Professional Documents
Culture Documents
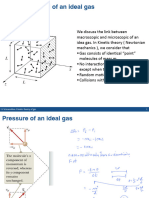
Kinetic Theory of Gases
Kinetic Theory of Gases
Uploaded by
Jawad AzizOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kinetic Theory of Gases
Kinetic Theory of Gases
Uploaded by
Jawad AzizCopyright:
Available Formats
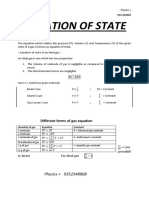
SPEEDS OF GAS MOLECULES SPECIAL RELATIONS RELATION BETWEEN KINETIC DEGREES OF FREEDOM SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY
. Pressure exerted by a gas, ENERGY AND TEMPERATURE
. Specific heat capacity for an ideal gas,
Root Mean square speed: 1 2
P= ρv rms CP − CV = R
. Square root of mean of square 3 3KT 1 . For monoatomic gas, f = 3
. Kinetic Energy = = mv 2rms
of speed of different molecules, 2 2 CP 5
. Relation between pressure . For monoatomic gas, =γ =
v1 + v2 +............... + vn CV 3
vrms =
2 2 2
and Kinetic Energy. Kinetic Energy of gas molecule.
. For diatomic gas,
n 3 1 3RT CP γ 7
E= PV . K.E = mv rms =
2
(a) at room temperature, f = 5 . For diatomic gas, = =
3RT 3P 2 2 2 CV 5
vrms = = ρ (b) at high temperature, f = 7
M Kinetic energy of one mole of gas molecule. CP γ 4 + f
. For polyatomic gas, = =
Average Speed: 1 = 3RT CV 3+f
Most probable speed:
. K.E = mvrms
2
. Arithmatic mean of speed of 2 2m . For polyatomic gas, and f is degrees of freedom.
molecules of gas at given . Speed possessed by maximum Kinetic energy of one gram of gas molecule.
temperature. number of molecules of gas. (a) at room temperature , f = 6 . CP = (1 + f ) R , C = f R
(b) at high temperature, f = 8, f degree of 2 V
2
vavg = I v1 I + I v2 I + ....... + I vnI
n vmp = 2RT = 2P
ρ
freedom. Cp 2
Mo . γ = = 1+
CV f
vavg = 8RT = 8P
πM πρ
MEAN FREE PATH
Average distance travelled by
ASSUMPTIONS IN KINETIC IDEAL GAS LAWs molecules between two
THEORY OF GASES successive collision
1
Gas consists of small . Pressure, Temperature and λ mean =
particles known as Molecules. volume of Gas are related to 2 πd2n
each other by following
Molecules of Gas are equation, PV = nRT. d = diameter of molecules.
identical rigid sphere and n = no. of molecules per
elastic points mass. . P – pressure, V – volume, n – no. unit volume
of moles , R = Universal Gas
Molecules of Gas moves Constant = 8.314 J/mol.k ,
randomly in al directions T – Temperature.
with possible velocity.
m n
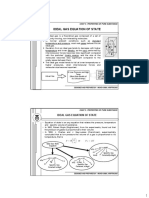
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
. PV = RT ; PV = nA
KT DALTON’S LAW OF PARTIAL
mA
PRESSURE
Boyle’s Law Charle’s Law Gay lussac’s law LAW OF EQUIPARTITION OF ENERGY
. The total Kinetic energy of a gas molecule
is equally distributed among it’s all degrees
P PV V V/T of freedom.
P P/T
f
U = k BT
V V
T V
2
T P
f = degrees of freedom.
. For Fixed mass, pressure of gas . For a Fixed mass, volume of gas . For a fixed mass, pressure of a
is inversely proportional to is directly proportional to gas is directly proportional to kB = Boltzmann Constant. Total pressure of a mixture of non –
volume. temperature. its temperature. reacting gas is equal to summation of
3 pressure of individual Gasses.
. PV = constant, if T = Cosntant P . For monoatomic gas, U= k BT
. V α T; v = constant; P = constant. . P α T; = constant; V = constant. 2
T T
. P1V1 = P2V2 ,When gas changes it’s P = P1 + P2 + P3 +………+ Pn
. v 1 = v 2 ,When gas change its state P1 P2 5
state under constant
T1 T2 under constant pressure.
. = ,When gas change its state
. For diatomic gas, U= k BT
temperature. T1 T2 under constant Volume. 2
anand_mani16 DR. Anand Mani https://www.anandmani.com/ https://discord.io/anandmani t.me/anandmani001
You might also like
- Steven Weinberg - Foundations of Modern Physics-Cambridge University Press (2021)Document325 pagesSteven Weinberg - Foundations of Modern Physics-Cambridge University Press (2021)puceiroale100% (14)
- Principles of Gas-Solid Flows-Fan, Zhu PDFDocument575 pagesPrinciples of Gas-Solid Flows-Fan, Zhu PDFcankushbjk100% (1)
- Solutions Manual For Mechanics and ThermodynamicsDocument112 pagesSolutions Manual For Mechanics and ThermodynamicsPaduraru Giani83% (24)
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument20 pagesKinetic Molecular TheorySumera SarwarNo ratings yet
- 11 DP Physics - Topic 3 Thermal Physics ProgramDocument7 pages11 DP Physics - Topic 3 Thermal Physics ProgrampixelhoboNo ratings yet
- KTG & ThermodynamicsDocument20 pagesKTG & ThermodynamicsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Kinetic TheoryDocument21 pagesKinetic TheoryDebayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- KTG and Thermo (Bansal)Document20 pagesKTG and Thermo (Bansal)RoNNo ratings yet
- XII H - 03 Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation - 64d6447ca0283Document17 pagesXII H - 03 Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation - 64d6447ca0283leogg2765No ratings yet
- 10 May 2022 PhysicsDocument14 pages10 May 2022 PhysicsSandeep PlaysNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument7 pagesKinetic Theory of GasesAnsh Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Assignment_Therodynamics_and_KTG_Physics_Yakeen_2_0_2024_MR_SirDocument3 pagesAssignment_Therodynamics_and_KTG_Physics_Yakeen_2_0_2024_MR_Sirkunjankhanal987No ratings yet
- Opportunities For A Liquid Rocket Feed System Based On Electric PumpsDocument7 pagesOpportunities For A Liquid Rocket Feed System Based On Electric PumpsdiegolenNo ratings yet
- 6582e741d388fa0018c74962_##_Kinetic Theory of Gases Mind MapsDocument1 page6582e741d388fa0018c74962_##_Kinetic Theory of Gases Mind Mapsn9134152No ratings yet
- HeatDocument2 pagesHeatAdeel MajeedNo ratings yet
- Low Pressure Effusion of GasesDocument10 pagesLow Pressure Effusion of Gasesglen-576661No ratings yet
- Physics: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Document15 pagesPhysics: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Ayush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Apznza 1Document7 pagesApznza 1kshitijchavan1018No ratings yet
- KTG SolutionDocument8 pagesKTG SolutionDeb PradhanNo ratings yet
- Final Phat 2304103 5 KineticTheoryOfGasEx 2566Document28 pagesFinal Phat 2304103 5 KineticTheoryOfGasEx 2566buzologyNo ratings yet
- Ebook Article CP-CV Ratio For Air-Experimental ValuesDocument3 pagesEbook Article CP-CV Ratio For Air-Experimental Valuesgiovannimazza21120No ratings yet
- Formulario Fluidodinamica-3Document13 pagesFormulario Fluidodinamica-3Dario NeNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics - IDocument56 pagesThermal Physics - Ibhawanar3950No ratings yet
- 10th Chapter Copy Converted 2Document21 pages10th Chapter Copy Converted 2SM Abdullah Al KabidNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Complete Outlines 2017Document20 pagesPhysical Chemistry Complete Outlines 2017Aicha DahmaniNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument8 pagesKinetic Theory of Gasesmr_anilpawarNo ratings yet
- 2.gaseous State PDFDocument13 pages2.gaseous State PDFP. E. I. AcademicsNo ratings yet
- Real Gas vs. Ideal Gas - Tan Chun WeiDocument5 pagesReal Gas vs. Ideal Gas - Tan Chun WeiConradodaMattaNo ratings yet
- Magneto HydrodynamicDocument10 pagesMagneto HydrodynamicMoney CapNo ratings yet
- WS28 Gas Law (III)Document4 pagesWS28 Gas Law (III)hiu nok kwanNo ratings yet
- Kinetic TheoryDocument2 pagesKinetic TheoryWong Chun LamNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Kinetic Theory of Gases: AssumptionDocument6 pages9.1 Kinetic Theory of Gases: AssumptionRishi GuptaNo ratings yet
- 659521892a385f001876d5c5 - ## - Kinetic Theory of Gases Short NotesDocument1 page659521892a385f001876d5c5 - ## - Kinetic Theory of Gases Short Notesjnvsahilb9No ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument6 pagesKinetic Theory of GasesAyushNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Equation of StateDocument18 pagesIdeal Gas Equation of StateOssama BohamdNo ratings yet
- Important Question: N N N N K SDocument5 pagesImportant Question: N N N N K SPUNEET SHARMANo ratings yet
- 12 Heat Part2 Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument8 pages12 Heat Part2 Formula Sheets Getmarks AppSubir Nath BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics 2015 Lecture 3Document53 pagesThermal Physics 2015 Lecture 3Swee Boon OngNo ratings yet
- West Bengal State University: Hemistry OnoursDocument4 pagesWest Bengal State University: Hemistry OnoursSwwwwwNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument6 pagesKinetic Theory of GasesSasidaran SasiNo ratings yet
- Degree of Freedom PDFDocument13 pagesDegree of Freedom PDFAnasNo ratings yet
- Course 1 Laboratory: Second Semester Experiment: Specific Heats RatioDocument6 pagesCourse 1 Laboratory: Second Semester Experiment: Specific Heats RatioTariq MograbiNo ratings yet
- 360equipartition PDFDocument2 pages360equipartition PDFkurakidNo ratings yet
- 360 Equi PartitionDocument2 pages360 Equi PartitionMeisy RadhistaNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES Updated1Document29 pagesENGINEERING PRINCIPLES Updated1Albert LappiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 431 Problem Set 9 Fall 2018Document3 pagesChemistry 431 Problem Set 9 Fall 2018Al StudentNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Astronomy 1 - Paper 1 and Stars & PlanetsDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet For Astronomy 1 - Paper 1 and Stars & PlanetsprashinNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument8 pagesKinetic Theory of GasesAditya SallyNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws and Kinetic TheoryDocument14 pagesGas Laws and Kinetic Theorybrianouko25No ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument37 pagesThermodynamicsAyushmaan DhanaiNo ratings yet
- Cata Surface Sheet 4Document8 pagesCata Surface Sheet 4Youssef AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 13 Kinetic TheoryDocument20 pagesChapter - 13 Kinetic TheorySiddharth Singh JadonNo ratings yet
- 2.3 GasDocument31 pages2.3 Gashamza alqadasiNo ratings yet
- Combustion and ThermochemistryDocument21 pagesCombustion and ThermochemistryMukul ChandraNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2022 Kinetic Theory of Gases Study Notes PDF DownloadDocument5 pagesJEE Main 2022 Kinetic Theory of Gases Study Notes PDF DownloadarvindmanusharmaNo ratings yet
- Equation of StateDocument7 pagesEquation of StateJack SparrowNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.3Document45 pagesLecture 1.3mido AANo ratings yet
- State of Matter Gases and Liquids - Short Notes - Arjuna NEET 2024Document2 pagesState of Matter Gases and Liquids - Short Notes - Arjuna NEET 2024shraddha2572sharmaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Transport Phenomena Module 9 Lecture 39: Students Exercises: Numerical Questions (Modules 1-5)Document19 pagesAdvanced Transport Phenomena Module 9 Lecture 39: Students Exercises: Numerical Questions (Modules 1-5)shashwatNo ratings yet
- 2022 YIJC Prelims H2Phy 9749 03Document24 pages2022 YIJC Prelims H2Phy 9749 03RanNo ratings yet
- Week/day 3: Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument57 pagesWeek/day 3: Properties of Pure Substancesronni bermudezNo ratings yet
- 2.1.3 Ideal Rocket Theory Part 1Document13 pages2.1.3 Ideal Rocket Theory Part 1paulo gontranNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasDocument4 pagesKinetic Theory of GasTawhidul AlamNo ratings yet
- Energy (The Ability To Do Work) That Accompany Those Transformations. The Potential For TheDocument6 pagesEnergy (The Ability To Do Work) That Accompany Those Transformations. The Potential For TheMeisy RadhistaNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Jee Physics SyllabusDocument11 pagesJee Physics SyllabusAkshit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chem Chapter05 LECDocument112 pagesChem Chapter05 LECsaxman011No ratings yet
- 6 Gases PDFDocument70 pages6 Gases PDFRogerine RoyNo ratings yet
- Course Objective QuestionDocument243 pagesCourse Objective Questionahmish kabbaxeNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Model of Gases: Section 1.3 of Atkins, 6th Ed. Section 24.1 of Atkins, 7th Ed. Section 21.1 of Atkins, 8th EdDocument18 pagesKinetic Model of Gases: Section 1.3 of Atkins, 6th Ed. Section 24.1 of Atkins, 7th Ed. Section 21.1 of Atkins, 8th EdJerome JavierNo ratings yet
- Mesh DiscretIzationDocument45 pagesMesh DiscretIzationdfcortesvNo ratings yet
- Factors That Affect Gas PressureDocument5 pagesFactors That Affect Gas PressureYing FlaviaNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument91 pagesThe Kinetic Theory of GasesEbony Edwards100% (1)
- CH05Document146 pagesCH05GYun Pyo BofNo ratings yet
- Pravindra Singh PWSFAC75824 20225511125526807058Document228 pagesPravindra Singh PWSFAC75824 20225511125526807058jkNo ratings yet
- Problem CozumleriDocument252 pagesProblem CozumleriSadman IshrakNo ratings yet
- Simak Ui KkiDocument17 pagesSimak Ui Kkigerry_liyanaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Document11 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Gases NotesDocument4 pagesPhysical Chemistry Gases NotesMartin AlvinNo ratings yet
- Ebook Chemistry The Central Science 12Th Edition Brown Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument60 pagesEbook Chemistry The Central Science 12Th Edition Brown Test Bank Full Chapter PDFformatbalanoidyxl100% (13)
- SCIENCE WORKSHEET For GRADE 10 Fourth Quarter (WEEK 2)Document3 pagesSCIENCE WORKSHEET For GRADE 10 Fourth Quarter (WEEK 2)Sitti Rohima MarajanNo ratings yet
- QSP Chapter5 Kinetic TheoryDocument17 pagesQSP Chapter5 Kinetic Theorynarasimha raoNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 10: Quarter 4 - Behavior of GasesDocument15 pagesScience Grade 10: Quarter 4 - Behavior of GasesalindongaprilmaeNo ratings yet
- Tyagi 2009Document16 pagesTyagi 2009ianNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument33 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaWiwik AnjajariNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 4 Module 1.3Document4 pagesScience Quarter 4 Module 1.3Christian AlbosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Three States of MatterDocument16 pagesChapter 2: Three States of MatterNaveed Khan SheraniNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Basics: Kinetic Theory of GasDocument19 pagesVacuum Basics: Kinetic Theory of GasFederico LeonNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Electron Theory of MetalsDocument9 pages5.2 Electron Theory of MetalsSrî HárshàNo ratings yet
- Sample IB Questions ThermalDocument8 pagesSample IB Questions ThermalEthan KangNo ratings yet