Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes #9 - Enzyme Structure & Function SE (23-24)
Notes #9 - Enzyme Structure & Function SE (23-24)
Uploaded by
allisonejett0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pages1) Enzymes are organic molecules made of amino acids that act as catalysts in chemical reactions in living things. They speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy required.
2) Enzymes fit into substrates like a key in a lock. They bind to substrates at the active site in a "lock and key" model.
3) The four basic steps of enzyme action are: 1) the substrate enters the active site of the enzyme, 2) the enzyme and substrate form an enzyme-substrate complex, 3) the enzyme catalyzes the reaction and a product is formed, 4) the enzyme and products separate and the enzyme can catalyze another reaction.
Original Description:
Original Title
Notes #9- Enzyme Structure & Function SE (23-24)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Enzymes are organic molecules made of amino acids that act as catalysts in chemical reactions in living things. They speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy required.
2) Enzymes fit into substrates like a key in a lock. They bind to substrates at the active site in a "lock and key" model.
3) The four basic steps of enzyme action are: 1) the substrate enters the active site of the enzyme, 2) the enzyme and substrate form an enzyme-substrate complex, 3) the enzyme catalyzes the reaction and a product is formed, 4) the enzyme and products separate and the enzyme can catalyze another reaction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesNotes #9 - Enzyme Structure & Function SE (23-24)
Notes #9 - Enzyme Structure & Function SE (23-24)
Uploaded by
allisonejett1) Enzymes are organic molecules made of amino acids that act as catalysts in chemical reactions in living things. They speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy required.
2) Enzymes fit into substrates like a key in a lock. They bind to substrates at the active site in a "lock and key" model.
3) The four basic steps of enzyme action are: 1) the substrate enters the active site of the enzyme, 2) the enzyme and substrate form an enzyme-substrate complex, 3) the enzyme catalyzes the reaction and a product is formed, 4) the enzyme and products separate and the enzyme can catalyze another reaction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Name: ___________________________________ Date: _______________ Period: _______ Notes #
Notes: Enzyme Structure & Function 9
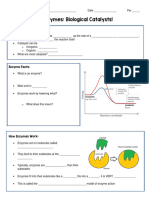
WHAT IS AN ENZYME?
• An enzyme is an organic _______________ made of
_______________
• Most enzymes end in –_______
Examples: _______ase, _______ase, & _______ase
• Enzymes work by ________________ the
__________________ energy of a chemical reaction. This means
it lowers the amount of energy needed to start the reaction, so the
reaction happens ______________!
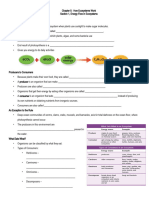
HOW ENZYMES WORK
• Enzymes act on molecules called ______________________
• They bind to their substrates at the _____________ _________
• Typically, enzymes are ______________ than their substrates
• Enzymes fit into their substrates like a ________ fits into a
__________ - it is VERY _______________ !
• This is called the “________________________” model of enzyme
action
STEPS OF ENZYME ACTION
Step #1: Step #2: Step #3: Step #4:
Substrate enters Enzyme and substrate Enzyme action takes Enzyme and products
___________ form an ___________ place and an ______________.
_________ of -_______________ ___________ - The enzyme is
enzyme. _____________. _______________ unchanged and can be
_____________ is _________!
formed.
TEMPERATURE AND ENZYMES
• All enzymes have an ______________ or _______
temperature at which they will work most effectively
• Optimal temperature for humans is 37°C,
or _______ to _______ °F.
• Optimal temperature for dogs is _______ °C,
or 101 to 102°F
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN TEMPERATURES GET TOO HIGH?
• Enzymes _____________ ___________ (kind of like melting)
• When this happens, we say the enzyme is
____________________ or goes through a process called
denaturation
• If the enzyme is not shaped correctly, it _____________ _______
with its substrate and can no longer do its job
You might also like
- Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Nature of ScienceDocument2 pagesAmoeba Sisters Video Recap: Nature of ScienceAlejandro Roblox63% (24)
- 2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetDocument7 pages2.2.5 Respiration WorksheeterikabeltranNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Guided NotesDocument4 pagesEnzymes Guided Notescristian gonzalezNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3 Enzymes WorksheetDocument8 pages2.2.3 Enzymes WorksheetGrace Ann Matanguihan RentoriaNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3 Enzymes WorksheetDocument8 pages2.2.3 Enzymes Worksheetchen weiNo ratings yet
- Enzymes WorksheetDocument8 pagesEnzymes WorksheetClaudia PinnaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes WorksheetDocument5 pagesEnzymes WorksheetgyunimNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Worksheet For LADocument1 pageEnzymes Worksheet For LAAndy DlobelaNo ratings yet
- Apple Experiment: Come Down and Get An Apple and A Slice of Lemon. When You Get Back To Your SeatDocument24 pagesApple Experiment: Come Down and Get An Apple and A Slice of Lemon. When You Get Back To Your SeatArun SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Enzymes NotesDocument4 pagesBiochemistry Enzymes NotesQUEENMAIEYNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: The Effect of Temperature EnzymesDocument2 pagesEnzymes: The Effect of Temperature EnzymesananthNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Macromolecules Guided Notes - 4th BlockDocument6 pagesUnit 2 - Macromolecules Guided Notes - 4th Blockapi-375285021No ratings yet
- Enzymes: Handbook: MetabolismDocument2 pagesEnzymes: Handbook: Metabolismsmol ukeleleNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living Things Study Guide: Most Organisms Need These 5 ThingsDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Living Things Study Guide: Most Organisms Need These 5 ThingsFredrick WedderburnNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Activity ADocument3 pagesEnzyme Activity AKyla QuilantangNo ratings yet
- Bio EnzymesDocument2 pagesBio EnzymesnitinNo ratings yet
- C H A R A C T E R I S T I C O F E N Z Y M E S: Enzymes / Enzim WORKSHEET 4.12: General Characteristic of EnzymesDocument3 pagesC H A R A C T E R I S T I C O F E N Z Y M E S: Enzymes / Enzim WORKSHEET 4.12: General Characteristic of EnzymesHamirah Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- 2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetDocument7 pages2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetSherisa100% (1)
- Cell Respiration Notes!: Energy Needs of LifeDocument2 pagesCell Respiration Notes!: Energy Needs of LifeHaley HaunNo ratings yet
- Constants and VariablesDocument6 pagesConstants and VariablesChristine KaszanekNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY NO. 9 ProceduresDocument5 pagesACTIVITY NO. 9 ProceduresJohanna Marie GantalaoNo ratings yet
- 01 HW P&id 2018 SepDocument4 pages01 HW P&id 2018 Sephafizi naim IsmailNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Worksheet1Document3 pagesEnzyme Worksheet1Iram AzizNo ratings yet
- 2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetDocument7 pages2.2.5 Respiration WorksheeterikabeltranNo ratings yet
- C1.1 NotesDocument19 pagesC1.1 NotesteddyenNo ratings yet
- The Busy Persons Guide To Achieving More Workbook EDITABLEDocument13 pagesThe Busy Persons Guide To Achieving More Workbook EDITABLEKatarina StankovićNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 10 & 11 GenBio1Document6 pagesActivity Sheet 10 & 11 GenBio1Marlou GayaneloNo ratings yet
- SC Form 1Document4 pagesSC Form 1Nurul NadiaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic and Organic Chemistry Experiment No. 4: Preparation of ColloidsDocument4 pagesInorganic and Organic Chemistry Experiment No. 4: Preparation of ColloidsDanzel MalicNo ratings yet
- Yeast Experiment SheetDocument3 pagesYeast Experiment SheetNissreen SapryNo ratings yet
- BioGT - Enzyme Notes - Digging Deeper in The Class of ProteinsDocument4 pagesBioGT - Enzyme Notes - Digging Deeper in The Class of Proteinsanna rothNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition RevisionDocument1 pagePlant Nutrition Revisionapi-3098934090% (1)
- M3L1 Enrichment Activity Cell Defense WorksheetDocument3 pagesM3L1 Enrichment Activity Cell Defense WorksheetHannah Althea Hijan JocsonNo ratings yet
- Examen Diagnostico#4 PDFDocument9 pagesExamen Diagnostico#4 PDFAbigail PQNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and Their Functions - Activity SheetsDocument20 pagesEnzymes and Their Functions - Activity SheetsHazel Ann Oseña MaderaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Practice Test Nov 2020 No EnzymesDocument4 pagesBiochem Practice Test Nov 2020 No EnzymesWen CenaNo ratings yet
- Test 1ST GradeDocument38 pagesTest 1ST GradeanrNo ratings yet
- Iyana Gatling - WDI Notes (B2022)Document3 pagesIyana Gatling - WDI Notes (B2022)Iyana GatlingNo ratings yet
- B2.2 NotesDocument13 pagesB2.2 NotesteddyenNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Human Body TestDocument1 page7th Grade Human Body TestTiago GarrosNo ratings yet
- Evaluations (Formato Word)Document36 pagesEvaluations (Formato Word)Maria Jose Fuentes DiazNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecology Notes PPT Worksheet: NAME: - DATE: - PERIODDocument6 pagesBasic Ecology Notes PPT Worksheet: NAME: - DATE: - PERIODPeng MacNo ratings yet
- A Model For Teaching Writing To Struggling Writers: ExamplesDocument32 pagesA Model For Teaching Writing To Struggling Writers: Examplestabit100% (1)
- 1st Periodical Test ReviewerDocument5 pages1st Periodical Test Reviewerva.cheryllNo ratings yet
- Classes TestsDocument3 pagesClasses Testsenayatullah12jamaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 5 NotesshamptonNo ratings yet
- 2Document9 pages2api-372548146No ratings yet
- Testes Gonads 23 Ovaries Meiosis Hormones Gametes Species HalfDocument15 pagesTestes Gonads 23 Ovaries Meiosis Hormones Gametes Species HalfElla PuiseyNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Cell Growth, Division and ReproductionDocument6 pages10.1 Cell Growth, Division and ReproductionJJNo ratings yet
- Activity - Enzyme WorksheetDocument1 pageActivity - Enzyme WorksheetImay ParaderoNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Grammar 3star Unit4Document2 pagesVocabulary Grammar 3star Unit4marinaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Daily Routine 3gradoDocument2 pagesWorksheet Daily Routine 3gradoarevalovasquezrosa03No ratings yet
- Frog Dissection Computer Pre-Lab Day 2Document5 pagesFrog Dissection Computer Pre-Lab Day 2Kayla McIntoshNo ratings yet
- Evaluations (SCIENCE SM3º)Document35 pagesEvaluations (SCIENCE SM3º)María José Guzmán Santos100% (1)
- InglesDocument29 pagesInglesMERY SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Grammar and Vocabulary PracticeDocument8 pagesUnit 3. Grammar and Vocabulary PracticeCristina Ramón0% (1)
- Parts of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesParts of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsRose Yan JiNo ratings yet
- Using the Right Brain for Math -Multiplication and Division for KidsFrom EverandUsing the Right Brain for Math -Multiplication and Division for KidsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect: Advanced English Grammar for ESL Learners, Second EditionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect: Advanced English Grammar for ESL Learners, Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsNo ratings yet