Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Patho Acute Bronchi
Patho Acute Bronchi
Uploaded by
Marianne Bagui DinglasanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Patho Acute Bronchi
Patho Acute Bronchi
Uploaded by
Marianne Bagui DinglasanCopyright:
Available Formats
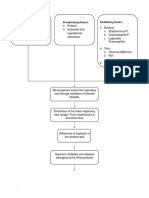
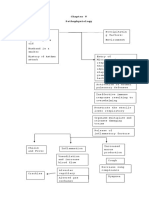
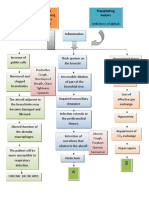
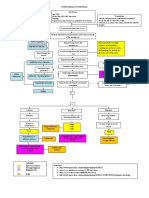
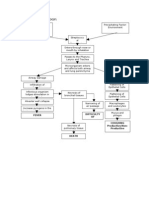
ETIOLOGICAL FACTOR
Cough
Cold
Fever
Compromised Immune System
Bacteria
esp. in children
Becomes trapped in sticky mucus &
swept upwards and outwards by cilia
Building of Cilia slows down and Bacteria release toxins to further damage
becomes paralyzed and disappear the cilia and epithelial cells
Cilia cells are replaced by goblet
cells as bronchitis progress
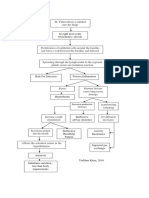
Constant Coughing tends to
be a combination of:
Air Inflammation Excessive Bronchial
Increased Cough
Secretion
Receptor Sensitivity
Inflammatory cells
begin with chemical
alarm
Release of Macrophages release
Released by intruder stress
Interleukin 4,5 & cytokines & interferon
tissue cells & immune cells
histamine gamma
Inflammation of Bronchial Wall
Goblet Cell Hyperplasia and Thickening of wall
Hypertrophy narrows passages
Increase obstruction to Air passages becomes clogged
airflow
Crackles/Crackling
Hypersecretion of Mucus Sound
Diminishing Bronchial Mucociliary Function
You might also like
- Cellulitis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCellulitis PathophysiologyWilfredo Mata Jr.100% (8)
- Pathophysiology of Neonatal Sepsis Secondary To Neonatal PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Neonatal Sepsis Secondary To Neonatal Pneumoniapaul andrew laranjo asuncion80% (5)
- Pathophysiology of TuberculosisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of TuberculosisMonica Marie Morales87% (15)
- Ajon Codp Web CausationDocument3 pagesAjon Codp Web Causationapi-383804230No ratings yet
- 7.2 PlasmapheresisDocument13 pages7.2 PlasmapheresisBALAJI100% (1)
- Pcap - PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesPcap - PathophysiologyAyla Mar100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of AsthmaDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of AsthmaEden Mae100% (4)
- Community Acquired Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia Pathophysiologyjordan aguilar67% (3)
- Sensory Diet: Prepared by Christy E. Yee, OTRDocument12 pagesSensory Diet: Prepared by Christy E. Yee, OTRAlexandra StăncescuNo ratings yet
- Dictyosome: Modifying, and Packaging Proteins and Lipids Into Vesicles ForDocument11 pagesDictyosome: Modifying, and Packaging Proteins and Lipids Into Vesicles ForASHFAQ AHMAD100% (1)
- 61 Point Relaxation TechniqueDocument7 pages61 Point Relaxation Techniquesaintx100% (1)
- San Gabriel, GMA, Cavite College of Nursing: Iv. Pathophysiology by The BookDocument2 pagesSan Gabriel, GMA, Cavite College of Nursing: Iv. Pathophysiology by The BookSTEPHANIE LIBO-ONNo ratings yet
- Copd PathoDocument2 pagesCopd PathoAlvin RamirezNo ratings yet
- Patient Based PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPatient Based PathophysiologyDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Person With Silicosis, DM, Post Gastrectomy StateDocument6 pagesPerson With Silicosis, DM, Post Gastrectomy StatekhleeoNo ratings yet
- Book Based: Etiology: Tubercle Bacilli Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsDocument7 pagesBook Based: Etiology: Tubercle Bacilli Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsIrish EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Patient Based PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPatient Based PathophysiologyJeizel IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: Republic of The Philippines San Fabian, Echague, Isabela Activity 2 Medical-Surgical NursingDocument9 pagesIsabela State University: Republic of The Philippines San Fabian, Echague, Isabela Activity 2 Medical-Surgical Nursingpinoy HubNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Acute BronchitisDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY Acute BronchitisFrancine kimberlyNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsDocument6 pagesPredisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsKen SimonNo ratings yet
- Bacteria: PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBacteria: PathophysiologyPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- 55-Year-Old, Male With CopdDocument3 pages55-Year-Old, Male With CopdRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaAzria John DemetriNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of TuberculosisDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of TuberculosisFlauros Ryu JabienNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PathoDocument2 pagesPneumonia PathoDerick Nyl PascualNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus: LentiruvirusDocument5 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus: Lentiruvirusjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Patho of COPD and CorP NewDocument5 pagesPatho of COPD and CorP NewInchan Montesines100% (1)
- Parhway: Secretions Pushed Into The MouthDocument1 pageParhway: Secretions Pushed Into The MouthFitria NorkhalidaNo ratings yet
- Pcap Patho FinalDocument3 pagesPcap Patho FinalChrls JhayneNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaJesselle LasernaNo ratings yet
- Patho TonsillectomyDocument1 pagePatho TonsillectomyVar SantosNo ratings yet
- PathophyDocument1 pagePathophyPsalms Aubrey Domingo AcostaNo ratings yet
- WK 3b Immune System 2023Document18 pagesWK 3b Immune System 2023Basmala HebaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaJeffrey Ramos100% (1)
- Final PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesFinal Pathophysiologyemely p. tangoNo ratings yet
- Asthma Pathophysiology: Ixsy Ramirez, MD, MPH Pediatric Pulmonology University of Michigan, C.S. Mott Children's HospitalDocument21 pagesAsthma Pathophysiology: Ixsy Ramirez, MD, MPH Pediatric Pulmonology University of Michigan, C.S. Mott Children's HospitalAru VermaNo ratings yet
- B. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyDocument3 pagesB. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyKenneth Torres100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaJuneNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of PneumoniaMary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Patho PTBDocument3 pagesPatho PTBRenalyn Domingo JoseNo ratings yet
- Bordetella: Drying - Highly Susceptible To Toxic Substance andDocument38 pagesBordetella: Drying - Highly Susceptible To Toxic Substance andkrstnkyslNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaMaria Cristina100% (1)
- TuberkulosisanakDocument106 pagesTuberkulosisanakUdin NicotinicNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Tuberculous Peritonisis (Myobacterium Tuberculosis)Document1 pagePathophysiology of Tuberculous Peritonisis (Myobacterium Tuberculosis)Nathaniel SupanNo ratings yet
- PATHODocument1 pagePATHOAmal MUTIANo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology: Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsDocument2 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology: Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsAl-Mujib TanogNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Genitourinary TuberculosisDocument8 pagesPathophysiology of Genitourinary Tuberculosisace_51891No ratings yet
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsDocument1 pageMycobacterium Tuberculosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsYoko Mae Yano100% (1)
- Bronchiectasis: Causes and DiagnosisDocument25 pagesBronchiectasis: Causes and DiagnosisRathchapon BuranasawadNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDocument3 pagesSchematic Diagram: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDamie FernandezNo ratings yet
- Etiology PCAPDocument2 pagesEtiology PCAPClark SavageNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Shortness of Breathing Crackles and Wheezes Dull PercussionDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Shortness of Breathing Crackles and Wheezes Dull Percussionjudith dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Typhoid FeverDocument1 pageTyphoid FeverMarkChesterSaguidNagen100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Typhoid FeverDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Typhoid FeverIan ParrochaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Asthma PDFDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Diagram of Asthma PDFYhenlee Rhizelle MarquezNo ratings yet
- Group 3 BSN3D CapDocument6 pagesGroup 3 BSN3D CapJingky AnquillanoNo ratings yet
- Cleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of SarcoidosisDocument1 pageCleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of SarcoidosisCleobebs AgustinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology PneumoniaSheila Mae Escalante67% (3)
- Pcap Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesPcap Pathophysiology PDFMikaela RamosNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument1 pagePa Tho PhysiologyEjra EjraNo ratings yet
- Age - Weather: Aspiration of Secretions Containing MicrobesDocument4 pagesAge - Weather: Aspiration of Secretions Containing Microbeslouie john abilaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology FinalDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology Finalrhan0330No ratings yet
- Traditional Chinese MedicineDocument27 pagesTraditional Chinese MedicineAivis BlumersNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 MiDocument16 pagesNCP 2 MiWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Heart Rhythm Interpretation ECG Strips 2019Document21 pagesHeart Rhythm Interpretation ECG Strips 2019daniel situngkirNo ratings yet
- Tissue BiochemistryDocument40 pagesTissue BiochemistryZahid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Nephroprotective Plants: Project ON AT DR - Apj Abdul Kalam Technical UniversityDocument40 pagesNephroprotective Plants: Project ON AT DR - Apj Abdul Kalam Technical UniversityVinayKumarNo ratings yet
- Perception and CoordinationDocument32 pagesPerception and CoordinationFerdie Marcial B. AureaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesDocument43 pagesLecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotessyafiqahNo ratings yet
- Changing Your MindDocument0 pagesChanging Your MindmeterabNo ratings yet
- Botany LectureDocument4 pagesBotany LectureGraceAbarcaNo ratings yet
- Ap Biology Exam Essay (Free Response) Questions: Unit 1 Biochemistry, Water, EnzymesDocument37 pagesAp Biology Exam Essay (Free Response) Questions: Unit 1 Biochemistry, Water, EnzymesBeatrice MallariNo ratings yet
- ToxicologyDocument76 pagesToxicologyiwahyu26No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesBasic Concepts in MicrobiologyHazelle RoxasNo ratings yet
- DM LectureDocument106 pagesDM LectureaitikoNo ratings yet
- Starting Strength: Gripping MattersDocument5 pagesStarting Strength: Gripping MattersFetogNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Appendicular - Skeleton - AtlasDocument58 pagesLab Manual - Appendicular - Skeleton - AtlasShao KahnNo ratings yet
- 2022 MPLS Provider ManualDocument122 pages2022 MPLS Provider Manualsenkchung86No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factorsrozj07No ratings yet
- Debelica2009 AtlasKeyHairTerrestTexasMammalsDocument108 pagesDebelica2009 AtlasKeyHairTerrestTexasMammalsJorge Manuel Cardenas CallirgosNo ratings yet
- 2012 Medf 1011 RRDocument12 pages2012 Medf 1011 RRLam Sin WingNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Document14 pagesUnit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Kripa NNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Management of The Pediatric Patient With Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument14 pagesPerioperative Management of The Pediatric Patient With Traumatic Brain InjuryBaha MirzaeifarNo ratings yet
- Designing Acrylic RPDDocument3 pagesDesigning Acrylic RPDmustafa_tambawalaNo ratings yet
- Absolute Neurocritical Care Review 2017Document252 pagesAbsolute Neurocritical Care Review 2017Luis Muñoz ChaccNo ratings yet
- CAPE Communication Studies 2009 P3BDocument4 pagesCAPE Communication Studies 2009 P3BRiaz JokanNo ratings yet
- Exer 6 - Dipeptide Sequence DeterminationDocument6 pagesExer 6 - Dipeptide Sequence DeterminationAsi JenNo ratings yet
- Kaqun RightsDocument17 pagesKaqun Rightsapi-238648403No ratings yet