Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lamellar Settler: © Toro Equipment 2009
Lamellar Settler: © Toro Equipment 2009
Uploaded by
Douglas TondelloOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lamellar Settler: © Toro Equipment 2009
Lamellar Settler: © Toro Equipment 2009
Uploaded by
Douglas TondelloCopyright:
Available Formats
LAMELLAR SETTLER
The function of the lamellar settler is to remove
suspended semi-heavy and heavy particles (grit, clay and
lime) from the water. These elements hinder subsequent
treatment by producing deposits in hydraulic conduits,
piping and channels and causing abrasion to pump
impellers and equipment etc.
Lamellar settlers are designed for the continuous
separation of sediments from water and they have two
basic purposes: to increase the settling area and to
obtain a laminar flow.
The concept of the lamellar settler is based on the fact
3 2
that the surface load (m /m /day) of a freefall settling tank
does not depend on its depth. It is therefore possible to
increase the capacity of a settling tank by dividing it,
thereby creating a number of “settling tanks”, or by using
plates inclined at a certain angle.
© Toro Equipment 2009 1
LAMELLAR SETTLER
DESCRIPTION OF THE EQUIPMENT
The lamellar settler is an open rectangular GRP tank
divided into three main chambers:
• Inlet chamber.
The influent flows directly into this chamber
before going to the settling stage.
• Settling chamber.
The lamellar packs, made up of several GRP
plates, are located in the settling chamber. The
packs are arranged in parallel with an inclination
angle of 60º to enable a larger settling area for
the decantation of suspended solids.
• Outlet chamber.
The clean and clarified water is sent to this
chamber for direct evacuation.
© Toro Equipment 2009 2
LAMELLAR SETTLER
DESCRIPTION OF PROCESS
The influent is fed through a connection pipe to the
settling chamber. Slots in the pipes located on the lower
part of the lamellae allow uniform feeding of the liquid to
the lamellar packs.
As the inflow passes between the plates, the solid
particles slide along the inclines of the lamellae towards
the bottom of the tank, while the clean water rises to the
surface of the settler.
The lamellar system means that the distance travelled
by a particle before settling is less than in a conventional
settling tank, thereby increasing clarification capacity. A
pneumatic valve at the bottom of the tank enables the
settled solids to be discharged in accordance with needs.
The clean clarified water in the upper part of the settling
tank falls to a collection weir located along the length of the
settling chamber. From this weir, it goes to the outlet
chamber to be evacuated by means of a pipeline.
© Toro Equipment 2009 3
LAMELLAR SETTLER
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Model DCL-2 DCL-5 DCL-10 DCL-15 DCL-20 DCL-40
N ominal flow rate (m3 /h) 2 5 10 15 20 40
Dimensions
Maximum width A (mm) 795 1,885 1,805 1,885 1,845 2,546
Maximum height B (mm) 1,3 2,525 2,525 2,525 2,525 2,525
Length L (mm) 2,12 2,33 3,36 4,67 5,9 7,2
R equired space (m) 3.5×2 3.7×3 4.7×3 6×3 7×3 8.5×4
Material G.R.P. G.R.P. G.R.P. G.R.P. G.R.P. G.R.P.
Rising velocity Vs (m/h) 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8
APPLICATIONS
The lamellar settler has applications in industries using materials that can be easily decanted and in potabilisation processes.
• Potabilisation plants.
• Water reuse.
• Mining industry.
• Construction materials industry.
• Industrial applications.
© Toro Equipment 2009 4
LAMELLAR SETTLER
You might also like
- Coiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!From EverandCoiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Trident 2 PowerscreenDocument9 pagesTrident 2 PowerscreenRomuald PogorzelczykNo ratings yet
- Cabletorq Thickeners/Clarifiers: Gl&V/Dorr-Oliver100Ft - Dia.Type"S"CabletorqthickenerDocument4 pagesCabletorq Thickeners/Clarifiers: Gl&V/Dorr-Oliver100Ft - Dia.Type"S"Cabletorqthickenerdgomez686No ratings yet
- (KENR8398-01) Schematic - 793F OHT Hydraulic SystemDocument2 pages(KENR8398-01) Schematic - 793F OHT Hydraulic SystemGabriel YucraNo ratings yet
- Tube Settler Leaflet Rev 2Document6 pagesTube Settler Leaflet Rev 2Rabindra SinghNo ratings yet
- Catalogues Au MyDocument28 pagesCatalogues Au MyChu Hữu LạcNo ratings yet
- Luis MagneDocument19 pagesLuis Magnerichard gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Tsurumi Options: Submersible Sewage PumpsDocument5 pagesTsurumi Options: Submersible Sewage PumpsTài AnhNo ratings yet
- MSF 618-619 591Document4 pagesMSF 618-619 591Barak VinklerNo ratings yet
- VIN027 Draincoil Product CatalogueDocument16 pagesVIN027 Draincoil Product CatalogueZhenhe SongNo ratings yet
- S7 14 - 20 Douglas Teyhan - REVDocument21 pagesS7 14 - 20 Douglas Teyhan - REVCesar Rodriguez GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Practice 2020 04Document7 pagesEngineering Practice 2020 04Chenchulakshmi MNo ratings yet
- Engineering Practice 2020 04Document35 pagesEngineering Practice 2020 04AUDIO CLIPS BLOGNo ratings yet
- WWTP Chap 5 (p28-41) - Mech PurificationDocument14 pagesWWTP Chap 5 (p28-41) - Mech PurificationKaustav PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Sepro Equipment BrochuresDocument26 pagesSepro Equipment BrochuresIvan Zurita100% (1)
- 36 PRCCC1 IDocument2 pages36 PRCCC1 IKashif MasudNo ratings yet
- Hydrocyclone Design For Large Sag Mill CircuitsDocument12 pagesHydrocyclone Design For Large Sag Mill CircuitsFrancisco CampbellNo ratings yet
- Cement Dump BailerDocument2 pagesCement Dump BailerWahiba EnergyNo ratings yet
- Krebs - GMax BrochureDocument8 pagesKrebs - GMax BrochurejadetorresNo ratings yet
- Design, Installation and Testing of The No 250 Wemco Smartcell™ Flotation Machine at Minera Los Pelambres A Weber, L Macnamara, H SchreiberDocument17 pagesDesign, Installation and Testing of The No 250 Wemco Smartcell™ Flotation Machine at Minera Los Pelambres A Weber, L Macnamara, H SchreiberOvidio Jaime CruzNo ratings yet
- O-Max Septic TankDocument8 pagesO-Max Septic TankTeknik produksi wikonNo ratings yet
- Applicational Design and Sizing of Decanter Centrifuges - American ...Document10 pagesApplicational Design and Sizing of Decanter Centrifuges - American ...Thang VuNo ratings yet
- BCE - H2SO4 Tower InternalsDocument3 pagesBCE - H2SO4 Tower InternalsDũng LêNo ratings yet
- Ind TRRNGDocument60 pagesInd TRRNGShankar AchallaNo ratings yet
- MS-2003-Recent Advances in Temper and Skin-Pass RollingDocument8 pagesMS-2003-Recent Advances in Temper and Skin-Pass Rollingsurajit7guptaNo ratings yet
- 4082WWT Grit RemovalDocument21 pages4082WWT Grit Removalahmedmagdi2009No ratings yet
- Swell Packer Case HistoriesDocument32 pagesSwell Packer Case Historiesapi-16218084No ratings yet
- BRANDT COBRA and KING COBRA Mud Conditioners Spec SheetDocument2 pagesBRANDT COBRA and KING COBRA Mud Conditioners Spec Sheetjimmy__428No ratings yet
- D Silter SwacoDocument4 pagesD Silter SwacoJuan Sebastian Diaz CuadrosNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Conversión de GasesDocument2 pagesTabla de Conversión de GasesGiulianno Alv MayNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Lab Manual 2016-17Document37 pagesReservoir Lab Manual 2016-17Amit Verma100% (1)
- D-Sander SwacoDocument5 pagesD-Sander SwacoJuan Sebastian Diaz CuadrosNo ratings yet
- DeltaStak BrochureDocument8 pagesDeltaStak Brochurerichard gutierrezNo ratings yet
- 06c Mudsystems 100513092031 Phpapp01Document18 pages06c Mudsystems 100513092031 Phpapp01FabianBauerNo ratings yet
- Ote Floodaf Microflotation System enDocument2 pagesOte Floodaf Microflotation System enENNYMRNo ratings yet
- G.A.N.G.F.O.R.M: Enunciation of A ProposalDocument18 pagesG.A.N.G.F.O.R.M: Enunciation of A ProposalVietpapayaNo ratings yet
- Coal Benefication PDFDocument22 pagesCoal Benefication PDFAnonymous W1uxdlRPHMNo ratings yet
- SedimentationDocument51 pagesSedimentationdstar13No ratings yet
- Cyclonic Desander: Sand and Solids Handling For All ApplicationsDocument2 pagesCyclonic Desander: Sand and Solids Handling For All Applicationsgacm98No ratings yet
- Drain CoilDocument12 pagesDrain CoilBerlinNo ratings yet
- Chemsorb Fitler GranulesDocument4 pagesChemsorb Fitler GranulesJeffersonNo ratings yet
- HDPE Geomembrane - AlvatechDocument10 pagesHDPE Geomembrane - AlvatechshgsuhermanNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Treatment Process of Waste WaDocument9 pagesPreliminary Treatment Process of Waste WaArjun MulluNo ratings yet
- Mill Lines by FlSmidthDocument4 pagesMill Lines by FlSmidthIrving Dirzo CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Above Ground Brochure EnglishDocument6 pagesCorrosion Above Ground Brochure EnglishsyammohansNo ratings yet
- Filtro de Gas - MUELLERDocument2 pagesFiltro de Gas - MUELLERCarlos BaezaNo ratings yet
- SpecificationDocument2 pagesSpecificationToxic ToucanNo ratings yet
- Decanter CentrifugeDocument10 pagesDecanter Centrifugewgao201067% (3)
- Sam McCoy MFG - Catalogue 2004 - 2Document29 pagesSam McCoy MFG - Catalogue 2004 - 2Sam McCoy ManufacturingNo ratings yet
- Hydrogenation Reactor DesignDocument10 pagesHydrogenation Reactor DesignasdfNo ratings yet
- SATAM-zc17-12 24 48 80 150 250 330Document2 pagesSATAM-zc17-12 24 48 80 150 250 330Mr. AlferditomaNo ratings yet
- 7 Prelim Unite Operations HTTP WWW - Eng.uottawa - Ca Profs Kennedy CHG4302Document12 pages7 Prelim Unite Operations HTTP WWW - Eng.uottawa - Ca Profs Kennedy CHG4302Dr Carlos Estrada VázquezNo ratings yet
- 75 KLD MBBR STP Offer For Residential SocietyDocument11 pages75 KLD MBBR STP Offer For Residential SocietyrepublicfoodsindiaNo ratings yet
- Gravitational SedimentationDocument75 pagesGravitational SedimentationAlexNo ratings yet
- 2022 11 21 Ai 1Document4 pages2022 11 21 Ai 1Romnick PascuaNo ratings yet
- Atk Microtunnelling Presentation R1Document29 pagesAtk Microtunnelling Presentation R1Gaurav MathurNo ratings yet
- Drilling Parameter Analysis in Solving Pipe Sticking in A Total Loss Circulation Zone Case Study: Well "X" and Well "Y" Geothermal Well Ulubelu FieldDocument21 pagesDrilling Parameter Analysis in Solving Pipe Sticking in A Total Loss Circulation Zone Case Study: Well "X" and Well "Y" Geothermal Well Ulubelu FieldJeva VienaNo ratings yet
- DtEC Mist Eliminators Brochure 140709Document4 pagesDtEC Mist Eliminators Brochure 140709a0aryanNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For Design of Slurry Flow DistributionsDocument11 pagesBest Practices For Design of Slurry Flow Distributionsfelipe muñozNo ratings yet
- Sewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionFrom EverandSewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshFrom EverandPneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshNo ratings yet
- Continuous Disc Dryer: Use and FunctionDocument4 pagesContinuous Disc Dryer: Use and FunctionDouglas TondelloNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Drying On DDGS Protein QualityDocument31 pagesThe Effects of Drying On DDGS Protein QualityDouglas TondelloNo ratings yet
- Dryhouse Technologies and DDGS Production: January 2009Document21 pagesDryhouse Technologies and DDGS Production: January 2009Douglas TondelloNo ratings yet
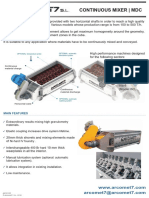
- MEZCLADORA CONTINUA Ingles PDFDocument2 pagesMEZCLADORA CONTINUA Ingles PDFDouglas TondelloNo ratings yet
- FE2-FFE Distributor - 2016.11.30 - Ver2Document33 pagesFE2-FFE Distributor - 2016.11.30 - Ver2Douglas TondelloNo ratings yet
- United States PatentDocument7 pagesUnited States PatentDouglas TondelloNo ratings yet
- Runxin - Valvula Automatica Abrandador F74a3Document49 pagesRunxin - Valvula Automatica Abrandador F74a3Douglas Tondello100% (1)
- VT TubeBundleDryer PDFDocument2 pagesVT TubeBundleDryer PDFDouglas TondelloNo ratings yet
- Discor: Rotary Disc Cooker/DryerDocument2 pagesDiscor: Rotary Disc Cooker/DryerDouglas TondelloNo ratings yet
- ISJ 2014 BMA-Evaporator 02Document6 pagesISJ 2014 BMA-Evaporator 02Douglas TondelloNo ratings yet
- Pennant Purgadores PDFDocument101 pagesPennant Purgadores PDFDouglas TondelloNo ratings yet
- Especificação de GraxasDocument1 pageEspecificação de GraxasDouglas TondelloNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Purgador PT65-40Document2 pagesData Sheet Purgador PT65-40Douglas Tondello100% (1)
- Hongo 1994Document4 pagesHongo 1994rich0501No ratings yet
- Casing Desain PengeboranDocument52 pagesCasing Desain PengeboranDhenny Adriana Rachman100% (1)
- Applied Thermodynamics 5Document206 pagesApplied Thermodynamics 5Neil BotesNo ratings yet
- Base Ring and SkirtDocument8 pagesBase Ring and Skirtduazo2009No ratings yet
- Convection and Radiation Heat TransferDocument14 pagesConvection and Radiation Heat TransferSalman ShalwaniNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Store Separation Characteristics From Aircraft Using Aerodynamic TechnologyDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Store Separation Characteristics From Aircraft Using Aerodynamic Technologyflateric74@yandex.ruNo ratings yet
- KLM - Fluid Flow Measurement Selection and SizingDocument16 pagesKLM - Fluid Flow Measurement Selection and SizingShakeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- "Artificial Lift Technology": Course / Project DescriptionDocument1 page"Artificial Lift Technology": Course / Project DescriptionNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- The Puck Theory of Failure in Laminates in The Context of The New Guideline VDI 2014 Part 3Document12 pagesThe Puck Theory of Failure in Laminates in The Context of The New Guideline VDI 2014 Part 3fabukeNo ratings yet
- Converting Primary/Secondary Chilled Water Systems To All Variable FlowDocument4 pagesConverting Primary/Secondary Chilled Water Systems To All Variable FlowPradeep SukumaranNo ratings yet
- STP 415-1967Document551 pagesSTP 415-1967Tim Schouw50% (2)
- Custody Transfer Temperature Measurement API MPMS Ch. 7Document27 pagesCustody Transfer Temperature Measurement API MPMS Ch. 7tanathos18100% (1)
- Thesis ExampleDocument407 pagesThesis ExampleJigar Kishor Joshi100% (1)
- Flow Measurement GuidelinesDocument27 pagesFlow Measurement GuidelinesAkram DriraNo ratings yet
- Silo-O - Slope Stability Analysis Report Rev B - TO REVIEWDocument13 pagesSilo-O - Slope Stability Analysis Report Rev B - TO REVIEWJulian SandovalNo ratings yet
- Vaporizacao Da GlicerinaDocument1 pageVaporizacao Da GlicerinaCharlesDayanNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy Prac Prob 204qiudDocument5 pagesWork and Energy Prac Prob 204qiudsaparullahNo ratings yet
- So Do Thuy Luc 345C PDFDocument2 pagesSo Do Thuy Luc 345C PDFdoxuanquylcNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow Notes - BasicDocument9 pagesPipe Flow Notes - BasicMwine Isaac NormanNo ratings yet
- Another Lecture Found On The Internet!: Elastic Properties of SolidsDocument31 pagesAnother Lecture Found On The Internet!: Elastic Properties of SolidsLight HouseNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Mariam El GharibDocument19 pagesThermodynamics: Mariam El GharibAbo Alphotoh GamingNo ratings yet
- HydraulicskoDocument12 pagesHydraulicskoJestan MagatNo ratings yet
- BoiloffDocument8 pagesBoiloffJetul PatelNo ratings yet
- Domestic Electrolux Refrigeration SystemDocument22 pagesDomestic Electrolux Refrigeration SystemTanviNo ratings yet
- Algorithm For Isothermal Reactor Design-EjemplosDocument17 pagesAlgorithm For Isothermal Reactor Design-EjemplosEduardo CruzNo ratings yet
- Mcq-Engineering - Blogspot.in-Strength of Materials Torsion of Shafts2Document2 pagesMcq-Engineering - Blogspot.in-Strength of Materials Torsion of Shafts2sirsa11No ratings yet
- Boiler Efficiency Improvement and EnergyDocument6 pagesBoiler Efficiency Improvement and EnergyBerkefedeNo ratings yet
- Bda 31003Document4 pagesBda 31003Nadia BalqisNo ratings yet
- Sample Data Sheet For Pressure Safety Valve As Per API 597Document16 pagesSample Data Sheet For Pressure Safety Valve As Per API 597Yurizki LhzNo ratings yet