Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answers 10th Isce Bio Test
Answers 10th Isce Bio Test
Uploaded by
Arshadkhan A JahagirdarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers 10th Isce Bio Test
Answers 10th Isce Bio Test
Uploaded by
Arshadkhan A JahagirdarCopyright:
Available Formats
.
Fill in the Blanks:
(i) A hormone which influences the ossification of bones is calcitonin. (ii) The
endocrine part of the pancreas is the Islets of Langerhans. (iii) Insulin makes
the liver turn blood sugar into glycogen. (iv) The activities of the thyroid
gland are controlled by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) secreted by the
pituitary gland. (v) A nerve chain between a receptor and an effector organ is
called reflex arc. (vi) Cerebrum is the site of consciousness, memory, and
intelligence. (vii) Cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. (viii) The organ of
balance and hearing in the body is the ear.
2. True & False:
(i) False - Adrenal cortex produces emergency hormone cortisol. Adrenaline is
produced by the adrenal medulla. (ii) False - Iodine is the main element of
thyroxin. (iii) True - Thyroxin regulates metabolism. (iv) True - A nerve impulse
passes from one neuron to another across a synapse. (v) False - Reflex action
does not necessarily involve the brain; it can occur at the spinal cord level.
3. Multiple Choice Questions:
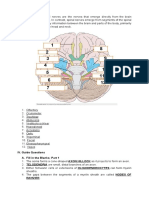
(i) Cerebellum is the part of the brain which is responsible for: c) Maintaining
posture and equilibrium. (ii) A reflex arc in man is best described as
movement of stimuli from: g) Receptor cell, spinal cord, motor neuron,
relaying neuron (iii) Which statement is not for a hormone? c) They are used
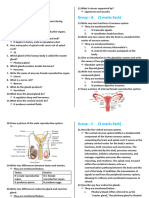
again and again like catalysts. (iv) Secretin is secreted by: c) Small intestine
and stimulates pancreas (v) Pancreas is a mixed gland in which: a) All cells
secrete enzymes and hormones. (vi) Leydig cells are meant for: c) To
produce testosterone
4. Give Technical Terms:
(i) When your mouth dries up and the heart begins to beat faster, which
hormone brings about the feeling? Adrenaline (ii) Name the cells of islets of
Langerhans in the pancreas, which secretes insulin and glucagon. Alpha cells
(for glucagon) and Beta cells (for insulin) (iii) The chemical messenger by
which the nerve impulse travels from one neuron to the other.
Neurotransmitter (iv) The fluid which fills the central canal of the spinal cord.
Cerebrospinal fluid
5. Name the hormones which lead to the following conditions:
(a) Diabetes mellitus - Insulin deficiency (b) Growth of beard in women -
Excess of Androgens (like testosterone) (c) Myxedema - Hypothyroidism
(d) Gigantism - Excess of Growth Hormone (GH) (e) Exophthalmic goitre -
Hyperthyroidism
6. Choose the odd one out:
(f) Insulin, Glucagon, Diabetes insipidus, Diabetes mellitus. - Diabetes
insipidus
7. Differentiate between Endocrine gland and Exocrine gland:
Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, while
exocrine glands secrete substances through ducts.
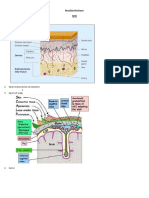
8. Write about some functions of:
(a) Adrenal glands: Produce hormones like cortisol, aldosterone, and
adrenaline; involved in stress response and electrolyte balance. (b) Synapse:
Junction between two nerve cells allowing the transmission of nerve impulses.
(c) Medulla Oblongata: Controls vital functions like heartbeat, breathing, and
blood pressure. (d) Cochlea: Part of the inner ear responsible for hearing. (e)
Auditory nerve: Carries auditory information from the ear to the brain. (f)
Ciliary muscle: Controls the shape of the lens in the eye for focusing.
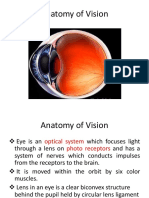
9. Draw a neat labeled diagram of the human eye.
10. Differentiate between Cretinism and Myxedema:
Cretinism is a condition of severe hypothyroidism in infants, leading to
stunted physical and mental development.
Myxedema is hypothyroidism in adults, characterized by general swelling,
lethargy, and slow mental function.
11. Differentiate between nervous control and hormonal control:
Nervous control involves rapid and specific responses, using nerve impulses.
Hormonal control is slower, involving the release of hormones into the
bloodstream to regulate various physiological processes.
12. Draw a neat labeled diagram of a neuron.
Neuron Diagram
13. What is meant by 'reflex action'?
Reflex action is an involuntary and automatic response to a stimulus, often
without involving conscious thought, designed to protect the body.
14. Differentiate between the blind spot and the yellow spot:
Blind spot: Area on the retina without light-sensitive cells where the optic
nerve exits the eye.
Yellow spot: Area on the retina with a high concentration of cones,
responsible for detailed central vision.
15. Differentiate between rods and cones:
Rods: Photoreceptor cells in the retina responsible for vision in low light
conditions.
Cones: Photoreceptor cells responsible for color vision and high acuity in
bright light.
16. Differentiate between aqueous humor and vitreous humor:
Aqueous humor: Clear fluid in the front part of the eye, maintaining
intraocular pressure.
Vitreous humor: Gel-like substance filling the space between the lens and
retina, providing structural support.
17. Name the following:
(a) Three layers of the eyeball:
. Sclera
. Choroid
. Retina
(b) Two pigments of the sensory cells:
. Rhodopsin (in rods)
. Iodopsin (in cones)
18. Name the defects caused due to:
(a) Lens turns opaque: Cataract (b) Deficiency of vitamin-A: Night
blindness (c) Lens becomes too flat: Hypermetropia (Farsightedness) (d)
Uneven curvature of the cornea: Astigmatism
You might also like
- 10th Isce - Biology - TestDocument3 pages10th Isce - Biology - TestArshadkhan A JahagirdarNo ratings yet
- Nlknpast AppDocument7 pagesNlknpast AppUCL SportsNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Control (Ch#12) (1) .PDF FinalDocument19 pagesCoordination and Control (Ch#12) (1) .PDF FinalUmme AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Biology (Sem-2) 2022 Set - 5Document6 pagesBiology (Sem-2) 2022 Set - 5Kamaljeet DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Nervous System QuizDocument3 pagesNervous System QuizMay RodeoNo ratings yet
- E Learning FinalsDocument7 pagesE Learning Finalsnorma BernardoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Activity 8Document6 pagesAnaphy Activity 8PENNY KEDAWENNo ratings yet
- Te-Control and Coordination Final Revisor (2023-24)Document69 pagesTe-Control and Coordination Final Revisor (2023-24)Gautam SharrmaNo ratings yet
- Coordination & Response QuestionDocument18 pagesCoordination & Response QuestionTeddy BooNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Solution For Term 2 Exam 2021 22Document8 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Solution For Term 2 Exam 2021 22VedantNo ratings yet
- Biology Class X: Assignment No.4 Chapter 12: Coordination and ControlDocument2 pagesBiology Class X: Assignment No.4 Chapter 12: Coordination and ControlAbdullah ButtNo ratings yet
- Bio Sci QuestionsDocument45 pagesBio Sci QuestionsAiza BaleñaNo ratings yet
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 7 2017 PDFDocument10 pagesStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 7 2017 PDFLakshay SinglaNo ratings yet
- Sensory Sensory Motor Motor Mixed Motor Mixed Sensory Mixed Mixed Motor MotorDocument5 pagesSensory Sensory Motor Motor Mixed Motor Mixed Sensory Mixed Mixed Motor MotorKAUSTUBH SAWANTNo ratings yet
- Terminal Exam Answer Key (Biology)Document8 pagesTerminal Exam Answer Key (Biology)KES SCIENCE FYJC PHYSICSNo ratings yet
- Eye Movements Clinical CorrelationDocument8 pagesEye Movements Clinical CorrelationAsena TuiketeiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Human Body System Lesson 5: The Nervous and Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesUnit 1: Human Body System Lesson 5: The Nervous and Endocrine SystemeisachannelestNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - I: Biology XDocument5 pagesWorksheet - I: Biology XDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- DPP-Control and Coordination (Prashant Kirad)Document9 pagesDPP-Control and Coordination (Prashant Kirad)ABHI TECH 983No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Past Papers of BSN 2nd SemesterDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Past Papers of BSN 2nd Semestertamseelabano63No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nervous SystemDocument59 pagesAnatomy of Nervous SystemSeema ChapagainNo ratings yet
- Coordination System Encircle The Best Answer of The Following QuestionsDocument13 pagesCoordination System Encircle The Best Answer of The Following Questionsnon elfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07 Control and Coordination Imp Questions and AnswersDocument31 pagesChapter 07 Control and Coordination Imp Questions and Answersgnilakiya2008No ratings yet
- Endocrine-System Important-Qs Important-QuestionsDocument4 pagesEndocrine-System Important-Qs Important-Questionssshashvat810No ratings yet
- Class 10 Notes ControlcoordinationDocument6 pagesClass 10 Notes ControlcoordinationVijayasimha rao RavooriNo ratings yet
- SSLC Biology 2022 EWLA Model KeyDocument2 pagesSSLC Biology 2022 EWLA Model KeyCrazy BoyNo ratings yet
- Biology Question Bank 3Document11 pagesBiology Question Bank 3bhargavthegreat123No ratings yet
- Exercise 5a Nervous System CNSDocument8 pagesExercise 5a Nervous System CNSbansarigadhvi23No ratings yet
- Chapter-9 Endocrine System: Revision NotesDocument3 pagesChapter-9 Endocrine System: Revision NotesKamaljeet DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Summative Exam On Nervous System and Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesSummative Exam On Nervous System and Endocrine SystemKhiyah RhueNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument25 pagesEndocrine SystemLits KhoNo ratings yet
- AD 7 The Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesAD 7 The Nervous SystemBernard SalimNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs PDFDocument5 pagesSense Organs PDFTanzila SarfrazNo ratings yet
- 12 - Endocrine SystemDocument20 pages12 - Endocrine SystemNovie Roycell Fernandez RueloNo ratings yet
- International Post-Baccalaureate Pharmd. Program (Ipbp) Internal Assessment (Ia) Exam Study GuideDocument19 pagesInternational Post-Baccalaureate Pharmd. Program (Ipbp) Internal Assessment (Ia) Exam Study Guideapi-3752144No ratings yet
- Revalida ReviewerDocument63 pagesRevalida ReviewerJam ChuaNo ratings yet
- 8th ClassDocument7 pages8th ClassSadi YousufNo ratings yet
- Model of Answer Endocrine Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesModel of Answer Endocrine Tutorial QuestionsBOUBA ABDOURAMANNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Week 4 - 2nd QuarterDocument5 pagesScience 6 - Week 4 - 2nd QuarterHoneylet Alberto Castro ArilloNo ratings yet
- CVD Case StudyDocument24 pagesCVD Case Studyjracan0% (1)
- CVD Case StudyDocument12 pagesCVD Case StudySean MercadoNo ratings yet
- D) COORDINATIONDocument10 pagesD) COORDINATIONamarashah182No ratings yet
- 12 Cranial NervesDocument61 pages12 Cranial NervesAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNo ratings yet
- Control & Coordination - Expected Q&ADocument15 pagesControl & Coordination - Expected Q&Apallab mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Biology (Sem-2) 2022 Set - 4Document6 pagesBiology (Sem-2) 2022 Set - 4Kamaljeet DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System WorksheetDocument4 pagesEndocrine System Worksheetsamhi96No ratings yet
- Bio310 March 2014Document8 pagesBio310 March 2014Minatour RogNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument27 pagesControl and Coordinationanitaagarwal19891984No ratings yet
- Practice Paper Zoology II 2024Document6 pagesPractice Paper Zoology II 2024meerab uroojNo ratings yet
- Nervous System and Special Senses-FINALDocument5 pagesNervous System and Special Senses-FINALcandido evanNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-09 at 6.16.09 PMDocument9 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-09 at 6.16.09 PMdtj2g94qfyNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument7 pagesFinalShourok GabrNo ratings yet
- Health ChapterwiseDocument31 pagesHealth Chapterwiseadityakautuksen77No ratings yet
- Development and Plasticity of The Brain: Chapter OutlineDocument5 pagesDevelopment and Plasticity of The Brain: Chapter OutlineSusie SofrankoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7, Control and Co Ordination PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 7, Control and Co Ordination PDFaustin40043No ratings yet
- Embriology and Anatomy of The Endocrine SystemDocument87 pagesEmbriology and Anatomy of The Endocrine SystemfaiziaNo ratings yet
- Neurobiology: Review Questions For AnatomyDocument8 pagesNeurobiology: Review Questions For AnatomyRu LiliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MCQDocument10 pagesAnatomy MCQnistaraNo ratings yet
- Biology-Class 10Th Chapter: Control and Co-Ordination: Very Short Answer Type Question (1 Mark)Document5 pagesBiology-Class 10Th Chapter: Control and Co-Ordination: Very Short Answer Type Question (1 Mark)junaidNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy of the Brain and its functionalities: 1, #172From EverandNeuroanatomy of the Brain and its functionalities: 1, #172No ratings yet
- Psychology: Perspectives and ConnectionsDocument12 pagesPsychology: Perspectives and ConnectionsEnrea Dela Cruz CasquejoNo ratings yet
- Special Sense Eye HistologyDocument49 pagesSpecial Sense Eye HistologyjacobsNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/42Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/42Ashtav ArunNo ratings yet
- The Special SensesDocument11 pagesThe Special SensesRyan Kim FabrosNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Guide To The Basics of Efficient LightingDocument152 pagesUltimate Guide To The Basics of Efficient LightinggivepleaseNo ratings yet
- Image Processing 2017Document133 pagesImage Processing 2017Edwin Okoampa BoaduNo ratings yet
- Into The NightDocument16 pagesInto The NightSBolgerNo ratings yet
- Revised ROP Guidelines-Web Optimized PDFDocument100 pagesRevised ROP Guidelines-Web Optimized PDFAshok Karnam0% (1)
- Control and Coordination 12Document18 pagesControl and Coordination 12Ronnith NandyNo ratings yet
- 05 - Human Eye & The Colourful WorldDocument26 pages05 - Human Eye & The Colourful WorldAmogh Suman100% (2)
- 8 Science 16 Light TextBook QnADocument20 pages8 Science 16 Light TextBook QnAkumaran RNo ratings yet
- Compound Eye in InsectDocument8 pagesCompound Eye in InsectAnupam GhoshNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 3 December Holiday AssignmentDocument38 pagesBiology Form 3 December Holiday Assignmenterastuskamunya1No ratings yet
- Color and Shade Matching in Operative DentistryDocument19 pagesColor and Shade Matching in Operative DentistryMarco Antonio García Luna100% (1)
- HCI Chap 2Document37 pagesHCI Chap 2alemneh bayehNo ratings yet
- Pra PTS Xi SMS 2Document11 pagesPra PTS Xi SMS 2Ammar KhadafiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 SENSESDocument13 pagesChapter 10 SENSESMark Owen QuilatanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Gr10 (Eye and Ear) - 1Document5 pagesWorksheet Gr10 (Eye and Ear) - 1ahlamNo ratings yet
- Cs408 Final Term Mcqs by Arslan Vu Students CompressDocument85 pagesCs408 Final Term Mcqs by Arslan Vu Students Compresshowtoplaygames38No ratings yet
- The Amazing Human BodyDocument77 pagesThe Amazing Human Bodycititor1111100% (1)
- The Effect of Hypoxia On Visual FunctionDocument6 pagesThe Effect of Hypoxia On Visual FunctionenNo ratings yet
- Wa0041Document161 pagesWa0041SULDAANUL CAASHIQIINNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Laser Safety - Unit 01Document90 pagesIntroduction To Laser Safety - Unit 01TEBATSONo ratings yet
- Question Bank EBB 2023Document46 pagesQuestion Bank EBB 2023Muhammad SamyNo ratings yet
- Human ExpDocument19 pagesHuman ExpCaren PerilloNo ratings yet
- Mod 2Document30 pagesMod 2mailtopiyush18No ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN Chap 11 Eye and WorldDocument3 pagesLESSON PLAN Chap 11 Eye and Worldneerajkunj22No ratings yet
- Microanatomy (Histology) - Key Identification Points - 57 MUHS Exam Slides (Anatomy Decoded YouTube)Document15 pagesMicroanatomy (Histology) - Key Identification Points - 57 MUHS Exam Slides (Anatomy Decoded YouTube)ASHISH RANJANNo ratings yet
- Human Factors in AviationDocument103 pagesHuman Factors in AviationJustus JosephNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of VisionDocument119 pagesAnatomy of VisionjaheerNo ratings yet