Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsChapter 6 Using Mole
Chapter 6 Using Mole
Uploaded by
chitminthu560345This document discusses using moles to perform stoichiometric calculations for chemical reactions. It defines key terms like the mole, molar mass, molar volume, and concentration. It provides examples of how to:
1) Calculate masses of substances using moles and molar mass
2) Derive balanced chemical equations and use them to calculate theoretical reactant and product masses
3) Calculate gas volumes using moles, molar volume, and reaction stoichiometry
4) Determine concentration of solutions
5) Derive empirical formulas from combustion analysis data
6) Calculate percent yield and purity of products from experimental results
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 17 Quantitative Aspects of Chemical ChangeDocument30 pages17 Quantitative Aspects of Chemical Changeapi-235269401No ratings yet
- Stoichiometry 1Document60 pagesStoichiometry 1Aryan Anchan0% (1)
- Stoichiometry - Mole Concepts PDFDocument47 pagesStoichiometry - Mole Concepts PDFmeher singhNo ratings yet
- Formula StoichiometryDocument48 pagesFormula StoichiometryJCBNo ratings yet
- The Mole Concept PDFDocument12 pagesThe Mole Concept PDFIftikhar Ahmed0% (2)
- MOLE NotesDocument12 pagesMOLE NotesShanzay WaqarNo ratings yet
- Chapt 10Document48 pagesChapt 10Dionisio BrinosaNo ratings yet
- Relative Atomic MassDocument8 pagesRelative Atomic Massgkawsar22No ratings yet
- The Mole Concept PDFDocument12 pagesThe Mole Concept PDFZeeshan KhanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Chem STOICHIOMETRYDocument46 pagesPrinciples of Chem STOICHIOMETRYALIGARBES, Rhonna May L.No ratings yet
- Chap1 StoichiometryDocument42 pagesChap1 StoichiometryAndré QianNo ratings yet
- Moles, Titration, RedoxDocument28 pagesMoles, Titration, RedoxDoveNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument26 pagesStoichiometryJesusa Potenciano ErniNo ratings yet
- The Mole ConceptDocument13 pagesThe Mole Conceptsabrina_sarranNo ratings yet
- 4.2 The Mole Con220the20mole20conceptDocument14 pages4.2 The Mole Con220the20mole20conceptjessy cahNo ratings yet
- Quick Notes: Relative Atomic MassDocument20 pagesQuick Notes: Relative Atomic Massanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Moles and Empirical FormulaDocument11 pagesMoles and Empirical FormulaZenoxu 7zNo ratings yet
- 20171101131106chapter 5b - Mole and Stoichiometry PDFDocument50 pages20171101131106chapter 5b - Mole and Stoichiometry PDFShah100% (1)
- Mole ConceptDocument90 pagesMole ConcepthariniNo ratings yet
- Stochiometry Grade 9th Short Note For Grade 12thDocument8 pagesStochiometry Grade 9th Short Note For Grade 12thWesNo ratings yet
- Stoich PDFDocument13 pagesStoich PDFJesza Mei GanironNo ratings yet
- Stoich PDFDocument13 pagesStoich PDFJesza Mei GanironNo ratings yet
- Stoich PDFDocument13 pagesStoich PDFJesza Mei GanironNo ratings yet
- XI Chemistry Chapterwise Advanced Study MaterialDocument537 pagesXI Chemistry Chapterwise Advanced Study MaterialregisNo ratings yet
- CHE 203 Chap 3 Part 1Document22 pagesCHE 203 Chap 3 Part 1Mariel ann GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 - The Mole ConceptDocument37 pagesLec 3 - The Mole ConceptRonaldo 1986100% (2)
- Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryDocument5 pagesAtoms, Molecules and StoichiometryAreeba EjazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical Equations and Reactions StichiometryDocument49 pagesChapter 3 Chemical Equations and Reactions StichiometryNathan MulewaNo ratings yet
- Moles and FormulaeDocument8 pagesMoles and FormulaeSunnyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - CalculationsDocument27 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - CalculationsChemistryKlipz100% (14)
- Chapter 5 Chemical Calculations Calculat PDFDocument37 pagesChapter 5 Chemical Calculations Calculat PDFAbdullah Sabry AzzamNo ratings yet
- NOTES - 10.3 - Empirical - Molecular - Form - Slideshow - NEWDocument29 pagesNOTES - 10.3 - Empirical - Molecular - Form - Slideshow - NEWFaiz KhanNo ratings yet
- Chap 9: The Mole (Part 1)Document5 pagesChap 9: The Mole (Part 1)Atif Baloch28No ratings yet
- CH 14-VP-Stoichiometry - 2020Document37 pagesCH 14-VP-Stoichiometry - 2020Mlamuli MlarhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fundamental Concepts of Chemistry For Class XIDocument62 pagesIntroduction To Fundamental Concepts of Chemistry For Class XIJaf Shah100% (7)
- 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships IDocument25 pages1 - Stoichiometric Relationships IKamil Lamtiri SaidNo ratings yet
- Moles and Mole CalculationsDocument14 pagesMoles and Mole CalculationsAhmadElgindyNo ratings yet
- Marky Stoichiometry 150227040814Document20 pagesMarky Stoichiometry 150227040814tamorromeo908No ratings yet
- The Mole & Avogadro's ConstantDocument16 pagesThe Mole & Avogadro's ConstantKamran ArshadNo ratings yet
- Mole - Chapter 9Document52 pagesMole - Chapter 9shanesha blackhoodNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Chapter 9Document24 pagesZumdahl Chapter 9Master NistroNo ratings yet
- As Chemistry Unit 1 NotesDocument71 pagesAs Chemistry Unit 1 NotesUmer Mohammed100% (2)
- Revision Checklist:4.3 Quantitative Chemistry: Relative Formula MassDocument8 pagesRevision Checklist:4.3 Quantitative Chemistry: Relative Formula MassJadyn Mc SweenNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry & The Mole Concept: Writing Ionic EquationsDocument5 pagesStoichiometry & The Mole Concept: Writing Ionic EquationsThaarvena RetinaNo ratings yet
- Mole and Molar MassDocument25 pagesMole and Molar MassAlexandra BlascoNo ratings yet
- MolesDocument18 pagesMolesApril Mae BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Quantities Section 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of MatterDocument17 pagesChemical Quantities Section 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of MatterHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument12 pagesChemical ReactionLuna eukharisNo ratings yet
- Mol Concepts and Calculation of ChemicalDocument7 pagesMol Concepts and Calculation of ChemicalMuna LasenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Chemical QuantitiesDocument44 pagesChapter 10 - Chemical Quantitiesapi-256257174No ratings yet
- Mass Volume RelationshipDocument9 pagesMass Volume Relationshiprabiumuhsin7No ratings yet
- Ch3 CompleteDocument48 pagesCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- The MoleDocument19 pagesThe MoleAboahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document104 pagesChapter 1Sarathy Hari KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson PS 10 StoichiometryDocument60 pagesLesson PS 10 StoichiometryMaria Angelica SandoyNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document22 pagesChap 3Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Topic 1, Fundamental Concepts First Year MCATDocument29 pagesTopic 1, Fundamental Concepts First Year MCATKhubaib Khan100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- HCH416A - Inorg. Syst. Metal Clusters 2Document19 pagesHCH416A - Inorg. Syst. Metal Clusters 2Rangwani NesbitNo ratings yet
- B951.927 - MG Alloy Naming and CompsDocument7 pagesB951.927 - MG Alloy Naming and Compswanghongxuan66No ratings yet
- PV SystemDocument10 pagesPV SystemVictor ImehNo ratings yet
- Weight-Volume Relationships: Quiz Gt102Document8 pagesWeight-Volume Relationships: Quiz Gt102Sharon Rose OcampoNo ratings yet
- JoSAA 2023 Choice FillingDocument4 pagesJoSAA 2023 Choice Fillingbhanuteja2794No ratings yet
- GOC Functional Certification Flow ChartDocument1 pageGOC Functional Certification Flow ChartKAABECHE SlimaneNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry - Mole To MoleDocument14 pagesStoichiometry - Mole To MoleClaudia JaukinNo ratings yet
- Soldering (Acetate)Document11 pagesSoldering (Acetate)Maridee Bitalac AdiongNo ratings yet
- How Plants Gain Energy: Life Science, Plant BiologyDocument11 pagesHow Plants Gain Energy: Life Science, Plant BiologyJoanne Mae MontanoNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science 2014+ Year Two POS v2bDocument27 pagesKS3 Science 2014+ Year Two POS v2bMhmd AlrashedNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Starch Nanoparticles in A New Ionic Liquid-in-Oil MicroemulsionDocument12 pagesPreparation of Starch Nanoparticles in A New Ionic Liquid-in-Oil MicroemulsionPaula NancyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Grade 12 PDFDocument317 pagesChemistry-Grade 12 PDFviktoria dizon75% (4)
- Sodium BisulphateDocument14 pagesSodium BisulphatemelvinkuriNo ratings yet
- Experiment oDocument8 pagesExperiment oChirlei SousaNo ratings yet
- Week's Citation Classic®Document1 pageWeek's Citation Classic®Cherif Abdourahmane DiopNo ratings yet
- E A R T H Science PPT 1Document7 pagesE A R T H Science PPT 1Bon BonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Coulomb's Law and Electric Field IntensityDocument2 pagesChapter 2: Coulomb's Law and Electric Field IntensityvpkvikasNo ratings yet
- Zhang Lift OffDocument28 pagesZhang Lift OffAustin Lane0% (1)
- The Van Der Pauw Method of Measurements in High-TcDocument12 pagesThe Van Der Pauw Method of Measurements in High-Tcpinkpanther nonsenseNo ratings yet
- Well Logging and Interpretation PDFDocument171 pagesWell Logging and Interpretation PDFMohit PatelNo ratings yet
- Induction NotesDocument15 pagesInduction NotesKartikNo ratings yet
- Silicon Solar Cell TechnologyDocument87 pagesSilicon Solar Cell TechnologyJack BuzzNo ratings yet
- Metal and Non M MetalDocument25 pagesMetal and Non M MetalDebasish MohantyNo ratings yet
- Thermoelectricity BookDocument275 pagesThermoelectricity BookHaramiNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Section 1: Product and Company IdentificationDocument7 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Section 1: Product and Company IdentificationJUAN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Science Quiz Bee ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience Quiz Bee ReviewerMonica Morales MaañoNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument27 pagesPresentationJhonatan Gerardo Soto PuellesNo ratings yet
- Answers: CHAPTER 1 MicroorganismsDocument17 pagesAnswers: CHAPTER 1 MicroorganismsJing Yi ChyeNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of Solidification 1Document6 pagesThermodynamics of Solidification 1Anonymous T02GVGzBNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium: March 2016Document35 pagesChemical Equilibrium: March 2016Nfor KlinsmanNo ratings yet
Chapter 6 Using Mole
Chapter 6 Using Mole
Uploaded by
chitminthu5603450 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views22 pagesThis document discusses using moles to perform stoichiometric calculations for chemical reactions. It defines key terms like the mole, molar mass, molar volume, and concentration. It provides examples of how to:
1) Calculate masses of substances using moles and molar mass
2) Derive balanced chemical equations and use them to calculate theoretical reactant and product masses
3) Calculate gas volumes using moles, molar volume, and reaction stoichiometry
4) Determine concentration of solutions
5) Derive empirical formulas from combustion analysis data
6) Calculate percent yield and purity of products from experimental results
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses using moles to perform stoichiometric calculations for chemical reactions. It defines key terms like the mole, molar mass, molar volume, and concentration. It provides examples of how to:
1) Calculate masses of substances using moles and molar mass
2) Derive balanced chemical equations and use them to calculate theoretical reactant and product masses
3) Calculate gas volumes using moles, molar volume, and reaction stoichiometry
4) Determine concentration of solutions
5) Derive empirical formulas from combustion analysis data
6) Calculate percent yield and purity of products from experimental results
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views22 pagesChapter 6 Using Mole
Chapter 6 Using Mole
Uploaded by
chitminthu560345This document discusses using moles to perform stoichiometric calculations for chemical reactions. It defines key terms like the mole, molar mass, molar volume, and concentration. It provides examples of how to:
1) Calculate masses of substances using moles and molar mass
2) Derive balanced chemical equations and use them to calculate theoretical reactant and product masses
3) Calculate gas volumes using moles, molar volume, and reaction stoichiometry
4) Determine concentration of solutions
5) Derive empirical formulas from combustion analysis data
6) Calculate percent yield and purity of products from experimental results
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 22
Using Moles
6.1 The mole
6.2 Calculation from equations, using the mole
6.3 Reaction involving gases
6.4 Concentration of solution
6.5 Finding the empirical formula
6.6 The empirical to final formula
6.7 The % yield and % purity
The mole
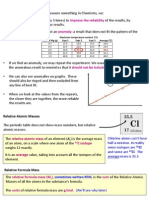
The unit for amount of substance. The symbol for unit of mole is mol.
The number of atoms, molecules or ions in a moles of given substance.
Avogadro’s constant = 6.02 x 10 23
Finding the mass of a mole
1. Write down the symbol or formula of the substance.
2. Find its Ar or Mr.
3. Express that mass in grams (g)
Substance Symbol or formula Ar Mr Mass of 1 mole
Helium He He = 4 Exists as single atoms 4g
oxygen O2 O =16 2 x 16 32g
ethanol C2H5OH C =12
O = 16
H=1
Example 1: Calculate the mass of 0.5 moles of bromine atoms.
Example 2: Calculate the mass of 0.5 moles of bromine molecules.
Example 3: How many moles of oxygen molecules are in 64 g of oxygen?
Calculations from equations, using the mole
When carbon burns in oxygen,
Carbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide
C + O2 → CO2
1 carbon atom react with 1 molecule oxygen to give 1 molecule of carbon
dioxide
1 mole of Carbon atom react with 1 mol of oxygen to give 1 mole of carbon
dioxide
12 g of C react with 32 g of O2 to give 44 g of CO2
Calculating masses from equations
1. Write the balanced equation for the reaction. ( it gives moles)
2. Write down the Ar or Mr for each substance that takes part.
3. Using Ar or Mr, change the mole in the equation to grams.
4. Once you know the theoretical masses from the equation, you can
then find any actual mass.
Example: Hydrogen burns in oxygen to form water. What mass of oxygen is
needed for 1 g of hydrogen, and what mass of water is obtained?
Reaction involving gases
Each gas is at room temperature and pressure, or rtp
Room temperature and pressure (rtp) = 20◦C and 1 atmosphere
1 mole of every gas occupies the same volume, at the same temperature and
pressure. At room temperature and pressure, this volume is 24 dm3 or 24000
cm3.
The volume occupied by 1 mole of a gas is called its molar volume.
The molar volume of a gas is 24 dm3 at rtp.
Calculating gas volumes from moles and grams
Example: What volume does 0.25 moles of a gas occupy at rtp?
Example 1: What volume of hydrogen will react with 24dm3 of oxygen to
form water?
Concentration of a solution
The concentration of a solution is the amount of solute, in grams or moles,
that is dissolved in 1 dm3 of solution.
Concentration of a solution
Finding the empirical formula and Final Formula
Finding % yield and % purity
You might also like
- 17 Quantitative Aspects of Chemical ChangeDocument30 pages17 Quantitative Aspects of Chemical Changeapi-235269401No ratings yet
- Stoichiometry 1Document60 pagesStoichiometry 1Aryan Anchan0% (1)
- Stoichiometry - Mole Concepts PDFDocument47 pagesStoichiometry - Mole Concepts PDFmeher singhNo ratings yet
- Formula StoichiometryDocument48 pagesFormula StoichiometryJCBNo ratings yet
- The Mole Concept PDFDocument12 pagesThe Mole Concept PDFIftikhar Ahmed0% (2)
- MOLE NotesDocument12 pagesMOLE NotesShanzay WaqarNo ratings yet
- Chapt 10Document48 pagesChapt 10Dionisio BrinosaNo ratings yet
- Relative Atomic MassDocument8 pagesRelative Atomic Massgkawsar22No ratings yet
- The Mole Concept PDFDocument12 pagesThe Mole Concept PDFZeeshan KhanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Chem STOICHIOMETRYDocument46 pagesPrinciples of Chem STOICHIOMETRYALIGARBES, Rhonna May L.No ratings yet
- Chap1 StoichiometryDocument42 pagesChap1 StoichiometryAndré QianNo ratings yet
- Moles, Titration, RedoxDocument28 pagesMoles, Titration, RedoxDoveNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument26 pagesStoichiometryJesusa Potenciano ErniNo ratings yet
- The Mole ConceptDocument13 pagesThe Mole Conceptsabrina_sarranNo ratings yet
- 4.2 The Mole Con220the20mole20conceptDocument14 pages4.2 The Mole Con220the20mole20conceptjessy cahNo ratings yet
- Quick Notes: Relative Atomic MassDocument20 pagesQuick Notes: Relative Atomic Massanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Moles and Empirical FormulaDocument11 pagesMoles and Empirical FormulaZenoxu 7zNo ratings yet
- 20171101131106chapter 5b - Mole and Stoichiometry PDFDocument50 pages20171101131106chapter 5b - Mole and Stoichiometry PDFShah100% (1)
- Mole ConceptDocument90 pagesMole ConcepthariniNo ratings yet
- Stochiometry Grade 9th Short Note For Grade 12thDocument8 pagesStochiometry Grade 9th Short Note For Grade 12thWesNo ratings yet
- Stoich PDFDocument13 pagesStoich PDFJesza Mei GanironNo ratings yet
- Stoich PDFDocument13 pagesStoich PDFJesza Mei GanironNo ratings yet
- Stoich PDFDocument13 pagesStoich PDFJesza Mei GanironNo ratings yet
- XI Chemistry Chapterwise Advanced Study MaterialDocument537 pagesXI Chemistry Chapterwise Advanced Study MaterialregisNo ratings yet
- CHE 203 Chap 3 Part 1Document22 pagesCHE 203 Chap 3 Part 1Mariel ann GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 - The Mole ConceptDocument37 pagesLec 3 - The Mole ConceptRonaldo 1986100% (2)
- Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryDocument5 pagesAtoms, Molecules and StoichiometryAreeba EjazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical Equations and Reactions StichiometryDocument49 pagesChapter 3 Chemical Equations and Reactions StichiometryNathan MulewaNo ratings yet
- Moles and FormulaeDocument8 pagesMoles and FormulaeSunnyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - CalculationsDocument27 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - CalculationsChemistryKlipz100% (14)
- Chapter 5 Chemical Calculations Calculat PDFDocument37 pagesChapter 5 Chemical Calculations Calculat PDFAbdullah Sabry AzzamNo ratings yet
- NOTES - 10.3 - Empirical - Molecular - Form - Slideshow - NEWDocument29 pagesNOTES - 10.3 - Empirical - Molecular - Form - Slideshow - NEWFaiz KhanNo ratings yet
- Chap 9: The Mole (Part 1)Document5 pagesChap 9: The Mole (Part 1)Atif Baloch28No ratings yet
- CH 14-VP-Stoichiometry - 2020Document37 pagesCH 14-VP-Stoichiometry - 2020Mlamuli MlarhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fundamental Concepts of Chemistry For Class XIDocument62 pagesIntroduction To Fundamental Concepts of Chemistry For Class XIJaf Shah100% (7)
- 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships IDocument25 pages1 - Stoichiometric Relationships IKamil Lamtiri SaidNo ratings yet
- Moles and Mole CalculationsDocument14 pagesMoles and Mole CalculationsAhmadElgindyNo ratings yet
- Marky Stoichiometry 150227040814Document20 pagesMarky Stoichiometry 150227040814tamorromeo908No ratings yet
- The Mole & Avogadro's ConstantDocument16 pagesThe Mole & Avogadro's ConstantKamran ArshadNo ratings yet
- Mole - Chapter 9Document52 pagesMole - Chapter 9shanesha blackhoodNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Chapter 9Document24 pagesZumdahl Chapter 9Master NistroNo ratings yet
- As Chemistry Unit 1 NotesDocument71 pagesAs Chemistry Unit 1 NotesUmer Mohammed100% (2)
- Revision Checklist:4.3 Quantitative Chemistry: Relative Formula MassDocument8 pagesRevision Checklist:4.3 Quantitative Chemistry: Relative Formula MassJadyn Mc SweenNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry & The Mole Concept: Writing Ionic EquationsDocument5 pagesStoichiometry & The Mole Concept: Writing Ionic EquationsThaarvena RetinaNo ratings yet
- Mole and Molar MassDocument25 pagesMole and Molar MassAlexandra BlascoNo ratings yet
- MolesDocument18 pagesMolesApril Mae BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Quantities Section 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of MatterDocument17 pagesChemical Quantities Section 10.1 The Mole: A Measurement of MatterHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument12 pagesChemical ReactionLuna eukharisNo ratings yet
- Mol Concepts and Calculation of ChemicalDocument7 pagesMol Concepts and Calculation of ChemicalMuna LasenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Chemical QuantitiesDocument44 pagesChapter 10 - Chemical Quantitiesapi-256257174No ratings yet
- Mass Volume RelationshipDocument9 pagesMass Volume Relationshiprabiumuhsin7No ratings yet
- Ch3 CompleteDocument48 pagesCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- The MoleDocument19 pagesThe MoleAboahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document104 pagesChapter 1Sarathy Hari KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson PS 10 StoichiometryDocument60 pagesLesson PS 10 StoichiometryMaria Angelica SandoyNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document22 pagesChap 3Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Topic 1, Fundamental Concepts First Year MCATDocument29 pagesTopic 1, Fundamental Concepts First Year MCATKhubaib Khan100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- HCH416A - Inorg. Syst. Metal Clusters 2Document19 pagesHCH416A - Inorg. Syst. Metal Clusters 2Rangwani NesbitNo ratings yet
- B951.927 - MG Alloy Naming and CompsDocument7 pagesB951.927 - MG Alloy Naming and Compswanghongxuan66No ratings yet
- PV SystemDocument10 pagesPV SystemVictor ImehNo ratings yet
- Weight-Volume Relationships: Quiz Gt102Document8 pagesWeight-Volume Relationships: Quiz Gt102Sharon Rose OcampoNo ratings yet
- JoSAA 2023 Choice FillingDocument4 pagesJoSAA 2023 Choice Fillingbhanuteja2794No ratings yet
- GOC Functional Certification Flow ChartDocument1 pageGOC Functional Certification Flow ChartKAABECHE SlimaneNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry - Mole To MoleDocument14 pagesStoichiometry - Mole To MoleClaudia JaukinNo ratings yet
- Soldering (Acetate)Document11 pagesSoldering (Acetate)Maridee Bitalac AdiongNo ratings yet
- How Plants Gain Energy: Life Science, Plant BiologyDocument11 pagesHow Plants Gain Energy: Life Science, Plant BiologyJoanne Mae MontanoNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science 2014+ Year Two POS v2bDocument27 pagesKS3 Science 2014+ Year Two POS v2bMhmd AlrashedNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Starch Nanoparticles in A New Ionic Liquid-in-Oil MicroemulsionDocument12 pagesPreparation of Starch Nanoparticles in A New Ionic Liquid-in-Oil MicroemulsionPaula NancyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Grade 12 PDFDocument317 pagesChemistry-Grade 12 PDFviktoria dizon75% (4)
- Sodium BisulphateDocument14 pagesSodium BisulphatemelvinkuriNo ratings yet
- Experiment oDocument8 pagesExperiment oChirlei SousaNo ratings yet
- Week's Citation Classic®Document1 pageWeek's Citation Classic®Cherif Abdourahmane DiopNo ratings yet
- E A R T H Science PPT 1Document7 pagesE A R T H Science PPT 1Bon BonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Coulomb's Law and Electric Field IntensityDocument2 pagesChapter 2: Coulomb's Law and Electric Field IntensityvpkvikasNo ratings yet
- Zhang Lift OffDocument28 pagesZhang Lift OffAustin Lane0% (1)
- The Van Der Pauw Method of Measurements in High-TcDocument12 pagesThe Van Der Pauw Method of Measurements in High-Tcpinkpanther nonsenseNo ratings yet
- Well Logging and Interpretation PDFDocument171 pagesWell Logging and Interpretation PDFMohit PatelNo ratings yet
- Induction NotesDocument15 pagesInduction NotesKartikNo ratings yet
- Silicon Solar Cell TechnologyDocument87 pagesSilicon Solar Cell TechnologyJack BuzzNo ratings yet
- Metal and Non M MetalDocument25 pagesMetal and Non M MetalDebasish MohantyNo ratings yet
- Thermoelectricity BookDocument275 pagesThermoelectricity BookHaramiNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Section 1: Product and Company IdentificationDocument7 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Section 1: Product and Company IdentificationJUAN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Science Quiz Bee ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience Quiz Bee ReviewerMonica Morales MaañoNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument27 pagesPresentationJhonatan Gerardo Soto PuellesNo ratings yet
- Answers: CHAPTER 1 MicroorganismsDocument17 pagesAnswers: CHAPTER 1 MicroorganismsJing Yi ChyeNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of Solidification 1Document6 pagesThermodynamics of Solidification 1Anonymous T02GVGzBNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium: March 2016Document35 pagesChemical Equilibrium: March 2016Nfor KlinsmanNo ratings yet