Professional Documents
Culture Documents
E Function of Providing Professional Advisory (Consulting) Services
E Function of Providing Professional Advisory (Consulting) Services
Uploaded by
jao jaoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Risk Management in Banking Sector MainDocument54 pagesRisk Management in Banking Sector MainJahanvi Bansal55% (11)
- TQM ReviewerDocument14 pagesTQM ReviewerKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- b2b Chap 4 ReviewerDocument10 pagesb2b Chap 4 ReviewerLee TeukNo ratings yet
- TQM ReviewerDocument11 pagesTQM ReviewerKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Differences of Financial Accounting & Management Accounting: Competence Confidentialit Y Integrity CredibilityDocument2 pagesDifferences of Financial Accounting & Management Accounting: Competence Confidentialit Y Integrity CredibilitySweet Little one MusicNo ratings yet
- Strat ReviewerDocument2 pagesStrat Reviewer21-67400No ratings yet
- Bus. Polices & StrategiesDocument5 pagesBus. Polices & StrategiesMitchang ValdeviezoNo ratings yet
- Finals Reviewer SMDocument3 pagesFinals Reviewer SMlacasandile.danicaNo ratings yet
- StratmaDocument6 pagesStratmagjst102801No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveNina ManginsayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 OverviewDocument4 pagesChapter 1 OverviewAldrin YasuoNo ratings yet
- Notes of SCMDocument20 pagesNotes of SCMDianna Kate AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Org. MNGNT SMLL Buss.Document2 pagesOrg. MNGNT SMLL Buss.Romnick Pascua TuboNo ratings yet
- Busman U4 Aos 1Document19 pagesBusman U4 Aos 1Tania BakshiNo ratings yet
- Operation Management Answers-1Document27 pagesOperation Management Answers-1Manish PRAKASH (EA2252001010405)No ratings yet
- Chapter VIII. MEASURING RESULTS ORG.Document16 pagesChapter VIII. MEASURING RESULTS ORG.Arliz Ellaine SiquianNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Managment AccountingDocument5 pagesUnit 7 Managment AccountingLeigh018No ratings yet
- Operations Management Chapter 1 and 2Document8 pagesOperations Management Chapter 1 and 2NOOBONNo ratings yet
- STANDARD COSTING AND VARIANCE ANALYSIS (Repaired)Document24 pagesSTANDARD COSTING AND VARIANCE ANALYSIS (Repaired)Arlyn Alonzo100% (1)
- UCP - M - AccountingDocument377 pagesUCP - M - Accountingsara100% (1)
- PART 4 Chapters 8 To 10Document4 pagesPART 4 Chapters 8 To 10Hillary CanlasNo ratings yet
- Opman SoftDocument72 pagesOpman SoftEllen MaskariñoNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTINGDocument8 pagesACCOUNTINGRijohnna Moreen RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Competitiveness, Strategy & Productivity - 2Document46 pagesChapter 2 - Competitiveness, Strategy & Productivity - 2JeSsica Joy P. SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Manasa T OperationmanagementassignmentDocument5 pagesManasa T OperationmanagementassignmentMANASA TNo ratings yet
- Resume Frank Rothaermel - Strategic Management Chapter 2Document5 pagesResume Frank Rothaermel - Strategic Management Chapter 2Dani YustiardiNo ratings yet
- Operation Management 2Document45 pagesOperation Management 2sNo ratings yet
- Prelim Reviewer ManagerialDocument7 pagesPrelim Reviewer ManagerialMargaux Julienne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Job Order Costing 4Document10 pagesJob Order Costing 4Eross Jacob SalduaNo ratings yet
- Control TechniquesDocument37 pagesControl TechniquesAmit ShahNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Control: ControllingDocument7 pagesFoundations of Control: ControllingAnnamae MartinNo ratings yet
- Glosario de Términos KpiDocument7 pagesGlosario de Términos KpiKaren BonardyNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument31 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerAnika Kim DiamaNo ratings yet
- Review Handouts For The Midterm Exam in EntrepreneurshipDocument3 pagesReview Handouts For The Midterm Exam in EntrepreneurshipAi LeeneNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management Definition and ConceptDocument2 pagesStrategic Cost Management Definition and ConceptMia Joyce Roselada PanesaNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Hoorcollege Aantekeningen 2021Document39 pagesManagement Accounting Hoorcollege Aantekeningen 2021Ilion BarbosoNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesFinancial ManagementJason CabidogNo ratings yet
- Business's ObjectivesDocument31 pagesBusiness's ObjectivesMiddle BenchersNo ratings yet
- Business's Objectives: Nadeeka Kuruppu Lecturer/Consultant NibmDocument31 pagesBusiness's Objectives: Nadeeka Kuruppu Lecturer/Consultant NibmMiddle BenchersNo ratings yet
- Strategy: Strategy Is An Action That Managers Take To Attain One or More of The Organization's GoalsDocument4 pagesStrategy: Strategy Is An Action That Managers Take To Attain One or More of The Organization's Goalsma. isabella marcosNo ratings yet
- Balance Score CardDocument144 pagesBalance Score CardAmruta Pedlikar100% (7)
- Business Studies AS LevelDocument5 pagesBusiness Studies AS LevelJie LeenNo ratings yet
- 5301 EMBA Chap 13 24 sp2012Document190 pages5301 EMBA Chap 13 24 sp2012Judy Anne SalucopNo ratings yet
- II Cost Terms Concepts Classification BehaviorDocument18 pagesII Cost Terms Concepts Classification Behaviortnjm5vxg6kNo ratings yet
- Newell Rough WorkDocument2 pagesNewell Rough WorkArun PrakashNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document27 pagesWeek 4xinghe666No ratings yet
- Mapre PrelimDocument4 pagesMapre PrelimChelsie Casandra TrilloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Operations ManagementDocument6 pagesReviewer in Operations ManagementZie TanNo ratings yet
- Usl MS 01Document6 pagesUsl MS 01myrnabalisi8No ratings yet
- Cost Prelims ReviewerDocument6 pagesCost Prelims ReviewerNochook SatelliteNo ratings yet
- Poc Process MergedDocument5 pagesPoc Process MergedKumar SaurabhNo ratings yet
- Operations Strategy: Origins and New DirectionsDocument5 pagesOperations Strategy: Origins and New Directionsakarim23No ratings yet
- Business Studies - 9.2 Business ManagementDocument7 pagesBusiness Studies - 9.2 Business Managementabudy2147No ratings yet
- Actmana ReviewerDocument10 pagesActmana ReviewerBeatriz TanNo ratings yet
- Finals Reviwer For EntrepDocument3 pagesFinals Reviwer For EntrepMhaica GalagataNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Strategic TermsDocument15 pagesGlossary of Strategic TermsMohammad Javad HamidniaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AFAR Simple NotesDocument10 pagesIntroduction To AFAR Simple NotesCheese Butter100% (1)
- Management Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandManagement Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- The Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successFrom EverandThe Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Demonstrativo de Posição: Dayane David Duraes CPF / CNPJ: 582554608Document4 pagesDemonstrativo de Posição: Dayane David Duraes CPF / CNPJ: 582554608Fábio AndreuccettiNo ratings yet
- Derivatives and Risk ManagementDocument5 pagesDerivatives and Risk ManagementPuneet GargNo ratings yet
- Inscriptions 43 OCt2023Document37 pagesInscriptions 43 OCt2023Gopinath RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Ma 2019..Document6 pagesMa 2019..Ꮢ.Gᴀɴᴇsн ٭ʏт᭄No ratings yet
- Module 7Document28 pagesModule 7Tin ZamudioNo ratings yet
- PHS For Philippine Coast Guard AuxillaryDocument7 pagesPHS For Philippine Coast Guard AuxillaryRj Hush EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Ty Baf TaxationDocument4 pagesTy Baf TaxationAkki GalaNo ratings yet
- D Limited Is Preparing Its Annual Budgets For The YearDocument2 pagesD Limited Is Preparing Its Annual Budgets For The YearAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Macro Mankiw Ch13 20 Questions PDFDocument164 pagesIntermediate Macro Mankiw Ch13 20 Questions PDFYusuf Çubuk100% (1)
- F3 Chapter 4Document9 pagesF3 Chapter 4Ali ShahnawazNo ratings yet
- Major and Minor PairsDocument16 pagesMajor and Minor PairsAdam SehramNo ratings yet
- Alpha C&S and Thematic PortfolioDocument24 pagesAlpha C&S and Thematic PortfolioSaurabh KothariNo ratings yet
- Contract12 1Document3 pagesContract12 1ghostwriter83No ratings yet
- INTERNSHIP REPORT HBL Microfinance BankDocument38 pagesINTERNSHIP REPORT HBL Microfinance Bankbc200415735 TAHIRA RIAZ100% (1)
- 1.2 Nationalized Banks in India: Axis BankDocument4 pages1.2 Nationalized Banks in India: Axis BankUsman KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 2D46D407Document1 page2D46D407Dhyan MothukuriNo ratings yet
- 5-Dela Vina v. CIRDocument7 pages5-Dela Vina v. CIRjillian margaux royNo ratings yet
- Business Marketing Lecture 7 BlanchedDocument38 pagesBusiness Marketing Lecture 7 BlanchedAvdheshNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Entrepreneurship 4th Edition ZacharakisDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Entrepreneurship 4th Edition ZacharakisMonica Degan100% (37)
- Perfectly Competitive Supply and Monopolies-1Document62 pagesPerfectly Competitive Supply and Monopolies-1Samiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Grand Total 100.00: 1. (IMEI/Serial No:) 18.0 %Document4 pagesGrand Total 100.00: 1. (IMEI/Serial No:) 18.0 %Subasini Biswajit Narayan NayakNo ratings yet
- SBI PO Prelims Memory Based Paper (Held On 17th December 2022 Shift 1) (English)Document26 pagesSBI PO Prelims Memory Based Paper (Held On 17th December 2022 Shift 1) (English)mushahidNo ratings yet
- The Role of Project ManagementDocument8 pagesThe Role of Project ManagementTalks of MindsNo ratings yet
- FACTURA Folio FiscalDocument1 pageFACTURA Folio FiscalKarnak ProducerNo ratings yet
- part 5 6 thi onl 1 các thành phần của câuDocument8 pagespart 5 6 thi onl 1 các thành phần của câuNguyen Thi Phuong Y (K17 DN)No ratings yet
- BS 4662Document41 pagesBS 4662hessian123100% (1)
- Natureview Farm Case Calculations Pre-Class SpreadsheetDocument12 pagesNatureview Farm Case Calculations Pre-Class Spreadsheet1010478907No ratings yet
- Maila Rosario College: College of Business Administration Major in Financial ManagementDocument9 pagesMaila Rosario College: College of Business Administration Major in Financial ManagementEleine AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Floyd Jacobs FileDocument23 pagesFloyd Jacobs Filethe kingfishNo ratings yet
E Function of Providing Professional Advisory (Consulting) Services
E Function of Providing Professional Advisory (Consulting) Services
Uploaded by
jao jaoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
E Function of Providing Professional Advisory (Consulting) Services
E Function of Providing Professional Advisory (Consulting) Services
Uploaded by
jao jaoCopyright:
Available Formats
MAS The function of providing professional advisory (consulting) services.
-primary purpose is to improve the client’s use of its capabilities and resources.
Top level planning Also known as overall or strategic planning.
-encompasses the long-range objectives.
-concerned wtih corporate results rather than sectional objectives.
Business-level strategy Focuses on how to attain and satisfy customer, offer goods and services that meet
their needs.
Corporate-level Is when a business makes a decision that affects the whole company.
strategy
Operational strategies Methods companies use to reach their objectives.
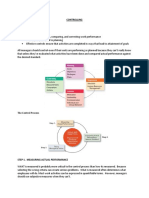
PLANNING -Basic function of management.
-deals with chalking out a future course of action and deciding in advance the most
appropriate course of actions
-deciding on company goals and objectives and figures out how to achieve them.
ORGANIZING -Process of bringing together physical, financial, and human resources
-deciding on how to use company resources to put plans into actions.
STAFFING -Function of manning the organizaton structure.
DIRECTING Actuates the organizations methods to work efficiently
-overseeing the day-to-day activities
CONTROLLING -Implies measurement of accomplishment against the standards and correction of
deviation
-checking the performance of activities against the plan or standards set
-deciding what corrective actions to take
LINE POSITIONS -Those that have the responsibility and authority for achieving the major goals of
corporation
-those directly involved in the daily operations of a business
-is the authority to give orders
-exercises direct downward authority
Staff positions -Provide assistance and specialized advice and expertise to colleagues in line
positions.
-is the authority to advise but not to command others
-commonly exercised laterally or upward in an organization.
Cost leadership Increasing profits by reducing costs, while charging industry-average prices.
strategy
Differentiation strategy Making your products different from and more attrative than your competitors.
Focus strategy Concentrate on particular niche markets and, by understanding the dynamics of that
market and the unique needs of customers.
CONTROLLER -The chief management accounting executive
-responsible for the accounting aspect of management control and whose job
normally covers financial reporting, cost and management accounting, etc.
-staff position
FINANCIAL concerns the duties of the financial manager, who is responsible for making
MANAGEMENT significant corporate investment and financing decisions.
COMPETENCE -maintain an appropriate level of professional expertise by continually developing
knowledge and skills.
-perform their professional duties in accordance with relevant laws, regulations, and
technical standards.
CONFIDENTIALITY Keep information confedential except when disclosures is authorized or legally
required.
INTEGRITY Mitigate actual conflict of interest.
-refrain from engaging in any conduct that would prejuridce carryiong out duties
ethically.
CREDIBILITY -Communicate information fairly and objectively.
-disclose all relevant information that could reasonably be expected to influence an
intended user’s understanding of the reports, or recommendations.
COST Monetary measure of the amount of resources given up or used for some purpose
COST DRIVER Any variable, like level of activity or volume that usually affects costs over a period of
time.
COST POOL Grouping of individual cost items (ex. WIP, FOH)
PRODUCT COST Costs incurred to manufacture the product, therefore inventoriable.
PERIOD COSTS Non-manufacturing costs that include selling, administrative, and R&D.
-expense when incurred.
MANUFACTURING Costs incurred in the factory to convert raw materials into finished goods.
COSTS
NON-MANUFACTURI Costs which are not incurred in transforming materials to finished goods.
NG COSTS
DIRECT COSTS Costs that are related to a particular object and economically and effectively be
traced.
INDIRECT COST Cannot practically, economically, and effextive be trade.
COST ASSIGNMENT Done by allocations the indirect cost to the related cost objects.
RELEVANT COSTS Future costs that will differ under alternative courses of action.
DIFFERENTIAL Difference in costs between any two alternative courses of action.
COSTS
INCREMENTAL Increase in cost from one alternatice to anothet
COSTS
DECREMENTAL Decrease in cost from one alternative to another
COST
OPPORTUNITY Income or benefit given up when one alternative is selected over another.
COSTS
SUNK/PAST OR Already incurred and cannot be changed by any decision made now or to be made in
HISTORICAL COST the future.
STEP COST When activity changes, a step cost shifts upwards or downward by a certain interval
or step.
CVP ANALYSIS A systematic examination of the relationships among cost, cost driver, and profit.
BREAK-EVEN POINT The sales volume level (in peso and in units) where total revenues equals total costs,
that is, there is neither profit or loss.
MARGIN OF SAFETY The amount of peso-sales or the number of units by which actual or budgeted sales
may be decreased without resulting into a loss.
OPERATING The extent to which a company uses fixed costs in its cost structure.
LEVERAGE
LEVERAGE Achieved by increasing fixed costs while lowering variable costs.
You might also like
- Risk Management in Banking Sector MainDocument54 pagesRisk Management in Banking Sector MainJahanvi Bansal55% (11)
- TQM ReviewerDocument14 pagesTQM ReviewerKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- b2b Chap 4 ReviewerDocument10 pagesb2b Chap 4 ReviewerLee TeukNo ratings yet
- TQM ReviewerDocument11 pagesTQM ReviewerKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Differences of Financial Accounting & Management Accounting: Competence Confidentialit Y Integrity CredibilityDocument2 pagesDifferences of Financial Accounting & Management Accounting: Competence Confidentialit Y Integrity CredibilitySweet Little one MusicNo ratings yet
- Strat ReviewerDocument2 pagesStrat Reviewer21-67400No ratings yet
- Bus. Polices & StrategiesDocument5 pagesBus. Polices & StrategiesMitchang ValdeviezoNo ratings yet
- Finals Reviewer SMDocument3 pagesFinals Reviewer SMlacasandile.danicaNo ratings yet
- StratmaDocument6 pagesStratmagjst102801No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveNina ManginsayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 OverviewDocument4 pagesChapter 1 OverviewAldrin YasuoNo ratings yet
- Notes of SCMDocument20 pagesNotes of SCMDianna Kate AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Org. MNGNT SMLL Buss.Document2 pagesOrg. MNGNT SMLL Buss.Romnick Pascua TuboNo ratings yet
- Busman U4 Aos 1Document19 pagesBusman U4 Aos 1Tania BakshiNo ratings yet
- Operation Management Answers-1Document27 pagesOperation Management Answers-1Manish PRAKASH (EA2252001010405)No ratings yet
- Chapter VIII. MEASURING RESULTS ORG.Document16 pagesChapter VIII. MEASURING RESULTS ORG.Arliz Ellaine SiquianNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Managment AccountingDocument5 pagesUnit 7 Managment AccountingLeigh018No ratings yet
- Operations Management Chapter 1 and 2Document8 pagesOperations Management Chapter 1 and 2NOOBONNo ratings yet
- STANDARD COSTING AND VARIANCE ANALYSIS (Repaired)Document24 pagesSTANDARD COSTING AND VARIANCE ANALYSIS (Repaired)Arlyn Alonzo100% (1)
- UCP - M - AccountingDocument377 pagesUCP - M - Accountingsara100% (1)
- PART 4 Chapters 8 To 10Document4 pagesPART 4 Chapters 8 To 10Hillary CanlasNo ratings yet
- Opman SoftDocument72 pagesOpman SoftEllen MaskariñoNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTINGDocument8 pagesACCOUNTINGRijohnna Moreen RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Competitiveness, Strategy & Productivity - 2Document46 pagesChapter 2 - Competitiveness, Strategy & Productivity - 2JeSsica Joy P. SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Manasa T OperationmanagementassignmentDocument5 pagesManasa T OperationmanagementassignmentMANASA TNo ratings yet
- Resume Frank Rothaermel - Strategic Management Chapter 2Document5 pagesResume Frank Rothaermel - Strategic Management Chapter 2Dani YustiardiNo ratings yet
- Operation Management 2Document45 pagesOperation Management 2sNo ratings yet
- Prelim Reviewer ManagerialDocument7 pagesPrelim Reviewer ManagerialMargaux Julienne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Job Order Costing 4Document10 pagesJob Order Costing 4Eross Jacob SalduaNo ratings yet
- Control TechniquesDocument37 pagesControl TechniquesAmit ShahNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Control: ControllingDocument7 pagesFoundations of Control: ControllingAnnamae MartinNo ratings yet
- Glosario de Términos KpiDocument7 pagesGlosario de Términos KpiKaren BonardyNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument31 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerAnika Kim DiamaNo ratings yet
- Review Handouts For The Midterm Exam in EntrepreneurshipDocument3 pagesReview Handouts For The Midterm Exam in EntrepreneurshipAi LeeneNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management Definition and ConceptDocument2 pagesStrategic Cost Management Definition and ConceptMia Joyce Roselada PanesaNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Hoorcollege Aantekeningen 2021Document39 pagesManagement Accounting Hoorcollege Aantekeningen 2021Ilion BarbosoNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesFinancial ManagementJason CabidogNo ratings yet
- Business's ObjectivesDocument31 pagesBusiness's ObjectivesMiddle BenchersNo ratings yet
- Business's Objectives: Nadeeka Kuruppu Lecturer/Consultant NibmDocument31 pagesBusiness's Objectives: Nadeeka Kuruppu Lecturer/Consultant NibmMiddle BenchersNo ratings yet
- Strategy: Strategy Is An Action That Managers Take To Attain One or More of The Organization's GoalsDocument4 pagesStrategy: Strategy Is An Action That Managers Take To Attain One or More of The Organization's Goalsma. isabella marcosNo ratings yet
- Balance Score CardDocument144 pagesBalance Score CardAmruta Pedlikar100% (7)
- Business Studies AS LevelDocument5 pagesBusiness Studies AS LevelJie LeenNo ratings yet
- 5301 EMBA Chap 13 24 sp2012Document190 pages5301 EMBA Chap 13 24 sp2012Judy Anne SalucopNo ratings yet
- II Cost Terms Concepts Classification BehaviorDocument18 pagesII Cost Terms Concepts Classification Behaviortnjm5vxg6kNo ratings yet
- Newell Rough WorkDocument2 pagesNewell Rough WorkArun PrakashNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document27 pagesWeek 4xinghe666No ratings yet
- Mapre PrelimDocument4 pagesMapre PrelimChelsie Casandra TrilloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Operations ManagementDocument6 pagesReviewer in Operations ManagementZie TanNo ratings yet
- Usl MS 01Document6 pagesUsl MS 01myrnabalisi8No ratings yet
- Cost Prelims ReviewerDocument6 pagesCost Prelims ReviewerNochook SatelliteNo ratings yet
- Poc Process MergedDocument5 pagesPoc Process MergedKumar SaurabhNo ratings yet
- Operations Strategy: Origins and New DirectionsDocument5 pagesOperations Strategy: Origins and New Directionsakarim23No ratings yet
- Business Studies - 9.2 Business ManagementDocument7 pagesBusiness Studies - 9.2 Business Managementabudy2147No ratings yet
- Actmana ReviewerDocument10 pagesActmana ReviewerBeatriz TanNo ratings yet
- Finals Reviwer For EntrepDocument3 pagesFinals Reviwer For EntrepMhaica GalagataNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Strategic TermsDocument15 pagesGlossary of Strategic TermsMohammad Javad HamidniaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AFAR Simple NotesDocument10 pagesIntroduction To AFAR Simple NotesCheese Butter100% (1)
- Management Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandManagement Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- The Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successFrom EverandThe Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Demonstrativo de Posição: Dayane David Duraes CPF / CNPJ: 582554608Document4 pagesDemonstrativo de Posição: Dayane David Duraes CPF / CNPJ: 582554608Fábio AndreuccettiNo ratings yet
- Derivatives and Risk ManagementDocument5 pagesDerivatives and Risk ManagementPuneet GargNo ratings yet
- Inscriptions 43 OCt2023Document37 pagesInscriptions 43 OCt2023Gopinath RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Ma 2019..Document6 pagesMa 2019..Ꮢ.Gᴀɴᴇsн ٭ʏт᭄No ratings yet
- Module 7Document28 pagesModule 7Tin ZamudioNo ratings yet
- PHS For Philippine Coast Guard AuxillaryDocument7 pagesPHS For Philippine Coast Guard AuxillaryRj Hush EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Ty Baf TaxationDocument4 pagesTy Baf TaxationAkki GalaNo ratings yet
- D Limited Is Preparing Its Annual Budgets For The YearDocument2 pagesD Limited Is Preparing Its Annual Budgets For The YearAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Macro Mankiw Ch13 20 Questions PDFDocument164 pagesIntermediate Macro Mankiw Ch13 20 Questions PDFYusuf Çubuk100% (1)
- F3 Chapter 4Document9 pagesF3 Chapter 4Ali ShahnawazNo ratings yet
- Major and Minor PairsDocument16 pagesMajor and Minor PairsAdam SehramNo ratings yet
- Alpha C&S and Thematic PortfolioDocument24 pagesAlpha C&S and Thematic PortfolioSaurabh KothariNo ratings yet
- Contract12 1Document3 pagesContract12 1ghostwriter83No ratings yet
- INTERNSHIP REPORT HBL Microfinance BankDocument38 pagesINTERNSHIP REPORT HBL Microfinance Bankbc200415735 TAHIRA RIAZ100% (1)
- 1.2 Nationalized Banks in India: Axis BankDocument4 pages1.2 Nationalized Banks in India: Axis BankUsman KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 2D46D407Document1 page2D46D407Dhyan MothukuriNo ratings yet
- 5-Dela Vina v. CIRDocument7 pages5-Dela Vina v. CIRjillian margaux royNo ratings yet
- Business Marketing Lecture 7 BlanchedDocument38 pagesBusiness Marketing Lecture 7 BlanchedAvdheshNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Entrepreneurship 4th Edition ZacharakisDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Entrepreneurship 4th Edition ZacharakisMonica Degan100% (37)
- Perfectly Competitive Supply and Monopolies-1Document62 pagesPerfectly Competitive Supply and Monopolies-1Samiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Grand Total 100.00: 1. (IMEI/Serial No:) 18.0 %Document4 pagesGrand Total 100.00: 1. (IMEI/Serial No:) 18.0 %Subasini Biswajit Narayan NayakNo ratings yet
- SBI PO Prelims Memory Based Paper (Held On 17th December 2022 Shift 1) (English)Document26 pagesSBI PO Prelims Memory Based Paper (Held On 17th December 2022 Shift 1) (English)mushahidNo ratings yet
- The Role of Project ManagementDocument8 pagesThe Role of Project ManagementTalks of MindsNo ratings yet
- FACTURA Folio FiscalDocument1 pageFACTURA Folio FiscalKarnak ProducerNo ratings yet
- part 5 6 thi onl 1 các thành phần của câuDocument8 pagespart 5 6 thi onl 1 các thành phần của câuNguyen Thi Phuong Y (K17 DN)No ratings yet
- BS 4662Document41 pagesBS 4662hessian123100% (1)
- Natureview Farm Case Calculations Pre-Class SpreadsheetDocument12 pagesNatureview Farm Case Calculations Pre-Class Spreadsheet1010478907No ratings yet
- Maila Rosario College: College of Business Administration Major in Financial ManagementDocument9 pagesMaila Rosario College: College of Business Administration Major in Financial ManagementEleine AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Floyd Jacobs FileDocument23 pagesFloyd Jacobs Filethe kingfishNo ratings yet