Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 10 Geography SST Notes Chapter 7
Class 10 Geography SST Notes Chapter 7
Uploaded by
clevermind2407Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class 10 Geography SST Notes Chapter 7
Class 10 Geography SST Notes Chapter 7
Uploaded by
clevermind2407Copyright:
Available Formats
Ch.
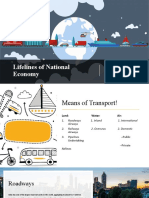
7 Life Lines of National Economy
Transport and Communication
Means of Transport
60
Land Water Airways
Roadway
Domestic International
E3
Railway
Pipelines Public
Private
Six types of Roads according to their capacity:-
ID
L Golden quadrilateral:- Links Delhi, Kolkata, Mumbai, Chennai
L National highways:- Link extreme parts of the country.
U
L State highways:- Link state capital with district head quarters.
L District roads:- Connect district headquarters with other places of district.
YG
L Other roads:- Rural roads, which link villages importance
L Border roads:- Link places of strategic more than border in northeast and
northern border areas.
D
Advantages of Roadways over Railways
L Construction cost is much lower
U
L Can be laid any where such as on slopes, mountains
L Economical in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller amount
ST
of goods over short distance
L Provides door to door service, thus cost of loading and unloading is much
lower
L Feeder to other models of transport as they provide a link between railway
stations, air and sea ports.
Class X - Social Science 154
Railways
Advantages Problems
* Principal mode of transport *Traveling without tickets
60
for freight and passengers. *Theft and damaging of
* Make it possible to conduct railway property
multifarious activities like *Pulling the chain unnecessarily
business, sightseeing, to stop the train.
E3
Pilgrinage transport of
goods over long distance.
* A great intergrating force
connecting different parts
of the country.
ID
Pipelines
U
YG
Use 3 important networks
In the past for water only Assam to Kanpur via
Now for crude oil, Petroleum products Guwahati, Baraui and
Natural gas to reneries for tizer factories Allahabad
D
and big thermal power plants From Salaya in Gujarat
Solids can be transported when to Jalandhar in Punjab
Converted into slurry From Hajira in Gujarat
U
to Jagdishpur in U.P.
via Vijaypur in MP
Interesting facts
ST
* If mile stone is blue or black then
you are heading towards district, Delhi
70
that is district road.
* Yellow colour milestone signies
National highways.
155 Class X - Social Science
Water Ways
Advantages National waterways of India
* Cheapest means of transport * National waterway no.1
60
* Most suitable for carrying between Allahabad and Haldia
heavy and bulky goods * NW no.2 In Brahmaputra
* Fuel efcient and river between Sadiya and
environment friendly. Dhubri
E3
* NW No.3 The west coast land
in Kerala.
* NW no. 4 Specied stretches
of godovari and krishna rivers
along with Kakinada puducherry
ID
stretches of canal.
* NW no.5 Specied stretches of
Bahmari along with Mata rivers.
U
Major Sea Ports and their states
Name of the port State Signicance
YG
Kandla Gujarat First port to be developed after
Mumbai independence
Marmagao Maharashtra Biggest Port
New Mangalore Goa 50% of iron ore export
D
Kochi Karnataka Export of iron ore from kudremukh mine
Tuticorin Kerala Located at entrance of lagoon with
Chennai natural hardbour
U
Vishakhapatnam Tamilnadu Natural harbour
Paradip Tamilnadu Oldest articial port
ST
Haldia Andhra Pradesh Deepest land located, outlet for iron
ore export
Odisha Export of iron ore
West Bengal Development to relieve growing pressure
on kolkata port.
Class X - Social Science 156
Airways
L Fastest, Most comfortable and prestigious mode of transport.
L Can cover difcult terrains like high mountains, dreary deserts, dense
forest and long oceanic stretches.
L Provides help during natural disasters like oods and earthquakes.
60
* Not within the reach of the common people.
* Gets affected by weather conditions.
E3
Major Air ports of India
Name of the Airport State/City
Raja Sansi Amritsar (Punjab)
ID
Indira Gandhi International New Delhi
Chhatrapati Shivaji Mumbai
Meenam Bakkam Chennai
Netaji Subhash Chandra Kolkata
U
Rajiv Gandhi Hyderabad
YG
Communication
Personal communication Mass communication
(letters, cards, telephone) (Television, radio, press
D
lms)
U
International Trade
ST
Export Import
Favourable
Balance of trade L Export L Import
Unfavourable balance L Imports L Exports
of trade.
157 Class X - Social Science
Tourism as a Trade
Signicance :- * Promotes national integration
* Provides support to local handicrafts
60
* Helps in development of International understanding
about our culture and heritage.
E3
Types of Tourism * Heritage tourism
* Eco tourism
ID
* Adventure tourism
U
* Cultural tourism
* Medical tourism
YG
* Business tourism
D
U
ST
Class X - Social Science 158
Key points:
1. Life lines of a country-Modern means of communication and transport
which brings people together and helps in local, national and
international trade.
2. Means of Transport-Means of transports which make possible the
movement of goods, services and humans/animals from one place to
60
another place.
3. Means of communication-Methods through which information, news,
dialogue etc. communicated from one place and person to another place
E3
and person are called means of communication. Such as newspaper,
radio, T.V. telephone, mobile phone, e-mail etc.
4. Golden Quadrilateral-The six lane superhighways which being
implemented by National highway Authority of India(NHAI) and
connects Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai (the four metro cities)
5.
ID
National Highways-Four to six lane highways which connects or link
extreme parts of the country and maintained by Central Public Works
Department (CPWD)
U
6. Border Roads-Border Roads Organisation a Government of India
undertaking constructs and maintains roads in the bordering areas of
YG
the country. These roads are border roads and improve the accessibility
in areas of difficult terrain.
7. Trade-Exchange of goods and services among different peoples, states
and countries referred to as trade.
8. International Trade-Trade between two and more countries is called
D
International trade. 95% of country's trade volume is moved by sea.
9. Balance of Trade-The balance of trade of a country is the difference
U
between it's export and import.
10. Rail Transport-A major means of transport in India. The Indian Railways
is now reorganised in 16 zones in 2003.
ST
11. Gauge or track-It is the distance between the two tracks of rail.
12. Port -The manmade place or facility near the sea cost where ships, boats
and barges can be docked to load unload people, things etc. Fuel and
other needs can also be taken here. A port is different than a harbour.
13. Tidal port - A port in which the water level within the port is subject to
159 Class X - Social Science
change with the ocean tides. These ports are found in coastal region.
e.g. Kandla.
14. New forms of Tourism-Heritage tourism, eco tourism, adventure tourism,
cultural tourism, medical tourism and business tourism. Over 2.6 million
foreign tourists visit India every year.
Very Short Answer type Questions
60
1. Which two stations are linked by East-West corridor?
2. Where is the head quarter of Northern Railways situated?
3. When and where did the first train start running in India?
4. Which is the oldest artificial port in India?
E3
5. What do you understand by the road density?
6. Between which two place national waterways no.1 is navigable? How
long it is ?
7. Which two stations are linked by North-South corridor?
ID
8. What does pipeline transport mean?
9. What is the total length of India's coast line?
10. Which sea port is the major port in context to the export of Iron ore?
11. Which is the first port developed after the independence.
U
12. Name two inland waterways of India?
13. When did the airways nationalised in India?
YG
14. Which measures were taken to facilitate quick delivery of mails in large
towns and cities?
15. In which area of India the air transport has been provided to common
people as a special provision?
16. Which is the longest national highway?
D
17. Which two cities are connect through NH-1?
18. What is the total no of railway zones in India.
U
19. Which state has highest and lowest road density respectively?
20. Which is the busiest railway junction in Northern India?
21. Mention the two components of international trade.
ST
22. Apart from Hindi list out 2 language in which the largest no of newspaper
are published.
23. Which authority certifies both Indian foreign films?
24. Which is the longest gas pipeline?
25. Give two examples of first class mail.
Class X - Social Science 160
ANSWER KEY -:
1. Silchar (Assam) to Porbandar(Gujarat)
2. Delhi
3. On 16 April,1853 between Mumbai to Thane(34 km.)
4. Chennai
5. The length of road per hundred sq. km. of area is known as density of
60
roads.
6. Between Allahabad and Haldia (1620 km long).
7. Srinagar with Kanyakumari.
E3
8. A new means of transport. A new arrival on the transportation map of India.
Through which water is transported to houses and farms, and crude oil,
petrol products and natural gas transported to gas refineries and thermal
power stations.
ID
9. 7516.6 km
10. Marmagao.
11. Kandla Port.
12. (i) On river Ganga-between Allahabad and Haldia.
U
(ii) On river Brahmaputra-between Sadiya and Dhubri.
13. In 1953.
YG
14. Six mail channels have been introduced. They are called Rajdhani
channel, Metro channel, Green channel, Business channel, Bulk mail
channel and Periodical channel.
15. In North eastern states.
16. NH-7 Connecting Varanshi and Kanyakumari
D
17. Delhi and Amritsar
18. 16
U
19. Highest-Kerala, lowest-Jammu and Kashmir
20. Mughalsarai
ST
21. Exports and Imports
22. English and Urdu
23. Central board of film certification
24. Hajira-Vijaypur-Jagdishpur
25. Cards and Envelops
161 Class X - Social Science
LONG/SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS -:
1. Describe any three advantages of Mass communication?
2. Describe the advantages of Pipeline Transport?
3. Write any three features of Golden Quadrilateral super highways?
60
4. Write the name of any three Railway zones and their headquarters?
5. 'Road transport is more important than the Rail transport'. Why?
6. Explain the importance of Air transport ?
E3
7. What are the major challenges of road transport?
8. Write the reasons behind the unequal distribution of Rail network in
India?
9. How is the tourism is helpful in the development of economy as a trade or
industry?
ID
10. Classify the Indian roads on the basis of their capacity?
11. Differentiates between the International and local trade?
12. Why the transport and means of communication are called the lifelines of
U
an economy?
13. Which means of Transport is being used mostly in the North-Eastern
YG
states of India? Why this means of transport is used in these states give
four reasons?
14. "The progress of international trade of a country indicates the economic
prosperity of that country."Prove this statement with five logics.
D
U
ST
Class X - Social Science 162
ANSWER KEY -:
A.1. (i) Mass communication provides entertainment.
(ii) Creates awareness among people about various National
programme and policies.
(iii) It spreads knowledge.
(iv) It broadcasts a variety of programmes from entertainment,
60
educational to sports, etc.
(v) Doordarshan, the national television channel of India is the medium
of national message and is one of the largest terrestrial networks in
the world.
E3
A.2. (i) Pipeline transport network is used to transport water to cities and
industries, crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from oil
and natural gas fields to refineries, fertilizer factories and big
thermal power plants.
ID
(ii) Initial cost of laying pipelines is high but subsequent running costs
are minimal.
(iii) It rules out trans-shipment losses or delays.
(iv) Pipelines make transport fast, safe and easy.
U
(v) It saves time and reduce pressure on rail transport.
A.3. (i) It's a six lane super highways.
YG
(ii) It links the mega cities of India i.e. Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai-Mumbai
and Delhi.
(iii) It reduces the time and distance between the mega cities of India.
(iv) It is under the NHAI.
(v) it's a major road development project of our country.
D
A.4. (i) Northern Railway Zone-New Delhi
(ii) Western Railway zone-Mumbai
U
(iii) Southern Railway zone-Chennai
A.5. (i) Road transport was started before the rail transport.
(ii) Construction and management is easy thus can built and
ST
maintained easily.
(iii) Construction cost of roads is much lower than that of railway lines.
(iv) Can be constructed on mountains, and difficult terrains.
(v) It also provide door- to- door service, thus the cost of loading and
unloading is much lower.
163 Class X - Social Science
(vi) Road transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport
such as they provide a link between railway stations, air and sea ports.
A.6. (i) It is fastest among all. Take lesser time to reach one place to
another.
(ii) It is a most comfortable.
(iii) It's prestigious mode of transport.
60
(iv) It can cover very difficult terrains like high mountains, dreary
deserts, dense forests and also long oceanic stretches with great
ease.
(v) On the border, to maintain the force and to provide them food and
E3
ration at earliest.
A.7. (i) Almost half of the roads are unmetalled roads and go out of use in
the rainy season.
(ii) Roads are insufficient in compare to transport and commuters.
ID
(iii) Roads are narrow and crowded due to the increasing number of
vehicles.
(iv) It leads to traffic jams and road rage.
(v) Even National highways are insufficient.
U
A.8. (i) It is difficult to lay railway lines on mountainous region and it is
expensive too.
YG
(ii) The northern plains with their vast level land provides favourable
condition for Rail construction. Here construction is easy and
construction cost is low.
(iii) High population density and rich agricultural resources provide the
most favourable condition for the growth.
D
(iv) Due to sparse population and lack of economic activities it was
difficult to lay railway lines on the sandy plains of western Rajasthan
and in the hilly terrains of the peninsular region.
U
(v) Due to administrative reasons and Government policies also the
development of Railways effected.
ST
A.9. (i) Tourism in India has grown substantially over the last three
decades.
(ii) More than 15 million(150 lakhs)people are directly engaged in this
industry.
(iii) Tourism also promotes national integration.
Class X - Social Science 164
(iv) It also helps in the development of international understanding
about our culture and heritage.
(v) It also provide support to local handicrafts and cultural pursuits.
(vi) It contributes significantly in earning foreign exchange.
A.10.(i) Golden Quadrilateral superhighways-It is a superhighway of six
lanes.
60
(ii) National Highways-Links extreme parts of the country.
(iii) State Highways-Roads linking a state capital with different district
headquarters.
(iv) District Roads-These roads connect the district headquarters with
E3
other places of the district.
(v) Border Roads-Border Roads Organisation construct and maintains
roads in the bordering area of the country. These roads have
improved accessibility in areas of difficult terrain and have helped in
the economic development of these areas.
A.11.
International Trade
1. Carried between two countries.
ID Local Trade
U
1. Carried among village, town and
cities.
2. At a large scale. 2. At a small scale.
YG
3. Foreign currency is exchanged 3. Currency remains in the same
country.
4. Fulfil needs for the entire public 4. Fulfils the need and necessities of
welfare. (whole world) local people only.
5. Advancement of international 5. Advancement of local trade also
D
trade of a country is an index to its benefits a country indirectly.
economic prosperity.
A.12. i) The trade, transport and communication are complementary to
U
each other.
ii) Connects the far reaching areas of the country and the world
ST
iii) Encourage the national and international tourism.
iv) Brings foreign exchange.
v) Life gets comfortable and easy.
vi) The whole country unites in emergency.
A.13. Though the air travel has made transportation in north-eastern
states easier with the presence of big rivers, dissected relief, dense
165 Class X - Social Science
forests and frequent floods and international frontiers, etc. but it is not in
the reach of the common man, as it is expensive. Therefore mostly
inland waterways are being used as the most common means of
transport in the north-eastern states of India. The reason behind are-
(i) Waterways are the cheapest means of transport.
(ii) They are most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods.
60
(iii) It is fuel-efficient and environment friendly mode of transport.
(iv) Road and Rail transport are not very much developed in north-
eastern states.
(v) Here rivers make harbours and ports for the inland navigation
E3
waterways.
A.14. Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to it's
economic prosperity. It is, therefore, considered the economic
barometer for a country. Following facts justifies and prove this-
(i) Due to the progress of the international trade the living
ID
standard of the people of a country prospers.
(ii) Developed nations get foreign exchange by selling their high
quality goods to other countries.
(iii) Developed countries produce/manufacture goods more than
U
their requirements and exports in foreign countries.
(iv) Developing countries depends on developed countries in
YG
many ways.
(v) Under developed countries depends on other countries and
have to give a big part of their income to developed countries.
(vi) It increases employment opportunities.
(vii) Much needed foreign currency stock increases.
D
MAP WORK
Study the following maps related to the chapter and answer the given
U
questions.
Q. Locate and label the major sea ports and airports on the outline map of
India.
ST
Class X - Social Science 166
60
E3
ID
U
YG
D
U
ST
167 Class X - Social Science
You might also like
- Importance of Transport in IndiaDocument5 pagesImportance of Transport in IndiaJay Malaney100% (1)
- Lifelines of EconomyDocument8 pagesLifelines of EconomytanishqNo ratings yet
- Lifelines of National Economy 2Document55 pagesLifelines of National Economy 2Anamika Singh PariharNo ratings yet
- Lifelines of National Economy - YT - 1Document60 pagesLifelines of National Economy - YT - 1Gargi SapteNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Subject-Geography Lifelines of Indian Economy Means of TransportDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Subject-Geography Lifelines of Indian Economy Means of TransportSwapnil MaladkarNo ratings yet
- LifelinesOfNationalEconomy GeographyDocument7 pagesLifelinesOfNationalEconomy Geographymohayaan098No ratings yet
- Lifelines of National Economy - Class Notes - Foundation Mind-MapDocument27 pagesLifelines of National Economy - Class Notes - Foundation Mind-MapYug “Kapoor”No ratings yet
- Lifelines of Indian EconomyDocument11 pagesLifelines of Indian EconomyhhNo ratings yet
- Lifelines of National EconomyDocument5 pagesLifelines of National EconomyMiriam JomonNo ratings yet
- Lifelines of National Economy Class 10 Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 7 (PDF)Document4 pagesLifelines of National Economy Class 10 Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 7 (PDF)shaantanupurabNo ratings yet
- CH - 7 Lifelines of National Economy NotesDocument8 pagesCH - 7 Lifelines of National Economy NotesSoniaNo ratings yet
- Ch-7 Life Lines of National Economy-GEODocument6 pagesCh-7 Life Lines of National Economy-GEOInderpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Geography 02-Dec-2022Document2 pagesWorksheet Geography 02-Dec-2022TECHNIALBGNo ratings yet
- Lifelines of National Economy Class 10 Notes Geography Chapter 7Document6 pagesLifelines of National Economy Class 10 Notes Geography Chapter 7sonamkheriaNo ratings yet
- Lifelines of National Economy (Notes)Document10 pagesLifelines of National Economy (Notes)MAN IFESTONo ratings yet
- Rail and Water Transport in India - 6427323 - 2022 - 08!29!08 - 44Document12 pagesRail and Water Transport in India - 6427323 - 2022 - 08!29!08 - 44Hall of SilenceNo ratings yet
- Lifelines of National EconomyDocument6 pagesLifelines of National EconomyRokdaNo ratings yet
- APznzaZ9LTjrymCB22VYSsosVzNdihUiX2MGJNafR6XaHbSz9QMCWXILKKnBevckr-bA46DkqLy_O68bgD_v7XVveC0Y5AEmZcJp8TkSC_VXXLsPrT8tAlFPfe4G5o4ZKVmmIaGs6UlzTwV4bQIsxRR57qyh0FZVLPVUSTj2QI_SWXy8WU7uottI50gnlo2QSojAg7t19ZfRNbnAxAcAnW7yXFDocument10 pagesAPznzaZ9LTjrymCB22VYSsosVzNdihUiX2MGJNafR6XaHbSz9QMCWXILKKnBevckr-bA46DkqLy_O68bgD_v7XVveC0Y5AEmZcJp8TkSC_VXXLsPrT8tAlFPfe4G5o4ZKVmmIaGs6UlzTwV4bQIsxRR57qyh0FZVLPVUSTj2QI_SWXy8WU7uottI50gnlo2QSojAg7t19ZfRNbnAxAcAnW7yXFmrprathyu13No ratings yet
- C1 G10 S8 Ch7 1 - Txt77 - 5314Document5 pagesC1 G10 S8 Ch7 1 - Txt77 - 5314Pandurang DeoreNo ratings yet
- India Mapping Chapter - 1: Major Ports of India: State Port Other InformationDocument42 pagesIndia Mapping Chapter - 1: Major Ports of India: State Port Other InformationsiddharthinupNo ratings yet
- Geo Mapping. - Chapter-1Document6 pagesGeo Mapping. - Chapter-1AMIL TESAAM SAIKHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Lifelines of National Economy: CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science GeographyDocument4 pagesChapter 7 - Lifelines of National Economy: CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science GeographyManjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Lifelines of National EconomyDocument4 pagesLifelines of National EconomyStudent011No ratings yet
- Important Cities and Ports in India 90Document8 pagesImportant Cities and Ports in India 90Nishant SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Geo Notes Life Lines of Indian EconomyDocument7 pagesCH 7 Geo Notes Life Lines of Indian EconomyPoorvi MathurNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7 Lifelines - of - National - Economy - WatermarkDocument24 pagesChapter - 7 Lifelines - of - National - Economy - WatermarkchingneizoutawtahNo ratings yet
- XII Transport and Communication (Notes)Document14 pagesXII Transport and Communication (Notes)Saurav kumarNo ratings yet
- D32e44d0 3681 11ee 9ac5 7d6785594bef Snghprafulgmail - Com UnlockedDocument54 pagesD32e44d0 3681 11ee 9ac5 7d6785594bef Snghprafulgmail - Com UnlockedsiddharthinupNo ratings yet
- 9th GeoDocument4 pages9th GeoMayank JainNo ratings yet
- Indian Geography FactsDocument56 pagesIndian Geography FactsShambhavi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Major Ports in India: List of Western & Eastern Coast Ports in IndiaDocument3 pagesMajor Ports in India: List of Western & Eastern Coast Ports in Indiaabhishek patialNo ratings yet
- Inland WaterwaysDocument33 pagesInland WaterwaysKavi Raj50% (2)
- The List of Important Ports in India Is Given BelowDocument5 pagesThe List of Important Ports in India Is Given BelowSanskrita VermaNo ratings yet
- CRUX Major and Minor Ports in IndiaDocument12 pagesCRUX Major and Minor Ports in Indiaamit soniNo ratings yet
- Lifelines of National EconomyDocument13 pagesLifelines of National EconomyPriyanka MalikNo ratings yet
- Question and Answer Lifeline of National EconomyDocument7 pagesQuestion and Answer Lifeline of National EconomyIDK SUPERNo ratings yet
- Life Lines of National Economy PDFDocument5 pagesLife Lines of National Economy PDFAlok Yadav57% (7)
- Test 04 - SolutionDocument23 pagesTest 04 - SolutionAlok ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Indian Transport SystemDocument2 pagesIndian Transport SystemHimanshu Sekhar PaulNo ratings yet
- Wel Come To 10 STD Social Science WorldDocument34 pagesWel Come To 10 STD Social Science Worldmithul souravNo ratings yet
- 11 - Saummary Transport & TelecomDocument4 pages11 - Saummary Transport & Telecom6rgsqzrtswNo ratings yet
- Indian Railways-Where The Commuter Is The King!: Ram Chandra AcharyaDocument12 pagesIndian Railways-Where The Commuter Is The King!: Ram Chandra AcharyaPratul BatraNo ratings yet
- Clarify Knowledge: TransportDocument13 pagesClarify Knowledge: TransportIndia CreatorsNo ratings yet
- GMR Kakinada Special Investment Region Overview PresentationDocument11 pagesGMR Kakinada Special Investment Region Overview PresentationkalaiNo ratings yet
- SocialDocument14 pagesSocialshubhved1051221No ratings yet
- Chap 24 TransportDocument5 pagesChap 24 TransportAdnan QureshiNo ratings yet
- 5 Life Lines of National EconomyDocument13 pages5 Life Lines of National EconomyRamjeeNagarajanNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument28 pagesGeographyBA20-042 DambaruNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-05-01 at 5.33.32 PMDocument5 pagesScreenshot 2024-05-01 at 5.33.32 PMmadanmohanagarwal997No ratings yet
- MaritimeDocument3 pagesMaritimeAnonymous GIakHbqNo ratings yet
- Kashmiri Gate IsbtDocument6 pagesKashmiri Gate IsbthuhuhahaheheNo ratings yet
- Geography - Chapter 7 - Lifelines of National Economy - Handwritten Notes - Geography - Chapter 7 - Lifelines of National Economy - Handwritten NotesDocument16 pagesGeography - Chapter 7 - Lifelines of National Economy - Handwritten Notes - Geography - Chapter 7 - Lifelines of National Economy - Handwritten NotesSaket RajNo ratings yet
- Transport Class 10 IcseDocument11 pagesTransport Class 10 Icsemitraaarav08No ratings yet
- Lifelines of National EconomyDocument13 pagesLifelines of National EconomysurajyeleailNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument7 pagesBrochureKjhllsjjNo ratings yet
- Life Lines of Indian Economy - EconomicsDocument4 pagesLife Lines of Indian Economy - EconomicsV A Prem Kumar100% (1)
- Transport Book 2Document38 pagesTransport Book 2Chandu SeekalaNo ratings yet
- The Chin People: A Selective History and Anthropology of the Chin PeopleFrom EverandThe Chin People: A Selective History and Anthropology of the Chin PeopleNo ratings yet
- Mexican Nahuatl HymnsDocument8 pagesMexican Nahuatl HymnsAhmed AnzalduaNo ratings yet
- J.C. PenneyDocument17 pagesJ.C. PenneypratikNo ratings yet
- Practice Set in Inorganic ChemistryDocument3 pagesPractice Set in Inorganic ChemistryKalachuchiNo ratings yet
- Kimono - Fabrics and Decoration TechniquesDocument5 pagesKimono - Fabrics and Decoration TechniquesSaji JimenoNo ratings yet
- Call Transcript q4-Fy-20-TranscriptDocument18 pagesCall Transcript q4-Fy-20-TranscriptAyush JhunjhunwalaNo ratings yet
- How To InstallDocument2 pagesHow To InstallZbamChemicalNo ratings yet
- Task 1&2Document3 pagesTask 1&2mehdi_hoseineeNo ratings yet
- Stanford CS193p Developing Applications For iOS Fall 2013-14Document66 pagesStanford CS193p Developing Applications For iOS Fall 2013-14AbstractSoft100% (1)
- Moby Dick - NotesDocument13 pagesMoby Dick - NotesCismaru ElenaNo ratings yet
- Global Remittance:: SGD (Singapore Dollar) Is An Eligible Currency For Wire Transfers.21Document7 pagesGlobal Remittance:: SGD (Singapore Dollar) Is An Eligible Currency For Wire Transfers.21Susmita JakkinapalliNo ratings yet
- Dan Guerrero's Emails On Steve Alford - Part 2Document479 pagesDan Guerrero's Emails On Steve Alford - Part 2Joe PiechowskiNo ratings yet
- Angie Foell Resume 2015Document2 pagesAngie Foell Resume 2015api-270500986No ratings yet
- Person-Centered Counseling Applied To Stan's CaseDocument2 pagesPerson-Centered Counseling Applied To Stan's CaseREMY JOY CABANNo ratings yet
- LP 1 SS 19Document15 pagesLP 1 SS 19Jomar LomentigarNo ratings yet
- Pan CR FormDocument7 pagesPan CR FormMuthu Kumar RNo ratings yet
- ASEAN CentralityDocument3 pagesASEAN Centralityjt9pkdbj6cNo ratings yet
- EstimationDocument106 pagesEstimationasdasdas asdasdasdsadsasddssa0% (1)
- Analysis of Rainfall Intensity For Southern Nigeria: S.O. Oyegoke, A. S. Adebanjo, E.O. Ajani, and J.T. JegedeDocument12 pagesAnalysis of Rainfall Intensity For Southern Nigeria: S.O. Oyegoke, A. S. Adebanjo, E.O. Ajani, and J.T. JegedeAdebanjo Adeshina SamuelNo ratings yet
- Catholic Ghost Stories of Western PennsylvaniaDocument5 pagesCatholic Ghost Stories of Western PennsylvaniaeclarexeNo ratings yet
- Friction Buffer Stop DesignDocument4 pagesFriction Buffer Stop DesignGphone100% (1)
- KarmaDocument5 pagesKarmaRichelle Palasan50% (4)
- IJSRDV6I30594Document3 pagesIJSRDV6I30594Tanuja B RNo ratings yet
- Mohammed Ismail Borkar CVDocument3 pagesMohammed Ismail Borkar CVgourav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Plural of NounsDocument1 pagePlural of NounsStrafalogea Serban100% (2)
- Benefits of Educational Data MiningDocument5 pagesBenefits of Educational Data MiningShujat Hussain GadiNo ratings yet
- MSDS (E) - CX Af CoolantDocument4 pagesMSDS (E) - CX Af CoolantUnurbat ByambajavNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Quarter 3 Las 3Document4 pagesCookery 10 Quarter 3 Las 3Michole Godwin RegalaNo ratings yet
- 000 SRS Software Feasibility Study TemplateDocument19 pages000 SRS Software Feasibility Study TemplateWeyNo ratings yet
- Gate Induced Drain Leakage For Ultra Thin MOSFET Devices Using SilvacoDocument2 pagesGate Induced Drain Leakage For Ultra Thin MOSFET Devices Using Silvacosiddhant gangwalNo ratings yet
- Dorfman v. UCSD Ruling - California Court of Appeal, Fourth Appellate DivisionDocument20 pagesDorfman v. UCSD Ruling - California Court of Appeal, Fourth Appellate DivisionThe College FixNo ratings yet