainance ManualDocument66 pagesCLG418 Operation &maintainance ManualLYCANTROPOFAGO89% (9)
- ElectricityDocument4 pagesElectricityaishwarya meenaNo ratings yet
- Physics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-2) - PaperDocument13 pagesPhysics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-2) - PaperRachit JainNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic Induction - 3: SANKALP 2014 - EMI - 3 Phase - ViDocument4 pagesElectro Magnetic Induction - 3: SANKALP 2014 - EMI - 3 Phase - ViAnmolNo ratings yet
- SS CPP 03 Physics Chemistry Mathematics 2020Document36 pagesSS CPP 03 Physics Chemistry Mathematics 2020incognitosigmaextraNo ratings yet
- DPP 3Document11 pagesDPP 3mstudy1009No ratings yet
- AAI ATC - Previous Year Physics QuesDocument14 pagesAAI ATC - Previous Year Physics Quesarmaan626742No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument3 pagesElectricityUncle IrodovNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: AC Voltage Applied To A ResistorDocument4 pagesAlternating Current: AC Voltage Applied To A ResistorAdarsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- 12 Electricity and Magnetisium - 1Document32 pages12 Electricity and Magnetisium - 1Harsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2014-2015B Fiz102E FDocument2 pages2014-2015B Fiz102E FesinyvsNo ratings yet
- CL 12 Phy Preboard 1 Tearm 1 - 2021Document10 pagesCL 12 Phy Preboard 1 Tearm 1 - 2021Amaan SurtiNo ratings yet
- 2PU - Physics - RWS - 5-2-Current Electricity - Q + SolnDocument11 pages2PU - Physics - RWS - 5-2-Current Electricity - Q + SolnGayathri. PrasadNo ratings yet
- Online Classroom Contact Programme: (Academic Session: 2023 - 2024)Document36 pagesOnline Classroom Contact Programme: (Academic Session: 2023 - 2024)bhumi14369No ratings yet
- Major Test - 2 GR-XII JEE 1Document13 pagesMajor Test - 2 GR-XII JEE 1DeaDShoT 618No ratings yet
- Paper 1Document5 pagesPaper 1Dhruv TailorNo ratings yet
- APA-1 (100Q) (Electrostatics, DC Circuits, Capacitors, Magnetism) (JEE 2020)Document22 pagesAPA-1 (100Q) (Electrostatics, DC Circuits, Capacitors, Magnetism) (JEE 2020)Vedant TodiNo ratings yet
- Physics SampleDocument102 pagesPhysics Sampleshrutianand8915No ratings yet
- Current Electricity: TopicDocument31 pagesCurrent Electricity: Topicashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024Document5 pagesCurrent Electricity - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024abcprnshshsbNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument16 pagesCurrent ElectricityNavya RastogiNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023G Fiz102E 2vDocument2 pages2022-2023G Fiz102E 2vesinyvsNo ratings yet
- Board Test Phy Paper-3Document9 pagesBoard Test Phy Paper-3shrawantiyaNo ratings yet
- Board Test Phy Paper-3Document9 pagesBoard Test Phy Paper-3shrawantiyaNo ratings yet
- Nas QuestionDocument7 pagesNas QuestionMOBILE ASSASSINNo ratings yet
- Cbse PMT 2012Document33 pagesCbse PMT 2012Vishal RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- 2022-JEE Main-10 - PaperDocument14 pages2022-JEE Main-10 - PaperHalfborn GundersonNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument8 pagesCurrent Electricityhj48khy8jjNo ratings yet
- Revision DPP - JEE Advance - DPP-3 - P - DPP-3 - DPP - 03 PDFDocument11 pagesRevision DPP - JEE Advance - DPP-3 - P - DPP-3 - DPP - 03 PDFvijay kakarlaNo ratings yet
- Term 1 Test Current ElectricityDocument5 pagesTerm 1 Test Current ElectricityPradhyumn SinghNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Exercise - MCQ - Bc-OddDocument12 pagesCurrent Electricity - Exercise - MCQ - Bc-OddRaaghav SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- DPP 5Document11 pagesDPP 5mstudy1009No ratings yet
- 1stterm G11 2015Document15 pages1stterm G11 2015Adham TamerNo ratings yet
- AY1920S2 EE2111A-Quiz1Document12 pagesAY1920S2 EE2111A-Quiz1ZubinJainNo ratings yet
- XII - PHYSICS - HY - Question - PaperDocument7 pagesXII - PHYSICS - HY - Question - Papernrusinghsamal2006No ratings yet
- Gate 2015 PDFDocument81 pagesGate 2015 PDFsameer meshramNo ratings yet
- Unsolved Problem SheetDocument20 pagesUnsolved Problem SheetDeveshNo ratings yet
- Physics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1) - PaperDocument16 pagesPhysics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1) - PaperSaravanan BNo ratings yet
- Neet Current Electricity Important Questions PDFDocument28 pagesNeet Current Electricity Important Questions PDFVINOD KUMARNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Objective WorksheetDocument7 pagesCurrent Electricity - Objective Worksheetansh1510No ratings yet
- Current-Electricity MCQ 2Document9 pagesCurrent-Electricity MCQ 2Anant KumarNo ratings yet
- WWW Learncbse in Electricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 ScienceDocument34 pagesWWW Learncbse in Electricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 ScienceVikas PratikNo ratings yet
- Ese Ee Con 1 QueDocument6 pagesEse Ee Con 1 Queyash9714No ratings yet
- Semi ConductorDocument4 pagesSemi ConductorSchrodinger's CatNo ratings yet
- Physics - Detailed SolutionsDocument25 pagesPhysics - Detailed SolutionsPoorni RenuNo ratings yet
- Aptransco Electronic Engn 2011 Previous Paper 5c60dbb7Document22 pagesAptransco Electronic Engn 2011 Previous Paper 5c60dbb7Navyadeepika. KokkiralaNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Sample Question Paper-1 Phyiscs 2022-23Document7 pagesClass Xii Sample Question Paper-1 Phyiscs 2022-23Anonymous NV7nnJDeNo ratings yet
- Solutions On Topicwise Examination Questions: Ec: Electronics and CommunicationsDocument67 pagesSolutions On Topicwise Examination Questions: Ec: Electronics and CommunicationsMallik's ChannelNo ratings yet
- Test-1: Self-Induction and R-L-circuit Multi Choice Single Correct (+3,-1)Document9 pagesTest-1: Self-Induction and R-L-circuit Multi Choice Single Correct (+3,-1)Nil KamalNo ratings yet
- 14 - GR (Current Electricity) - Eng Allen ImportantDocument6 pages14 - GR (Current Electricity) - Eng Allen ImportantNeil ShettigarNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity 1Document3 pagesCurrent Electricity 1NK NikhilNo ratings yet
- CurrentElectricity Exercise-3Document5 pagesCurrentElectricity Exercise-3Shreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Arihant Sample Paper Term 1 Class 12 PhysicsDocument17 pagesArihant Sample Paper Term 1 Class 12 PhysicsHitesh Yadav100% (1)
- Current Electricity - CC - E - WADocument12 pagesCurrent Electricity - CC - E - WAHussain Ali PioneerNo ratings yet
- UnitTest - D03 Aug 2023 (1) K.Document61 pagesUnitTest - D03 Aug 2023 (1) K.krishgj19ab3232No ratings yet
- ALPS 2322 Physics Assignment PaperDocument17 pagesALPS 2322 Physics Assignment Papervikram singhNo ratings yet
- Part - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 10 April - Morning Shift MathongoDocument37 pagesPart - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 10 April - Morning Shift Mathongorohit574No ratings yet
- NEET UG 2024 Sample Paper 01Document20 pagesNEET UG 2024 Sample Paper 01VARSHAN GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Aramco Specific Evaluations For WeldingDocument6 pagesAramco Specific Evaluations For WeldingTrived MahankaliNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Hydro-Pneumatic Suspension SystemDocument11 pagesDesign and Development of Hydro-Pneumatic Suspension SystemzhenyupanNo ratings yet
- Wind Noise Sources and ReductionDocument10 pagesWind Noise Sources and ReductionAchintya MehrotraNo ratings yet
- Certificado Calidad-Canal CDocument1 pageCertificado Calidad-Canal CALENo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis For The Geometrical Section Properties of Thin Walled BeamDocument11 pagesFinite Element Analysis For The Geometrical Section Properties of Thin Walled BeammagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Multi - Choice Question Paper (MSR-WI-2)Document8 pagesMulti - Choice Question Paper (MSR-WI-2)Karit Hawichit100% (1)
- CE3155 Introduction To ETABS (Multi-Storey)Document42 pagesCE3155 Introduction To ETABS (Multi-Storey)Imran SaikatNo ratings yet
- Blade-St: The Complete Steam Turbine Blade Analysis ToolDocument8 pagesBlade-St: The Complete Steam Turbine Blade Analysis Toolramnadh803181No ratings yet
- Effect of Soil Temperature On Am Pa City ValuesDocument10 pagesEffect of Soil Temperature On Am Pa City ValuesAnupong JINo ratings yet
- S.No Acc No Title of The BookDocument12 pagesS.No Acc No Title of The BookmechhodNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Nuclear Medicine & RadiologyDocument8 pagesAssignment On Nuclear Medicine & RadiologyMinhajur RahmanNo ratings yet
- uploads1642069265DPP-1 NLM - Free Body DiagramDocument20 pagesuploads1642069265DPP-1 NLM - Free Body Diagramsharmaneraj80No ratings yet
- Akcome Single-Axis Tracker Structure Calculation Report 2PDocument26 pagesAkcome Single-Axis Tracker Structure Calculation Report 2PRajaa KodadNo ratings yet
- Meh ENG2 PDFDocument37 pagesMeh ENG2 PDFInkeNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Degree Examination Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument2 pagesB.Tech. Degree Examination Electronics & Communication EngineeringPuneeth HNNo ratings yet
- Effects of Processing Parameters of Infrared Based Automated F 2023 CompositDocument11 pagesEffects of Processing Parameters of Infrared Based Automated F 2023 CompositGUANCI ZHUNo ratings yet
- ENCH607-ENPE625 Assignment-04 - 28 Fall 2020Document3 pagesENCH607-ENPE625 Assignment-04 - 28 Fall 2020Ghost RiderNo ratings yet
- 5 Lifetime Extension For SiemensDocument21 pages5 Lifetime Extension For Siemenssdiaman100% (2)
- Pharmaceutical Study of Shatadhauta Ghrita Prepared by Two Different MethodsDocument10 pagesPharmaceutical Study of Shatadhauta Ghrita Prepared by Two Different MethodsBhavesh TanwaniNo ratings yet
- Steel and Timber Structures Part Two:: Design of Structural Steel MembersDocument28 pagesSteel and Timber Structures Part Two:: Design of Structural Steel MembersDhinesh KalaimaranNo ratings yet
- E797Document7 pagesE797Sergio MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chap9 Fan Noise MeasurementDocument5 pagesChap9 Fan Noise Measurementshehbazi2001No ratings yet
- ICE PAPER Biaxial Bending of RC BeamDocument5 pagesICE PAPER Biaxial Bending of RC BeamMk2No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document10 pagesAssignment 1Rajkumar MahadevanNo ratings yet
- Advances in Medical Linear Accelerator TechnologyDocument22 pagesAdvances in Medical Linear Accelerator TechnologyNawel MorjanNo ratings yet
- Verco ER 2078P 2002Document57 pagesVerco ER 2078P 2002jatinNo ratings yet
- Guielines For Specifying and Evaluating New and Rerated Multistage Centrifugal Compressors - PAPERDocument18 pagesGuielines For Specifying and Evaluating New and Rerated Multistage Centrifugal Compressors - PAPERVILLANUEVA_DANIEL2064No ratings yet
- Protecting BoilerAssets With REDOX Stress Control TechnologyDocument42 pagesProtecting BoilerAssets With REDOX Stress Control TechnologyVenkat SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Settlement of A Large Raft FoundationDocument1 pageSettlement of A Large Raft Foundationsb1966No ratings yet
02-2001cja101021230041-Enthuse Act Paper - 1
02-2001cja101021230041-Enthuse Act Paper - 1
Uploaded by
bothravarun39Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
02-2001cja101021230041-Enthuse Act Paper - 1
02-2001cja101021230041-Enthuse Act Paper - 1
Uploaded by
bothravarun39Copyright:
Available Formats
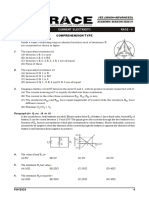
Topic :
Electro Magnetic Induction, Alternating Current, Ray Optics + Optical Instruments, NLM & Friction
PART-1 : PHYSICS
SECTION-I : (Maximum Marks: 80) 3. Given below are two statements: one is labelled as
This section contains 20 questions. Each question has 4 Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason
options for correct answer. Multiple-Choice Questions (R).
(MCQs) Only one option is correct. For each question, Assertion (A) : Transformer can't be used to step up
marks will be awarded as follows: or step down the steady dc voltage
Full Marks : +4 If correct answer is selected. Reason (R) : Transformers are based upon the
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the option is selected. principle of mutual induction for which a time
Negative Marks : –1 If wrong option is selected. varying voltage is necessary.
In the light of the above statements, choose the
1. The reading of the ammeter and voltmeters are
most appropriate answer from the options given
(both the instruments are ac meters and measures
below:
rms value)
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the
correct explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is NOT the
correct explanation of (A).
(A) 2A, 110V (B) 2A, 0V (C) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(C) 2A, 55V (D) 1A, 0V (D) (A) is false but (R) is true.
2. Magnetic flux ( ϕ ) linked with a coil depends on 4. An ac source of angular frequency ω is fed across
time t as ϕ = atn. Where a is a constant. The a resistor r and a capacitor C in series. The current
induced emf in the coil is e. Then which is wrong registered is I If the frequency of source is changed
(A) If 0 < n < 1, e ≠ 0 and |e| decreases with time to ω /3 (maintaining the same voltage), the current
(B) If n = 1, e is constant in the circuit is found to be halved. Calculate the
ratio of reactance to resistance at the original
(C) If n > 1, |e| increases with time frequency ω -
(D) None of these 3 2 1 4
(A) √ (B) √ (C) √ (D) √
5 5 5 5
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
English / 05112023 Space for Rough Work Page 1/20
5. A coil has an inductance of 0.7 H and is joined in 7. EMF of the battery shown in the circuit varies with
series with a resistance of 220 Ω . When an time, so that the current is given by i = 3 + 5t where
alternating e.m.f. of 220 V at 50 cycle per second is i is in ampere and t is in second. The expression for
applied to it, then the wattless component of the battery emf as a function of time is
22
peak current in the circuit is- π =
( )
7
(A) 5 ampere (B) 0.5 ampere
(C) 0.7 ampere (D) 7 ampere
6. In the cylindrical region shown, magnetic field is
diminishing at the rate of α (T/s). The force on the (A) 10t + 32 (B) 20t + 42
electron at a distance r along y-axis is (C) 20t + 18 (D) 10t + 22
8. A bar magnet is moved between two circular coils
A and B with a constant velocity v as shown. Then
the coils
r r
(A) Repel each other
ˆ ˆ
(A) α e(−i) (B) α e(i)
2 2 (B) Attract each other
r2 ˆ r2 ˆ
(C) α e(−i) (D) α e(i) (C) Neither attract nor repel each other
2 2
(D) May attract or repel depending upon size of
coils
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
Page 2/20 Space for Rough Work English / 05112023
9. A uniform wire of length ℓ can be bent into 10. A wire bent as a parabola y = 4x2 is located in a
several configurations as shown in List I to form a uniform magnetic field of 2T, perpendicular to xy
closed loop. The loop is kept in the time varying plane. At t = 0, a connecting bar AB starts sliding
magnetic field B = B0t2. Due to some phenomenon, from origin with constant acceleration of 2 m/s2
the length of the wire is also changing with time as along +vc y-axis. Find the emf (in volts) induced in
ℓ = ℓ 0 t. List II gives the induced emf for the the loop thus formed at y = 2m.
various situation. (given B0 = 0.1 SI unit, ℓ 0 = 5 SI
unit, π 2 = 10)
List-I List-II
2.5 SI
(P) (I)
unit (A) 8V (B) 9V (C) 10V (D) 11V
11. In the shown arrangement if f1, f2 and T be the
frictional forces on 2 kg block, 3kg block & tension
(Q) (II) 25 SI unit in the string respectively, then their values are:
3.75 SI
(R) (III) (A) 2N, 6N 3.2N
unit
(B) 2N, 2N, 0N
(C) 1N, 6N, 2N
(S) (IV) 5 SI unit (D) Date insufficient to calculate the required
value
(A) P → III;Q → II;R → IV;S → I
(B) P → II;Q → I;R → III;S → IV
(C) P → II;Q → III;R → I;S → IV
(D) P → II;Q → III;R → IV;S → I
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
English / 05112023 Space for Rough Work Page 3/20
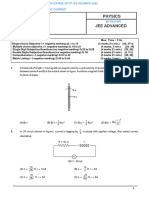
12. There is an inclined surface of inclination θ = 30°. 14. An object O is kept in air in front of a thin plano-
A smoolh groove is cut into it forming angle α convex lens of radius of curvature 10 cm. Its
with AB. A steel ball is free to slide along the refractive index is 3/2 and the medium towards
groove. If the ball is released from the point O at right of the plane surface is water of refractive
top end of the groove, the speed when it comes to index 4/3. What should be distance x of the object
A is: [ g = 10 m/s2] so that the rays become parallel finally?
(A) 5 cm (B) 10 cm
(C) 20 cm (D) 15 cm
(A) √ 40 m/s (B) √ 20 m/s
15. A point object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from
(C) √ 10 m/s (D) √ 15 m/s a thin plano-convex lens of focal length 15cm and
13. In figure, an air lens of radius of curvature of each µ = 1.5. The curved surface is silvered. The image
surface equal to 10 cm is cut into a cylinder of will form at
glass of refractive index 1.5. The focal length and
the nature of lens are
(A) 60 cm left of AB (B) 30 cm left of AB
(A) 15 cm diverging (B) 15 cm converging 20
(C) cm left of AB (D) 60 cm right of AB
(C) 10 cm diverging (D) 10 cm converging 7
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
Page 4/20 Space for Rough Work English / 05112023
16. In the figure shown, the angle made by the light ray 18. In the figure, a block of mass M is placed on a table
with the normal in the medium of refractive index with rough surface having coefficient of friction µ1.
√ 2 is Another block of m mass is placed on vertical
rough surface of this block with coefficient of
µ2(µ2 may be greater than 1). If system is released
from rest, find the maximum mass of block A, so
that the block of mass m does not slip.
(A) 30° (B) 60°
(C) 90° (D) None of these
17. In the arrangement shown in figure a, block of (M + m)( μ 1 μ 2 + 1) (M + 2m)( μ 1 μ 2 + 1)
(A) (B)
mass M = 20 kg is placed on rough horizontal ( μ 2 − 1) ( μ 2 − 1)
surface with µ = 0.5. A block of mass m is arranged (M + m)( μ 1 μ 2 + 1)
(C) (D) None of these
as shown. The maximum value of 'm' in order that ( μ 2 + 1)
system remains an equilibrium: 19. An astronomical telescope has an angular
magnification of magnitude 5 for distance objects.
The separation between the objective and the eye-
piece is 36 cm and the final image is formed at
infinity. the focal length f0 of the objective and fe
of the eye-piece are
(A) f0 = 45 cm and fe = – 9 cm
10
(A) kg (B) 10 kg (B) f0 = 50 cm and fe = 10 cm
3
40 20 (C) f0 = 7.2 cm and fe = 5 cm
(C) kg (D) kg
3 3
(D) f0 = 30 cm and fe = 6 cm
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
English / 05112023 Space for Rough Work Page 5/20
20. In order to increase the magnifying power of a 1. A pair of long conducting rails are held vertical at a
telescope separation l = 50 cm. The top ends are connected
(A) The focal powers of the objective and the eye- by a resistance of R = 0.5 Ω and a fuse (F) of
piece should be large negligible resistance. A conducting rod is free to
slide along the rails under gravity. The whole
(B) Objective should have small focal length and system is in a uniform horizontal magnetic field B
the eye-piece large = 1.5 T as shown. Resistance of the rod and rails
(C) Both should have large focal length are negligible and the rod remains horizontal as it
(D) The objective should have large focal length moves. The rod is released from rest. Find the
and the eye-piece should have small minimum weight of the rod that will ensure that the
fuse blows out. It is known that rating of the fuse is
SECTION-II : (Maximum Marks: 40) 4 A.
This section contains 10 questions Candidates have to
attempt any 5 questions out of 10. If more than 5
questions are attempted, then only first 5 attempted
questions will be evaluated.
The answer to each question is a Numerical Value.
For each question, enter the correct integer value (In case
of non-integer value, the answer should be rounded off to
the nearest Integer). 2. A conducting ring of mass m = π kg and radius
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to 1
R= m is kept on a flat horizontal surface (xy
2
the following marking scheme: plane). A uniform magnetic field is switched on in
Full Marks : +4 If correct answer is entered. the region which changes with time (t) as
Zero Marks : 0 If the question is unanswered. ˆ
→ = (2jˆ + t2 k)T
B . Resistance of the ring is r = π Ω
Negative Marks : –1 If wrong answer is entered. –2
and g = 10 ms .
Calculate the induced electric field at the
circumference of the ring at the instant it begins to
topple.
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
Page 6/20 Space for Rough Work English / 05112023
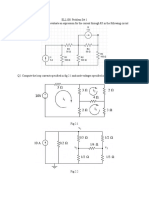
3. The capacitors shown in the circuit have 5. A series RLC circuit is in resonance with a source
capacitance C1 = C and C2 = 3C and they have of frequency ω 0 = 10 MHz. The current amplitude
been charged to potentials V1 = 2V0 and V2 = 3V0 in the circuit is I0. It was found that when a
respectively. Switch S is closed to connect them to different source of frequency ω = ω 0 + Δ ω [ Δ ω
the inductor L. = 10 KHz] was used the current amplitude in the
The potential difference across C1 when the current circuit was only 1% of I0. The inductance in the
nV0 circuit is x µH, then value x is (It is known that
in the inductor is maximum is , then find value
4 resistance in the circuit is R = 0.314 Ω )
of n .
6. In the given figure rays incident on an interface
would converge 2 cm below the interface if they
continued to move in straight lines without
bending. But due to refraction, the rays will bend
and meet somewhere else. Find the distance of
meeting point of refracted rays below the interface
(in cm), assuming the rays to be making small
angles with the normal to the interface.
4. In the circuit shown the transformer is ideal with
turn ratio N1 = 5 . The voltage of the source is Vs
N2 1
= 300 Volt. The voltage measured across the load
resistance RL = 100 Ω is 50 Volt. Find the value of
resistance R in the primary circuit.
7. The magnifying power of an astronomical
telescope in the normal adjustment position is 100.
The distance between the objective and the eye-
piece is 101 cm. What will be the focal lengths of
the objective lens (in cm)
8. Two converging lens have focal length f = 10 cm
and f'= 20 cm respectively. The optical axes of the
lenses coincide. This lens system is used to form an
image of an object kept at a certain distance from
the first lens. If the size of the final image does not
depend on the distance of the object from the first
lens. The distance (in cm) between the two lens ix
X. The value of X/2 is
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
English / 05112023 Space for Rough Work Page 7/20
9. For a prism, A = 60°, n = 7/3. Find the minimum
√
10. Block A of mass m/2 is connected to one end of
possible angle of incidence (in degree), so that the light rope which passes over a pully as shown in
light ray is refracted from the second surface. figure. A monkey of mass m climbes the other end
of rope with a relative acceleration of g/6 with
ng
respect to rope. The acceleration of block A is
9
m/s2. What will be n.
Applying Snell's law, we get
7
1 × sin imin = √ sin(A − C)
3
7
= √ (sinA cosC – cosA sinC)
3
=√7 ( sin 60√1 −
3 3
− cos 60√ ) =
1
3 7 7 2
∴ imin = 30°
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
Page 8/20 Space for Rough Work English / 05112023
Topic :
OC : General Organic Chemistry (XI), Aldehyde & Ketone, Carboxylic acid & Derivatives, Amines,
Aromatics Compounds (Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution)
PC : Atomic Structure, Chemical Kinetics, Radioactivity, Ionic Equillibrium
IC : Chemical Bonding (Complete), Metallurgy, Salt Analysis
PART-2 : CHEMISTRY
SECTION-I : (Maximum Marks: 80) 2. Which of the following is incorrect?
This section contains 20 questions. Each question has 4 (A) During N2+ formation, one electron is
options for correct answer. Multiple-Choice Questions removed from the bonding molecular orbital
(MCQs) Only one option is correct. For each question,
(B) During superoxide ion formation, one electron
marks will be awarded as follows:
is added to the bonding molecular orbital
Full Marks : +4 If correct answer is selected.
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the option is selected. (C) During formation of B2 , π 2px is filled before
Negative Marks : –1 If wrong option is selected. σ 2pz molecular orbital
1. Which of the following is incorrect? (D) NO can easily be oxidised as it has one
unpaired electron in the antibonding
molecular orbital
(A)
3. Statement I:
(B) This represents the correct order of reactivity
towards electrophile in acidic condition.
Statement II: Group which deactivates the benzene
ring towards Electrophilic aromatic substitution are
Acetanilide > Paracetamol (Double bond always meta director.
(C)
equivalent) (A) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(B) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(magnitude
(D) (C) Statement I is true ; Statement II is false
of heat of hydrogenation) (D) Statement I is false; Statement II is true
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
English / 05112023 Space for Rough Work Page 9/20
4. Consider the following statements 6. Consider the Ellingham diagram.
(I) Cryolite and fluorspar is mixed with Al2O3 to
improve the thermal conductivity of the mixture.
(II) In hydrometallurgy of copper, bacteria is used
to leach out the Copper ion from high grade ores.
(III) In froth floatation process, sodium cyanide is
used as activator to enhance wettability of ZnS with
oil.
(IV) Spelter zinc is the purified zinc obtained after
distillation process. At 800 K, oxide of Q can be reduced spontaneously
(V) Blister copper is obtained from Bessemer by
converter. (A) Only R (B) Both S and P
(VI) German silver contains 30 – 40% silver and
(C) Only S (D) Only P
rest is germanium.
Total number of correct statement(s) 7. For Cr, how many electrons can have n + l + |ml| =
4 with anti-clockwise spin in ground state?
(A) 1
(A) 2 (B) 4
(B) 2
(C) 6 (D) 8
(C) 3
8. Find the quantum number of the excited state of
(D) 4
electrons in He+ ion which on transition to first
5. In which of the followign pair, 1st is oxide ore and excited state emit photons of wavelengths 108.5
2nd sulphide ore nm.
(I) Pyrolusite, Argentite
(A) 6
(II) Bauxite, Rutile
(III) Magnetite, Chalcocite (B) 5
(IV) Azurite, Cuprite (C) 4
(A) I & III (D) 2
(B) II & IV
(C) I & IV
(D) II & III
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
Page 10/20 Space for Rough Work English / 05112023
9. 12. k
List-I List-II The reaction A → Product, is zero order while the
k
(P) XeO3 (I) Maximum number of lone pair reaction B → Product, is first order reaction. For
(Q) I3 – (II) Symmetrical species what initial concentration of A are the half lives of
the two reactions equal? (Rate constant value are
(R) SF4 (III) d orbital involved in bonding
same for oth two reaction).
Maximum number of p π - p π
(S) COF2 (IV) (A) (loge4) M (B) 2 M
bonds
Correct option is (C) log2 M (D) ln 2M
(A) P → I;Q → III;R → II;S → IV 13. If a reaction, A + B → C, is exothermic to the
extent of 30 kJ/mol and the forward reaction has an
(B) P → III;Q → II;R → III;S → I activation energy 70 kJ/mol, the activation energy
(C) P → III;Q → II;R → I;S → IV for teh reverse reaction is
(D) P → IV;Q → I;R → II;S → III (A) 30 kJ/mol (B) 40 kJ/mol
10. The order of reactivity of the following compounds (C) 70 kJ/mol (D) 100 kJ/mol
in electrophilic monochlorination towards the most 14. Which of the following will be most readily
favourable position is dehydrated in acidic conditions?
(A)
(A) I < II < IV < III (B) III < IV < I < II
(C) IV < III < II < I (D) III < II < IV < I
(B)
11. The correct order of increasing boiling point of the
followign compound is
(I) CH3 – CONH2
(II) CH3COCl
(III) CH3COOCH3 (C)
(IV)
(A) I < II < III < IV (B) II < III < IV < I
(D)
(C) II < IV < III < I (D) II < III < IV
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
English / 05112023 Space for Rough Work Page 11/20
15. Statement-1 : During diazotization, excess of HCl 17.
is used with NaNO2.
(i) NaH /T HF
Statement-2 : Excess of HCl prevents the −−−−−−−−−→ (A)
(ii) CH3 COCl
hydrolysis of diazonium salt.
(A) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; (i) dil.KOH
Statement-2 is a correct explanation for −−−−−−− −−→ (B)
(ii) H2 O/H , Δ
+
Statement-1. The product (B) in the above sequence of reaction
(B) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; is
Statement-2 is a not correct explanation for
Statement-1.
(A)
(C) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False.
(D) Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True.
16. Among the following which statement is incorrect
statement?
(B)
will not respond to haloform
(A)
test
(C)
Schiff's reagent and Schiff's base are different
(B)
compounds
Fchling solution is a good reagent to detect
(C) (D)
aromatic aldehydes
Both aldehydes and ketones can reast with 2,
(D)
4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent 18. Aqueous solution of a salt (Y) is alkaline to litmus.
On strong heating, it swells-up to give a glassy
material. When conc. H2SO4 is added to a hot
concentrated solution of (Y), white crystals of a
weak acid separates out. Hence, the compound (Y)
is
(A) Na2SO4.10H2O (B) Ca2B6O11.10H2O
(C) Na2B6O11 (D) Na2B4O7.10H2O
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
Page 12/20 Space for Rough Work English / 05112023
19. Which gas gives yellow ppt. with chloroplatinic 2. Solubility of sparingly soluble salt MX of weak
acid? acid HX is 0.001 M at pH 3 and 10 – 4 M at pH = 7.
(A) SO2 (B) NH3 (C) CO (D) NO2 pKa of HX is
20. A white powder when strongly heated gives off 3. How many of the following compounds can
brown fumes. A solution of this powder gives a liberate CO2 with NaHCO3?
yellow precipitate with a solution of KI. When a (1) Salicylic acid
solution of barium chloride is added to a solution of (2) Pthalic acid
powder, a white precipitate results. This white (3) Picric acid
powder may be (4) Resorcinol
(5) Carbolic acid
(A) A soluble sulphate (B) KBr or NaBr (6) Aspirin
(C) Ba(NO3)2 (D) AgNO3 (7) Anisole
(8) Tartaric acid
SECTION-II : (Maximum Marks: 40)
(9) Squaric acid
This section contains 10 questions Candidates have to (10) Ascorbic acid
attempt any 5 questions out of 10. If more than 5
questions are attempted, then only first 5 attempted 4. How many statements are correct?
questions will be evaluated. (A) No primary kinetic isotope effect is observed
The answer to each question is a Numerical Value. during nitration of benzene.
For each question, enter the correct integer value (In case (B) KH/ KD = 1 for halogenation of benzene.
of non-integer value, the answer should be rounded off to (C) KH / KD = 1 for sulphonation of benzene.
the nearest Integer). (D) Nitrobenzene will give meta-nitrotoluene on
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to reaction with CH3Cl/AlCl3.
the following marking scheme: (E) Toluene can be obtained in better yield when
Full Marks : +4 If correct answer is entered. excess of benzene will react with CH3Cl/AlCl3.
Zero Marks : 0 If the question is unanswered. (F) Chlorobenzene will give meta-substituted
Negative Marks : –1 If wrong answer is entered. product on electrophilic substitution since it exerts
– I > + M effect.
1. pH of solution obtained on treating 100 ml of 0.1 (G) n-Propyl benzene can be easily obtained on
M Na2X with 50 ml of 0.1 M HCl is 8. Determine
Friedal crafts alkylation of benzene with n-propyl
the pH of 0.1 M H2X solution, if pH of 0.1 M
chloride.
NaHX is 6.5.
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
English / 05112023 Space for Rough Work Page 13/20
5. If the bond energy of B2, C2, O2 , F2 can have 10. Amongest the following, the total number of
following values (in kJ/mol) compounds which undergo dehydration on heating
620, 498, 159,290 (data not in order) is
Which is the best possible match for C2?
6. What is the number of optically active structural
isomers of C4H8O3 which evolve CO2 with aq.
NaHCO3.
7. Which one of he following pairs of ions cannot be
separate by H2S in dilute HCl.
(1) Bi3+, Sn4+
(2) Al3+, Hg2+
(3) Cu2+, Zn2+
(4) Ni2+, Cu2+
8. Concentrated aqueous sodium hydroxide can
separate a mixture of
(1) Al3+ and Sn2+
(2)Al3+ and Fe3+
(3) Cu2+, Zn2+
(4) Ni2+ and Pb2+
9. 5-hydroxyhexanal forms a six member hemiacetal,
which predominates at equilibrium in aqueous
solution. how many stereoisomers are possible for
this cyclic hemiacetal?
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
Page 14/20 Space for Rough Work English / 05112023
Topic : Integration ( Definite Integration + Indefinite Integration), Area Under the Curve, Differential
Equation, Conic Section, Vector 3D
PART-3 : MATHEMATICS
SECTION-I : (Maximum Marks: 80) 3. −−
→ −−
→ −→
− −→ −−
→ −−
→
Let the vectors P Q, QR, RS, ST , T U and UP
This section contains 20 questions. Each question has 4 represent the sides of a regular hexagon.
options for correct answer. Multiple-Choice Questions −−
→ −→
− −→
Assertion : P Q × ( RS + ST ) ≠ →0.
(MCQs) Only one option is correct. For each question,
marks will be awarded as follows: Because
−−
→ −→ − −−
→ −→
Full Marks : +4 If correct answer is selected. Reason : P Q × RS = →0 and P Q × ST ≠ →0.
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the option is selected. (A) Assertion is true, Reason is true; Reason is a
Negative Marks : –1 If wrong option is selected. correct explanation for Assertion.
1. Let a vector →a
be coplanar with vectors (B) Assertion is true, Reason is true; Reason is
→b = 2i + j + k and →c = ^i − ^j + k^ . If →a is
^ ^ ^
NOT a correct explanation for Assertion.
perpendicular to →d = 3i^ + 2j^ + 6k^ and |→a | = 10. √
(C) Assertion is true, Reason is false
Then a possible value of →a →b →c + [ ]
(D) Assertion is false, Reason is true
a →b →d] + [→a →c →d] is equal to
[→
4. The edges of a parallelpiped are unit length and are
^ ^
^ b,
(A) – 42 parallel to non-coplanar unit vectors a, c such
(B) – 40 that a^ ⋅ b^ = b^ ⋅ c^ = c^ ⋅ a^ = 1 . Then, then volume of
2
(C) – 29 the parallelpiped is →a , →b, →c is given by
(D) – 38 1 1
(A) (B)
√ 2 2 √2
2. Let α , β , γ be distinct real numbers. The points
3 1
with position vectors α ^i + β ^j + γ k^ , β ^i + γ ^j + α k^ ,
√
(C) (D)
2 √ 3
^ ^ ^
γ i + αj + βk 5. ABC is triangle in a plane with vertices A(2, 3, 5),
(A) Are collinear B( – 1, 3, 2) and C( λ , 5, μ ). If the median through
(B) Form an equilateral triangle A is equally inclined to the coordinate axes, then
the value of ( λ 3 + μ 3 + 5) is :
(C) Form an scalene triangle
(A) 1130 (B) 1348
(D) Form a right angled triangle
(C) 1077 (D) 676
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
English / 05112023 Space for Rough Work Page 15/20
6. The shortest distance between the lines 9. x2 y2
Consider the ellipse + = 1.
x+7 y−6 7−x 4 3
= = z and = y – 2 = z – 6 is : Let H( α , 0), 0 < α < 2, be a point. A straight line
−6 7 2
2√29
drawn through H parallel to the y-axis crosses the
(A)
ellipse and its auxiliary circle at points E and F
(B) 1 respectively, in the first quadrant. The tangent to
the ellipse at the point E intersects the positive x-
37
(C) √
axis at a point G suppose the straight line joining F
29
√ 29
and the origin makes an angle ϕ with the positive
(D) x-axis.
2
7. If L1 is the line of intersection of the planes 2x – List-I List-II
2y + 3z – 2 = 0, x – y + z + 1 = 0 and L2 is the line If ϕ = π , then the area
4
(I) 4 (P) (√ 3 − 1)
of intersection of the planes x + 2y – z – 3 = 0, 3x of the triangle FGH is 8
– y + 2z – 1 = 0, then t he distance of the origin
from the plane, containing the lines L1 and L2, is : If ϕ = π , then the area
(II) 3 (Q) 1
1 of the triangle FGH is
(A)
3 √2 If ϕ = π , then the area 3
1
(III) 6 (R)
of the triangle FGH is 4
(B)
2 √2
1 If ϕ = π , then the
12 1
(C) (IV) area of the triangle (S)
√ 2 2 √3
1 FGH is
(D)
4 √2 (T) 3 √3
8. For non-zero vectors →a , →b, →c , ∣
→a × →b) ⋅ →c ∣
( = 2
∣ ∣
The correct option is :
|→a | ∣∣→b∣∣ |→c | holds if and only if
(A) (I) → (R); (II) → (S); (III) → (Q);(IV) →
(A) →a ⋅ →b = 0, →b ⋅ →c = 0 (P)
(B) →b ⋅ →c = 0, →c ⋅ →a = 0 (B) (I) → (R); (II) → (T); (III) → (S);(IV) →
(P)
(C) →c ⋅ →a = 0, →a ⋅ →b = 0
(C) (I) → (Q); (II) → (T); (III) → (S);(IV) →
(D) →a ⋅ →b = →b ⋅ →c = →c ⋅ →a = 0
(P)
(D) (I) → (Q); (II) → (S); (III) → (Q);(IV) →
(P)
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
Page 16/20 Space for Rough Work English / 05112023
10. The equation of a common tangent to the parabolas 14. Let a solution y = y(x) of the differential equation
y = x2 and y = – (x – 2)2 is x√x2 − 1dy − y√y 2 − 1 dx = 0 satisfy y(2) =
2
.
√ 3
(A) y = 4(x – 2) (B) y = 4(x – 1) π
Statement-1 : y(x) = sec ( sec−1 x − ) and
(C) y = 4(x + 1) (D) y = 4(x + 2) 6
Statement-2 : y(x) is given by
11. 2
1 2 √3 √ 1
1 1 = − 1−
If 5f(x) + 4f ( ) = + 3, then 18 ∫ f(x)dx is
x x y x x2
1
(A) Statment-1 is true, statement-2 is true;
(A) 10log2 + 6 Statement-2 is a correct explanation for
(B) 10log2 − 6 Statement-1.
(C) 5log2 + 6 (B) Statment-1 is true, statement-2 is true;
(D) 5log2 − 6 Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for
Statement-1.
12. x2 (xsec2 x + tan x)
The integration ∫ dx is (C) Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false
(x tan x + 1)2
x (D) Statement-1 is false, Statement-2 is true
(A) + log| x sinx + cosx| + c
x tan x + 1 15. The area of the region
x
(B) – log| x sinx + cosx| + c x, y : x2 ≤ y ≤ |x2 – 4| , y ≥ 1 is
x tan x + 1
−x2 4
(C) + 2log| x sinx + cosx| + c (A) ( 4 √2 − 1 )
x tan x + 1 3
x2 4 √
(B) (4 2 + 1)
(D) + 2log| x sinx + cosx| + c 3
x tan x + 1
π 3 √
13. (C) (4 2 + 1)
−π
4
e 4 + ∫ e−x tan50 xdx 4
0 3 √
The value of π is (D) (4 2 − 1)
4 4
∫ e−x (tan49 x + tan51 x) dx 16. The distance of the point 6, −2 2 from the
( √ )
0
common tangent y = mx + c, m > 0, of the curves x
(A) 51
= 2y2 and x = 1 + y2 is
(B) 50 14 1
(A) (B)
(C) 25 3 3
(C) 5 √3 (D) 5
(D) 49
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
English / 05112023 Space for Rough Work Page 17/20
17. 2x 1 19. The tangents at the points A(1, 3) and B(1, – 1) on
Let f(x) = ∫ dx. If f(3) =
(x2 + 1)(x2 + 3) 2 the parabola y2 – 2x – 2y = 1 meet at the point P.
(loge5 – loge6), then f(4) is equal to Then the area (in unit2) of the triangle PAB is:
(A) loge17 – loge18 (A) 4
(B) loge19 – loge20 (B) 6
1 (C) 7
(C) (loge17 – loge19)
2
(D) 8
1
(D) (loge19 – loge17)
2 20. The population P = P(t) at time 't' of a certain
18. Let y = y(x) be the solution curve of the differential species follows the differential equation dP = 0.5
dy y dt
equation = (1 + xy2(1 + logex)), x > 0, y(1) P – 450. If P(0) = 850, then the time at which
dx x
y 2 (x) population becomes zero is
= 3. Then is equal to
9
x2 (A) loge18
(A)
7 − 3x3 (2 + loge x2 ) (B) loge9
x2
(B) 1
2x3 (2 + loge x3 ) − 3 (C) loge18
2
x2
(C) (D) 2loge18
5 − 2x3 (2 + loge x3 )
x2
(D)
3x3 (1 + loge x2 ) − 2
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
Page 18/20 Space for Rough Work English / 05112023
SECTION-II : (Maximum Marks: 40) 5. x−3 y−2 z−3
Let the line = = intersect the
This section contains 10 questions Candidates have to 7 −1 −4
y+1
attempt any 5 questions out of 10. If more than 5 plane containing the lines x − 4 = z
= and
1 −2 1
questions are attempted, then only first 5 attempted 4ax – y + 5z – 7a = 0 2x – 5y – z – 3, a ∈ R at
questions will be evaluated. the point P( α , β , γ ). Then the value of α + β + γ
The answer to each question is a Numerical Value. equals ________.
For each question, enter the correct integer value (In case 6. Let the area enclosed by the lines x + y = 2, y = 0,
of non-integer value, the answer should be rounded off to 3
the nearest Integer). x = 0 and the curve f(x) = min { x2 + , 1 + [x]}
4
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to where [x] denotes the greatest integer ≤ x, be A.
the following marking scheme: Then the value of 12A is _______.
Full Marks : +4 If correct answer is entered.
7. The ordinates of the points P and Q on the parabola
Zero Marks : 0 If the question is unanswered.
with focus (3, 0) and directrix x = – 3 are in the
Negative Marks : –1 If wrong answer is entered.
ratio 3 : 1. If R( α , β ) is the point of intersection of
1. Let →p = 2i^ + 3j^ + k^ and →q = ^i + 2j^ + k^ be the two β2
the tangents to the parabola at P and Q, then is
vectors. If a vector →r = α ^i + β ^j + γ k^ is
( )
equal to ________.
α
perpendicular to each of the vectors (→p + →q) and
8. Let [t] denote the greatest integer function. If
(→p − →q), and |→r | = 3, then | α | + | β | + | γ | is equal to
√
2.4
_______. ∫ [x2 ]dx = α +β √ 2 + γ √3 + δ √5, then α +β+γ
2. Let →a , →b, →c
be three mutually perpendicular vectors 0
of the same magnitude and equally inclined at an + δ is equal to _________.
angle θ , with the vector →a + →b + →c . Then 36 cos2 2 θ 9. If y = y(x) is the solution of the differential
is equal is _______. dy 4x x+2
equation + y= , x > 1 such
dx (x2 − 1) 5
(x2 − 1) 2
3. Let S be the mirror image of the point Q(1, 3, 4)
with respect to the plane 2x – y + z + 3 = 0 and let that y(2) = 2 loge 2 + 3 and y 2 = α loge(
( √ ) (√ )
9
R(3, 5, γ ) be a point of this plane. Then the square √ α + β ) + β – γ , α , β , γ ∈ N, then α β γ is
√
of the length of the line segment SR is _________. equal to _______.
4. Let →a , →b and →c be three non-coplanar unit vectors 10. In the area enclosed by the parabolas P1 : 2y =
such that the angle between every pair of them is 5x2 and P2 : x2 – y + 6 = 0 is equal to the area
π
. If →a × →b + →b × →c = p→a + q→b + r→c , where p, q and r enclosed by P1 and y = ax, a > 0, then a3 is equal to
3 _______.
p2 + 2q 2 + r2
are scalars, then the value of is
q2
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
English / 05112023 Space for Rough Work Page 19/20
SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK
Enthusiast - 1 2001CJA101021230041
Page 20/20 English / 05112023
You might also like
- CLG418 Operation &maintainance ManualDocument66 pagesCLG418 Operation &maintainance ManualLYCANTROPOFAGO89% (9)
- ElectricityDocument4 pagesElectricityaishwarya meenaNo ratings yet
- Physics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-2) - PaperDocument13 pagesPhysics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-2) - PaperRachit JainNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic Induction - 3: SANKALP 2014 - EMI - 3 Phase - ViDocument4 pagesElectro Magnetic Induction - 3: SANKALP 2014 - EMI - 3 Phase - ViAnmolNo ratings yet
- SS CPP 03 Physics Chemistry Mathematics 2020Document36 pagesSS CPP 03 Physics Chemistry Mathematics 2020incognitosigmaextraNo ratings yet
- DPP 3Document11 pagesDPP 3mstudy1009No ratings yet
- AAI ATC - Previous Year Physics QuesDocument14 pagesAAI ATC - Previous Year Physics Quesarmaan626742No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument3 pagesElectricityUncle IrodovNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: AC Voltage Applied To A ResistorDocument4 pagesAlternating Current: AC Voltage Applied To A ResistorAdarsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- 12 Electricity and Magnetisium - 1Document32 pages12 Electricity and Magnetisium - 1Harsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2014-2015B Fiz102E FDocument2 pages2014-2015B Fiz102E FesinyvsNo ratings yet
- CL 12 Phy Preboard 1 Tearm 1 - 2021Document10 pagesCL 12 Phy Preboard 1 Tearm 1 - 2021Amaan SurtiNo ratings yet
- 2PU - Physics - RWS - 5-2-Current Electricity - Q + SolnDocument11 pages2PU - Physics - RWS - 5-2-Current Electricity - Q + SolnGayathri. PrasadNo ratings yet
- Online Classroom Contact Programme: (Academic Session: 2023 - 2024)Document36 pagesOnline Classroom Contact Programme: (Academic Session: 2023 - 2024)bhumi14369No ratings yet
- Major Test - 2 GR-XII JEE 1Document13 pagesMajor Test - 2 GR-XII JEE 1DeaDShoT 618No ratings yet
- Paper 1Document5 pagesPaper 1Dhruv TailorNo ratings yet
- APA-1 (100Q) (Electrostatics, DC Circuits, Capacitors, Magnetism) (JEE 2020)Document22 pagesAPA-1 (100Q) (Electrostatics, DC Circuits, Capacitors, Magnetism) (JEE 2020)Vedant TodiNo ratings yet
- Physics SampleDocument102 pagesPhysics Sampleshrutianand8915No ratings yet
- Current Electricity: TopicDocument31 pagesCurrent Electricity: Topicashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024Document5 pagesCurrent Electricity - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024abcprnshshsbNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument16 pagesCurrent ElectricityNavya RastogiNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023G Fiz102E 2vDocument2 pages2022-2023G Fiz102E 2vesinyvsNo ratings yet
- Board Test Phy Paper-3Document9 pagesBoard Test Phy Paper-3shrawantiyaNo ratings yet
- Board Test Phy Paper-3Document9 pagesBoard Test Phy Paper-3shrawantiyaNo ratings yet
- Nas QuestionDocument7 pagesNas QuestionMOBILE ASSASSINNo ratings yet
- Cbse PMT 2012Document33 pagesCbse PMT 2012Vishal RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- 2022-JEE Main-10 - PaperDocument14 pages2022-JEE Main-10 - PaperHalfborn GundersonNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument8 pagesCurrent Electricityhj48khy8jjNo ratings yet
- Revision DPP - JEE Advance - DPP-3 - P - DPP-3 - DPP - 03 PDFDocument11 pagesRevision DPP - JEE Advance - DPP-3 - P - DPP-3 - DPP - 03 PDFvijay kakarlaNo ratings yet
- Term 1 Test Current ElectricityDocument5 pagesTerm 1 Test Current ElectricityPradhyumn SinghNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Exercise - MCQ - Bc-OddDocument12 pagesCurrent Electricity - Exercise - MCQ - Bc-OddRaaghav SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- DPP 5Document11 pagesDPP 5mstudy1009No ratings yet
- 1stterm G11 2015Document15 pages1stterm G11 2015Adham TamerNo ratings yet
- AY1920S2 EE2111A-Quiz1Document12 pagesAY1920S2 EE2111A-Quiz1ZubinJainNo ratings yet
- XII - PHYSICS - HY - Question - PaperDocument7 pagesXII - PHYSICS - HY - Question - Papernrusinghsamal2006No ratings yet
- Gate 2015 PDFDocument81 pagesGate 2015 PDFsameer meshramNo ratings yet
- Unsolved Problem SheetDocument20 pagesUnsolved Problem SheetDeveshNo ratings yet
- Physics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1) - PaperDocument16 pagesPhysics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1) - PaperSaravanan BNo ratings yet
- Neet Current Electricity Important Questions PDFDocument28 pagesNeet Current Electricity Important Questions PDFVINOD KUMARNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Objective WorksheetDocument7 pagesCurrent Electricity - Objective Worksheetansh1510No ratings yet
- Current-Electricity MCQ 2Document9 pagesCurrent-Electricity MCQ 2Anant KumarNo ratings yet
- WWW Learncbse in Electricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 ScienceDocument34 pagesWWW Learncbse in Electricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 ScienceVikas PratikNo ratings yet
- Ese Ee Con 1 QueDocument6 pagesEse Ee Con 1 Queyash9714No ratings yet
- Semi ConductorDocument4 pagesSemi ConductorSchrodinger's CatNo ratings yet
- Physics - Detailed SolutionsDocument25 pagesPhysics - Detailed SolutionsPoorni RenuNo ratings yet
- Aptransco Electronic Engn 2011 Previous Paper 5c60dbb7Document22 pagesAptransco Electronic Engn 2011 Previous Paper 5c60dbb7Navyadeepika. KokkiralaNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Sample Question Paper-1 Phyiscs 2022-23Document7 pagesClass Xii Sample Question Paper-1 Phyiscs 2022-23Anonymous NV7nnJDeNo ratings yet
- Solutions On Topicwise Examination Questions: Ec: Electronics and CommunicationsDocument67 pagesSolutions On Topicwise Examination Questions: Ec: Electronics and CommunicationsMallik's ChannelNo ratings yet
- Test-1: Self-Induction and R-L-circuit Multi Choice Single Correct (+3,-1)Document9 pagesTest-1: Self-Induction and R-L-circuit Multi Choice Single Correct (+3,-1)Nil KamalNo ratings yet
- 14 - GR (Current Electricity) - Eng Allen ImportantDocument6 pages14 - GR (Current Electricity) - Eng Allen ImportantNeil ShettigarNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity 1Document3 pagesCurrent Electricity 1NK NikhilNo ratings yet
- CurrentElectricity Exercise-3Document5 pagesCurrentElectricity Exercise-3Shreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Arihant Sample Paper Term 1 Class 12 PhysicsDocument17 pagesArihant Sample Paper Term 1 Class 12 PhysicsHitesh Yadav100% (1)
- Current Electricity - CC - E - WADocument12 pagesCurrent Electricity - CC - E - WAHussain Ali PioneerNo ratings yet
- UnitTest - D03 Aug 2023 (1) K.Document61 pagesUnitTest - D03 Aug 2023 (1) K.krishgj19ab3232No ratings yet
- ALPS 2322 Physics Assignment PaperDocument17 pagesALPS 2322 Physics Assignment Papervikram singhNo ratings yet
- Part - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 10 April - Morning Shift MathongoDocument37 pagesPart - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 10 April - Morning Shift Mathongorohit574No ratings yet
- NEET UG 2024 Sample Paper 01Document20 pagesNEET UG 2024 Sample Paper 01VARSHAN GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Aramco Specific Evaluations For WeldingDocument6 pagesAramco Specific Evaluations For WeldingTrived MahankaliNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Hydro-Pneumatic Suspension SystemDocument11 pagesDesign and Development of Hydro-Pneumatic Suspension SystemzhenyupanNo ratings yet
- Wind Noise Sources and ReductionDocument10 pagesWind Noise Sources and ReductionAchintya MehrotraNo ratings yet
- Certificado Calidad-Canal CDocument1 pageCertificado Calidad-Canal CALENo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis For The Geometrical Section Properties of Thin Walled BeamDocument11 pagesFinite Element Analysis For The Geometrical Section Properties of Thin Walled BeammagdyamdbNo ratings yet
- Multi - Choice Question Paper (MSR-WI-2)Document8 pagesMulti - Choice Question Paper (MSR-WI-2)Karit Hawichit100% (1)
- CE3155 Introduction To ETABS (Multi-Storey)Document42 pagesCE3155 Introduction To ETABS (Multi-Storey)Imran SaikatNo ratings yet
- Blade-St: The Complete Steam Turbine Blade Analysis ToolDocument8 pagesBlade-St: The Complete Steam Turbine Blade Analysis Toolramnadh803181No ratings yet
- Effect of Soil Temperature On Am Pa City ValuesDocument10 pagesEffect of Soil Temperature On Am Pa City ValuesAnupong JINo ratings yet
- S.No Acc No Title of The BookDocument12 pagesS.No Acc No Title of The BookmechhodNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Nuclear Medicine & RadiologyDocument8 pagesAssignment On Nuclear Medicine & RadiologyMinhajur RahmanNo ratings yet
- uploads1642069265DPP-1 NLM - Free Body DiagramDocument20 pagesuploads1642069265DPP-1 NLM - Free Body Diagramsharmaneraj80No ratings yet
- Akcome Single-Axis Tracker Structure Calculation Report 2PDocument26 pagesAkcome Single-Axis Tracker Structure Calculation Report 2PRajaa KodadNo ratings yet
- Meh ENG2 PDFDocument37 pagesMeh ENG2 PDFInkeNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Degree Examination Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument2 pagesB.Tech. Degree Examination Electronics & Communication EngineeringPuneeth HNNo ratings yet
- Effects of Processing Parameters of Infrared Based Automated F 2023 CompositDocument11 pagesEffects of Processing Parameters of Infrared Based Automated F 2023 CompositGUANCI ZHUNo ratings yet
- ENCH607-ENPE625 Assignment-04 - 28 Fall 2020Document3 pagesENCH607-ENPE625 Assignment-04 - 28 Fall 2020Ghost RiderNo ratings yet
- 5 Lifetime Extension For SiemensDocument21 pages5 Lifetime Extension For Siemenssdiaman100% (2)
- Pharmaceutical Study of Shatadhauta Ghrita Prepared by Two Different MethodsDocument10 pagesPharmaceutical Study of Shatadhauta Ghrita Prepared by Two Different MethodsBhavesh TanwaniNo ratings yet
- Steel and Timber Structures Part Two:: Design of Structural Steel MembersDocument28 pagesSteel and Timber Structures Part Two:: Design of Structural Steel MembersDhinesh KalaimaranNo ratings yet
- E797Document7 pagesE797Sergio MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chap9 Fan Noise MeasurementDocument5 pagesChap9 Fan Noise Measurementshehbazi2001No ratings yet
- ICE PAPER Biaxial Bending of RC BeamDocument5 pagesICE PAPER Biaxial Bending of RC BeamMk2No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document10 pagesAssignment 1Rajkumar MahadevanNo ratings yet
- Advances in Medical Linear Accelerator TechnologyDocument22 pagesAdvances in Medical Linear Accelerator TechnologyNawel MorjanNo ratings yet
- Verco ER 2078P 2002Document57 pagesVerco ER 2078P 2002jatinNo ratings yet
- Guielines For Specifying and Evaluating New and Rerated Multistage Centrifugal Compressors - PAPERDocument18 pagesGuielines For Specifying and Evaluating New and Rerated Multistage Centrifugal Compressors - PAPERVILLANUEVA_DANIEL2064No ratings yet
- Protecting BoilerAssets With REDOX Stress Control TechnologyDocument42 pagesProtecting BoilerAssets With REDOX Stress Control TechnologyVenkat SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Settlement of A Large Raft FoundationDocument1 pageSettlement of A Large Raft Foundationsb1966No ratings yet