Professional Documents
Culture Documents
P.E Reviewer
P.E Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jullien Tañedo MarcelinoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- MODULE 12 Gross Anatomy of The Muscular SystemDocument3 pagesMODULE 12 Gross Anatomy of The Muscular SystemPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Outline of Anatomy and Physiology (Prelim-Midterm)Document11 pagesOutline of Anatomy and Physiology (Prelim-Midterm)Jhason John J. Cabigon100% (3)
- Muscles To RememberDocument3 pagesMuscles To RememberKayla CunananNo ratings yet
- Biosci Chap6 (Muscular System Notes)Document3 pagesBiosci Chap6 (Muscular System Notes)Man DejeloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PathfitDocument4 pagesReviewer in PathfitvelardecrazelleNo ratings yet
- Anaphy W5 ReviewerDocument5 pagesAnaphy W5 Reviewerangelmalang41No ratings yet
- Muscular System - Bio 2 ADocument44 pagesMuscular System - Bio 2 A20181539No ratings yet
- The Skeletal System NOTESDocument2 pagesThe Skeletal System NOTESAngelica RamosNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesReviewer For Muscular SystemRegNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Muscular ReviewerDocument7 pagesSkeletal and Muscular ReviewerJainessa SinsuatNo ratings yet
- PE Bones and MuscleDocument2 pagesPE Bones and MuscleSophia Mitz Aya-ayNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument110 pagesMuscular SystemJang WonyoungNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Biology 2 - Group 1Document86 pagesMuscular System: Biology 2 - Group 1haylo100% (1)
- MusclesDocument89 pagesMusclesSelena ReyesNo ratings yet
- GA&E 6 - Intro To MyologyDocument47 pagesGA&E 6 - Intro To MyologySu ZikaiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System ReviewerDocument4 pagesSkeletal System ReviewerMadelle Capending DebutonNo ratings yet
- Muscles in The Human BodyDocument24 pagesMuscles in The Human BodydenisemauryNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Wps Office1Document6 pagesSkeletal System Wps Office1Brent LorenzNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Report GuideDocument6 pagesMusculoskeletal Report GuideIrish CostalesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ReviewerDocument5 pagesAnatomy Reviewercath draftNo ratings yet
- The Ability To Move Is An Essential Activity of The Human Body Our Body Weight Comes From Muscles Consists of Over 600 Individual Muscles. 3 PurposesDocument25 pagesThe Ability To Move Is An Essential Activity of The Human Body Our Body Weight Comes From Muscles Consists of Over 600 Individual Muscles. 3 PurposesJoanna Poshnja100% (1)
- Introduction To Body StructureDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Body StructureBrady DeNioNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy: IME 549 Industrial Ergonomics Spring 2011 Dr. Michael JorgensenDocument30 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy: IME 549 Industrial Ergonomics Spring 2011 Dr. Michael Jorgensenanon_379343No ratings yet
- WEEK 7 LAB EXERCISE - Muscular SystemDocument11 pagesWEEK 7 LAB EXERCISE - Muscular SystemMARY KATE L. CEBALLOSNo ratings yet
- P.E Quarter 3 (REVIEWER) : Muscular FitnessDocument3 pagesP.E Quarter 3 (REVIEWER) : Muscular Fitnessmonica regalaNo ratings yet
- The Science of Human Movement ModuleDocument5 pagesThe Science of Human Movement ModuleJerome SagunNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument27 pagesMuscular SystemJOHN ANDREI ZARSADIASNo ratings yet
- Muscular System ReviewerDocument4 pagesMuscular System ReviewerMadelle Capending DebutonNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy. The Human Muscles.Document70 pagesHuman Anatomy. The Human Muscles.Stefania Ungureanu100% (1)
- Lecture 8Document15 pagesLecture 8abood kofahiNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument5 pagesScienceannakristineilisan091682No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument32 pagesMuscular SystemHarini kumaranNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 Midterm Exam Reviewer 2023 2024Document2 pagesPe 1 Midterm Exam Reviewer 2023 2024xbautista124No ratings yet
- Skeletal System UpdatedDocument55 pagesSkeletal System UpdatedAlthea OcaslaNo ratings yet
- Naw TrainingDocument34 pagesNaw Trainingganesh pNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of MusclesDocument58 pagesAnatomy of MusclesJowie SooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ANAPHY Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 7 ANAPHY Muscular Systemrobh0026No ratings yet
- The Muscular System Powerpoint 1227697713114530 8Document44 pagesThe Muscular System Powerpoint 1227697713114530 8ninya puella100% (1)
- Health Sci g12Document4 pagesHealth Sci g12api-427920673No ratings yet
- Muscles of The Human Body PDFDocument13 pagesMuscles of The Human Body PDFPalma, Arrabela M.No ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Facts About Muscular Fitness: Tips On How To Improve Muscle FitnessDocument3 pagesChapter 9: Facts About Muscular Fitness: Tips On How To Improve Muscle FitnessTyrhon Howard VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- M. M. College of Nursing Mullana Ambala: Topic: Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesM. M. College of Nursing Mullana Ambala: Topic: Muscular SystemBhawna PandhuNo ratings yet
- Muscular System2Document43 pagesMuscular System2LeocadiaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Excitability Contractility Extensibility ElasticityDocument5 pagesElectrical Excitability Contractility Extensibility ElasticityMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- Joints: Bones in The Shoulder and Chest: Types of Movable JointsDocument2 pagesJoints: Bones in The Shoulder and Chest: Types of Movable JointsLloyd LagadNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy,: Chapter 12 Lecture Outline: Appendicular MusclesDocument70 pagesHuman Anatomy,: Chapter 12 Lecture Outline: Appendicular MusclesdewkmcNo ratings yet
- E. Muscular System RevisedDocument41 pagesE. Muscular System RevisedGenelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- 1muscles ObjectivesDocument20 pages1muscles ObjectivesZahra AdanNo ratings yet
- Secondary 5 Musclular SystemDocument3 pagesSecondary 5 Musclular SystemyunnNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument33 pagesANATOMYPhoebe LiasosNo ratings yet
- Physiology: MusclesDocument88 pagesPhysiology: MusclesMielah Ruth100% (4)
- Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesSkeletal SystemMa Khristina S WongNo ratings yet
- K00429 - 20180831110050 - Muscular SystemDocument14 pagesK00429 - 20180831110050 - Muscular Systemroesil juniNo ratings yet
- Refined Muscular SystemDocument54 pagesRefined Muscular SystemogatojohnsonNo ratings yet
- Muscles Back&Neck STUDENTDocument15 pagesMuscles Back&Neck STUDENTMarikit2012No ratings yet
- Anatomy ASS Two FinishedDocument8 pagesAnatomy ASS Two Finishedhakimabrahim77No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument90 pagesMuscular SystemAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- Biological Science, An IntroductionDocument25 pagesBiological Science, An IntroductionTristan BabaylanNo ratings yet
- Invertebrates - Are Animals Without A Backbone or Bony SkeletonDocument2 pagesInvertebrates - Are Animals Without A Backbone or Bony SkeletonAnthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument15 pagesMuscular SystemReina Grace PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Antigen and Antibody NotesDocument35 pagesAntigen and Antibody NotesVlad Lipsam100% (1)
- IAH AC ImmunomodulationDocument33 pagesIAH AC ImmunomodulationJoão FrancoNo ratings yet
- 0111inflammation PDFDocument5 pages0111inflammation PDFAshiniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - The Human BodyDocument8 pagesLesson 1 - The Human BodyGilmar ManzanoNo ratings yet
- E6 U2 Semana5 PresentacionDocument14 pagesE6 U2 Semana5 PresentacionEdwin DavidNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument27 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationMouhammad DawoudNo ratings yet
- DNB Immunohematology and Blood Transfusion Paper1Document2 pagesDNB Immunohematology and Blood Transfusion Paper1Dr.vidyaNo ratings yet
- LIPS - Histological StructureDocument4 pagesLIPS - Histological StructureivkovictNo ratings yet
- Marking Key Bio 10 2023-24 TrialsDocument15 pagesMarking Key Bio 10 2023-24 TrialsAaraNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes During PregnancyDocument24 pagesPhysiological Changes During PregnancyerlinNo ratings yet
- The Larynx An PharynxDocument46 pagesThe Larynx An PharynxDerick SemNo ratings yet
- المصطلحات - الطبيه - بالعربية - مبارك - عبدالهادي - موقع المكتبة نتDocument199 pagesالمصطلحات - الطبيه - بالعربية - مبارك - عبدالهادي - موقع المكتبة نتAli AimanNo ratings yet
- Selective Eviction of Deformed Horny Cells by JRKs Psorolin Derma Skin Care SoapDocument5 pagesSelective Eviction of Deformed Horny Cells by JRKs Psorolin Derma Skin Care SoapAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Week 4B Science 7 LasDocument7 pagesWeek 4B Science 7 LasJonah Labine Jabulin-RadazaNo ratings yet
- Neck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Document40 pagesNeck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Hauwa shitu.B100% (1)
- RHIANNA JOHNSON - Portfolio P.EDocument12 pagesRHIANNA JOHNSON - Portfolio P.ERhianna JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Notes (Tortora)Document3 pagesRespiratory Notes (Tortora)Eli MinchaiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lower Face and Botulinum Toxin.16Document8 pagesAnatomy of The Lower Face and Botulinum Toxin.16Dogan TuncaliNo ratings yet
- Fundus GastricusDocument4 pagesFundus GastricusAndrie Devin Susilo HadiNo ratings yet
- Interactive PowerpointDocument12 pagesInteractive PowerpointRahul DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 48 Urine EliminationDocument10 pagesChapter 48 Urine EliminationKathleen FrugalidadNo ratings yet
- The Finale: Multiple Choice: Anatomy & Physiology Coloring WorkbookDocument3 pagesThe Finale: Multiple Choice: Anatomy & Physiology Coloring WorkbookJonash Morales0% (1)
- 10th 100 Marks MCQs Test The HopeDocument63 pages10th 100 Marks MCQs Test The Hopegmian9012100% (1)
- Pages From MAF Nextcare 2Document1 pagePages From MAF Nextcare 2Fahad ThahaNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Diagnosis of Penoscrotal Transposition With 2-And 3-Dimensional UltrasonographyDocument5 pagesPrenatal Diagnosis of Penoscrotal Transposition With 2-And 3-Dimensional UltrasonographyIndach ZyadarifnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document48 pagesLecture 8Anthony FajardoNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Illustration in Arabic ManuscDocument16 pagesAnatomical Illustration in Arabic ManuscABDOULAYE BANo ratings yet
- L2 Introduction To HematologyDocument3 pagesL2 Introduction To HematologyJamil LausNo ratings yet
- EP - 02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - One Shot - NEET 2022 PreparationDocument85 pagesEP - 02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - One Shot - NEET 2022 PreparationSindhuja C SNo ratings yet
P.E Reviewer
P.E Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jullien Tañedo MarcelinoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
P.E Reviewer
P.E Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jullien Tañedo MarcelinoCopyright:
Available Formats
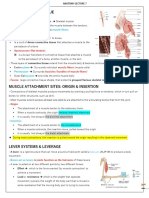
Physical Education- instruction of physical REACTION TIME- response
exercise
WARM-UP EXERCISE (stretching)-
-related to maintaining human body improve performance
-develops competence and confidence -decrease your risk injuries
Physical Fitness- state of health and well- 2 ways of warm-up exercise
being
Dynamic stretching- move into
-generally achieved through proper nutrition another
Static Stretching- stay on your
To be health we need
place
HAPPINESS > GOOD DIET
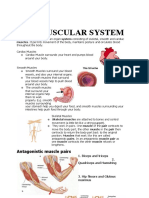
MUSCULAR SYSTEM- movement of an
SLEEP > EXERCISE
organ/body
WATER
SKELETAL MUSCLE- move bones
HEALTH- state of absolute physical,
mental & social well-being CARDIAC MUSCLE- heart to pumps
blood
-test design to measure physical strength
SMOOTH MUSCLE- contract without any
Component of Physical Fitness
voluntary control
Health Related Fitness- improve
Voluntary muscles- can be controlled by
body condition & well-being
our conscious thought. – skeletal muscle
CARDIOVASCULAR
Involuntary muscles- do not require
FITNESS/ENDURANCE- heart rate
conscious thought. -Cardiac muscle, Smooth
MUSCULAR STRENGTH- exert force muscle
MUSCULAR ENDURANCE- continue to FRONTALIS - responsible for raising the
perform eyebrows
BODY COMPOSITION- body fat to lean Orbicularis Oculi - a muscle located in the
mass eyelids.
Skill Related Fitness- have a Zygomaticus - muscle that controls facial
relationship with motor skills expression
SPEED- quick movement Masseter- the elevation of the mandible
AGILITY- change direction Orbicularis Oris - to close the mouth
BALANCE- maintain posture Sternocleidomastoid - a muscle that runs
from the base of the skull
COORDINATION- hand & foot
integration Latissimus dorsi- the lower posterior
thorax.
POWER- combination of speed & strength
External abdominal- superficial of the PERONEUS LONGUS - Produce the
lateral abdominal muscles. plantarflexion
Rectus Abdominis- six-pack HAMSTRING MUSCLES - extend the hip
and flex the knee
Deltoid- triangular shoulder muscle.
TIBIALIS ANTERIOR - the largest of
Pectoralis Major- largest muscle of the
four muscles
anterior chest wall.
Extensor Digitorum Longus - located
Biceps brachii- large, thick muscle on the
lateral to the tibialis anterior
ventral portion of the upper arm.
ACHILLES TENDON - thick cord you can
Flexor carpi ulnaris - a superficial flexor
feel at the back of your ankle
muscle of the forearm
POLYMYOSITIS (PM)- is marked by
Triceps Brachii - the extension of the elbow
muscle inflammation and weakness.
joint.
MYOSITIS simply means inflammation of
Flexor Digitorium Superficialis - flexes
muscles.
the middle phalanges
DERMATOMYOSITIS (DM)- is a rare
EXTENSOR DIGITORUM COMMUNIS
inflammatory muscle disease.
- extends medial four digits
Muscular Dystrophy (MD) is a group of
EXTENSOR CARPI ULNARIS - to
inherited myopathies
extend and adduct the wrist.
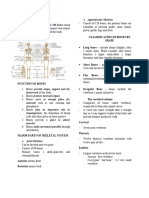
SKELETAL SYSTEM-framework of the
EXTERNAL ABDOMINAL OBLIQUE -
body
movement of the spine.
AXIAL SKELETON (80 bones)
SATORIUS - important part in stabilisation
APPENDICULAR
of the pelvis
SKELETON(126 bones)
ILIOPSOAS - external rotation of the hip
Skull- 22 bones
joint
Cranial Bones- 8 bones
ADDUCTOR LONGUS - to adduct the
thigh Facial Bones- 14 bones
QUADRICEPS FEMORIS GROUP - Ossicles- small bones your middle
Extend the leg at the knee joint
ear
GLUTEUS MEDIUS - Assists in flexion &
•Hyoid bone of your neck
medial rotation of hip
•Vertebra- (bones of your spine)
GLUTEUS MAXIMUS - main extensor of
the hip joint •Thoracic cage (Ribcage)
GASTROCNEMIUS - to plantarflex your
ankle.
PECTORAL GIRDLE Calcaneus (heel bone): large bone forming
the heel
Clavicles -collarbones/long s-shaped
OSTEOPOROSIS - occurs when bones
Scapula- shoulder blades/flat triangles
become weak
UPPER LIMB
FRACTURE - is a break in a bone
Humerus- upper arm bone
BONE CANCER - a rare type of cancer
Shaft- surrounded by large arm that begins in the bones.
Deltoid tuberosity- lies proximally OSTEOARTHRITIS- A degenerative joint
diseases
Radial Groove- shallow oblique depression
Circulatory system- is made up of blood
Radial Nerve- brachial plexus vessels
Ulna (medial) Radius (lateral) BLOOD VESSELS- that carry blood
Metacarpals Bone- five long bones in hand throughout your body
Limb- is a jointed, muscled appendage VEINS- collect oxygen-poor blood
throughout your body
LOWER LIMB
ARTERY/ARTERIES- rich blood from
Femur (thigh) - the longest, strongest bone your heart to all of your body's cells
in your body
CAPILLARY- a minute thin-walled vessel
Patella (kneecap) - covers and protects the of the body
knee joint.
HEART- a hollow muscular organ that
Tibia and fibula (leg) - two long bones in pumps the blood
the lower leg
AORTA-supplying oxygenated blood
Fibula- the smaller bone of lower leg
BLOOD- plasma, platelets, and red and
Tarsals (ankle) - set of seven irregularly white
shaped bones
ATRIUM- An anatomical cavity or passage
Metatarsals (foot) - five long bones found
in each foot. PULMONARY VEIN- a large vein
carrying deoxygenated blood into the heart
Phalanges (toes)- make up the fingers of the
hand and the toes Inferior Vena Cava- (carrying blood from
the lower body)
TIBIA- shinbone
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE-
ANKLE- tarsus hypertension, it means the force is higher
Talus - the small bone that sits between the Stroke- the condition centers around blood
heel bone flow
Heart Attack-the heart muscle is cut off TEMPORAL LOBE- most commonly
associated with processing auditory
Heart failure- congestive heart failure,
information
refers to the heart not pumping blood
SPINAL CORD- long, tube-like band of
Arrhythmia- abnormal rhythm of the heart
tissue
HEART VALVE- Complications Like
CERVICAL CORD- top portion of the
arrhythmias
spinal cord
Respiratory System- network of organs and
THORACIC CORD- built for stability
tissues
LUMBAR CORD- provide stability for
Parts
your back
-NASAL CAVITY -PHARYNX
SACRUM CORD- is located below the
LARYNX
lumbar spine
Asthma- Symptoms can include coughing,
COCCYGEAL- tailbone nerves are the last
wheezing, shortness of breath and chest
tightness. Parasympathetic system- helps maintain
normal body functions
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
(COPD)- cough, sometimes with phlegm Sympathetic system- regulating the flight-
or-fight response
Bronchiectasis - gradually become worse
NERVOUS SYTEM- complex of
interconnected systems in which larger
systems are
BRAIN- is a complex organ that controls
thought, memory, emotion
CEREBRUM- largest part of the brain, the
cerebrum initiates and coordinates
CEREBELLUM- (little brain) coordinate
voluntary muscle movements
BRAINSTEM- control these functions, like
your heart rate, breathing
FRONTAL LOBE- involved in personality
characteristics
PARIETAL LOBE- sensory perception and
integration,
OCCIPITAL LOBE- the visual processing
area of the brain
You might also like
- MODULE 12 Gross Anatomy of The Muscular SystemDocument3 pagesMODULE 12 Gross Anatomy of The Muscular SystemPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Outline of Anatomy and Physiology (Prelim-Midterm)Document11 pagesOutline of Anatomy and Physiology (Prelim-Midterm)Jhason John J. Cabigon100% (3)
- Muscles To RememberDocument3 pagesMuscles To RememberKayla CunananNo ratings yet
- Biosci Chap6 (Muscular System Notes)Document3 pagesBiosci Chap6 (Muscular System Notes)Man DejeloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PathfitDocument4 pagesReviewer in PathfitvelardecrazelleNo ratings yet
- Anaphy W5 ReviewerDocument5 pagesAnaphy W5 Reviewerangelmalang41No ratings yet
- Muscular System - Bio 2 ADocument44 pagesMuscular System - Bio 2 A20181539No ratings yet
- The Skeletal System NOTESDocument2 pagesThe Skeletal System NOTESAngelica RamosNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesReviewer For Muscular SystemRegNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Muscular ReviewerDocument7 pagesSkeletal and Muscular ReviewerJainessa SinsuatNo ratings yet
- PE Bones and MuscleDocument2 pagesPE Bones and MuscleSophia Mitz Aya-ayNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument110 pagesMuscular SystemJang WonyoungNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Biology 2 - Group 1Document86 pagesMuscular System: Biology 2 - Group 1haylo100% (1)
- MusclesDocument89 pagesMusclesSelena ReyesNo ratings yet
- GA&E 6 - Intro To MyologyDocument47 pagesGA&E 6 - Intro To MyologySu ZikaiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System ReviewerDocument4 pagesSkeletal System ReviewerMadelle Capending DebutonNo ratings yet
- Muscles in The Human BodyDocument24 pagesMuscles in The Human BodydenisemauryNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Wps Office1Document6 pagesSkeletal System Wps Office1Brent LorenzNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Report GuideDocument6 pagesMusculoskeletal Report GuideIrish CostalesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ReviewerDocument5 pagesAnatomy Reviewercath draftNo ratings yet
- The Ability To Move Is An Essential Activity of The Human Body Our Body Weight Comes From Muscles Consists of Over 600 Individual Muscles. 3 PurposesDocument25 pagesThe Ability To Move Is An Essential Activity of The Human Body Our Body Weight Comes From Muscles Consists of Over 600 Individual Muscles. 3 PurposesJoanna Poshnja100% (1)
- Introduction To Body StructureDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Body StructureBrady DeNioNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy: IME 549 Industrial Ergonomics Spring 2011 Dr. Michael JorgensenDocument30 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy: IME 549 Industrial Ergonomics Spring 2011 Dr. Michael Jorgensenanon_379343No ratings yet
- WEEK 7 LAB EXERCISE - Muscular SystemDocument11 pagesWEEK 7 LAB EXERCISE - Muscular SystemMARY KATE L. CEBALLOSNo ratings yet
- P.E Quarter 3 (REVIEWER) : Muscular FitnessDocument3 pagesP.E Quarter 3 (REVIEWER) : Muscular Fitnessmonica regalaNo ratings yet
- The Science of Human Movement ModuleDocument5 pagesThe Science of Human Movement ModuleJerome SagunNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument27 pagesMuscular SystemJOHN ANDREI ZARSADIASNo ratings yet
- Muscular System ReviewerDocument4 pagesMuscular System ReviewerMadelle Capending DebutonNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy. The Human Muscles.Document70 pagesHuman Anatomy. The Human Muscles.Stefania Ungureanu100% (1)
- Lecture 8Document15 pagesLecture 8abood kofahiNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument5 pagesScienceannakristineilisan091682No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument32 pagesMuscular SystemHarini kumaranNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 Midterm Exam Reviewer 2023 2024Document2 pagesPe 1 Midterm Exam Reviewer 2023 2024xbautista124No ratings yet
- Skeletal System UpdatedDocument55 pagesSkeletal System UpdatedAlthea OcaslaNo ratings yet
- Naw TrainingDocument34 pagesNaw Trainingganesh pNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of MusclesDocument58 pagesAnatomy of MusclesJowie SooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ANAPHY Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 7 ANAPHY Muscular Systemrobh0026No ratings yet
- The Muscular System Powerpoint 1227697713114530 8Document44 pagesThe Muscular System Powerpoint 1227697713114530 8ninya puella100% (1)
- Health Sci g12Document4 pagesHealth Sci g12api-427920673No ratings yet
- Muscles of The Human Body PDFDocument13 pagesMuscles of The Human Body PDFPalma, Arrabela M.No ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Facts About Muscular Fitness: Tips On How To Improve Muscle FitnessDocument3 pagesChapter 9: Facts About Muscular Fitness: Tips On How To Improve Muscle FitnessTyrhon Howard VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- M. M. College of Nursing Mullana Ambala: Topic: Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesM. M. College of Nursing Mullana Ambala: Topic: Muscular SystemBhawna PandhuNo ratings yet
- Muscular System2Document43 pagesMuscular System2LeocadiaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Excitability Contractility Extensibility ElasticityDocument5 pagesElectrical Excitability Contractility Extensibility ElasticityMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- Joints: Bones in The Shoulder and Chest: Types of Movable JointsDocument2 pagesJoints: Bones in The Shoulder and Chest: Types of Movable JointsLloyd LagadNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy,: Chapter 12 Lecture Outline: Appendicular MusclesDocument70 pagesHuman Anatomy,: Chapter 12 Lecture Outline: Appendicular MusclesdewkmcNo ratings yet
- E. Muscular System RevisedDocument41 pagesE. Muscular System RevisedGenelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- 1muscles ObjectivesDocument20 pages1muscles ObjectivesZahra AdanNo ratings yet
- Secondary 5 Musclular SystemDocument3 pagesSecondary 5 Musclular SystemyunnNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument33 pagesANATOMYPhoebe LiasosNo ratings yet
- Physiology: MusclesDocument88 pagesPhysiology: MusclesMielah Ruth100% (4)
- Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesSkeletal SystemMa Khristina S WongNo ratings yet
- K00429 - 20180831110050 - Muscular SystemDocument14 pagesK00429 - 20180831110050 - Muscular Systemroesil juniNo ratings yet
- Refined Muscular SystemDocument54 pagesRefined Muscular SystemogatojohnsonNo ratings yet
- Muscles Back&Neck STUDENTDocument15 pagesMuscles Back&Neck STUDENTMarikit2012No ratings yet
- Anatomy ASS Two FinishedDocument8 pagesAnatomy ASS Two Finishedhakimabrahim77No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument90 pagesMuscular SystemAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- Biological Science, An IntroductionDocument25 pagesBiological Science, An IntroductionTristan BabaylanNo ratings yet
- Invertebrates - Are Animals Without A Backbone or Bony SkeletonDocument2 pagesInvertebrates - Are Animals Without A Backbone or Bony SkeletonAnthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument15 pagesMuscular SystemReina Grace PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Antigen and Antibody NotesDocument35 pagesAntigen and Antibody NotesVlad Lipsam100% (1)
- IAH AC ImmunomodulationDocument33 pagesIAH AC ImmunomodulationJoão FrancoNo ratings yet
- 0111inflammation PDFDocument5 pages0111inflammation PDFAshiniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - The Human BodyDocument8 pagesLesson 1 - The Human BodyGilmar ManzanoNo ratings yet
- E6 U2 Semana5 PresentacionDocument14 pagesE6 U2 Semana5 PresentacionEdwin DavidNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument27 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationMouhammad DawoudNo ratings yet
- DNB Immunohematology and Blood Transfusion Paper1Document2 pagesDNB Immunohematology and Blood Transfusion Paper1Dr.vidyaNo ratings yet
- LIPS - Histological StructureDocument4 pagesLIPS - Histological StructureivkovictNo ratings yet
- Marking Key Bio 10 2023-24 TrialsDocument15 pagesMarking Key Bio 10 2023-24 TrialsAaraNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes During PregnancyDocument24 pagesPhysiological Changes During PregnancyerlinNo ratings yet
- The Larynx An PharynxDocument46 pagesThe Larynx An PharynxDerick SemNo ratings yet
- المصطلحات - الطبيه - بالعربية - مبارك - عبدالهادي - موقع المكتبة نتDocument199 pagesالمصطلحات - الطبيه - بالعربية - مبارك - عبدالهادي - موقع المكتبة نتAli AimanNo ratings yet
- Selective Eviction of Deformed Horny Cells by JRKs Psorolin Derma Skin Care SoapDocument5 pagesSelective Eviction of Deformed Horny Cells by JRKs Psorolin Derma Skin Care SoapAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Week 4B Science 7 LasDocument7 pagesWeek 4B Science 7 LasJonah Labine Jabulin-RadazaNo ratings yet
- Neck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Document40 pagesNeck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Hauwa shitu.B100% (1)
- RHIANNA JOHNSON - Portfolio P.EDocument12 pagesRHIANNA JOHNSON - Portfolio P.ERhianna JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Notes (Tortora)Document3 pagesRespiratory Notes (Tortora)Eli MinchaiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lower Face and Botulinum Toxin.16Document8 pagesAnatomy of The Lower Face and Botulinum Toxin.16Dogan TuncaliNo ratings yet
- Fundus GastricusDocument4 pagesFundus GastricusAndrie Devin Susilo HadiNo ratings yet
- Interactive PowerpointDocument12 pagesInteractive PowerpointRahul DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 48 Urine EliminationDocument10 pagesChapter 48 Urine EliminationKathleen FrugalidadNo ratings yet
- The Finale: Multiple Choice: Anatomy & Physiology Coloring WorkbookDocument3 pagesThe Finale: Multiple Choice: Anatomy & Physiology Coloring WorkbookJonash Morales0% (1)
- 10th 100 Marks MCQs Test The HopeDocument63 pages10th 100 Marks MCQs Test The Hopegmian9012100% (1)
- Pages From MAF Nextcare 2Document1 pagePages From MAF Nextcare 2Fahad ThahaNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Diagnosis of Penoscrotal Transposition With 2-And 3-Dimensional UltrasonographyDocument5 pagesPrenatal Diagnosis of Penoscrotal Transposition With 2-And 3-Dimensional UltrasonographyIndach ZyadarifnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document48 pagesLecture 8Anthony FajardoNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Illustration in Arabic ManuscDocument16 pagesAnatomical Illustration in Arabic ManuscABDOULAYE BANo ratings yet
- L2 Introduction To HematologyDocument3 pagesL2 Introduction To HematologyJamil LausNo ratings yet
- EP - 02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - One Shot - NEET 2022 PreparationDocument85 pagesEP - 02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - One Shot - NEET 2022 PreparationSindhuja C SNo ratings yet