Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fractional Distillation
Fractional Distillation
Uploaded by
fintan.mulganOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fractional Distillation
Fractional Distillation
Uploaded by
fintan.mulganCopyright:
Available Formats
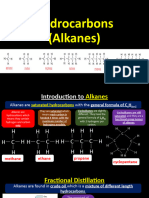
The crude oils are added to a column and burnt at very high temperatures.
The crude oil is then
separated into different length hydrocarbons and the lighter, shorter hydrocarbons are gathered near
the top of the fractional distillation chamber. The different hydrocarbons are then taken out the
chambers and are used for different things such as car fuel, jet fuel or lube. Mention temperature
decreases as you go up the column, crude oil must be vaporized, when boiling point is reached, they
love the column as a liquid and are separated, group of chain lengths.
05/12/2023
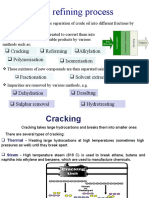
CH2=CH2 + Br2 -> BrCH2BrCH2
C11H24 -> C6H14 + C5H10 (Hexane + Pent-2-ene
It forms a smaller alkane hydrocarbon and an alkene hydrocarbon which uses up the remaining
carbon atoms. The alkenes are unsaturated meaning they are branched.
Catalysts
Speed up the rate of reaction but are not chemically changed or used up in the reaction. May be
specific for a particular reaction – applies especially to enzymes in biological reactions.
Homogeneous catalysts – reactants are catalyst in same state.
Heterogeneous catalysts – reactants and catalysts in different states.
Catalysts are usually solid.
Heterogeneous catalysts – Reactants are absorbed onto catalyst surface – i.e., weak bonds formed
between reactants and catalysts. Bonds within reactant molecules are weakened and break. New
bonds form between the reactants. The product(s) leave the catalyst surface.
In heterogeneous catalysis, catalysts poised by a chemical binding to surface, poison bonds
irreversibly with catalyst.
Catalysts can sometimes be regenerated by blowing hot air over catalyst – oxidises chemical on
surface. Used to remove carbon (soot) after catalytic cracking.
You might also like
- Liquid and Gaseous FuelsDocument84 pagesLiquid and Gaseous Fuelsmohamed abdalla abo assyNo ratings yet
- Types of Reactions in Petroleum Refining NewDocument15 pagesTypes of Reactions in Petroleum Refining Newtariq fareedNo ratings yet
- 7.1. Carbon Compounds As Fuels and FeedstockDocument4 pages7.1. Carbon Compounds As Fuels and FeedstockAdellNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesOrganic ChemistrybethanyNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil RefiningDocument28 pagesCrude Oil RefiningtswNo ratings yet
- FuelsDocument16 pagesFuelsCogie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil Refining Process 15.12.2010Document9 pagesCrude Oil Refining Process 15.12.2010Sheheryar MirzaNo ratings yet
- Technical Description 3Document8 pagesTechnical Description 3Santosh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Industry - CPT150SDocument33 pagesPetroleum Industry - CPT150Smonkey manNo ratings yet
- Industry and The Environment - Crude OilDocument2 pagesIndustry and The Environment - Crude OilTekani TrimNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Refining NotesDocument4 pagesPetroleum Refining Notesapi-304149645No ratings yet
- Basics of Refinery1Document15 pagesBasics of Refinery1Sunil PatanwadiyaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Refining Notes 1Document5 pagesPetroleum Refining Notes 1api-304149645No ratings yet
- Crude OilDocument23 pagesCrude OilAgung Prasetyo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Processing: CrackingDocument5 pagesChemical Processing: CrackingJun VarNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Part1omkarDocument173 pagesInstrumentation Part1omkaromkarvadlooriNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons 1Document8 pagesHydrocarbons 1Priska ChristinaNo ratings yet
- Refining of Petroleum: Back To TopDocument11 pagesRefining of Petroleum: Back To TopMazhar AliNo ratings yet
- Overview of Fluid Catalytic Cracking Unit (FCC, Fccu) : Catalyst AluminumDocument4 pagesOverview of Fluid Catalytic Cracking Unit (FCC, Fccu) : Catalyst AluminumAdemola RabiuNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 FuelDocument27 pagesChapter-5 FueljeetNo ratings yet
- Chapter-04 Modification of Triglyceride OilsDocument10 pagesChapter-04 Modification of Triglyceride OilsabirNo ratings yet
- Crude OilDocument11 pagesCrude OildamochkaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum and Alkanes Fractional Distillation Cracking CombustionDocument10 pagesPetroleum and Alkanes Fractional Distillation Cracking CombustionCarlton GrantNo ratings yet
- Uses of The Components of Crude Oil As FuelsDocument6 pagesUses of The Components of Crude Oil As FuelsPearl LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Combustion and Fuel, Chapter CH 3Document53 pagesCombustion and Fuel, Chapter CH 301094255175 01094255175No ratings yet
- As Level - AlkanesDocument12 pagesAs Level - AlkanesRegine BalagtasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Petrochemical ProcessesDocument33 pagesChemistry of Petrochemical ProcessesKhaled ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument12 pagesOrganic ChemistryYoviNo ratings yet
- Fractional Distillation of Crude OilDocument2 pagesFractional Distillation of Crude OilchikeruNo ratings yet
- Alkanes ClassDocument27 pagesAlkanes ClassRyan JamesNo ratings yet
- Petroleum and Petroleum ProductsDocument44 pagesPetroleum and Petroleum Productspiyushrao655No ratings yet
- IVAN Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesIVAN Organic ChemistryYoviNo ratings yet
- Fractional DistillationDocument19 pagesFractional Distillationamindur100% (2)
- Topic 4 Lesson 1 Composition and Production of FODocument7 pagesTopic 4 Lesson 1 Composition and Production of FOcarltalves1No ratings yet
- DPV20412-Unit3 1Document45 pagesDPV20412-Unit3 1afiq hayqalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project: By: Ouail BalahDocument9 pagesChemistry Project: By: Ouail BalahOuail BalahNo ratings yet
- Refining of PetroleumDocument10 pagesRefining of PetroleumHanyszShalNo ratings yet
- How Fractional Distillation Separates Crude Oil in - 240110 - 164232Document2 pagesHow Fractional Distillation Separates Crude Oil in - 240110 - 164232neelayadakshi.harishankarNo ratings yet
- How Oil Refining WorksDocument13 pagesHow Oil Refining WorksHerman_ms2000No ratings yet
- HD Ro FinishingDocument6 pagesHD Ro FinishingMuhammad sherazNo ratings yet
- AFL Units 1 To 3 NOLDocument47 pagesAFL Units 1 To 3 NOLpavanraneNo ratings yet
- How Oil Refining WorksDocument6 pagesHow Oil Refining WorksAnonymous NyvKBWNo ratings yet
- Refining ProcessDocument15 pagesRefining Processtechy TalksNo ratings yet
- 4 FuelsDocument54 pages4 FuelsteddiyfentawNo ratings yet
- The Refining Process: Cracking Reforming Isomerisation Alkylation PolymerisationDocument15 pagesThe Refining Process: Cracking Reforming Isomerisation Alkylation Polymerisationdana mohammedNo ratings yet
- Simple Guide To Oil RefiningDocument5 pagesSimple Guide To Oil RefiningPatel AshokNo ratings yet
- CPT4Document5 pagesCPT4daddarioalexander01No ratings yet
- ReactorsDocument19 pagesReactorsluisNo ratings yet
- Module 4. Lesson 2 Liquid FuelsDocument10 pagesModule 4. Lesson 2 Liquid FuelsVJ CarbonellNo ratings yet
- On Average, Crude Oils Are Made ofDocument19 pagesOn Average, Crude Oils Are Made ofbalajiupesNo ratings yet
- 1-Processing of PetroleumDocument28 pages1-Processing of PetroleumNurfatihah UmairahNo ratings yet
- Refining of PetroleumDocument6 pagesRefining of Petroleumzb khanNo ratings yet
- AT6504 AFL Notes PDFDocument52 pagesAT6504 AFL Notes PDFmeetbalakumarNo ratings yet
- How Oil Refining WorksDocument12 pagesHow Oil Refining WorkssubashNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Refining Crude Oil Refining Processes PDFDocument6 pagesPetroleum Refining Crude Oil Refining Processes PDFJAPAN NANAVATI0% (1)
- Applied Thermodynamics MR Rajkishor SinghDocument267 pagesApplied Thermodynamics MR Rajkishor SinghHerlina Pebriani 5No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Crude Petroleum analysis handbook: Crude oil Quality control, #1From EverandCrude Petroleum analysis handbook: Crude oil Quality control, #1Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Ethanol Fuel Learn to Make and Use Ethanol to Power Your VehiclesFrom EverandEthanol Fuel Learn to Make and Use Ethanol to Power Your VehiclesNo ratings yet