Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anti Arrhythmic Drugs
Anti Arrhythmic Drugs
Uploaded by
g.4ssilaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anti Arrhythmic Drugs
Anti Arrhythmic Drugs
Uploaded by
g.4ssilaCopyright:
Available Formats
ANTI-ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS 1
Potassium Efflux
Calcium Influx
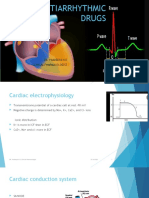
Classification Schemes The most common classification scheme used is the Vaughan Williams Classification. This
Membrane potential (mV)
30
0
describes the various antiarrythmic medications in terms of their mechanism of action with regard to the cardiac action
Fast
potential. This is useful when conceptualising in terms of the slow and fast cardiac action potential, but several of the
Sodium
antiarrythmics are not easily categorised such as amiodarone which may be included in several categories and some are
Influx ignored and lumped into the other category including digoxin, adenosine, and magnesium. It also is of little clinical benefit it
-90
4
terms of treatment modalities for various arrythmias. It also makes no allowance for the fact that some medications work
-100 differently in diseased and non diseased hearts.
0 100 200 300 400 500
Time (ms)
Vaughan Williams Classification
Class Action Effect Drugs Therapeutic Indications
I Blocks Sodium Channels
Ia Prolongs refractory period of action potential Procainamide Atrial and ventricular arrhythmias especially post MI
Ib Shortens refractory period of action potential Lignocaine, Phenytoin Ventricular arrhythmias post MI, digoxin induced arrhythmias
Ic No effect on period of action potential Flecainide Refractory arrhythmias
II Beta Adrenergic Blockers Reduced SA firing Propanolol / Sotalol
* ^
Rate control in AF, AT, Flutter and VT
III Potassium Channel Blockers Prolong refractory period of the action potential Amiodarone#, ilbutalide AF / Flutter termination
IV Calcium Channel Blockers AV conduction, PR prolonged, decreased contractility Verapamil, Diltiazem SVT and AF or Flutter
OTHER Blocks Na /K+ +
ATPASE,
leads to Ca , K , Ach
2+ +
Increased contractility and AV conduction Digoxin AF rate control and heart failure
Opens K+ channels via adenosine receptors Hyperpolarises myocardium , AV conduct, SA firing Adenosine Terminate SVT or reveal underlying rhythm in tachycardias
Stimulates Na /K + +
ATPASE
Membrane stabilisation Magnesium VF / Torsades de Pointes
Notes * Propanolol also has sodium channel blocking activity
^ Sotalol has two isomers, and is presented as a racemic mixture. One is an effective beta blocker and both have class III action potential prolongation activity
# Amiodarone is a special case. It blocks sodium, calcium, and potassium channels and exhibits beta blockade, although is usually categorised into Class III
1A
Sodium Channel Blockers
Membrane potential (mV)
30
Procainamide is a Class 1A prototype. Other drugs with group 1A actions include quinidine and disopyramide. Amiodarone , 0
often classified in group 3, also has typical group 1A actions. These drugs affect both atrial and ventricular arrhythmias. They Action
Potential
block INa, and therefore slow conduction velocity in the atria, Purkinje fibers, and ventricular cells. At high doses they also slow Lengthened
AV conduction. The reduction in ventricular conduction results in increased QRS duration in the ECG. In addition, the 1A -90
-100
drugs block IK and slow repolarization. Therefore, they increase AP duration and the effective refractory period (ERP) in 0 100 200 300 400 500
addition to slowing conduction velocity and ectopic pacemakers. The increase in AP duration generates an increase in QT Time (ms)
interval. Amiodarone has similar effects on sodium current (INa block) and has the greatest AP-prolonging effect (IK block). 1B
Membrane potential (mV)
30
0
Class IB Lignocaine is the prototype 1B drug and is used exclusively by the IV or IM routes. Lignocaine selectively affects
Action
ischemic or depolarized Purkinje and ventricular tissue and has little effect on atrial tissue; the drug reduces AP duration in Potential
some cells, but because it slows recovery of sodium channels from inactivation it does not shorten (and may even prolong) -90
Shortened
the effective refractory period. Because these agents have little effect on normal cardiac cells, they have little effect on the -100
ECG. Phenytoin , an anticonvulsant and not a true local anesthetic, is sometimes classified with the group 1B antiarrhythmic 0 100 200
Time (ms)
300 400 500
agents because it can be used to reverse digitalis-induced arrhythmias. It resembles lignocaine in lacking significant effects
1C
on the normal ECG.
Membrane potential (mV)
30
Action
Class IC Flecainide is the prototype drug with group 1C actions. These drugs have no effect on ventricular AP duration or Potential
the QT interval. They are powerful depressants of sodium current, however, and can markedly slow conduction velocity in -90 Unchanged
atrial and ventricular cells. They increase the QRS duration of the ECG. -100
0 100 200 300 400 500
Time (ms)
Beta adrenergic blockers Propranolol and esmolol are prototypic antiarrhythmic blockers. The antidysrhythmic effects of II
Membrane potential (mV)
20
beta-adrenergic antagonists most likely reflect a blockade of the responses to beta-receptors in the heart to sympathetic nervous system 0
stimulation (decreasing G-protien S responses and reducing intracellular cAMP), as well as the effects of circulating catecholamines. As a 0 3 Rate
Decreased
result, the rate of spontaneous phase 4 depolarization is decreased and the rate of sinoatrial node discharge is decreased. The AV node is -40
4
Beta
Blocker
particularly sensitive to blockers and the PR interval is usually prolonged by group 2 drugs. Sotalol and amiodarone, generally classified Effect
as group 3 drugs, also have group 2 -blocking effects. -80
0 100 200 300 400
Time (ms)
Potassium Channel Blockers The hallmark of group 3 drugs is prolongation of the AP duration. This AP prolongation is caused by
blockade of IK potassium channels that are responsible for the repolarization of the AP. AP prolongation results in an increase in effective III
Membrane potential (mV)
30
refractory period and reduces the ability of the heart to respond to rapid tachycardias. Sotalol, ibutilide, dofetilide, and amiodarone (and 0
group 1A drugs; see above) produce this effect on most cardiac cells; the action of these drugs is, therefore, apparent in the ECG as an Action
increase in QT interval. Antiarrhythmic agents that prolong the duration of the action potential may be of value in the management Potential
of patients with supraventricular tachyarrhythmias, or in arrhythmias associated with anomalous conduction pathways. Nevertheless, all -90
Lengthened
drugs that prolong the ventricular action potential may induce torsade de pointes (prolongation of the Q-T interval followed by -100
episodes of polymorphic tachycardia). 0 100 200
Time (ms)
300 400 500
Calcium Channel Blockers Verapamil is the prototype. Diltiazem is also an effective antiarrhythmic drug. Nifedipine and the other
dihydropyridines are not useful as antiarrhythmics, probably because they decrease arterial pressure enough to evoke a compensatory IV
Membrane potential (mV)
20
Conduction
sympathetic discharge to the heart. Pacemaker cells in the SA and the AV node are almost entirely dependent on inward Ca2+ currents for 0
0 Velocity
depolarization. Verapamil and Diltiazem cause a state- and use-dependent selective depression of calcium current in tissues that require Decreased
-40
the participation of L-type calcium channels. AV conduction velocity is decreased and effective refractory period increased by these drugs.
PR interval is consistently increased. Drugs that block Ca2+ channels are particularly effective in preventing reentrant arrhythmias in the AV -80
node and including nodal tachycardia. 0 100 200 300 400
Time (ms)
Christopher R Andersen 2012
You might also like
- Kin 2G03 - Sleep Assign #1Document5 pagesKin 2G03 - Sleep Assign #1YurNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs - AMBOSS TWO PDFDocument6 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs - AMBOSS TWO PDFRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Important Things To RememberDocument5 pagesPharmacology Important Things To RememberHydie100% (1)
- Respiratory Module TestDocument14 pagesRespiratory Module TestMuhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Anti Arrhythmics 2Document1 pageAnti Arrhythmics 2Babu RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Classification of Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument5 pagesClassification of Antiarrhythmic DrugsRadijska Postaja KoprivnicaNo ratings yet
- Antiarrythmic Agents: Antiarrythmic Drugs For HorsesDocument3 pagesAntiarrythmic Agents: Antiarrythmic Drugs For HorsesMageja TatendaNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs - AMBOSS TWODocument6 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs - AMBOSS TWOOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel BlockersDocument4 pagesLocal Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel Blockersmed testNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii: Drugs For Arrhythmia: ObjectivesDocument3 pagesUnit Ii: Drugs For Arrhythmia: ObjectivesJosa Camille BungayNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Agent - WikipediaDocument23 pagesAntiarrhythmic Agent - WikipediaSai Jeevan SampathiraoNo ratings yet
- Cardio: Non Nodal NodalDocument12 pagesCardio: Non Nodal NodallavNo ratings yet
- Obat AntiaritmiaDocument18 pagesObat AntiaritmiaWahyu JuliandaNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVT Drugs MOA Indication S/E NotesDocument1 pageAntiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVT Drugs MOA Indication S/E Notesmonica leeNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVT Drugs MOA Indication S/E NotesDocument1 pageAntiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVT Drugs MOA Indication S/E Notesmonica leeNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVTDocument1 pageAntiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVTmonica leeNo ratings yet
- 448 - 194246 - Drug For Arrythmia - HandoutDocument4 pages448 - 194246 - Drug For Arrythmia - HandoutAnaliza Kitongan LantayanNo ratings yet
- Cardio DrugsDocument4 pagesCardio DrugsAlex ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Glycosides, Antiarrhythemic Drugs-Dr - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, LecturerDocument15 pagesCardiac Glycosides, Antiarrhythemic Drugs-Dr - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, Lecturerjibachha sahNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of ArrhythmiasDocument37 pagesDrugs Used in The Treatment of ArrhythmiasChipego ChiyaamaNo ratings yet
- Pharma DR - Jawad Antiarrhythmic Agent Lec 4Document7 pagesPharma DR - Jawad Antiarrhythmic Agent Lec 4rkh647m7szNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Therapy of Arrhythmias (09.11.16)Document46 pagesPharmacological Therapy of Arrhythmias (09.11.16)Mariana CabralNo ratings yet
- Mdbsis09 CA A III 2017Document4 pagesMdbsis09 CA A III 2017Guneyden GuneydenNo ratings yet
- PHARMA R2.4 AntiarrhythmicsDocument12 pagesPHARMA R2.4 Antiarrhythmicscharmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs in EngDocument38 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs in EngBasit IqbalNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs - AMBOSSDocument4 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs - AMBOSSOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Slides Antiarrhythmics CardiovascularPharmaDocument31 pagesSlides Antiarrhythmics CardiovascularPharmaMajeed Qasim100% (1)
- Cardio ActiveDocument2 pagesCardio ActiveVeran, Arzel S.No ratings yet
- Understanding Amiodarone: Beta Adrenergic Receptor Blocking Slow Calcium Channel Blocking Fast Sodium Channel BlockingDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Amiodarone: Beta Adrenergic Receptor Blocking Slow Calcium Channel Blocking Fast Sodium Channel BlockingAdi PuteraNo ratings yet
- Imd - Usmlerx - Usmle Step 1 Qbank - 2020 - Question 1 of 40Document2 pagesImd - Usmlerx - Usmle Step 1 Qbank - 2020 - Question 1 of 40Ubaud JhanNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs - Classification & MechanismDocument1 pageAntihypertensive Drugs - Classification & MechanismAhmed YT100% (1)
- Agents Used in Cardiac ArrythmiasDocument79 pagesAgents Used in Cardiac ArrythmiasBrother GeorgeNo ratings yet
- ArythmicDocument40 pagesArythmicChia Yin NgNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: More To Inactivated Na Channels Arrhythmias During Myocardial Ischaemia or Due To DigoxinDocument3 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs: More To Inactivated Na Channels Arrhythmias During Myocardial Ischaemia or Due To DigoxinChia Yin NgNo ratings yet
- ANTI ARRHTYMIC DRUG IncompleteDocument9 pagesANTI ARRHTYMIC DRUG IncompleteJustine CastilloNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument7 pagesPharmacologyscjkyd5cvrNo ratings yet
- Taller Nacional de Muerte Súbita JOANNADocument9 pagesTaller Nacional de Muerte Súbita JOANNAOscar AlaveNo ratings yet
- نسخة ANTI-ARRHYTHMICDocument49 pagesنسخة ANTI-ARRHYTHMICManWol JangNo ratings yet
- HemodialysisDocument2 pagesHemodialysisAr JayNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0885392411004659Document17 pagesPi Is 0885392411004659rudin walterNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhytmic DrugsDocument4 pagesAntiarrhytmic Drugssinemkaraoglan6819No ratings yet
- Pharmacology FreebieDocument3 pagesPharmacology FreebieMohammad Farooq KhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiology PharmacologyDocument40 pagesCardiology PharmacologygvantsaNo ratings yet
- CL11 Principle of Diuretic UseDocument8 pagesCL11 Principle of Diuretic Usea189192No ratings yet
- CVS Drugs CologyDocument9 pagesCVS Drugs CologyAnuj panditNo ratings yet
- 2017-29-Digoxin and Amiodarone (A Vorster)Document10 pages2017-29-Digoxin and Amiodarone (A Vorster)Sadiq ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For ArrhythymiasDocument4 pagesDrugs For ArrhythymiasAdriane LustreNo ratings yet
- Cebu Institute of Technology - University College of NursingDocument2 pagesCebu Institute of Technology - University College of NursingSergi Lee OrateNo ratings yet
- Nitroglycerin Isosorbide Dinitrate: Class Class Use UseDocument17 pagesNitroglycerin Isosorbide Dinitrate: Class Class Use UseEdmond ChanNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs FinalDocument31 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs FinalAmanuel Maru50% (2)
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Dr. Sachana KC 1 Year Resident Department of AnesthesiaDocument67 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs: Dr. Sachana KC 1 Year Resident Department of AnesthesiaKshitizma GiriNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Agent: Class Known As Examples Mechanism Clinical Uses in CardiologyDocument2 pagesAntiarrhythmic Agent: Class Known As Examples Mechanism Clinical Uses in CardiologyMUBIERAMZINo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Drugs Used in ArrhythymiasDocument27 pagesChapter 4 Drugs Used in ArrhythymiasKaye ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- AntihypertensionDocument17 pagesAntihypertension백지원 (소네트리)No ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Quinidine Procainamide Disopyramide Quinidine Flecainide: Class 1A Class 1B Class 1CDocument3 pagesQuinidine Procainamide Disopyramide Quinidine Flecainide: Class 1A Class 1B Class 1CAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmias: Table 33-13Document25 pagesDysrhythmias: Table 33-13ZeoFateXNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs Classification (Vaughan Williams)Document8 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs Classification (Vaughan Williams)ana100% (1)
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs Part 2Document4 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs Part 2AVINASH PvkNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Dr. Pradeepa H D Clinical PharmacologistDocument16 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs: Dr. Pradeepa H D Clinical PharmacologistpradeephdNo ratings yet
- DuPont Altacor For OP 2014Document35 pagesDuPont Altacor For OP 2014Ruth LeeNo ratings yet
- Case Study - CVDDocument2 pagesCase Study - CVDJenny JendersNo ratings yet
- Coq10 (Coenzyme Q10) : By:Ester N HaindoboDocument9 pagesCoq10 (Coenzyme Q10) : By:Ester N HaindoboTabea Tic-leeNo ratings yet
- Postural HypotensionDocument3 pagesPostural HypotensionSimran JosanNo ratings yet
- Management of Hypertensive EmergencyDocument17 pagesManagement of Hypertensive EmergencyGiovanna AlguNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport SystemsDocument20 pagesPlant Transport Systemscale suarezNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Science 10 Week 3Document28 pages3rd Quarter Science 10 Week 3Aple RigorNo ratings yet
- BTL CardioPoint-CPET CLIN ClinicalBackground EN100Document26 pagesBTL CardioPoint-CPET CLIN ClinicalBackground EN100stoicea catalinNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart Disease - Patho - DiagramDocument10 pagesRheumatic Heart Disease - Patho - DiagramJoann100% (12)
- Yoga Body - SplitsDocument4 pagesYoga Body - Splitsmdsay09No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice CraverDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice Cravertroul.cubit.nwjkgf100% (44)
- Unit 2 - AP Classroom Video HW SheetDocument8 pagesUnit 2 - AP Classroom Video HW SheetAubrey HovanNo ratings yet
- 16 Biochemistry Lecture - BioenergeticsDocument39 pages16 Biochemistry Lecture - BioenergeticsAMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- 6 - BurnsDocument17 pages6 - BurnsRENEROSE TORRESNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review SheetDocument2 pagesFinal Exam Review Sheetapi-264668182No ratings yet
- Assessment of The Respiratory System MTDocument15 pagesAssessment of The Respiratory System MTChilled Moo MooNo ratings yet
- Blood Cell Formation (Hematopoiesis)Document44 pagesBlood Cell Formation (Hematopoiesis)Ery BureniNo ratings yet
- Ghhs General Q&A-newDocument1 pageGhhs General Q&A-newmonishaaNo ratings yet
- 1.cardiac CycleDocument43 pages1.cardiac CycleNatasha Grace NtembwaNo ratings yet
- CH 04 DDocument34 pagesCH 04 DVijayRajNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic NeurotransmittersDocument18 pagesAdrenergic Neurotransmittersparmarkeval1610No ratings yet
- Thesis Topics in Cardiac AnaesthesiaDocument6 pagesThesis Topics in Cardiac AnaesthesiaHelpWritingCollegePapersUK100% (2)
- 1.1 Human Breathing Mechanism (A)Document20 pages1.1 Human Breathing Mechanism (A)Sselvi SubramoniamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Respiratory Systems NotesDocument11 pagesChapter 9 Respiratory Systems NotesCaleb DodgeNo ratings yet
- Cue and Clue PL Idx PDX PTX Pmo&Ed: Mr. T/86Yo/ Ward 26 Subjective Non PharmacologyDocument8 pagesCue and Clue PL Idx PDX PTX Pmo&Ed: Mr. T/86Yo/ Ward 26 Subjective Non PharmacologyIka AyuNo ratings yet
- Thyroidhormone 180220171148Document51 pagesThyroidhormone 180220171148Hasan Al MasudNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Abnormal Psychology 8th Edition Durand Test BankDocument24 pagesEssentials of Abnormal Psychology 8th Edition Durand Test Bankthenarkaraismfq9cn100% (32)
- Anatomy and Physiology Pre Lim ReviewerDocument44 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Pre Lim ReviewerKRISTIAN DRAZEN MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 The Heart Lesson Plan For Caroline 1Document3 pagesChapter 13 The Heart Lesson Plan For Caroline 1api-546738847No ratings yet