Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Offsetting On CNC Milling Machine
Offsetting On CNC Milling Machine
Uploaded by
khayam khanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Echobox Mock Sales Call 1Document1 pageEchobox Mock Sales Call 1Maria LivaniouNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introduction of CNC Turning MachineDocument9 pages1.0 Introduction of CNC Turning Machineeizhar50% (4)
- SAP Fiori Analytical Apps For Sales (1BS) : Test Script SAP S/4HANA - 28-08-18Document29 pagesSAP Fiori Analytical Apps For Sales (1BS) : Test Script SAP S/4HANA - 28-08-18MihaiNo ratings yet
- Dharwar Drilling Society: Case Analysis ReportDocument8 pagesDharwar Drilling Society: Case Analysis Reportchelsea1989No ratings yet
- Ir Advance c5255/5250/5240/5235 SeriesDocument222 pagesIr Advance c5255/5250/5240/5235 Series-TT-0% (1)
- Assignment of Software Test PlanDocument15 pagesAssignment of Software Test Plankafeel afridi100% (1)
- Experiment No 6Document11 pagesExperiment No 6harisraja47985No ratings yet
- CAM-CIM Manual - M.tech - Jan 2022Document46 pagesCAM-CIM Manual - M.tech - Jan 2022KUNAL SHIMPINo ratings yet
- CNC Machine Tool OffsetsDocument1 pageCNC Machine Tool OffsetsAllan HarrisNo ratings yet
- TE415 Machine Tool Probe CalibrationDocument6 pagesTE415 Machine Tool Probe CalibrationLjubo ObleščakNo ratings yet
- Cad, CamDocument16 pagesCad, CamRakhi Mol BVNo ratings yet
- Location Dependency of Positioning Error in A 3-Axes CNC Milling MachineDocument6 pagesLocation Dependency of Positioning Error in A 3-Axes CNC Milling MachineIrfan RfcNo ratings yet
- Heidenhain Touch ProbeDocument72 pagesHeidenhain Touch ProbeHoho Hahov100% (1)
- CNC Part ProgrammingDocument40 pagesCNC Part ProgrammingmsshahenterNo ratings yet
- CNC Part ProgrammingDocument53 pagesCNC Part ProgrammingmsshahenterNo ratings yet
- NC & CNC MachinesDocument12 pagesNC & CNC MachinesRenjith Rajendraprasad100% (1)
- Lab Manual CNC LatheDocument10 pagesLab Manual CNC LatheSai Naga Sri Harsha100% (1)
- Unit 3Document17 pagesUnit 3rufeenaNo ratings yet
- CNC PresentationDocument37 pagesCNC PresentationMarvin BelenNo ratings yet
- G and M Coding Lab 03Document24 pagesG and M Coding Lab 03Mohsin Qazi100% (1)
- Cnccuttingtools 140314063757 Phpapp01Document26 pagesCnccuttingtools 140314063757 Phpapp01Taha BardanwalaNo ratings yet
- Lab No 9Document4 pagesLab No 9khayam khanNo ratings yet
- Study of CNC MachinesDocument53 pagesStudy of CNC MachinesPreethi VadivelNo ratings yet
- Typical CNC Machining Centre: Horizontal Axis Milling Vertical Axis MillingDocument82 pagesTypical CNC Machining Centre: Horizontal Axis Milling Vertical Axis MillingAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Title Objective: Figure 1: Hitachi Seiki Hitec-Turn20SiiDocument11 pagesTitle Objective: Figure 1: Hitachi Seiki Hitec-Turn20SiiSilang KataNo ratings yet
- Ipe 509 Presentation DraftDocument10 pagesIpe 509 Presentation Draftalozie alexanderNo ratings yet
- Cad/Cam: NC, CNC, DNC TechnologiesDocument37 pagesCad/Cam: NC, CNC, DNC TechnologiesVijay ShakarNo ratings yet
- Report 1 (Jack)Document9 pagesReport 1 (Jack)Mark SelvanNo ratings yet
- Week 7+8 Lect 5 - CNCDocument18 pagesWeek 7+8 Lect 5 - CNCmuhammadarshadnaveed346No ratings yet
- Metal Removal Rate (MRR) Tool Wear Rate (TWR)Document2 pagesMetal Removal Rate (MRR) Tool Wear Rate (TWR)Chethan K NarayanNo ratings yet
- CNC Machines: By: Mohammed YousifDocument37 pagesCNC Machines: By: Mohammed Yousifمحمد عبد الرحيمNo ratings yet
- Cncpresentation PDFDocument37 pagesCncpresentation PDFCorey YoungNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document14 pagesCH 3abdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Fast, Accurate Contour Milling With High Surface Defi NitionDocument6 pagesFast, Accurate Contour Milling With High Surface Defi NitionRadoslaw JoczNo ratings yet
- CNC TitanDocument58 pagesCNC TitanGV Ragunathan100% (1)
- MT Ii Unit VDocument73 pagesMT Ii Unit VRavigggNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Manufacturing Part 1Document76 pagesComputer Aided Manufacturing Part 1lelisadiriba849No ratings yet
- 9.pmat M-01Document94 pages9.pmat M-01mailtome126100% (1)
- CAMpres AashishDocument31 pagesCAMpres AashishAshishJoshiNo ratings yet
- Response Surface Methodology in CNC Turning-A ReviewDocument12 pagesResponse Surface Methodology in CNC Turning-A Reviewjaniesh bhartiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CNC MachiningDocument36 pagesIntroduction To CNC MachiningNavya VelagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - 2Document7 pagesChapter 3 - 2viet vuNo ratings yet
- Unit - 7: CNC Machining Centers: Numerical ControlDocument56 pagesUnit - 7: CNC Machining Centers: Numerical ControlnenadNo ratings yet
- G J U S T S M e D M LDocument4 pagesG J U S T S M e D M LZlo6No ratings yet
- CNC NotesDocument55 pagesCNC NotesFRANCIS THOMASNo ratings yet
- Digital Differential AnalyzerDocument53 pagesDigital Differential AnalyzerAbin PmNo ratings yet
- Unit7 Nan PDFDocument56 pagesUnit7 Nan PDFkdtkopNo ratings yet
- Tool & Mold MakingDocument18 pagesTool & Mold MakingAtul BhattNo ratings yet
- CMMDocument26 pagesCMMSanjeev kumar Verma100% (1)
- CNC Ipme 710Document73 pagesCNC Ipme 710vajram1No ratings yet
- Unit7-CNC Machining CentresDocument56 pagesUnit7-CNC Machining Centresvasudevanrv9405No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Machine Tools and Computer Numerical Control (CNC)Document32 pagesAn Introduction To Machine Tools and Computer Numerical Control (CNC)Abey FrancisNo ratings yet
- CAD Assignment IIDocument17 pagesCAD Assignment IIBappi ChamuaNo ratings yet
- CNC Lab ReportDocument5 pagesCNC Lab ReportMuhammad SanaNo ratings yet
- Computer and Numerically Controlled Machines Numerically Controlled (NC)Document7 pagesComputer and Numerically Controlled Machines Numerically Controlled (NC)pranav29No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - 1Document13 pagesChapter 4 - 1khalil alhatabNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 NC and CNDocument115 pagesLesson 2 NC and CNyiheyis mulatuNo ratings yet
- CNC and NC MachineDocument36 pagesCNC and NC MachineShaaf AmjadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CNC MachinesDocument15 pagesIntroduction To CNC Machinespranjal priyeNo ratings yet
- Computer Numerical Control CNC: Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument43 pagesComputer Numerical Control CNC: Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering DepartmentSreedhar PugalendhiNo ratings yet
- Cam Lab Manual - New PDFDocument78 pagesCam Lab Manual - New PDFSreedhar PugalendhiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CNC Programming and Industrial RoboticsDocument50 pagesIntroduction To CNC Programming and Industrial RoboticstaridanNo ratings yet
- TLSL 3428Document232 pagesTLSL 3428viniciusemanuelNo ratings yet
- Cisco 827 Router Cabling and Setup Quick Start Guide: Parts ListDocument12 pagesCisco 827 Router Cabling and Setup Quick Start Guide: Parts ListCarlos Alberto Paez TNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh University Program: Day (Fall 2019 Class Schedule) SaturdayDocument7 pagesBangladesh University Program: Day (Fall 2019 Class Schedule) SaturdayMD Abu Ahammed BabuNo ratings yet
- 01 Become A PostgreSQL DBA Understanding The ArchitectureDocument10 pages01 Become A PostgreSQL DBA Understanding The ArchitectureStephen EfangeNo ratings yet
- Metashape Python Reference - Agisoft LLCDocument175 pagesMetashape Python Reference - Agisoft LLCKentner Chavez CorreaNo ratings yet
- Creo Trendsetter Error, Command, NVS, ArchiveDocument4 pagesCreo Trendsetter Error, Command, NVS, ArchiveZevnik d.o.o.No ratings yet
- Abhw 4BDocument18 pagesAbhw 4Bablancheth01No ratings yet
- Oracle Unified Method White PaperDocument17 pagesOracle Unified Method White PaperRanjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Gaddis Python 4e Chapter 11Document14 pagesGaddis Python 4e Chapter 11Cali CaliNo ratings yet
- Cellusys Signalling Firewall v6.7Document4 pagesCellusys Signalling Firewall v6.7Lucky AmaanNo ratings yet
- Mixing Util HelpDocument32 pagesMixing Util HelpJason WangNo ratings yet
- Relay G10 Guitar CompatibilityDocument3 pagesRelay G10 Guitar CompatibilityRoberto GherloneNo ratings yet
- ASA TCP Connection FlagsDocument4 pagesASA TCP Connection Flagsjsinghengineer1No ratings yet
- PR2 Q2 Module 3Document9 pagesPR2 Q2 Module 3Ashes VillNo ratings yet
- Nite and Day Power Provides Battery Backup and Ups BackupDocument4 pagesNite and Day Power Provides Battery Backup and Ups BackupNiteandDayPowerNo ratings yet
- Derek NexusDocument4 pagesDerek NexusNitin PatilNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-Unit 2: MATH 2300Document8 pagesQuestion Bank-Unit 2: MATH 2300ROHAN TRIVEDI 20SCSE1180013No ratings yet
- Chapter Three: System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Document10 pagesChapter Three: System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Gemechis Lema100% (1)
- ISM WM200 Partner Manual PT BRDocument32 pagesISM WM200 Partner Manual PT BREduardo Villas BoasNo ratings yet
- GEO118 Analysis 4Document6 pagesGEO118 Analysis 4MR. HAFIZ GAMMINGNo ratings yet
- Co-Product and By-Product in Production OrderDocument12 pagesCo-Product and By-Product in Production OrderVivek KalchuriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Deep Learning - With Complexe Python and TensorFlow Examples - Jürgen Brauer PDFDocument245 pagesIntroduction To Deep Learning - With Complexe Python and TensorFlow Examples - Jürgen Brauer PDFMecobioNo ratings yet
- A0013300a - Quick Start Guide - IN700 750 US Hasler BD PDFDocument1 pageA0013300a - Quick Start Guide - IN700 750 US Hasler BD PDFVaijayanti JoshiNo ratings yet
- SQL Select From V$SGADocument16 pagesSQL Select From V$SGAsaravanand1983100% (2)
- ProjekatDocument5 pagesProjekatNenad FemicNo ratings yet
Offsetting On CNC Milling Machine
Offsetting On CNC Milling Machine
Uploaded by
khayam khanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Offsetting On CNC Milling Machine
Offsetting On CNC Milling Machine
Uploaded by
khayam khanCopyright:
Available Formats
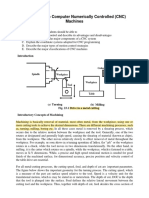
Lab 12
Offsetting on CNC Milling Machine
Main Objective:
Tool Length Offsets: Tool length offsets are used to compensate for the
length of the cutting tool. By setting the tool length offset, the machine
knows the exact position of the tool tip relative to the machine's reference
point. This allows for accurate machining operations. Tool length offsets are
usually designated with G43 or G44 codes.
Workpiece Offsets: Workpiece offsets are used to define the position of the
workpiece on the machine's table. By setting the workpiece offsets, the
machine knows the exact position of the workpiece relative to the machine's
reference point. This allows for precise machining operations. Workpiece
offsets are typically designated with G54 to G59 codes.
Tool Diameter Offsets: Tool diameter offsets are used to compensate for the
diameter of the cutting tool. By setting the tool diameter offset, the machine
knows the exact size of the tool and can adjust the tool path accordingly.
This ensures accurate machining operations. Tool diameter offsets are
usually designated with D codes.
Introduction:
Offset on a CNC milling machine involves adjusting the position of the cutting tool
relative to the workpiece to achieve precise machining. Tool offsets compensate
for tool dimensions, while workpiece offsets account for workpiece variations. It
ensures accurate alignment and compensates for tool wear. Coordinate systems,
tool length compensation, and cutter compensation are key aspects. Proper
offsetting techniques enable precise and consistent results in CNC milling
operations.
Procedure:
The for offsetting on a CNC milling machine in a professional manner typically
1
involves the following steps:
Page
Lab 12
Establish Workpiece Offsets: Measure specific reference points on the
workpiece using precision measuring tools. Enter these measurements
into the CNC machine's control system as workpiece offsets, aligning the
programmed tool path with the actual workpiece.
Set Coordinate System: Choose the appropriate coordinate system (e.g.,
Cartesian, polar, cylindrical) based on the machining requirements.
Ensure the coordinate system is properly aligned with the workpiece and
tooling.
Apply Tool Length Compensation: If necessary, set tool length
compensation to account for variations in tool length. Use a tool presetter
or automatic tool length measurement system to determine the correct
offset value along the Z-axis.
Implement Cutter Compensation: If required, apply cutter compensation
using G41 (left compensation) or G42 (right compensation) commands in
the CNC program. Adjust the tool path along the X and Y axes to achieve
the desired part dimensions.
Monitor Tool Wear: Regularly inspect the cutting tool for wear and
measure its dimensions. Update the tool offsets accordingly to maintain
accuracy. Utilize tool monitoring systems, if available, to automate this
process.
By following this professional procedure for offsetting on a CNC milling machine,
operators can achieve precise and consistent results, minimize errors, and optimize
the machining process. It is important to adhere to safety guidelines, consult
machine manuals, and receive proper training to ensure efficient and accurate
offsetting operations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, offsetting on a CNC milling machine is a crucial process that allows
for precise and accurate machining. By setting tool and workpiece offsets,
adjusting coordinate systems, and applying tool length and cutter compensation,
operators can compensate for variations and achieve desired part dimensions.
Regular monitoring of tool wear and making necessary adjustments ensures
continued accuracy. Following a professional procedure and maintaining proper
documentation are essential for efficient and effective offsetting operations on a
CNC milling machine.
2
Page
You might also like
- Echobox Mock Sales Call 1Document1 pageEchobox Mock Sales Call 1Maria LivaniouNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introduction of CNC Turning MachineDocument9 pages1.0 Introduction of CNC Turning Machineeizhar50% (4)
- SAP Fiori Analytical Apps For Sales (1BS) : Test Script SAP S/4HANA - 28-08-18Document29 pagesSAP Fiori Analytical Apps For Sales (1BS) : Test Script SAP S/4HANA - 28-08-18MihaiNo ratings yet
- Dharwar Drilling Society: Case Analysis ReportDocument8 pagesDharwar Drilling Society: Case Analysis Reportchelsea1989No ratings yet
- Ir Advance c5255/5250/5240/5235 SeriesDocument222 pagesIr Advance c5255/5250/5240/5235 Series-TT-0% (1)
- Assignment of Software Test PlanDocument15 pagesAssignment of Software Test Plankafeel afridi100% (1)
- Experiment No 6Document11 pagesExperiment No 6harisraja47985No ratings yet
- CAM-CIM Manual - M.tech - Jan 2022Document46 pagesCAM-CIM Manual - M.tech - Jan 2022KUNAL SHIMPINo ratings yet
- CNC Machine Tool OffsetsDocument1 pageCNC Machine Tool OffsetsAllan HarrisNo ratings yet
- TE415 Machine Tool Probe CalibrationDocument6 pagesTE415 Machine Tool Probe CalibrationLjubo ObleščakNo ratings yet
- Cad, CamDocument16 pagesCad, CamRakhi Mol BVNo ratings yet
- Location Dependency of Positioning Error in A 3-Axes CNC Milling MachineDocument6 pagesLocation Dependency of Positioning Error in A 3-Axes CNC Milling MachineIrfan RfcNo ratings yet
- Heidenhain Touch ProbeDocument72 pagesHeidenhain Touch ProbeHoho Hahov100% (1)
- CNC Part ProgrammingDocument40 pagesCNC Part ProgrammingmsshahenterNo ratings yet
- CNC Part ProgrammingDocument53 pagesCNC Part ProgrammingmsshahenterNo ratings yet
- NC & CNC MachinesDocument12 pagesNC & CNC MachinesRenjith Rajendraprasad100% (1)
- Lab Manual CNC LatheDocument10 pagesLab Manual CNC LatheSai Naga Sri Harsha100% (1)
- Unit 3Document17 pagesUnit 3rufeenaNo ratings yet
- CNC PresentationDocument37 pagesCNC PresentationMarvin BelenNo ratings yet
- G and M Coding Lab 03Document24 pagesG and M Coding Lab 03Mohsin Qazi100% (1)
- Cnccuttingtools 140314063757 Phpapp01Document26 pagesCnccuttingtools 140314063757 Phpapp01Taha BardanwalaNo ratings yet
- Lab No 9Document4 pagesLab No 9khayam khanNo ratings yet
- Study of CNC MachinesDocument53 pagesStudy of CNC MachinesPreethi VadivelNo ratings yet
- Typical CNC Machining Centre: Horizontal Axis Milling Vertical Axis MillingDocument82 pagesTypical CNC Machining Centre: Horizontal Axis Milling Vertical Axis MillingAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Title Objective: Figure 1: Hitachi Seiki Hitec-Turn20SiiDocument11 pagesTitle Objective: Figure 1: Hitachi Seiki Hitec-Turn20SiiSilang KataNo ratings yet
- Ipe 509 Presentation DraftDocument10 pagesIpe 509 Presentation Draftalozie alexanderNo ratings yet
- Cad/Cam: NC, CNC, DNC TechnologiesDocument37 pagesCad/Cam: NC, CNC, DNC TechnologiesVijay ShakarNo ratings yet
- Report 1 (Jack)Document9 pagesReport 1 (Jack)Mark SelvanNo ratings yet
- Week 7+8 Lect 5 - CNCDocument18 pagesWeek 7+8 Lect 5 - CNCmuhammadarshadnaveed346No ratings yet
- Metal Removal Rate (MRR) Tool Wear Rate (TWR)Document2 pagesMetal Removal Rate (MRR) Tool Wear Rate (TWR)Chethan K NarayanNo ratings yet
- CNC Machines: By: Mohammed YousifDocument37 pagesCNC Machines: By: Mohammed Yousifمحمد عبد الرحيمNo ratings yet
- Cncpresentation PDFDocument37 pagesCncpresentation PDFCorey YoungNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document14 pagesCH 3abdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Fast, Accurate Contour Milling With High Surface Defi NitionDocument6 pagesFast, Accurate Contour Milling With High Surface Defi NitionRadoslaw JoczNo ratings yet
- CNC TitanDocument58 pagesCNC TitanGV Ragunathan100% (1)
- MT Ii Unit VDocument73 pagesMT Ii Unit VRavigggNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Manufacturing Part 1Document76 pagesComputer Aided Manufacturing Part 1lelisadiriba849No ratings yet
- 9.pmat M-01Document94 pages9.pmat M-01mailtome126100% (1)
- CAMpres AashishDocument31 pagesCAMpres AashishAshishJoshiNo ratings yet
- Response Surface Methodology in CNC Turning-A ReviewDocument12 pagesResponse Surface Methodology in CNC Turning-A Reviewjaniesh bhartiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CNC MachiningDocument36 pagesIntroduction To CNC MachiningNavya VelagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - 2Document7 pagesChapter 3 - 2viet vuNo ratings yet
- Unit - 7: CNC Machining Centers: Numerical ControlDocument56 pagesUnit - 7: CNC Machining Centers: Numerical ControlnenadNo ratings yet
- G J U S T S M e D M LDocument4 pagesG J U S T S M e D M LZlo6No ratings yet
- CNC NotesDocument55 pagesCNC NotesFRANCIS THOMASNo ratings yet
- Digital Differential AnalyzerDocument53 pagesDigital Differential AnalyzerAbin PmNo ratings yet
- Unit7 Nan PDFDocument56 pagesUnit7 Nan PDFkdtkopNo ratings yet
- Tool & Mold MakingDocument18 pagesTool & Mold MakingAtul BhattNo ratings yet
- CMMDocument26 pagesCMMSanjeev kumar Verma100% (1)
- CNC Ipme 710Document73 pagesCNC Ipme 710vajram1No ratings yet
- Unit7-CNC Machining CentresDocument56 pagesUnit7-CNC Machining Centresvasudevanrv9405No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Machine Tools and Computer Numerical Control (CNC)Document32 pagesAn Introduction To Machine Tools and Computer Numerical Control (CNC)Abey FrancisNo ratings yet
- CAD Assignment IIDocument17 pagesCAD Assignment IIBappi ChamuaNo ratings yet
- CNC Lab ReportDocument5 pagesCNC Lab ReportMuhammad SanaNo ratings yet
- Computer and Numerically Controlled Machines Numerically Controlled (NC)Document7 pagesComputer and Numerically Controlled Machines Numerically Controlled (NC)pranav29No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - 1Document13 pagesChapter 4 - 1khalil alhatabNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 NC and CNDocument115 pagesLesson 2 NC and CNyiheyis mulatuNo ratings yet
- CNC and NC MachineDocument36 pagesCNC and NC MachineShaaf AmjadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CNC MachinesDocument15 pagesIntroduction To CNC Machinespranjal priyeNo ratings yet
- Computer Numerical Control CNC: Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument43 pagesComputer Numerical Control CNC: Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering DepartmentSreedhar PugalendhiNo ratings yet
- Cam Lab Manual - New PDFDocument78 pagesCam Lab Manual - New PDFSreedhar PugalendhiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CNC Programming and Industrial RoboticsDocument50 pagesIntroduction To CNC Programming and Industrial RoboticstaridanNo ratings yet
- TLSL 3428Document232 pagesTLSL 3428viniciusemanuelNo ratings yet
- Cisco 827 Router Cabling and Setup Quick Start Guide: Parts ListDocument12 pagesCisco 827 Router Cabling and Setup Quick Start Guide: Parts ListCarlos Alberto Paez TNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh University Program: Day (Fall 2019 Class Schedule) SaturdayDocument7 pagesBangladesh University Program: Day (Fall 2019 Class Schedule) SaturdayMD Abu Ahammed BabuNo ratings yet
- 01 Become A PostgreSQL DBA Understanding The ArchitectureDocument10 pages01 Become A PostgreSQL DBA Understanding The ArchitectureStephen EfangeNo ratings yet
- Metashape Python Reference - Agisoft LLCDocument175 pagesMetashape Python Reference - Agisoft LLCKentner Chavez CorreaNo ratings yet
- Creo Trendsetter Error, Command, NVS, ArchiveDocument4 pagesCreo Trendsetter Error, Command, NVS, ArchiveZevnik d.o.o.No ratings yet
- Abhw 4BDocument18 pagesAbhw 4Bablancheth01No ratings yet
- Oracle Unified Method White PaperDocument17 pagesOracle Unified Method White PaperRanjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Gaddis Python 4e Chapter 11Document14 pagesGaddis Python 4e Chapter 11Cali CaliNo ratings yet
- Cellusys Signalling Firewall v6.7Document4 pagesCellusys Signalling Firewall v6.7Lucky AmaanNo ratings yet
- Mixing Util HelpDocument32 pagesMixing Util HelpJason WangNo ratings yet
- Relay G10 Guitar CompatibilityDocument3 pagesRelay G10 Guitar CompatibilityRoberto GherloneNo ratings yet
- ASA TCP Connection FlagsDocument4 pagesASA TCP Connection Flagsjsinghengineer1No ratings yet
- PR2 Q2 Module 3Document9 pagesPR2 Q2 Module 3Ashes VillNo ratings yet
- Nite and Day Power Provides Battery Backup and Ups BackupDocument4 pagesNite and Day Power Provides Battery Backup and Ups BackupNiteandDayPowerNo ratings yet
- Derek NexusDocument4 pagesDerek NexusNitin PatilNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-Unit 2: MATH 2300Document8 pagesQuestion Bank-Unit 2: MATH 2300ROHAN TRIVEDI 20SCSE1180013No ratings yet
- Chapter Three: System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Document10 pagesChapter Three: System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Gemechis Lema100% (1)
- ISM WM200 Partner Manual PT BRDocument32 pagesISM WM200 Partner Manual PT BREduardo Villas BoasNo ratings yet
- GEO118 Analysis 4Document6 pagesGEO118 Analysis 4MR. HAFIZ GAMMINGNo ratings yet
- Co-Product and By-Product in Production OrderDocument12 pagesCo-Product and By-Product in Production OrderVivek KalchuriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Deep Learning - With Complexe Python and TensorFlow Examples - Jürgen Brauer PDFDocument245 pagesIntroduction To Deep Learning - With Complexe Python and TensorFlow Examples - Jürgen Brauer PDFMecobioNo ratings yet
- A0013300a - Quick Start Guide - IN700 750 US Hasler BD PDFDocument1 pageA0013300a - Quick Start Guide - IN700 750 US Hasler BD PDFVaijayanti JoshiNo ratings yet
- SQL Select From V$SGADocument16 pagesSQL Select From V$SGAsaravanand1983100% (2)
- ProjekatDocument5 pagesProjekatNenad FemicNo ratings yet