Professional Documents
Culture Documents
130 - Neurology Physiology) Sacral Plexus
130 - Neurology Physiology) Sacral Plexus
Uploaded by
katerina.georgiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
130 - Neurology Physiology) Sacral Plexus
130 - Neurology Physiology) Sacral Plexus
Uploaded by
katerina.georgiCopyright:
Available Formats
Last edited: 9/9/2021
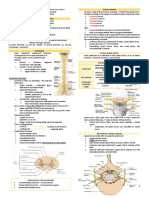
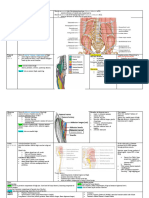
1. SACRAL PLEXUS
Sacral Plexus Medical Editor: Dr. Sarah Abimhamed
OUTLINE
I) BRANCHES OF SACRAL PLEXUS
II) HILTON’S LAW POSTERIOR DIVISION OF S1-S3
III) SCIATICA Forms the Posterior Cutaneous Nerve
IV) APPENDIX
V) REVIEW QUESTIONS
VI) REFERENCES Cutaneous supply:
- Inferior buttocks
- Posterior thigh
- Popliteal region
- Posterior calf
I) BRANCHES OF SACRAL PLEXUS
- Skin around heel
The sacral plexus is located on the posterolateral wall of the
lesser pelvis. The two main nerves arising from the sacral
plexus, the sciatic and pudendal nerves.
ROOTS OF THE SACRAL PLEXUS
The sacral plexus originates from L4-L5, S1-S5 and Co1
FIBERS FROM L4, L5 AND S1
Forms the Superior Gluteal Nerve
Figure 2. Branches that supply the obturator internus and
Motor supply: posterior cutaneous nerve
- Gluteus medius
- Gluteus minimus
L4, L5, S1-S3 BRANCHES
FIBERS L5, S1 AND S2 (DORSAL DIVISION) Forms the Sciatic Nerve
Forms the inferior gluteal nerve
BRANCHES OF THE SCIATIC NERVE
Motor supply:
At the knee it splits into:
- Gluteus maximus
Extension and lateral rotation of the hip Anterior division: Tibial nerve
Cutaneous supply:
o Posterior Leg Limb Thigh
o Popliteal Region
o Sole of the Foot
Motor supply:
o Hamstring Muscles
Biceps Femoris (Long head)
Figure 1. Branches that form the superior and inferior gluteal Semitendinosus
nerves Semi Membranous
o Adductor Magnus
L5, S1 AND S2 (VENTRAL DIVISION) o Popliteus
Forms the Obturator Internus Nerve o Plantaris
o Tibialis Posterior
o Flexor Digitorum Longus
Motor supply: o Flexor Hallucis Longus
o Triceps Surae (gastrocnemius and soleus)
- Superior Gemellus Muscle
o Intrinsic Muscles Of The Foot
- Obturator Internus Muscle
If there is compression of the sciatic nerve pain and lack
of function of all muscles
Sacral Plexus NEURO PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. 1 of 4
Posterior division: Common Fibular Nerve
S2-S4
Forms the Pudendal nerve
Cutaneous supply:
- Lateral aspect of the leg
Cutaneous supply:
Female and male perineum
Motor supply: o Scrotum
o Biceps femoris (short head) o Penis
Extension of the hip/flexion of the knee o Anus
o Fibularis brevis o Perineum
o Fibularis longus o Clitoris
Evert the ankle o labia majora
o Extensor halluces longus o mons pubis
Extends big toe
Motor supply:
o Extensor digitorum longus
Dorsiflexion, inversion of the ankle, o External Anal Sphincter
extend the digits. o External Urethral Sphincter
o Tibilas anterior
Inversion and dorsiflexion of the ankle
Figure 5. Fibers forming the pudendal nerve
S4, S5 AND CO1:
Forms the coccygeal plexus
Cutaneous supply:
o Supplies skin around the coccygeal
region
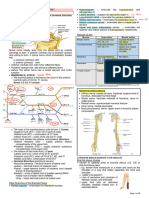
Figure 3. Sciatic Nerve and its branches (follow dark blue line)
S1-S2
Posterior division of sacral plexus
Forms the nerve to piriformis Figure 6. Coccygeal plexus
Motor supply:
- Piriformis muscle
Lateral rotator of the hip
II) HILTON’S LAW
“The nerve supplying the muscles
extending directly across and
acting at a given joint not only
supplies the muscle, but also
innervates the joint and the skin
overlying the muscle”
Figure 4. Fibers forming nerve to piriformis
2 of 4 NEURO PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. Sacral Plexus
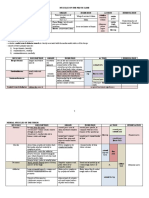
III) SCIATICA
CAUSES OF SCIATIC NERVE COMPRESSION:
CLINICAL PRESENTATION:
- Sciatica is often caused by a herniated lumbar L4-
Shooting pain in the posterior and lateral aspect of the leg.
S3 disc that compresses and compromises
nerves of that region of the sciatic nerve
TREATMENT:
Note: - Rest
- The posterior division (common fibular nerve) gets - NSAIDs
its fibers mainly from L4-S2 - Physiotherapy
- The anterior division (tibial nerve) gets fibers - Surgery
mainly from L4-S3.
Therefore, if there is sciatica, it affects mostly the
anterior division than the posterior division.
IV) APPENDIX
Table 1. Summary of the Sacral Plexus
Nerve Segment Motor Supply Cutaneous Supply
Superior Gluteal
L4, L5, S1
Nerve
L5, S1, S2
Inferior Gluteal
(dorsal
Nerve
division)
L5, S1, S2
Obturator
(ventral
Internus Nerve
division)
S1-S3
Posterior
(posterior
Cutaneous Nerve
division)
Sciatic Nerve L4, L5, S1-S3
Nerve To
S1-S2
Piriformis
Pudendal Nerve S2-S4
Coccygeal Plexus S4, S5, Co1
Sacral Plexus NEURO PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. 3 of 4
V) REVIEW QUESTIONS
1) Which nerve supplies the Gluteus Minimus?
a) Sciatic Nerve
b) Pudendal Nerve
c) Superior Gluteal Nerve
d) Inferior Gluteal Nerve
2) Which nerve innervates the female and male
perineum?
a) Obturator Internus Nerve
b) Superior Gluteal Nerve
c) Nerve To Piriformis
d) Pudendal Nerve
3) The tibial nerve provides a motor supply to which of
the following?
a) Triceps Surae
b) Fibularis brevis
c) Piriformis muscle
d) External Anal Sphincter
4) What are the roots of the sciatic nerve?
a) L1-S4
b) L4-S3
c) L5-Co1
d) S1-S5
5) Why does sciatica affect mainly the structures of the
tibial nerve than the common fibular nerve?
a) Because the anterior division gets fibers mainly from
L4-S3
b) Because the posterior division gets fibers mainly
from L4-S3.
c) Because the anterior division gets fibers mainly from
L4-S2
d) Because the posterior division gets fibers mainly
from L4-S2
6) Which nerve does the ventral division of L5-S2?
a) Obturator Internus Nerve
b) Inferior Gluteal Nerve
c) Nerve To Piriformis
d) Pudendal Nerve
7) What are the roots of the coccygeal plexus?
a) S1-Co1
b) Co1
c) S3-Co1
d) S4-Co1
8) Which area of the spinal cord is most affected in
sciatica?
a) L3-S5
b) L4-S3
c) L1-L5
d) S1-S5
VI) REFERENCES
● Moore, Keith L. et al. (2010) Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 6th Ed
4 of 4 NEURO PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. Sacral Plexus
You might also like
- Cranial Nerve AssessmentDocument42 pagesCranial Nerve AssessmentValeryn Quiman100% (8)
- The Limbic Brain. Andrew Lautin PDFDocument152 pagesThe Limbic Brain. Andrew Lautin PDFAntonio D LazodelaVegaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Clinical Examination 2016Document26 pagesCranial Nerves Clinical Examination 2016kartNo ratings yet
- Visual PathwayDocument36 pagesVisual PathwayVishakh Isloor100% (1)
- Mind MAP SSP PDFDocument1 pageMind MAP SSP PDFFarhan100% (1)
- Lumbar and Sacral PlexusDocument30 pagesLumbar and Sacral PlexusIndah YoulpiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument59 pagesUntitledNidhish K ShettigarNo ratings yet
- Muscle Table (Detail) 2Document13 pagesMuscle Table (Detail) 2keepcalmandbeawesomepeopleNo ratings yet
- The Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesDocument40 pagesThe Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesMona Mentari PagiNo ratings yet
- Safari - Feb 21, 2024 at 12:02 PMDocument1 pageSafari - Feb 21, 2024 at 12:02 PMsyansyncNo ratings yet
- GHSB2024 Superficial Structures of The Neck and Posterior TriangleDocument5 pagesGHSB2024 Superficial Structures of The Neck and Posterior Trianglekang seulgi can set me on fire with her gaze aloneNo ratings yet
- Nerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesNerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries: Learning ObjectivesUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Nerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesNerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries: Learning ObjectivesAli muradNo ratings yet
- Chapter06 - TheLowerLimb - 122 - 149 GrantDocument28 pagesChapter06 - TheLowerLimb - 122 - 149 GrantPopa AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Lower LimbDocument52 pagesAnatomy of Lower Limbdrkhan58No ratings yet
- 1.gluteal RegionDocument34 pages1.gluteal RegionGaurav ThapaNo ratings yet
- Gluteal and Thigh Region ReviewerDocument7 pagesGluteal and Thigh Region ReviewerKIARA VENICE DELGADONo ratings yet
- Limbs 1b - Overview of Anatomy of Upper and Lower LimbsDocument5 pagesLimbs 1b - Overview of Anatomy of Upper and Lower LimbsTarmizi Md NorNo ratings yet
- Muscle & Joints of Lower Limb PARA-SMS-compressedDocument48 pagesMuscle & Joints of Lower Limb PARA-SMS-compressedkiran kcNo ratings yet
- CFJ Hollingsworth HipDocument8 pagesCFJ Hollingsworth HipAlessandro PetrizzaNo ratings yet
- Gray - S Notes Lower LimbDocument10 pagesGray - S Notes Lower LimbCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Anterior and Medial Aspects of The Thigh andDocument23 pagesAnterior and Medial Aspects of The Thigh andHarshilNo ratings yet
- Gluteal Region Gluteal RegionDocument21 pagesGluteal Region Gluteal RegionPraneethaNo ratings yet
- LAB Gluteal Region & Posterior ThighDocument8 pagesLAB Gluteal Region & Posterior ThighnanaNo ratings yet
- Sport Related Peripheral Nerve InjuriesDocument7 pagesSport Related Peripheral Nerve InjurieswladjaNo ratings yet
- Posterior Compartment of The ThighDocument2 pagesPosterior Compartment of The ThighDana BarhoomNo ratings yet
- Upper Trapezius MuscleDocument6 pagesUpper Trapezius MusclejpNo ratings yet
- 1.12 Gluteal Region and Posterior Thigh Compartment PDFDocument5 pages1.12 Gluteal Region and Posterior Thigh Compartment PDFJuliaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesDocument65 pagesLecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without Notesellie marcusNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lower LimbDocument4 pagesAnatomy Lower Limbch yaqoobNo ratings yet
- GROSA OINA Shoulder Scapula PA Compartments of The ArmDocument8 pagesGROSA OINA Shoulder Scapula PA Compartments of The ArmRaissa DesiderioNo ratings yet
- Vascularised Free Fibula Flap - FFF - in Head and Neck ReconstructionDocument22 pagesVascularised Free Fibula Flap - FFF - in Head and Neck ReconstructionAbirame SivasNo ratings yet
- Same Nerve Supply As Obturator InternusDocument2 pagesSame Nerve Supply As Obturator InternusDana BarhoomNo ratings yet
- Unit4 DM - Vb.inddDocument31 pagesUnit4 DM - Vb.inddAlexNo ratings yet
- 20-Hip, Knee & Ankle JointsDocument9 pages20-Hip, Knee & Ankle JointsKainat LatifNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Conditions 1 SciDocument5 pagesNeurologic Conditions 1 SciEdward De LeonNo ratings yet
- Foramen Structures Conducted Cranial Fossa Cranial Bone Cribriform ForaminaDocument8 pagesForamen Structures Conducted Cranial Fossa Cranial Bone Cribriform ForaminaAchiever FayeNo ratings yet
- Methodic Materials MovementDocument20 pagesMethodic Materials MovementKapil PancholiNo ratings yet
- 01 Head and Neck JMDocument16 pages01 Head and Neck JMJowi SalNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord and Its Lesions - Dr. Mattheus (2023)Document8 pagesSpinal Cord and Its Lesions - Dr. Mattheus (2023)Noreen Hannah GabrielNo ratings yet
- MoinaDocument43 pagesMoinaMoo MinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-Ms Respi NeuroDocument10 pagesAnatomy-Ms Respi NeuroImmah PinedaNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Lower LimbDocument6 pagesFlashcards - Lower LimbKhanNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Arm and ForearmDocument8 pagesMuscles of The Arm and ForearmالبراءNo ratings yet
- Innervation of LimbsDocument3 pagesInnervation of LimbsNur NajminaNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Conditions 3Document18 pagesPelvic Conditions 3Princess DomingoNo ratings yet
- Knee and Leg ReviewerDocument3 pagesKnee and Leg ReviewerKIARA VENICE DELGADONo ratings yet
- Muscle Origin Insertion Nerve ActionDocument4 pagesMuscle Origin Insertion Nerve ActionKean Debert SaladagaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Gluteal RegionDocument19 pagesMuscles of The Gluteal RegionalhashemisaqrNo ratings yet
- ARMONIA ALEXA JOIE C. BSN 1B Manual Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesARMONIA ALEXA JOIE C. BSN 1B Manual Skeletal SystemJohanna Marie GantalaoNo ratings yet
- Nerves of The Lower Limb. 1Document5 pagesNerves of The Lower Limb. 1Prathap KumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Back MusclesDocument4 pagesAnatomy of Back Musclesfatima wribagNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Muscles TrimmedDocument6 pagesPelvic Muscles TrimmedDelfin UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 PNS & Spinal Cord AnswersDocument12 pagesLab 5 PNS & Spinal Cord AnswersCemre KuzeyNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step I Comprehensive ReviewDocument767 pagesUSMLE Step I Comprehensive ReviewMack LinfidioNo ratings yet
- Amano, Miles M. - Human AnaPhyW5-6Document4 pagesAmano, Miles M. - Human AnaPhyW5-6Khalil, Mikaela VictoriaNo ratings yet
- BIO223: Human Anatomy L14B: Muscles of Lower Limb UNC-Asheville, F2008Document6 pagesBIO223: Human Anatomy L14B: Muscles of Lower Limb UNC-Asheville, F2008د.موسى التويتيNo ratings yet
- Bio Report Koh..unaDocument5 pagesBio Report Koh..unamarty91190No ratings yet
- Muscular System ReviewDocument12 pagesMuscular System Reviewmaggie :DNo ratings yet
- Muscle Summary - Gluteal, Thigh, Leg and FootDocument8 pagesMuscle Summary - Gluteal, Thigh, Leg and FootUNI1111No ratings yet
- En Lower Extremity EnglishDocument7 pagesEn Lower Extremity EnglishOskar BrugrandNo ratings yet
- Illustrating the Anatomy and Muscular System of the Horse - Containing Extracts from Livestock for the Farmer and Stock OwnerFrom EverandIllustrating the Anatomy and Muscular System of the Horse - Containing Extracts from Livestock for the Farmer and Stock OwnerNo ratings yet
- Morpho: Skeleton and Bone Reference Points: Anatomy for ArtistsFrom EverandMorpho: Skeleton and Bone Reference Points: Anatomy for ArtistsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Anaphy LecDocument15 pagesAnaphy LecMarcoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System NotesDocument16 pagesNervous System NotesmorganicalNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve V - Trigeminal Nerve - FRCEM SuccessDocument1 pageCranial Nerve V - Trigeminal Nerve - FRCEM SuccessJohn CoxNo ratings yet
- Neuroimaging: Dr. Mashuri, SP - Rad (K) .,M.KesDocument61 pagesNeuroimaging: Dr. Mashuri, SP - Rad (K) .,M.KesGaluh EkaNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology 12th Edition Fox Test BankDocument49 pagesHuman Physiology 12th Edition Fox Test Bankhubertbak126100% (31)
- Slide HistoDocument66 pagesSlide Histomega_ayuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document8 pagesAssignment 1Muhammad ZohaibNo ratings yet
- Nerves Injury: Audi HidayatullahDocument42 pagesNerves Injury: Audi Hidayatullahayu100% (1)
- Nervous Tissue Modified 2020Document10 pagesNervous Tissue Modified 2020محمد ابن نوضىNo ratings yet
- Neuro Part 2Document6 pagesNeuro Part 2vetthamilNo ratings yet
- RADIOLOGY 1.7 Neuroradiology (CT)Document7 pagesRADIOLOGY 1.7 Neuroradiology (CT)ZazaNo ratings yet
- BDFC 1Document1 pageBDFC 1Misa AjversonNo ratings yet
- Pub - Principles and Practice of NeuropathologyDocument608 pagesPub - Principles and Practice of NeuropathologyArkham AsylumNo ratings yet
- Neuro-Ophthalmology: DR Jusuf Wijaya, SPM FK - Uki CawangDocument65 pagesNeuro-Ophthalmology: DR Jusuf Wijaya, SPM FK - Uki CawanggeorgyNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy BioDocument6 pagesNeuroanatomy BioLarry LeNo ratings yet
- Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and The Somatic Nervous System PDFDocument4 pagesNeural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and The Somatic Nervous System PDFAmandaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of Parotid Gland - Ommos - Edition-01-SoiDocument32 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Parotid Gland - Ommos - Edition-01-SoiDr Prashant Kumar100% (1)
- Hypoxic Encephalopathy Secondary To Status Epilepticus Secondary To Central Nervous System InfectionDocument158 pagesHypoxic Encephalopathy Secondary To Status Epilepticus Secondary To Central Nervous System Infectionallexiscampaner100% (1)
- Brain 2006 Stewart Music and BrainDocument21 pagesBrain 2006 Stewart Music and BrainAndrada Tatiana CrișanNo ratings yet
- Histology of Cerebrum and CerebellumDocument22 pagesHistology of Cerebrum and CerebellumUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Pathophysiology of SciaticaDocument14 pagesChapter 11: Pathophysiology of SciaticaTraian UrsuNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PowerpointDocument39 pagesNervous System PowerpointManveer SidhuNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy TractsDocument4 pagesNeuroanatomy TractsLoveHouseMDNo ratings yet
- Ectodermal Derivatives of Pig EmbryoDocument7 pagesEctodermal Derivatives of Pig EmbryoChristalie Bea FernandezNo ratings yet
- Corticospinal Tract Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesCorticospinal Tract Practice QuestionsAlexaNo ratings yet